(a) Scheme depicting the strategy used to generate the ko and conditional alleles. (b) RT-PCR for
|
|
|
- Andra Bryant
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Supplementary Figure 1 Generation of Diaph3 ko mice. (a) Scheme depicting the strategy used to generate the ko and conditional alleles. (b) RT-PCR for different regions of Diaph3 mrna from WT, heterozygote (ko/+) and mutant (ko) littermates showed that mrna is present downstream of the mutation. Sequencing of the cdna from ko embryo revealed a cryptic splice donor in the exon En2 resulting in premature and aberrant splicing of the cassette with insertion of 115 nucleotides (c, sequence in blue) between exons 9 (green) and 10 (black). A frameshift mutation was produced yielding 3 stop codons (bold underlined) in exon 10. The conditional allele was obtained by removal of the FTR-En2-IRES-LacZ-loxP-neo-FRT cassette after crossing with ROSA26-Flp mice. Exons 10 and 11, flanked by two loxp sites, were excised in dorsal telencephalon by crosses with Emx1-Cre mice. 1
2 Supplementary Figure 2 Phenotype of the adult brain. (a) DAPI-stained coronal sections from P25 brains of WT and Diaph3 ko littermates. Microcephaly and hydrocephalus are obvious in the mutant. (b) E13.5 brain sections stained for Isolectin B4. Blood vessels were more abundant and larger in ko than in controls. Scale bar is 1 mm in (a) and 200 µm in (b). 2
3 Supplementary Figure 3 Characterization of apoptotic cells Cortical walls from E10.5 embryos were co-stained for TUNEL and Tbr2 (a), Pax6 (b), and acas3 (c). TUNEL-stained cells in the vicinity of the VZ edge are shown by arrows in (a) and (b). (c) DAPI staining highlighting the presence of micronuclei and lagging chromosomes (arrows) in TUNEL and acas-3 positive mitotic (pvim + ) cells. Scale bars are 50 µm in (a,b) and 5 µm in (c). (d) Percentage of cells with mitotic errors in normal versus apoptotic cell populations. Error bars represent Standard Error of the Mean (SEM). 3
4 Supplementary Figure 4 No hypoxia in the dorsal telencephalon of Diaph3 mutants. (a) E10.5 cortical sections were stained with an anti-hypoxyprobe antibody. No difference was detected between WT and ko littermates. (b) Tumor xenografts were used as positive control for Hypoxyprobe staining. Different degrees of hypoxia are shown. Scale bar is 50 µm. 4
5 Supplementary Figure 5 Inactivation of Diaph3 in progenitors causes microcephaly. (a) Coronal sections from conditional mutants and controls were stained with acas3 (green). Numerous apoptotic cells were scattered through the cortical wall of Diaph3 flox/flox ;Emx1-Cre mice, whereas no positive cells were observed in Diaph3 flox/+ ;Emx1-Cre, or Diaph3 flox/flox littermates. Scale bar is 50 µm. (b d) Reduction of cortical size in Diaph3 conditional ko mice at E15.5 (b) and in the adult (c). (d) Quantification of the cortical size in Diaph3 conditional ko mice as measured along three axes (A, B, and C, left) and normalized to control littermates. Differences were statistically significant (axis A: P < ; axis B: P = ; axis C: P = 0.005; n = 4 brains for each genotype, Student s t-test). Error bars represent Standard Error of the Mean (SEM). 5
6 Supplementary Figure 6 Neuroepithelial cells maintain neural identity in vitro. Nestin immunostaining (green) of dissociated neurospheres from wild-type (WT) and mutant (ko) at passage 8 confirms their neural identity. Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI. Scale bar is 50 µm. 6
7 Supplementary Figure 7 Partial rescue of aneuploidy by BubR1 overexpression. Diaph3 ko dissociated neurospheres were infected with either IRES-GFP (Control) or BubR1- IRES-GFP (Rescue) lentiviral vectors (a). Fluorescent neurospheres (b) were amplified and processed for karyotype analysis (c). The number of euploid cells was almost twofold higher in BubR1-infected than in GFP-infected spheres (60,5% versus 33,9%, n = 76 for BubR1- and 59 for GFP-infected spheres). 7
8 Supplementary Figure 8: BubR1 downregulation has no effect on Diaph3 protein levels. Western blot analysis showing the downregulation of BubR1 in neurospheres (a), and in MEFs from control or Diaph3 transgenic (TG) mice (b). Note that Diaph3 levels were not affected upon BubR1 downregulation. (c) Karyotype analysis of control (top) and Diaph3-overexpressing (TG) (bottom) MEFs upon BubR1 knockdown (KD). No significant difference was observed between the two genotypes suggesting that the overexpression of Diaph3 could not rescue the aneuploidy induced upon BubR1 knockdown (n = 73 WT, 86 WT-BubRI KD, 91 Diaph3 TG, and 78 Diaph3 TG-BubR1 KD metaphases). 8
9 Supplementary Figure 9 Downregulation of DIAPH3 increases aneuploidy. (a) Western blot analysis showing a ~75% decrease in the levels of DIAPH3 in HEK-293T cells treated with DIAPH3 sirna (versus cells treated with sirna control). A concomitant (~40%) reduction of BUBR1 was detected. (b) Upon DIAPH3 knock-down, the percentage of hypotriploid metaphases (number of chromosomes ranging from 50 to 85) decreased dramatically (65% for controls versus 27% for knockdown cells), whereas the proportion of metaphase spreads with very low number of chromosomes (less than 20) increased to 49% in knockdown versus 19% in control cells (n = 112 control and 105 Diaph3 KD metaphases). 9
10 Supplementary Figure 10 Cellular localization of Diaph3. Cortical sections from E14.5 embryos that were electroporated in utero at E13.5, with a plasmid coding for GFP::Diaph3 fusion protein. In non-dividing cells (arrowheads), the GFP::Diaph3 was perinuclear and associated with apical and basal processes. In dividing cells (arrows) the signal was more diffusely distributed around the chromatin. Scale bar is 50 µm. 10
11 Supplementary Figure 11 Scans of original Western blots shown in Fig. 1f (a); Fig. 5h (b); Fig. 5j (c); Fig. 6 a (d); Supplementary Fig. 8a (e); Supplementary Fig. 8b (f); and Supplementary Fig. 9a (g) 11
12 Genotype (n) Examined cells Euploid cells Aneuploid cells Number of chromosomes in aneuploid cells < Diaph3 +/+ (2) Diaph3 ko/+ (2) Diaph3 ko/ko (4) Supplementary Table 1 Chromosome counts in neurospheres of indicated genotypes. 12
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Ricke et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201205115/dc1 Figure S1. Kinetochore localization of mitotic regulators in wild-type
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Ricke et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201205115/dc1 Figure S1. Kinetochore localization of mitotic regulators in wild-type
Revised: RG-RV2 by Fukuhara et al.
 Supplemental Figure 1 The generation of Spns2 conditional knockout mice. (A) Schematic representation of the wild type Spns2 locus (Spns2 + ), the targeted allele, the floxed allele (Spns2 f ) and the
Supplemental Figure 1 The generation of Spns2 conditional knockout mice. (A) Schematic representation of the wild type Spns2 locus (Spns2 + ), the targeted allele, the floxed allele (Spns2 f ) and the
DRG Pituitary Cerebral Cortex
 Liver Spinal cord Pons Atg5 -/- Atg5 +/+ DRG Pituitary Cerebral Cortex WT KO Supplementary Figure S1 Ubiquitin-positive IBs accumulate in Atg5 -/- tissues. Atg5 -/- neonatal tissues were fixed and decalcified.
Liver Spinal cord Pons Atg5 -/- Atg5 +/+ DRG Pituitary Cerebral Cortex WT KO Supplementary Figure S1 Ubiquitin-positive IBs accumulate in Atg5 -/- tissues. Atg5 -/- neonatal tissues were fixed and decalcified.
monoclonal antibody. (a) The specificity of the anti-rhbdd1 monoclonal antibody was examined in
 Supplementary information Supplementary figures Supplementary Figure 1 Determination of the s pecificity of in-house anti-rhbdd1 mouse monoclonal antibody. (a) The specificity of the anti-rhbdd1 monoclonal
Supplementary information Supplementary figures Supplementary Figure 1 Determination of the s pecificity of in-house anti-rhbdd1 mouse monoclonal antibody. (a) The specificity of the anti-rhbdd1 monoclonal
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information MicroRNA-212/132 family is required for epithelial stromal interactions necessary for mouse mammary gland development Ahmet Ucar, Vida Vafaizadeh, Hubertus Jarry, Jan Fiedler,
Supplementary Information MicroRNA-212/132 family is required for epithelial stromal interactions necessary for mouse mammary gland development Ahmet Ucar, Vida Vafaizadeh, Hubertus Jarry, Jan Fiedler,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of inducible BICD2 knock-out mice. A) The mouse BICD2 locus and gene targeting constructs. To generate an inducible Bicd2
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of inducible BICD2 knock-out mice. A) The mouse BICD2 locus and gene targeting constructs. To generate an inducible Bicd2
Schematic representation of the endogenous PALB2 locus and gene-disruption constructs
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of PALB2 -/- and BRCA2 -/- /PALB2 -/- DT40 cells. (A) Schematic representation of the endogenous PALB2 locus and gene-disruption constructs carrying
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of PALB2 -/- and BRCA2 -/- /PALB2 -/- DT40 cells. (A) Schematic representation of the endogenous PALB2 locus and gene-disruption constructs carrying
Nature Biotechnology: doi: /nbt.4166
 Supplementary Figure 1 Validation of correct targeting at targeted locus. (a) by immunofluorescence staining of 2C-HR-CRISPR microinjected embryos cultured to the blastocyst stage. Embryos were stained
Supplementary Figure 1 Validation of correct targeting at targeted locus. (a) by immunofluorescence staining of 2C-HR-CRISPR microinjected embryos cultured to the blastocyst stage. Embryos were stained
indicated numbers of pups at day of life (DOL) 10, or embryonic day (ED) B. Male mice of
 SUPPLEMENTRY FIGURE LEGENDS Figure S1. USP44 loss leads to chromosome missegregation.. Genotypes obtained from the indicated numbers of pups at day of life (DOL) 10, or embryonic day (ED) 13.5.. Male mice
SUPPLEMENTRY FIGURE LEGENDS Figure S1. USP44 loss leads to chromosome missegregation.. Genotypes obtained from the indicated numbers of pups at day of life (DOL) 10, or embryonic day (ED) 13.5.. Male mice
Pei et al. Supplementary Figure S1
 Pei et al. Supplementary Figure S1 C H-CUL9: + + + + + Myc-ROC1: - - + + + U2OS/pcDN3 U2OS/H-CUL9 U2OS/ + H-CUL9 IP: -H -myc input -H -myc 1 2 3 4 5 H-CUL9 Myc-ROC1 -H -H -H -H H-CUL9: wt RR myc-roc1:
Pei et al. Supplementary Figure S1 C H-CUL9: + + + + + Myc-ROC1: - - + + + U2OS/pcDN3 U2OS/H-CUL9 U2OS/ + H-CUL9 IP: -H -myc input -H -myc 1 2 3 4 5 H-CUL9 Myc-ROC1 -H -H -H -H H-CUL9: wt RR myc-roc1:
Supplementary Figure S1: (A) Schematic representation of the Jarid2 Flox/Flox
 Supplementary Figure S1: (A) Schematic representation of the Flox/Flox locus and the strategy used to visualize the wt and the Flox/Flox mrna by PCR from cdna. An example of the genotyping strategy is
Supplementary Figure S1: (A) Schematic representation of the Flox/Flox locus and the strategy used to visualize the wt and the Flox/Flox mrna by PCR from cdna. An example of the genotyping strategy is
Supplemental Information. Role of phosphatase of regenerating liver 1 (PRL1) in spermatogenesis
 Supplemental Information Role of phosphatase of regenerating liver 1 (PRL1) in spermatogenesis Yunpeng Bai ;, Lujuan Zhang #, Hongming Zhou #, Yuanshu Dong #, Qi Zeng, Weinian Shou, and Zhong-Yin Zhang
Supplemental Information Role of phosphatase of regenerating liver 1 (PRL1) in spermatogenesis Yunpeng Bai ;, Lujuan Zhang #, Hongming Zhou #, Yuanshu Dong #, Qi Zeng, Weinian Shou, and Zhong-Yin Zhang
The RRPA knock-in allele was generated by homologous recombination in TC1 ES cells.
 Supplemental Materials Materials & Methods Generation of RRPA and RAPA Knock-in Mice The RRPA knock-in allele was generated by homologous recombination in TC1 ES cells. Targeted ES clones in which the
Supplemental Materials Materials & Methods Generation of RRPA and RAPA Knock-in Mice The RRPA knock-in allele was generated by homologous recombination in TC1 ES cells. Targeted ES clones in which the
Supplementary Figure 1. Isolation of GFPHigh cells.
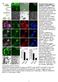 Supplementary Figure 1. Isolation of GFP High cells. (A) Schematic diagram of cell isolation based on Wnt signaling activity. Colorectal cancer (CRC) cell lines were stably transduced with lentivirus encoding
Supplementary Figure 1. Isolation of GFP High cells. (A) Schematic diagram of cell isolation based on Wnt signaling activity. Colorectal cancer (CRC) cell lines were stably transduced with lentivirus encoding
TRANSGENIC ANIMALS. -transient transfection of cells -stable transfection of cells. - Two methods to produce transgenic animals:
 TRANSGENIC ANIMALS -transient transfection of cells -stable transfection of cells - Two methods to produce transgenic animals: 1- DNA microinjection - random insertion 2- embryonic stem cell-mediated gene
TRANSGENIC ANIMALS -transient transfection of cells -stable transfection of cells - Two methods to produce transgenic animals: 1- DNA microinjection - random insertion 2- embryonic stem cell-mediated gene
Supplemental Material: Rev1 promotes replication through UV lesions in conjunction with DNA
 Supplemental Material: Rev1 promotes replication through UV lesions in conjunction with DNA polymerases,, and, but not with DNA polymerase Jung-Hoon Yoon, Jeseong Park, Juan Conde, Maki Wakamiya, Louise
Supplemental Material: Rev1 promotes replication through UV lesions in conjunction with DNA polymerases,, and, but not with DNA polymerase Jung-Hoon Yoon, Jeseong Park, Juan Conde, Maki Wakamiya, Louise
Supplementary Methods
 Supplementary Methods Reverse transcribed Quantitative PCR. Total RNA was isolated from bone marrow derived macrophages using RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen), DNase-treated (Promega RQ1), and reverse transcribed
Supplementary Methods Reverse transcribed Quantitative PCR. Total RNA was isolated from bone marrow derived macrophages using RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen), DNase-treated (Promega RQ1), and reverse transcribed
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 (Supplementary Methods and Materials) GST pull-down assay GST-fusion proteins Fe65 365-533, and Fe65 538-700 were expressed in BL21 bacterial cells and purified with glutathione-agarose beads (Sigma).
(Supplementary Methods and Materials) GST pull-down assay GST-fusion proteins Fe65 365-533, and Fe65 538-700 were expressed in BL21 bacterial cells and purified with glutathione-agarose beads (Sigma).
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/323/5911/256/dc1 Supporting Online Material for HDAC4 Regulates Neuronal Survival in Normal and Diseased Retinas Bo Chen and Constance L. Cepko E-mail: bochen@genetics.med.harvard.edu,
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/323/5911/256/dc1 Supporting Online Material for HDAC4 Regulates Neuronal Survival in Normal and Diseased Retinas Bo Chen and Constance L. Cepko E-mail: bochen@genetics.med.harvard.edu,
Supplementary Figure 1. Confirmation of sirna in PC3 and H1299 cells PC3 (a) and H1299 (b) cells were transfected with sirna oligonucleotides
 Supplementary Figure 1. Confirmation of sirna in PC3 and H1299 cells PC3 (a) and H1299 (b) cells were transfected with sirna oligonucleotides targeting RCP (SMARTPool (RCP) or two individual oligos (RCP#1
Supplementary Figure 1. Confirmation of sirna in PC3 and H1299 cells PC3 (a) and H1299 (b) cells were transfected with sirna oligonucleotides targeting RCP (SMARTPool (RCP) or two individual oligos (RCP#1
Supplementary Figure 1. Homozygous rag2 E450fs mutants are healthy and viable similar to wild-type and heterozygous siblings.
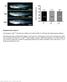 Supplementary Figure 1 Homozygous rag2 E450fs mutants are healthy and viable similar to wild-type and heterozygous siblings. (left) Representative bright-field images of wild type (wt), heterozygous (het)
Supplementary Figure 1 Homozygous rag2 E450fs mutants are healthy and viable similar to wild-type and heterozygous siblings. (left) Representative bright-field images of wild type (wt), heterozygous (het)
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Nowakowski et al. 10.1073/pnas.1219385110 SI Materials and Methods Primary Antibodies. Primary antibodies used in this study were raised against BrdU (rat, 1:50; Abcam), cleaved
Supporting Information Nowakowski et al. 10.1073/pnas.1219385110 SI Materials and Methods Primary Antibodies. Primary antibodies used in this study were raised against BrdU (rat, 1:50; Abcam), cleaved
Supplemental Information
 Supplemental Information Itemized List Materials and Methods, Related to Supplemental Figures S5A-C and S6. Supplemental Figure S1, Related to Figures 1 and 2. Supplemental Figure S2, Related to Figure
Supplemental Information Itemized List Materials and Methods, Related to Supplemental Figures S5A-C and S6. Supplemental Figure S1, Related to Figures 1 and 2. Supplemental Figure S2, Related to Figure
Hyper sensitive protein detection by Tandem-HTRF reveals Cyclin D1
 Hyper sensitive protein detection by Tandem-HTRF reveals Cyclin D1 dynamics in adult mouse Alexandre Zampieri, Julien Champagne, Baptiste Auzemery, Ivanna Fuentes, Benjamin Maurel and Frédéric Bienvenu
Hyper sensitive protein detection by Tandem-HTRF reveals Cyclin D1 dynamics in adult mouse Alexandre Zampieri, Julien Champagne, Baptiste Auzemery, Ivanna Fuentes, Benjamin Maurel and Frédéric Bienvenu
A Low salt diet. C Low salt diet + mf4-31c1 3. D High salt diet + mf4-31c1 3. B High salt diet
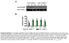 A Low salt diet GV [AU]:. [mmhg]: 0..... 09 9 7 B High salt diet GV [AU]:. [mmhg]: 7 8...0. 7.8 8.. 0 8 7 C Low salt diet + mf-c GV [AU]:. [mmhg]:.0.9 8.7.7. 7 8 0 D High salt diet + mf-c E Lymph capillary
A Low salt diet GV [AU]:. [mmhg]: 0..... 09 9 7 B High salt diet GV [AU]:. [mmhg]: 7 8...0. 7.8 8.. 0 8 7 C Low salt diet + mf-c GV [AU]:. [mmhg]:.0.9 8.7.7. 7 8 0 D High salt diet + mf-c E Lymph capillary
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Fig. 1 shrna mediated knockdown of ZRSR2 in K562 and 293T cells. (a) ZRSR2 transcript levels in stably transduced K562 cells were determined using qrt-pcr. GAPDH was
Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Fig. 1 shrna mediated knockdown of ZRSR2 in K562 and 293T cells. (a) ZRSR2 transcript levels in stably transduced K562 cells were determined using qrt-pcr. GAPDH was
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 AS-NMD modulates FLM-dependent thermosensory flowering response in Arabidopsis NATURE PLANTS www.nature.com/natureplants 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Genomic sequence of FLM along with the splice sites. Sequencing
AS-NMD modulates FLM-dependent thermosensory flowering response in Arabidopsis NATURE PLANTS www.nature.com/natureplants 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Genomic sequence of FLM along with the splice sites. Sequencing
TRANSGENIC ANIMALS. transient. stable. - Two methods to produce transgenic animals:
 Only for teaching purposes - not for reproduction or sale CELL TRANSFECTION transient stable TRANSGENIC ANIMALS - Two methods to produce transgenic animals: 1- DNA microinjection 2- embryonic stem cell-mediated
Only for teaching purposes - not for reproduction or sale CELL TRANSFECTION transient stable TRANSGENIC ANIMALS - Two methods to produce transgenic animals: 1- DNA microinjection 2- embryonic stem cell-mediated
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
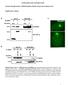 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Dynamic Phosphorylation of HP1 Regulates Mitotic Progression in Human Cells Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. NDR1 interacts with HP1. (a) Immunoprecipitation using
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Dynamic Phosphorylation of HP1 Regulates Mitotic Progression in Human Cells Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. NDR1 interacts with HP1. (a) Immunoprecipitation using
Supplementary Figure S1. Alterations in Fzr1( / );Nestin-Cre brains. (a) P10 Cdh1-deficient brains display low levels of Myelin basic protein (MBP)
 Supplementary Figure S1. Alterations in Fzr1( / );Nestin-Cre brains. (a) P10 Cdh1-deficient brains display low levels of Myelin basic protein (MBP) in the cortex (area 1 as defined in Fig. 2a), and corpus
Supplementary Figure S1. Alterations in Fzr1( / );Nestin-Cre brains. (a) P10 Cdh1-deficient brains display low levels of Myelin basic protein (MBP) in the cortex (area 1 as defined in Fig. 2a), and corpus
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI:.38/ncb327 a b Sequence coverage (%) 4 3 2 IP: -GFP isoform IP: GFP IP: -GFP IP: GFP Sequence coverage (%) 4 3 2 IP: -GFP IP: GFP 33 52 58 isoform 2 33 49 47 IP: Control IP: Peptide Sequence Start
DOI:.38/ncb327 a b Sequence coverage (%) 4 3 2 IP: -GFP isoform IP: GFP IP: -GFP IP: GFP Sequence coverage (%) 4 3 2 IP: -GFP IP: GFP 33 52 58 isoform 2 33 49 47 IP: Control IP: Peptide Sequence Start
beta-galactosidase (A420) ctrl
 0.6 beta-galactosidase (A420) 0.4 0.2 ctrl 2A 22A 35B 36B 58A 64A 68E 75C 86Fa 86Fb 102F Fig. S1. Levels of induced expression at various attp sites. The induced β-galactosidase activity was measured from
0.6 beta-galactosidase (A420) 0.4 0.2 ctrl 2A 22A 35B 36B 58A 64A 68E 75C 86Fa 86Fb 102F Fig. S1. Levels of induced expression at various attp sites. The induced β-galactosidase activity was measured from
Supplementary Figure 1. jmj30-2 and jmj32-1 produce null mutants. (a) Schematic drawing of JMJ30 and JMJ32 genome structure showing regions amplified
 Supplementary Figure 1. jmj30-2 and jmj32-1 produce null mutants. (a) Schematic drawing of JMJ30 and JMJ32 genome structure showing regions amplified by primers used for mrna expression analysis. Gray
Supplementary Figure 1. jmj30-2 and jmj32-1 produce null mutants. (a) Schematic drawing of JMJ30 and JMJ32 genome structure showing regions amplified by primers used for mrna expression analysis. Gray
Stargazin regulates AMPA receptor trafficking through adaptor protein. complexes during long term depression
 Supplementary Information Stargazin regulates AMPA receptor trafficking through adaptor protein complexes during long term depression Shinji Matsuda, Wataru Kakegawa, Timotheus Budisantoso, Toshihiro Nomura,
Supplementary Information Stargazin regulates AMPA receptor trafficking through adaptor protein complexes during long term depression Shinji Matsuda, Wataru Kakegawa, Timotheus Budisantoso, Toshihiro Nomura,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 a before amputation regeneration regenerated limb DERMIS SKELETON MUSCLE SCHWANN CELLS EPIDERMIS DERMIS SKELETON MUSCLE SCHWANN CELLS EPIDERMIS developmental origin: lateral plate mesoderm presomitic mesoderm
a before amputation regeneration regenerated limb DERMIS SKELETON MUSCLE SCHWANN CELLS EPIDERMIS DERMIS SKELETON MUSCLE SCHWANN CELLS EPIDERMIS developmental origin: lateral plate mesoderm presomitic mesoderm
Fig Hypoxia causes growth retardation and developmental delay. (A) Morphology of wildtype zebrafish embryos at 48 hours post fertilization
 FIGURES AND TABLES Fig. 1-1. Hypoxia causes growth retardation and developmental delay. (A) Morphology of wildtype zebrafish embryos at 48 hours post fertilization (hpf) after 24 h of normoxia or hypoxia
FIGURES AND TABLES Fig. 1-1. Hypoxia causes growth retardation and developmental delay. (A) Morphology of wildtype zebrafish embryos at 48 hours post fertilization (hpf) after 24 h of normoxia or hypoxia
Supplementary Figure 1. Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb.3494
 Supplementary Figure 1 Pol structure-function analysis (a) Inactivating polymerase and helicase mutations do not alter the stability of Pol. Flag epitopes were introduced using CRISPR/Cas9 gene targeting
Supplementary Figure 1 Pol structure-function analysis (a) Inactivating polymerase and helicase mutations do not alter the stability of Pol. Flag epitopes were introduced using CRISPR/Cas9 gene targeting
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL MATERIALS AND METHODS Generation of TSPOΔ/Δ murine embryonic fibroblasts Embryos were harvested from 13.5-day pregnant TSPOfl/fl mice. After dissection to eviscerate and remove the
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL MATERIALS AND METHODS Generation of TSPOΔ/Δ murine embryonic fibroblasts Embryos were harvested from 13.5-day pregnant TSPOfl/fl mice. After dissection to eviscerate and remove the
TRANSGENIC TECHNOLOGIES: Gene-targeting
 TRANSGENIC TECHNOLOGIES: Gene-targeting Reverse Genetics Wild-type Bmp7 -/- Forward Genetics Phenotype Gene or Mutations First Molecular Analysis Second Reverse Genetics Gene Phenotype or Molecular Analysis
TRANSGENIC TECHNOLOGIES: Gene-targeting Reverse Genetics Wild-type Bmp7 -/- Forward Genetics Phenotype Gene or Mutations First Molecular Analysis Second Reverse Genetics Gene Phenotype or Molecular Analysis
- Supplementary Information -
 TRIM32 dependent transcription in adult neural progenitor cells regulates neuronal differentiation. - Supplementary Information - Anna-Lena Hillje 1, 2#, Maria Angeliki S. Pavlou 1, 2#, Elisabeth Beckmann
TRIM32 dependent transcription in adult neural progenitor cells regulates neuronal differentiation. - Supplementary Information - Anna-Lena Hillje 1, 2#, Maria Angeliki S. Pavlou 1, 2#, Elisabeth Beckmann
mod-1::mcherry unc-47::gfp RME ser-4::gfp vm2 vm2 vm2 vm2 VNC
 A mod-1::mcherry unc-47::gfp RME B ser-4::gfp vm2 vm2 VNC vm2 vm2 VN Figure S1 Further details of mod- 1 and ser- 4 reporter expression patterns. (A) Adult head region showing mod- 1::mCherry and unc-
A mod-1::mcherry unc-47::gfp RME B ser-4::gfp vm2 vm2 VNC vm2 vm2 VN Figure S1 Further details of mod- 1 and ser- 4 reporter expression patterns. (A) Adult head region showing mod- 1::mCherry and unc-
Summary MicroRNAs (mirnas) are genomically encoded small RNAs used by organisms to regulate the expression of proteins generated from messenger RNA
 Summary MicroRNAs (mirnas) are genomically encoded small RNAs used by organisms to regulate the expression of proteins generated from messenger RNA transcripts. The in vivo requirement of specific mirnas
Summary MicroRNAs (mirnas) are genomically encoded small RNAs used by organisms to regulate the expression of proteins generated from messenger RNA transcripts. The in vivo requirement of specific mirnas
Regulation of axonal and dendritic growth by the extracellular calcium-sensing
 Regulation of axonal and dendritic growth by the extracellular calcium-sensing receptor (CaSR). Thomas N. Vizard, Gerard W. O Keeffe, Humberto Gutierrez, Claudine H. Kos, Daniela Riccardi, Alun M. Davies
Regulation of axonal and dendritic growth by the extracellular calcium-sensing receptor (CaSR). Thomas N. Vizard, Gerard W. O Keeffe, Humberto Gutierrez, Claudine H. Kos, Daniela Riccardi, Alun M. Davies
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1: Identification of new regulators of MuSC by a proteome-based shrna screen. (a) FACS plots of GFP + and GFP - cells from Pax7 ICN -Z/EG (upper panel) and
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1: Identification of new regulators of MuSC by a proteome-based shrna screen. (a) FACS plots of GFP + and GFP - cells from Pax7 ICN -Z/EG (upper panel) and
Genome-wide genetic screening with chemically-mutagenized haploid embryonic stem cells
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Supplementary Information Genome-wide genetic screening with chemically-mutagenized haploid embryonic stem cells Josep V. Forment 1,2, Mareike Herzog
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Supplementary Information Genome-wide genetic screening with chemically-mutagenized haploid embryonic stem cells Josep V. Forment 1,2, Mareike Herzog
Hitching Hunk meets Sleeping Beauty! a novel approach for random mutagenesis in the mouse based on genetic selection of intragenic integrations
 Hitching Hunk meets Sleeping Beauty! a novel approach for random mutagenesis in the mouse based on genetic selection of intragenic integrations genetically engineered murine models: applications models
Hitching Hunk meets Sleeping Beauty! a novel approach for random mutagenesis in the mouse based on genetic selection of intragenic integrations genetically engineered murine models: applications models
a KYSE270-CON KYSE270-Id1
 a KYSE27-CON KYSE27- shcon shcon sh b Human Mouse CD31 Relative MVD 3.5 3 2.5 2 1.5 1.5 *** *** c KYSE15 KYSE27 sirna (nm) 5 1 Id2 Id2 sirna 5 1 sirna (nm) 5 1 Id2 sirna 5 1 Id2 [h] (pg per ml) d 3 2 1
a KYSE27-CON KYSE27- shcon shcon sh b Human Mouse CD31 Relative MVD 3.5 3 2.5 2 1.5 1.5 *** *** c KYSE15 KYSE27 sirna (nm) 5 1 Id2 Id2 sirna 5 1 sirna (nm) 5 1 Id2 sirna 5 1 Id2 [h] (pg per ml) d 3 2 1
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Ihh interacts preferentially with its upstream neighboring gene Nhej1. Genes are indicated by gray lines, and Ihh and Nhej1 are highlighted in blue. 4C seq performed in E14.5 limbs
Supplementary Figure 1 Ihh interacts preferentially with its upstream neighboring gene Nhej1. Genes are indicated by gray lines, and Ihh and Nhej1 are highlighted in blue. 4C seq performed in E14.5 limbs
Supplementary Figure 1. Expressions of stem cell markers decreased in TRCs on 2D plastic. TRCs were cultured on plastic for 1, 3, 5, or 7 days,
 Supplementary Figure 1. Expressions of stem cell markers decreased in TRCs on 2D plastic. TRCs were cultured on plastic for 1, 3, 5, or 7 days, respectively, and their mrnas were quantified by real time
Supplementary Figure 1. Expressions of stem cell markers decreased in TRCs on 2D plastic. TRCs were cultured on plastic for 1, 3, 5, or 7 days, respectively, and their mrnas were quantified by real time
A population of Nestin expressing progenitors in the cerebellum exhibits increased tumorigenicity
 A population of Nestin expressing progenitors in the cerebellum exhibits increased tumorigenicity Peng Li 1,2, Fang Du 1, Larra W. Yuelling 1, Tiffany Lin 3, Renata E. Muradimova 1, Rossella Tricarico
A population of Nestin expressing progenitors in the cerebellum exhibits increased tumorigenicity Peng Li 1,2, Fang Du 1, Larra W. Yuelling 1, Tiffany Lin 3, Renata E. Muradimova 1, Rossella Tricarico
Mouse Engineering Technology. Musculoskeletal Research Center 2016 Summer Educational Series David M. Ornitz Department of Developmental Biology
 Mouse Engineering Technology Musculoskeletal Research Center 2016 Summer Educational Series David M. Ornitz Department of Developmental Biology Core service and new technologies Mouse ES core Discussions
Mouse Engineering Technology Musculoskeletal Research Center 2016 Summer Educational Series David M. Ornitz Department of Developmental Biology Core service and new technologies Mouse ES core Discussions
Supplementary Figure 1. Adipogenic protein expression in WT and KO MEFs after 7 days of adipogenic differentiation.
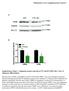 Merkestein et al. Supplementary Figure 1 A PLIN WT FTO KO 72 kda FABP4 17 kda HSC70 72 kda B Supplementary Figure 1. Adipogenic protein expression in WT and KO MEFs after 7 days of adipogenic differentiation.
Merkestein et al. Supplementary Figure 1 A PLIN WT FTO KO 72 kda FABP4 17 kda HSC70 72 kda B Supplementary Figure 1. Adipogenic protein expression in WT and KO MEFs after 7 days of adipogenic differentiation.
At E17.5, the embryos were rinsed in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and immersed in
 Supplementary Materials and Methods Barrier function assays At E17.5, the embryos were rinsed in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and immersed in acidic X-gal mix (100 mm phosphate buffer at ph4.3, 3 mm
Supplementary Materials and Methods Barrier function assays At E17.5, the embryos were rinsed in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and immersed in acidic X-gal mix (100 mm phosphate buffer at ph4.3, 3 mm
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.138/ncb3342 EV O/E 13 4 B Relative expression 1..8.6.4.2 shctl Pcdh2_1 C Pcdh2_2 Number of shrns 12 8 4 293T mterc +/+ G3 mterc -/- D % of GFP + cells 1 8 6 4 2 Per2 p=.2 p>
DOI: 1.138/ncb3342 EV O/E 13 4 B Relative expression 1..8.6.4.2 shctl Pcdh2_1 C Pcdh2_2 Number of shrns 12 8 4 293T mterc +/+ G3 mterc -/- D % of GFP + cells 1 8 6 4 2 Per2 p=.2 p>
GFP CCD2 GFP IP:GFP
 D1 D2 1 75 95 148 178 492 GFP CCD1 CCD2 CCD2 GFP D1 D2 GFP D1 D2 Beclin 1 IB:GFP IP:GFP Supplementary Figure 1: Mapping domains required for binding to HEK293T cells are transfected with EGFP-tagged mutant
D1 D2 1 75 95 148 178 492 GFP CCD1 CCD2 CCD2 GFP D1 D2 GFP D1 D2 Beclin 1 IB:GFP IP:GFP Supplementary Figure 1: Mapping domains required for binding to HEK293T cells are transfected with EGFP-tagged mutant
Easi CRISPR for conditional and insertional alleles
 Easi CRISPR for conditional and insertional alleles C.B Gurumurthy, University Of Nebraska Medical Center Omaha, NE cgurumurthy@unmc.edu Types of Genome edits Gene disruption/inactivation Types of Genome
Easi CRISPR for conditional and insertional alleles C.B Gurumurthy, University Of Nebraska Medical Center Omaha, NE cgurumurthy@unmc.edu Types of Genome edits Gene disruption/inactivation Types of Genome
Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of B2M -/- ESCs. Nature Biotechnology: doi: /nbt.3860
 Supplementary Figure 1 Generation of B2M -/- ESCs. (a) Maps of the B2M alleles in cells with the indicated B2M genotypes. Probes and restriction enzymes used in Southern blots are indicated (H, Hind III;
Supplementary Figure 1 Generation of B2M -/- ESCs. (a) Maps of the B2M alleles in cells with the indicated B2M genotypes. Probes and restriction enzymes used in Southern blots are indicated (H, Hind III;
Supplementary Figure S1. The tetracycline-inducible CRISPR system. A) Hela cells stably
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure S1. The tetracycline-inducible CRISPR system. A) Hela cells stably expressing shrna sequences against TRF2 were examined by western blotting. shcon, shrna
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure S1. The tetracycline-inducible CRISPR system. A) Hela cells stably expressing shrna sequences against TRF2 were examined by western blotting. shcon, shrna
Sperm cells are passive cargo of the pollen tube in plant fertilization
 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION VOLUME: 3 ARTICLE NUMBER: 17079 Sperm cells are passive cargo of the pollen tube in plant fertilization Jun Zhang 1, Qingpei
In the format provided by the authors and unedited. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION VOLUME: 3 ARTICLE NUMBER: 17079 Sperm cells are passive cargo of the pollen tube in plant fertilization Jun Zhang 1, Qingpei
Parthanatos mediates AIMP2-activated age-dependent dopaminergic neuronal loss
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Parthanatos mediates AIMP2-activated age-dependent dopaminergic neuronal loss Yunjong Lee, Senthilkumar S. Karuppagounder, Joo-Ho Shin, Yun-Il Lee, Han Seok Ko, Debbie Swing,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Parthanatos mediates AIMP2-activated age-dependent dopaminergic neuronal loss Yunjong Lee, Senthilkumar S. Karuppagounder, Joo-Ho Shin, Yun-Il Lee, Han Seok Ko, Debbie Swing,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb3164 Supplementary Figure 1 Validation of effective Gnas deletion and epithelial thickness. a, Representative genotyping in mice treated or not with tamoxifen to show Gnas deletion. To
DOI: 10.1038/ncb3164 Supplementary Figure 1 Validation of effective Gnas deletion and epithelial thickness. a, Representative genotyping in mice treated or not with tamoxifen to show Gnas deletion. To
Supplemental Fig. 1: PEA-15 knockdown efficiency assessed by immunohistochemistry and qpcr
 Supplemental figure legends Supplemental Fig. 1: PEA-15 knockdown efficiency assessed by immunohistochemistry and qpcr A, LβT2 cells were transfected with either scrambled or PEA-15 sirna. Cells were then
Supplemental figure legends Supplemental Fig. 1: PEA-15 knockdown efficiency assessed by immunohistochemistry and qpcr A, LβT2 cells were transfected with either scrambled or PEA-15 sirna. Cells were then
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng.3556 INTEGRATED SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE TEMPLATE. Supplementary Figure 1
 INTEGRATED SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE TEMPLATE Supplementary Figure 1 REF6 expression in transgenic lines. (a,b) Expression of REF6 in REF6-HA ref6 and REF6ΔZnF-HA ref6 plants detected by RT qpcr (a) and immunoblot
INTEGRATED SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE TEMPLATE Supplementary Figure 1 REF6 expression in transgenic lines. (a,b) Expression of REF6 in REF6-HA ref6 and REF6ΔZnF-HA ref6 plants detected by RT qpcr (a) and immunoblot
Supplementary Figure 1. APP cleavage assay. HEK293 cells were transfected with various
 Supplementary Figure 1. APP cleavage assay. HEK293 cells were transfected with various GST-tagged N-terminal truncated APP fragments including GST-APP full-length (FL), APP (123-695), APP (189-695), or
Supplementary Figure 1. APP cleavage assay. HEK293 cells were transfected with various GST-tagged N-terminal truncated APP fragments including GST-APP full-length (FL), APP (123-695), APP (189-695), or
Supplementary Table, Figures and Videos
 Supplementary Table, Figures and Videos Table S1. Oligonucleotides used for different approaches. (A) RT-qPCR study. (B) qpcr study after ChIP assay. (C) Probes used for EMSA. Figure S1. Notch activation
Supplementary Table, Figures and Videos Table S1. Oligonucleotides used for different approaches. (A) RT-qPCR study. (B) qpcr study after ChIP assay. (C) Probes used for EMSA. Figure S1. Notch activation
Xu et al., Supplementary Figures 1-7
 Xu et al., Supplementary Figures 1-7 Supplementary Figure 1. PIPKI is required for ciliogenesis. (a) PIPKI localizes at the basal body of primary cilium. RPE-1 cells treated with two sirnas targeting to
Xu et al., Supplementary Figures 1-7 Supplementary Figure 1. PIPKI is required for ciliogenesis. (a) PIPKI localizes at the basal body of primary cilium. RPE-1 cells treated with two sirnas targeting to
Supplementary information to accompany: A novel role for the DNA repair gene Rad51 in Netrin-1 signalling
 Supplementary information to accompany: A novel role for the DNA repair gene Rad51 in Netrin-1 signalling Glendining KA 1, Markie D 2, Gardner RJM 4, Franz EA 3, Robertson SP 4, Jasoni CL 1 Supplementary
Supplementary information to accompany: A novel role for the DNA repair gene Rad51 in Netrin-1 signalling Glendining KA 1, Markie D 2, Gardner RJM 4, Franz EA 3, Robertson SP 4, Jasoni CL 1 Supplementary
bronchial epithelial cells (I). Bronchi are outlined with dashed line. Scale bars = 25 µm, if not
 Supplemental Figure S1: ronchial epithelial cell polarity and integrity is maintained in bronchi. (A-E) Staining for selected markers of bronchial cell differentiation and intracellular compartments is
Supplemental Figure S1: ronchial epithelial cell polarity and integrity is maintained in bronchi. (A-E) Staining for selected markers of bronchial cell differentiation and intracellular compartments is
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb3240 Supplementary Figure 1 GBM cell lines display similar levels of p100 to p52 processing but respond differentially to TWEAK-induced TERT expression according to TERT promoter mutation
DOI: 10.1038/ncb3240 Supplementary Figure 1 GBM cell lines display similar levels of p100 to p52 processing but respond differentially to TWEAK-induced TERT expression according to TERT promoter mutation
MeCP2. MeCP2/α-tubulin. GFP mir1-1 mir132
 Conservation Figure S1. Schematic showing 3 UTR (top; thick black line), mir132 MRE (arrow) and nucleotide sequence conservation (vertical black lines; http://genome.ucsc.edu). a GFP mir1-1 mir132 b GFP
Conservation Figure S1. Schematic showing 3 UTR (top; thick black line), mir132 MRE (arrow) and nucleotide sequence conservation (vertical black lines; http://genome.ucsc.edu). a GFP mir1-1 mir132 b GFP
Theoretical cloning project
 Theoretical cloning project Needed to get credits Make it up yourself, don't copy Possible to do in groups of 2-4 students If you need help or an idea, ask! If you have no idea what to clone, I can give
Theoretical cloning project Needed to get credits Make it up yourself, don't copy Possible to do in groups of 2-4 students If you need help or an idea, ask! If you have no idea what to clone, I can give
Supplementary Figure 1: Expression of RNF8, HERC2 and NEURL4 in the cerebellum and knockdown of RNF8 by RNAi (a) Lysates of the cerebellum from rat
 Supplementary Figure 1: Expression of RNF8, HERC2 and NEURL4 in the cerebellum and knockdown of RNF8 by RNAi (a) Lysates of the cerebellum from rat pups at P6, P14, P22, P30 and adult (A) rats were subjected
Supplementary Figure 1: Expression of RNF8, HERC2 and NEURL4 in the cerebellum and knockdown of RNF8 by RNAi (a) Lysates of the cerebellum from rat pups at P6, P14, P22, P30 and adult (A) rats were subjected
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Gene replacements and insertions in rice by intron targeting using CRISPR Cas9 Table of Contents Supplementary Figure 1. sgrna-induced targeted mutations in the OsEPSPS gene in rice protoplasts. Supplementary
Gene replacements and insertions in rice by intron targeting using CRISPR Cas9 Table of Contents Supplementary Figure 1. sgrna-induced targeted mutations in the OsEPSPS gene in rice protoplasts. Supplementary
Supplementary Figure 1 Activities of ABEs using extended sgrnas in HEK293T cells.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Activities of ABEs using extended sgrnas in HEK293T cells. Base editing efficiencies of ABEs with extended sgrnas at Site 18 (a), Site 19 (b), the HBB-E2 site (c), and the HBB-E3
Supplementary Figure 1 Activities of ABEs using extended sgrnas in HEK293T cells. Base editing efficiencies of ABEs with extended sgrnas at Site 18 (a), Site 19 (b), the HBB-E2 site (c), and the HBB-E3
Supplementary Data. Generation and Characterization of Mixl1- Inducible Embryonic Stem Cells Under the Control of Oct3/4 Promoter or CAG Promoter
 Supplementary Data Generation and Characterization of Mixl1- Inducible Embryonic Stem Cells Under the Control of Oct3/4 Promoter or CAG Promoter We first introduced an expression unit composed of a tetresponse
Supplementary Data Generation and Characterization of Mixl1- Inducible Embryonic Stem Cells Under the Control of Oct3/4 Promoter or CAG Promoter We first introduced an expression unit composed of a tetresponse
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS Supplemental Figure S1 Mouse models for two types of human hereditary deafness with Cx26 mutations. (A) The construction of the transgene vector containing human Cx26 with dominant-negative
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS Supplemental Figure S1 Mouse models for two types of human hereditary deafness with Cx26 mutations. (A) The construction of the transgene vector containing human Cx26 with dominant-negative
To investigate the heredity of the WFP gene, we selected plants that were homozygous
 Supplementary information Supplementary Note ST-12 WFP allele is semi-dominant To investigate the heredity of the WFP gene, we selected plants that were homozygous for chromosome 1 of Nipponbare and heterozygous
Supplementary information Supplementary Note ST-12 WFP allele is semi-dominant To investigate the heredity of the WFP gene, we selected plants that were homozygous for chromosome 1 of Nipponbare and heterozygous
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Apoptosis analyses and quantification. Activated caspase3 immunostaining on sections of E9.0 Tcof1 +/ -;p53 +/- (a) and Tcof1 +/ -;p53 -/- (b) littermate embryos
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Apoptosis analyses and quantification. Activated caspase3 immunostaining on sections of E9.0 Tcof1 +/ -;p53 +/- (a) and Tcof1 +/ -;p53 -/- (b) littermate embryos
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 1.138/nature875 a promoter firefly luciferase CNS b Supplementary Figure 1. Dual luciferase assays on enhancer activity of CNS1, 2, and 3. a. promoter sequence was inserted upstream of firefly luciferase
doi: 1.138/nature875 a promoter firefly luciferase CNS b Supplementary Figure 1. Dual luciferase assays on enhancer activity of CNS1, 2, and 3. a. promoter sequence was inserted upstream of firefly luciferase
Supplementary Figure 1. Localization of MST1 in RPE cells. Proliferating or ciliated HA- MST1 expressing RPE cells (see Fig. 5b for establishment of
 Supplementary Figure 1. Localization of MST1 in RPE cells. Proliferating or ciliated HA- MST1 expressing RPE cells (see Fig. 5b for establishment of the cell line) were immunostained for HA, acetylated
Supplementary Figure 1. Localization of MST1 in RPE cells. Proliferating or ciliated HA- MST1 expressing RPE cells (see Fig. 5b for establishment of the cell line) were immunostained for HA, acetylated
Nature Biotechnology: doi: /nbt Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic and results of screening the combinatorial antibody library for Sox2 replacement activity. A single batch of MEFs were plated and transduced with doxycycline inducible
Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic and results of screening the combinatorial antibody library for Sox2 replacement activity. A single batch of MEFs were plated and transduced with doxycycline inducible
Supplementary Figure 1 Generation of migg1-yf mice. (A) Targeting strategy. Upper panel: schematic organization of the murine ɣ1 immunoglobulin
 Supplementary Figure 1 Generation of migg1-yf mice. (A) Targeting strategy. Upper panel: schematic organization of the murine ɣ1 immunoglobulin locus. The EcoRI restriction site between exons M1 and M2
Supplementary Figure 1 Generation of migg1-yf mice. (A) Targeting strategy. Upper panel: schematic organization of the murine ɣ1 immunoglobulin locus. The EcoRI restriction site between exons M1 and M2
Supplementary Figures and Legends.
 Supplementary Figures and Legends. Supplementary Figure 1: Impact of injury on Rb1 and PPARϒ expression. Following ipsilateral axotomy injury, adult DRG expression of Rb1 mrna declined (*p
Supplementary Figures and Legends. Supplementary Figure 1: Impact of injury on Rb1 and PPARϒ expression. Following ipsilateral axotomy injury, adult DRG expression of Rb1 mrna declined (*p
Experimental genetics - 2 Partha Roy
 Partha Roy Experimental genetics - 2 Making genetically altered animal 1) Gene knock-out k from: a) the entire animal b) selected cell-type/ tissue c) selected cell-type/tissue at certain time 2) Transgenic
Partha Roy Experimental genetics - 2 Making genetically altered animal 1) Gene knock-out k from: a) the entire animal b) selected cell-type/ tissue c) selected cell-type/tissue at certain time 2) Transgenic
We designed the targeting vector in such a way that the first exon was flanked by two LoxP sites and
 Mice We designed the targeting vector in such a way that the first exon was flanked by two LoxP sites and an Frt flanked neo cassette (Fig. S1A). Targeted BA1 (C57BL/6 129/SvEv) hybrid embryonic stem cells
Mice We designed the targeting vector in such a way that the first exon was flanked by two LoxP sites and an Frt flanked neo cassette (Fig. S1A). Targeted BA1 (C57BL/6 129/SvEv) hybrid embryonic stem cells
i-stop codon positions in the mcherry gene
 Supplementary Figure 1 i-stop codon positions in the mcherry gene The grnas (green) that can potentially generate stop codons from Trp (63 th and 98 th aa, upper panel) and Gln (47 th and 114 th aa, bottom
Supplementary Figure 1 i-stop codon positions in the mcherry gene The grnas (green) that can potentially generate stop codons from Trp (63 th and 98 th aa, upper panel) and Gln (47 th and 114 th aa, bottom
Supplementary Figure 1 Collision-induced dissociation (CID) mass spectra of peptides from PPK1, PPK2, PPK3 and PPK4 respectively.
 Supplementary Figure 1 lision-induced dissociation (CID) mass spectra of peptides from PPK1, PPK, PPK3 and PPK respectively. % of nuclei with signal / field a 5 c ppif3:gus pppk1:gus 0 35 30 5 0 15 10
Supplementary Figure 1 lision-induced dissociation (CID) mass spectra of peptides from PPK1, PPK, PPK3 and PPK respectively. % of nuclei with signal / field a 5 c ppif3:gus pppk1:gus 0 35 30 5 0 15 10
Supplementary Figures and Figure legends
 Supplementary Figures and Figure legends 3 Supplementary Figure 1. Conditional targeting construct for the murine Satb1 locus with a modified FLEX switch. Schematic of the wild type Satb1 locus; the conditional
Supplementary Figures and Figure legends 3 Supplementary Figure 1. Conditional targeting construct for the murine Satb1 locus with a modified FLEX switch. Schematic of the wild type Satb1 locus; the conditional
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Ho et al. 10.1073/pnas.0808899106 SI Materials and Methods In immunostaining, antibodies from Developmental Studies Hybridoma ank were -FasII (mouse, 1:200), - (mouse, 1:100), and
Supporting Information Ho et al. 10.1073/pnas.0808899106 SI Materials and Methods In immunostaining, antibodies from Developmental Studies Hybridoma ank were -FasII (mouse, 1:200), - (mouse, 1:100), and
Supplementary Materials
 Supplementary Materials Supplementary Figure 1. PKM2 interacts with MLC2 in cytokinesis. a, U87, U87/EGFRvIII, and HeLa cells in cytokinesis were immunostained with DAPI and an anti-pkm2 antibody. Thirty
Supplementary Materials Supplementary Figure 1. PKM2 interacts with MLC2 in cytokinesis. a, U87, U87/EGFRvIII, and HeLa cells in cytokinesis were immunostained with DAPI and an anti-pkm2 antibody. Thirty
The p53-puma axis suppresses ipsc generation
 The p53-puma axis suppresses ipsc generation Yanxin Li, Haizhong Feng, Haihui Gu, Dale W. Lewis, Youzhong Yuan, Lei Zhang, Hui Yu, Peng Zhang, Haizi Cheng, Weimin Miao, Weiping Yuan, Shi-Yuan Cheng, Susanne
The p53-puma axis suppresses ipsc generation Yanxin Li, Haizhong Feng, Haihui Gu, Dale W. Lewis, Youzhong Yuan, Lei Zhang, Hui Yu, Peng Zhang, Haizi Cheng, Weimin Miao, Weiping Yuan, Shi-Yuan Cheng, Susanne
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS
 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS Suppl. Fig. 1. Notch and myostatin expression is unaffected in the absence of p65 during postnatal development. A & B. Myostatin and Notch-1 expression levels were determined
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS Suppl. Fig. 1. Notch and myostatin expression is unaffected in the absence of p65 during postnatal development. A & B. Myostatin and Notch-1 expression levels were determined
amplify the conditional allele (2-lox) and recombined allele (1-lox) following tamoxifen
 Supplementary data Supplementary Table 1. Real-time PCR primer sequences Supplementary Fig. 1. (A) Genomic map of the Vhl (2-lox) conditional allele. Numbered boxes represent exon 1, which is targeted
Supplementary data Supplementary Table 1. Real-time PCR primer sequences Supplementary Fig. 1. (A) Genomic map of the Vhl (2-lox) conditional allele. Numbered boxes represent exon 1, which is targeted
Fig. S1. Molecular phylogenetic analysis of AtHD-ZIP IV family. A phylogenetic tree was constructed using Bayesian analysis with Markov Chain Monte
 Fig. S1. Molecular phylogenetic analysis of AtHD-ZIP IV family. A phylogenetic tree was constructed using Bayesian analysis with Markov Chain Monte Carlo algorithm for one million generations to obtain
Fig. S1. Molecular phylogenetic analysis of AtHD-ZIP IV family. A phylogenetic tree was constructed using Bayesian analysis with Markov Chain Monte Carlo algorithm for one million generations to obtain
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Endogenous gene tagging to study subcellular localization and chromatin binding. a, b, Schematic of experimental set-up to endogenously tag RNAi factors using the CRISPR Cas9 technology,
Supplementary Figure 1 Endogenous gene tagging to study subcellular localization and chromatin binding. a, b, Schematic of experimental set-up to endogenously tag RNAi factors using the CRISPR Cas9 technology,
Supplementary Data. Supplementary Methods Three-step protocol for spontaneous differentiation of mouse induced pluripotent stem (embryonic stem) cells
 Supplementary Data Supplementary Methods Three-step protocol for spontaneous differentiation of mouse induced pluripotent stem (embryonic stem) cells Mouse induced pluripotent stem cells (ipscs) were cultured
Supplementary Data Supplementary Methods Three-step protocol for spontaneous differentiation of mouse induced pluripotent stem (embryonic stem) cells Mouse induced pluripotent stem cells (ipscs) were cultured
Supplementary Information. Isl2b regulates anterior second heart field development in zebrafish
 Supplementary Information Isl2b regulates anterior second heart field development in zebrafish Hagen R. Witzel 1, Sirisha Cheedipudi 1, Rui Gao 1, Didier Y.R. Stainier 2 and Gergana D. Dobreva 1,3* 1 Origin
Supplementary Information Isl2b regulates anterior second heart field development in zebrafish Hagen R. Witzel 1, Sirisha Cheedipudi 1, Rui Gao 1, Didier Y.R. Stainier 2 and Gergana D. Dobreva 1,3* 1 Origin
Supplementary information for: Ten-Eleven Translocation-2 (Tet2) Is Involved in Myogenic Differentiation of Skeletal Myoblast Cells in
 Supplementary information for: Ten-Eleven Translocation-2 (Tet2) Is Involved in Myogenic Differentiation of Skeletal Myoblast Cells in Vitro Xia Zhong*, Qian-Qian Wang*, Jian-Wei Li, Yu-Mei Zhang, Xiao-Rong
Supplementary information for: Ten-Eleven Translocation-2 (Tet2) Is Involved in Myogenic Differentiation of Skeletal Myoblast Cells in Vitro Xia Zhong*, Qian-Qian Wang*, Jian-Wei Li, Yu-Mei Zhang, Xiao-Rong
Supplementary Figure S1. Immunodetection of full-length XA21 and the XA21 C-terminal cleavage product.
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure S1. Immunodetection of full-length XA21 and the XA21 C-terminal cleavage product. Total protein extracted from Kitaake wild type and rice plants carrying
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure S1. Immunodetection of full-length XA21 and the XA21 C-terminal cleavage product. Total protein extracted from Kitaake wild type and rice plants carrying
Nanog-Luc. R-Luc. 40 HA-Klf Relative protein level of Klf USP21. Vector USP2 USP21 *** *** *** ***
 :Flag Relative protein level of Relative protein level of : Flag Vec 21LV 21SV 2 : HA HA- HA- HA- HA-Klf4 Relative mrna expression Relative protein level of Relative protein level of Relative protein level
:Flag Relative protein level of Relative protein level of : Flag Vec 21LV 21SV 2 : HA HA- HA- HA- HA-Klf4 Relative mrna expression Relative protein level of Relative protein level of Relative protein level
