Eukaryotic Regulation
|
|
|
- Franklin Elvin Cain
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Eukaryotic Regulation Genomic Equivalence Every nucleated cell in an organism has exactly the same DNA as every other nucleated cell in the organism. Implications The different cells in an organism create different enzymes and proteins because of Genetic Regulation, not because of a different constitution. Because every cell has the same DNA, it is theoretically possible to clone an organism from a single cell. The different genes that are used during development are not lost from the cell, merely turned off.
2 Levels of Eukaryotic Regulation Levels for the control of gene expression goes from chromosomal control to transcriptional control to translational control 1. Regulation of Transcription 1A. Activation of Gene Structure Euchromatin vs. Heterochromatin DNA Changes Base modification methylation patterns Amplification and diminution extrachromosomal copies of DNA (rrna in Xenopus) tandem copies of DNA (rrna in Humans) Transposition e.g., mating type ( a vs. α ) Splicing Immunoglobulins 1B. Regulation of Transcription Positive control (Regulation at the Enhancer Region using Transcription Factores)
3 Levels of Eukaryotic Regulation 2. Regulation of Splicing (RNA Processing) Splicing and transcript stability Class Switching 3. Regulation of Transport (mrna to the cytoplasm) 4. Degradation of mrna mrna stability 5. Translational Regulation Masked or untranslated mrnas mrnas that do no translate by some enzymatic reaction masking the ribosome binding site. mrna codons -- Use of wobble to allow mrnas with different characteristics Some codons are more efficient (or numerous) than others. This allows for some proteins to be translated slow or fast depending on the specific codons they use. Stability of mrnas Some mrnas are more stable than others and are therefore translated more before they degrade. Related to specific sequence and to the length of the poly-a tail.
4 Levels of Eukaryotic Regulation 6. Posttranslational Regulation (Activity of Protein) Polyproteins Gets around one transcript/one cistron limitation by dividing primary polypeptide chain into parts after translation. We can regulate this by the rate of processing. Activation Control of rate of activation of enzymes. Enzymes are nonfunctional until activated. Inhibition Masking or destroying active enzymes to reduce their function. Stability of proteins Some proteins age more quickly than others -- related to their amino acid sequence, even in portions of the protein which are enzymatically inert.
5 Development & Differentiation 1. Gene Activity During Development Globin genes Polytene chromsomes and chromosome puffs 2. Immunogenetics Exception to Genomic Equivalence -- Loss of DNA to developed B cell DNA Differential RNA splicing to produce different gene products 3. Drosophila Development Embryonic Development Imaginal Discs Homeotic Genes
6 Developmental Fate Development Some Terms At some point in the development of an organism, a group of cells (and all the cells descended from them) are destined to become some single structure. At this time, their Developmental Fate is determined. Transdetermination When groups of cells have their developmental fate changed. For example, cells that were destined to become eyes are transdetermined to become wings. Imaginal Discs Thickening of the epidermis in Drosophila and other holometabolous insects. During pupation, the imaginal discs give rise to the adult organs & structures.
7 Drosophila Development Developmental Stages Egg Instars Pupa Adult
8 Developmental Genes Maternal Genes (e.g., Bicoid Protein) Segmentation Genes (e.g., gap, pair-rule, or polarity genes). Affects the number of segments or the polarity of the segments. Homeotic Genes Affect segment identity 70% - 90% Homology between Drosophila & Humans. Short (180 pb) Homology with DNA-binding proteins
CHAPTERS , 17: Eukaryotic Genetics
 CHAPTERS 14.1 14.6, 17: Eukaryotic Genetics 1. Review the levels of DNA packing within the eukaryote nucleus. Label each level. (A similar diagram is on pg 188 of your textbook.) 2. How do the coding regions
CHAPTERS 14.1 14.6, 17: Eukaryotic Genetics 1. Review the levels of DNA packing within the eukaryote nucleus. Label each level. (A similar diagram is on pg 188 of your textbook.) 2. How do the coding regions
Control of Eukaryotic Gene Expression (Learning Objectives)
 Control of Eukaryotic Gene Expression (Learning Objectives) 1. Compare and contrast chromatin and chromosome: composition, proteins involved and level of packing. Explain the structure and function of
Control of Eukaryotic Gene Expression (Learning Objectives) 1. Compare and contrast chromatin and chromosome: composition, proteins involved and level of packing. Explain the structure and function of
Themes: RNA and RNA Processing. Messenger RNA (mrna) What is a gene? RNA is very versatile! RNA-RNA interactions are very important!
 Themes: RNA is very versatile! RNA and RNA Processing Chapter 14 RNA-RNA interactions are very important! Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes have many important differences. Messenger RNA (mrna) Carries genetic
Themes: RNA is very versatile! RNA and RNA Processing Chapter 14 RNA-RNA interactions are very important! Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes have many important differences. Messenger RNA (mrna) Carries genetic
DNA Function: Information Transmission
 DNA Function: Information Transmission DNA is called the code of life. What does it code for? *the information ( code ) to make proteins! Why are proteins so important? Nearly every function of a living
DNA Function: Information Transmission DNA is called the code of life. What does it code for? *the information ( code ) to make proteins! Why are proteins so important? Nearly every function of a living
Chapter 13. From DNA to Protein
 Chapter 13 From DNA to Protein Proteins All proteins consist of polypeptide chains A linear sequence of amino acids Each chain corresponds to the nucleotide base sequenceof a gene The Path From Genes to
Chapter 13 From DNA to Protein Proteins All proteins consist of polypeptide chains A linear sequence of amino acids Each chain corresponds to the nucleotide base sequenceof a gene The Path From Genes to
From DNA to Protein: Genotype to Phenotype
 12 From DNA to Protein: Genotype to Phenotype 12.1 What Is the Evidence that Genes Code for Proteins? The gene-enzyme relationship is one-gene, one-polypeptide relationship. Example: In hemoglobin, each
12 From DNA to Protein: Genotype to Phenotype 12.1 What Is the Evidence that Genes Code for Proteins? The gene-enzyme relationship is one-gene, one-polypeptide relationship. Example: In hemoglobin, each
32 Gene regulation in Eukaryotes Lecture Outline 11/28/05. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes and Eukarykotes
 3 Gene regulation in Eukaryotes Lecture Outline /8/05 Gene regulation in eukaryotes Chromatin remodeling More kinds of control elements Promoters, Enhancers, and Silencers Combinatorial control Cell-specific
3 Gene regulation in Eukaryotes Lecture Outline /8/05 Gene regulation in eukaryotes Chromatin remodeling More kinds of control elements Promoters, Enhancers, and Silencers Combinatorial control Cell-specific
REGULATION OF PROTEIN SYNTHESIS. II. Eukaryotes
 REGULATION OF PROTEIN SYNTHESIS II. Eukaryotes Complexities of eukaryotic gene expression! Several steps needed for synthesis of mrna! Separation in space of transcription and translation! Compartmentation
REGULATION OF PROTEIN SYNTHESIS II. Eukaryotes Complexities of eukaryotic gene expression! Several steps needed for synthesis of mrna! Separation in space of transcription and translation! Compartmentation
EUKARYOTIC GENE CONTROL
 EUKARYOTIC GENE CONTROL THE BIG QUESTIONS How are genes turned on and off? How do cells with the same DNA/ genes differentiate to perform completely different and specialized functions? GENE EXPRESSION
EUKARYOTIC GENE CONTROL THE BIG QUESTIONS How are genes turned on and off? How do cells with the same DNA/ genes differentiate to perform completely different and specialized functions? GENE EXPRESSION
Wednesday, November 22, 17. Exons and Introns
 Exons and Introns Introns and Exons Exons: coded regions of DNA that get transcribed and translated into proteins make up 5% of the genome Introns and Exons Introns: non-coded regions of DNA Must be removed
Exons and Introns Introns and Exons Exons: coded regions of DNA that get transcribed and translated into proteins make up 5% of the genome Introns and Exons Introns: non-coded regions of DNA Must be removed
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Flow of Genetic Information The flow of genetic information can be symbolized as: DNA RNA Protein
 PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Flow of Genetic Information The flow of genetic information can be symbolized as: DNA RNA Protein This is also known as: The central dogma of molecular biology Protein Proteins are made
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Flow of Genetic Information The flow of genetic information can be symbolized as: DNA RNA Protein This is also known as: The central dogma of molecular biology Protein Proteins are made
Gene Expression: Transcription
 Gene Expression: Transcription The majority of genes are expressed as the proteins they encode. The process occurs in two steps: Transcription = DNA RNA Translation = RNA protein Taken together, they make
Gene Expression: Transcription The majority of genes are expressed as the proteins they encode. The process occurs in two steps: Transcription = DNA RNA Translation = RNA protein Taken together, they make
Chapter 18: Regulation of Gene Expression. 1. Gene Regulation in Bacteria 2. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes 3. Gene Regulation & Cancer
 Chapter 18: Regulation of Gene Expression 1. Gene Regulation in Bacteria 2. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes 3. Gene Regulation & Cancer Gene Regulation Gene regulation refers to all aspects of controlling
Chapter 18: Regulation of Gene Expression 1. Gene Regulation in Bacteria 2. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes 3. Gene Regulation & Cancer Gene Regulation Gene regulation refers to all aspects of controlling
CHAPTER 18 LECTURE NOTES: CONTROL OF GENE EXPRESSION PART B: CONTROL IN EUKARYOTES
 CHAPTER 18 LECTURE NOTES: CONTROL OF GENE EXPRESSION PART B: CONTROL IN EUKARYOTES I. Introduction A. No operon structures in eukaryotes B. Regulation of gene expression is frequently tissue specific.
CHAPTER 18 LECTURE NOTES: CONTROL OF GENE EXPRESSION PART B: CONTROL IN EUKARYOTES I. Introduction A. No operon structures in eukaryotes B. Regulation of gene expression is frequently tissue specific.
Hello! Outline. Cell Biology: RNA and Protein synthesis. In all living cells, DNA molecules are the storehouses of information. 6.
 Cell Biology: RNA and Protein synthesis In all living cells, DNA molecules are the storehouses of information Hello! Outline u 1. Key concepts u 2. Central Dogma u 3. RNA Types u 4. RNA (Ribonucleic Acid)
Cell Biology: RNA and Protein synthesis In all living cells, DNA molecules are the storehouses of information Hello! Outline u 1. Key concepts u 2. Central Dogma u 3. RNA Types u 4. RNA (Ribonucleic Acid)
Make the protein through the genetic dogma process.
 Make the protein through the genetic dogma process. Coding Strand 5 AGCAATCATGGATTGGGTACATTTGTAACTGT 3 Template Strand mrna Protein Complete the table. DNA strand DNA s strand G mrna A C U G T A T Amino
Make the protein through the genetic dogma process. Coding Strand 5 AGCAATCATGGATTGGGTACATTTGTAACTGT 3 Template Strand mrna Protein Complete the table. DNA strand DNA s strand G mrna A C U G T A T Amino
Lecture for Wednesday. Dr. Prince BIOL 1408
 Lecture for Wednesday Dr. Prince BIOL 1408 THE FLOW OF GENETIC INFORMATION FROM DNA TO RNA TO PROTEIN Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Genes are expressed as proteins A gene is a segment of DNA that
Lecture for Wednesday Dr. Prince BIOL 1408 THE FLOW OF GENETIC INFORMATION FROM DNA TO RNA TO PROTEIN Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Genes are expressed as proteins A gene is a segment of DNA that
Protein Synthesis. DNA to RNA to Protein
 Protein Synthesis DNA to RNA to Protein From Genes to Proteins Processing the information contained in DNA into proteins involves a sequence of events known as gene expression and results in protein synthesis.
Protein Synthesis DNA to RNA to Protein From Genes to Proteins Processing the information contained in DNA into proteins involves a sequence of events known as gene expression and results in protein synthesis.
Chapter 11. How Genes Are Controlled. Lectures by Edward J. Zalisko
 Chapter 11 How Genes Are Controlled PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Essential Biology, Fifth Edition, and Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology, Fourth Edition Eric J. Simon, Jean L. Dickey, and
Chapter 11 How Genes Are Controlled PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Essential Biology, Fifth Edition, and Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology, Fourth Edition Eric J. Simon, Jean L. Dickey, and
Review of Protein (one or more polypeptide) A polypeptide is a long chain of..
 Gene expression Review of Protein (one or more polypeptide) A polypeptide is a long chain of.. In a protein, the sequence of amino acid determines its which determines the protein s A protein with an enzymatic
Gene expression Review of Protein (one or more polypeptide) A polypeptide is a long chain of.. In a protein, the sequence of amino acid determines its which determines the protein s A protein with an enzymatic
RNA : functional role
 RNA : functional role Hamad Yaseen, PhD MLS Department, FAHS Hamad.ali@hsc.edu.kw RNA mrna rrna trna 1 From DNA to Protein -Outline- From DNA to RNA From RNA to Protein From DNA to RNA Transcription: Copying
RNA : functional role Hamad Yaseen, PhD MLS Department, FAHS Hamad.ali@hsc.edu.kw RNA mrna rrna trna 1 From DNA to Protein -Outline- From DNA to RNA From RNA to Protein From DNA to RNA Transcription: Copying
Control of Eukaryotic Genes. AP Biology
 Control of Eukaryotic Genes The BIG Questions How are genes turned on & off in eukaryotes? How do cells with the same genes differentiate to perform completely different, specialized functions? Evolution
Control of Eukaryotic Genes The BIG Questions How are genes turned on & off in eukaryotes? How do cells with the same genes differentiate to perform completely different, specialized functions? Evolution
Eukaryotic Gene Structure
 Eukaryotic Gene Structure Terminology Genome entire genetic material of an individual Transcriptome set of transcribed sequences Proteome set of proteins encoded by the genome 2 Gene Basic physical and
Eukaryotic Gene Structure Terminology Genome entire genetic material of an individual Transcriptome set of transcribed sequences Proteome set of proteins encoded by the genome 2 Gene Basic physical and
Lecture Overview. Overview of the Genetic Information. Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology. Chapter 3 DNA & RNA Protein Synthesis Lecture 6
 Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology Marieb Hoehn Chapter 3 DNA & RNA Protein Synthesis Lecture 6 Lecture Overview The Genetic Information Structure of DNA/RNA DNA Replication Overview of protein synthesis
Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology Marieb Hoehn Chapter 3 DNA & RNA Protein Synthesis Lecture 6 Lecture Overview The Genetic Information Structure of DNA/RNA DNA Replication Overview of protein synthesis
8/21/2014. From Gene to Protein
 From Gene to Protein Chapter 17 Objectives Describe the contributions made by Garrod, Beadle, and Tatum to our understanding of the relationship between genes and enzymes Briefly explain how information
From Gene to Protein Chapter 17 Objectives Describe the contributions made by Garrod, Beadle, and Tatum to our understanding of the relationship between genes and enzymes Briefly explain how information
The Genetic Code and Transcription. Chapter 12 Honors Genetics Ms. Susan Chabot
 The Genetic Code and Transcription Chapter 12 Honors Genetics Ms. Susan Chabot TRANSCRIPTION Copy SAME language DNA to RNA Nucleic Acid to Nucleic Acid TRANSLATION Copy DIFFERENT language RNA to Amino
The Genetic Code and Transcription Chapter 12 Honors Genetics Ms. Susan Chabot TRANSCRIPTION Copy SAME language DNA to RNA Nucleic Acid to Nucleic Acid TRANSLATION Copy DIFFERENT language RNA to Amino
BIO 311C Spring Lecture 36 Wednesday 28 Apr.
 BIO 311C Spring 2010 1 Lecture 36 Wednesday 28 Apr. Synthesis of a Polypeptide Chain 5 direction of ribosome movement along the mrna 3 ribosome mrna NH 2 polypeptide chain direction of mrna movement through
BIO 311C Spring 2010 1 Lecture 36 Wednesday 28 Apr. Synthesis of a Polypeptide Chain 5 direction of ribosome movement along the mrna 3 ribosome mrna NH 2 polypeptide chain direction of mrna movement through
Section 10.3 Outline 10.3 How Is the Base Sequence of a Messenger RNA Molecule Translated into Protein?
 Section 10.3 Outline 10.3 How Is the Base Sequence of a Messenger RNA Molecule Translated into Protein? Messenger RNA Carries Information for Protein Synthesis from the DNA to Ribosomes Ribosomes Consist
Section 10.3 Outline 10.3 How Is the Base Sequence of a Messenger RNA Molecule Translated into Protein? Messenger RNA Carries Information for Protein Synthesis from the DNA to Ribosomes Ribosomes Consist
Regulation of Gene Expression
 Chapter 18 Regulation of Gene Expression Edited by Shawn Lester PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley
Chapter 18 Regulation of Gene Expression Edited by Shawn Lester PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley
BIOLOGY. Chapter 16 GenesExpression
 BIOLOGY Chapter 16 GenesExpression CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 18 Gene Expression 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 16.1 Differential Gene Expression results
BIOLOGY Chapter 16 GenesExpression CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 18 Gene Expression 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 16.1 Differential Gene Expression results
Unit IX Problem 3 Genetics: Basic Concepts in Molecular Biology
 Unit IX Problem 3 Genetics: Basic Concepts in Molecular Biology - The central dogma (principle) of molecular biology: Information from DNA are transcribed to mrna which will be further translated to synthesize
Unit IX Problem 3 Genetics: Basic Concepts in Molecular Biology - The central dogma (principle) of molecular biology: Information from DNA are transcribed to mrna which will be further translated to synthesize
BEADLE & TATUM EXPERIMENT
 FROM DNA TO PROTEINS: gene expression Chapter 14 LECTURE OBJECTIVES What Is the Evidence that Genes Code for Proteins? How Does Information Flow from Genes to Proteins? How Is the Information Content in
FROM DNA TO PROTEINS: gene expression Chapter 14 LECTURE OBJECTIVES What Is the Evidence that Genes Code for Proteins? How Does Information Flow from Genes to Proteins? How Is the Information Content in
Control of Eukaryotic Genes
 Control of Eukaryotic Genes 2007-2008 The BIG Questions How are genes turned on & off in eukaryotes? How do cells with the same genes differentiate to perform completely different, specialized functions?
Control of Eukaryotic Genes 2007-2008 The BIG Questions How are genes turned on & off in eukaryotes? How do cells with the same genes differentiate to perform completely different, specialized functions?
Additional Practice Problems for Reading Period
 BS 50 Genetics and Genomics Reading Period Additional Practice Problems for Reading Period Question 1. In patients with a particular type of leukemia, their leukemic B lymphocytes display a translocation
BS 50 Genetics and Genomics Reading Period Additional Practice Problems for Reading Period Question 1. In patients with a particular type of leukemia, their leukemic B lymphocytes display a translocation
CH 17 :From Gene to Protein
 CH 17 :From Gene to Protein Defining a gene gene gene Defining a gene is problematic because one gene can code for several protein products, some genes code only for RNA, two genes can overlap, and there
CH 17 :From Gene to Protein Defining a gene gene gene Defining a gene is problematic because one gene can code for several protein products, some genes code only for RNA, two genes can overlap, and there
NOTES Gene Expression ACP Biology, NNHS
 Name Date Block NOTES Gene Expression ACP Biology, NNHS Model 1: Transcription the process of genes in DNA being copied into a messenger RNA 1. Where in the cell is DNA found? 2. Where in the cell does
Name Date Block NOTES Gene Expression ACP Biology, NNHS Model 1: Transcription the process of genes in DNA being copied into a messenger RNA 1. Where in the cell is DNA found? 2. Where in the cell does
Genetics Biology 331 Exam 3B Spring 2015
 Genetics Biology 331 Exam 3B Spring 2015 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) DNA methylation may be a significant mode of genetic regulation
Genetics Biology 331 Exam 3B Spring 2015 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) DNA methylation may be a significant mode of genetic regulation
Big Idea 3C Basic Review
 Big Idea 3C Basic Review 1. A gene is a. A sequence of DNA that codes for a protein. b. A sequence of amino acids that codes for a protein. c. A sequence of codons that code for nucleic acids. d. The end
Big Idea 3C Basic Review 1. A gene is a. A sequence of DNA that codes for a protein. b. A sequence of amino acids that codes for a protein. c. A sequence of codons that code for nucleic acids. d. The end
From Gene to Protein transcription, messenger RNA (mrna) translation, RNA processing triplet code, template strand, codons,
 From Gene to Protein I. Transcription and translation are the two main processes linking gene to protein. A. RNA is chemically similar to DNA, except that it contains ribose as its sugar and substitutes
From Gene to Protein I. Transcription and translation are the two main processes linking gene to protein. A. RNA is chemically similar to DNA, except that it contains ribose as its sugar and substitutes
Genes found in the genome include protein-coding genes and non-coding RNA genes. Which nucleotide is not normally found in non-coding RNA genes?
 Midterm Q Genes found in the genome include protein-coding genes and non-coding RNA genes Which nucleotide is not normally found in non-coding RNA genes? G T 3 A 4 C 5 U 00% Midterm Q Which of the following
Midterm Q Genes found in the genome include protein-coding genes and non-coding RNA genes Which nucleotide is not normally found in non-coding RNA genes? G T 3 A 4 C 5 U 00% Midterm Q Which of the following
Fig Ch 17: From Gene to Protein
 Fig. 17-1 Ch 17: From Gene to Protein Basic Principles of Transcription and Translation RNA is the intermediate between genes and the proteins for which they code Transcription is the synthesis of RNA
Fig. 17-1 Ch 17: From Gene to Protein Basic Principles of Transcription and Translation RNA is the intermediate between genes and the proteins for which they code Transcription is the synthesis of RNA
DNA is the MASTER PLAN. RNA is the BLUEPRINT of the Master Plan
 Sec. 12-3 RNA and Protein Synthesis Roles of DNA and RNA DNA is the MASTER PLAN RNA is the BLUEPRINT of the Master Plan 1 RNA uses the information from DNA to make proteins Differs from DNA: 1. Ribose
Sec. 12-3 RNA and Protein Synthesis Roles of DNA and RNA DNA is the MASTER PLAN RNA is the BLUEPRINT of the Master Plan 1 RNA uses the information from DNA to make proteins Differs from DNA: 1. Ribose
Gene Expression Transcription/Translation Protein Synthesis
 Gene Expression Transcription/Translation Protein Synthesis 1. Describe how genetic information is transcribed into sequences of bases in RNA molecules and is finally translated into sequences of amino
Gene Expression Transcription/Translation Protein Synthesis 1. Describe how genetic information is transcribed into sequences of bases in RNA molecules and is finally translated into sequences of amino
Control of Eukaryotic Genes. AP Biology
 Control of Eukaryotic Genes The BIG Questions How are genes turned on & off in eukaryotes? How do cells with the same genes differentiate to perform completely different, specialized functions? Evolution
Control of Eukaryotic Genes The BIG Questions How are genes turned on & off in eukaryotes? How do cells with the same genes differentiate to perform completely different, specialized functions? Evolution
Lecture 20: Drosophila melanogaster
 Lecture 20: Drosophila melanogaster Model organisms Polytene chromosome Life cycle P elements and transformation Embryogenesis Read textbook: 732-744; Fig. 20.4; 20.10; 20.15-26 www.mhhe.com/hartwell3
Lecture 20: Drosophila melanogaster Model organisms Polytene chromosome Life cycle P elements and transformation Embryogenesis Read textbook: 732-744; Fig. 20.4; 20.10; 20.15-26 www.mhhe.com/hartwell3
Ch Molecular Biology of the Gene
 Ch. 12 - Molecular Biology of the Gene AP BIOLOGY CHAPTER GUIDE 1. In the middle of the unraveling the mysteries of DNA, researchers knew that genetic material must be able to. It must be stable so it
Ch. 12 - Molecular Biology of the Gene AP BIOLOGY CHAPTER GUIDE 1. In the middle of the unraveling the mysteries of DNA, researchers knew that genetic material must be able to. It must be stable so it
RNA & PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
 RNA & PROTEIN SYNTHESIS DNA & RNA Genes are coded DNA instructions that control the production of proteins within the cell. The first step in decoding these genetic messages is to copy part of the nucleotide
RNA & PROTEIN SYNTHESIS DNA & RNA Genes are coded DNA instructions that control the production of proteins within the cell. The first step in decoding these genetic messages is to copy part of the nucleotide
Chapter 13 - Regulation of Gene Expression
 Chapter 13 - Regulation of Gene Expression 1. Describe the typical components of an operon in an E. coli (prokaryotic) cell. (p. 238-239) a. regulator gene - b. promoter - c. operator - d. structural gene
Chapter 13 - Regulation of Gene Expression 1. Describe the typical components of an operon in an E. coli (prokaryotic) cell. (p. 238-239) a. regulator gene - b. promoter - c. operator - d. structural gene
DNA is the genetic material. DNA structure. Chapter 7: DNA Replication, Transcription & Translation; Mutations & Ames test
 DNA is the genetic material Chapter 7: DNA Replication, Transcription & Translation; Mutations & Ames test Dr. Amy Rogers Bio 139 General Microbiology Hereditary information is carried by DNA Griffith/Avery
DNA is the genetic material Chapter 7: DNA Replication, Transcription & Translation; Mutations & Ames test Dr. Amy Rogers Bio 139 General Microbiology Hereditary information is carried by DNA Griffith/Avery
Concepts and Methods in Developmental Biology
 Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Concepts and Methods in Developmental Biology June 16, 2009 Conceptual and Methodological Tools Concepts Genomic equivalence Differential gene expression Differentiation/de-differentiation
Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Concepts and Methods in Developmental Biology June 16, 2009 Conceptual and Methodological Tools Concepts Genomic equivalence Differential gene expression Differentiation/de-differentiation
Chapter 8 From DNA to Proteins. Chapter 8 From DNA to Proteins
 KEY CONCEPT Section 1 DNA was identified as the genetic material through a series of experiments. Griffith finds a transforming principle. Griffith experimented with the bacteria that cause pneumonia.
KEY CONCEPT Section 1 DNA was identified as the genetic material through a series of experiments. Griffith finds a transforming principle. Griffith experimented with the bacteria that cause pneumonia.
What happens after DNA Replication??? Transcription, translation, gene expression/protein synthesis!!!!
 What happens after DNA Replication??? Transcription, translation, gene expression/protein synthesis!!!! Protein Synthesis/Gene Expression Why do we need to make proteins? To build parts for our body as
What happens after DNA Replication??? Transcription, translation, gene expression/protein synthesis!!!! Protein Synthesis/Gene Expression Why do we need to make proteins? To build parts for our body as
Chapter 12 Packet DNA 1. What did Griffith conclude from his experiment? 2. Describe the process of transformation.
 Chapter 12 Packet DNA and RNA Name Period California State Standards covered by this chapter: Cell Biology 1. The fundamental life processes of plants and animals depend on a variety of chemical reactions
Chapter 12 Packet DNA and RNA Name Period California State Standards covered by this chapter: Cell Biology 1. The fundamental life processes of plants and animals depend on a variety of chemical reactions
Transcription and Translation
 Biology Name: Morales Date: Period: Transcription and Translation Directions: Read the following and answer the questions in complete sentences. DNA is the molecule of heredity it determines an organism
Biology Name: Morales Date: Period: Transcription and Translation Directions: Read the following and answer the questions in complete sentences. DNA is the molecule of heredity it determines an organism
Transcription Eukaryotic Cells
 Transcription Eukaryotic Cells Packet #20 1 Introduction Transcription is the process in which genetic information, stored in a strand of DNA (gene), is copied into a strand of RNA. Protein-encoding genes
Transcription Eukaryotic Cells Packet #20 1 Introduction Transcription is the process in which genetic information, stored in a strand of DNA (gene), is copied into a strand of RNA. Protein-encoding genes
RNA and PROTEIN SYNTHESIS. Chapter 13
 RNA and PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Chapter 13 DNA Double stranded Thymine Sugar is RNA Single stranded Uracil Sugar is Ribose Deoxyribose Types of RNA 1. Messenger RNA (mrna) Carries copies of instructions from
RNA and PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Chapter 13 DNA Double stranded Thymine Sugar is RNA Single stranded Uracil Sugar is Ribose Deoxyribose Types of RNA 1. Messenger RNA (mrna) Carries copies of instructions from
Protein Synthesis Notes
 Protein Synthesis Notes Protein Synthesis: Overview Transcription: synthesis of mrna under the direction of DNA. Translation: actual synthesis of a polypeptide under the direction of mrna. Transcription
Protein Synthesis Notes Protein Synthesis: Overview Transcription: synthesis of mrna under the direction of DNA. Translation: actual synthesis of a polypeptide under the direction of mrna. Transcription
Protein Synthesis
 HEBISD Student Expectations: Identify that RNA Is a nucleic acid with a single strand of nucleotides Contains the 5-carbon sugar ribose Contains the nitrogen bases A, G, C and U instead of T. The U is
HEBISD Student Expectations: Identify that RNA Is a nucleic acid with a single strand of nucleotides Contains the 5-carbon sugar ribose Contains the nitrogen bases A, G, C and U instead of T. The U is
Transcription in Eukaryotes
 Transcription in Eukaryotes Biology I Hayder A Giha Transcription Transcription is a DNA-directed synthesis of RNA, which is the first step in gene expression. Gene expression, is transformation of the
Transcription in Eukaryotes Biology I Hayder A Giha Transcription Transcription is a DNA-directed synthesis of RNA, which is the first step in gene expression. Gene expression, is transformation of the
Genomics and Gene Recognition Genes and Blue Genes
 Genomics and Gene Recognition Genes and Blue Genes November 3, 2004 Eukaryotic Gene Structure eukaryotic genomes are considerably more complex than those of prokaryotes eukaryotic cells have organelles
Genomics and Gene Recognition Genes and Blue Genes November 3, 2004 Eukaryotic Gene Structure eukaryotic genomes are considerably more complex than those of prokaryotes eukaryotic cells have organelles
Protein Synthesis & Gene Expression
 DNA provides the instructions for how to build proteins Each gene dictates how to build a single protein in prokaryotes The sequence of nucleotides (AGCT) in DNA dictates the order of amino acids that
DNA provides the instructions for how to build proteins Each gene dictates how to build a single protein in prokaryotes The sequence of nucleotides (AGCT) in DNA dictates the order of amino acids that
MOLECULAR GENETICS PROTEIN SYNTHESIS. Molecular Genetics Activity #2 page 1
 AP BIOLOGY MOLECULAR GENETICS ACTIVITY #2 NAME DATE HOUR PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Molecular Genetics Activity #2 page 1 GENETIC CODE PROTEIN SYNTHESIS OVERVIEW Molecular Genetics Activity #2 page 2 PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
AP BIOLOGY MOLECULAR GENETICS ACTIVITY #2 NAME DATE HOUR PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Molecular Genetics Activity #2 page 1 GENETIC CODE PROTEIN SYNTHESIS OVERVIEW Molecular Genetics Activity #2 page 2 PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
Higher Human Biology Unit 1: Human Cells Pupils Learning Outcomes
 Higher Human Biology Unit 1: Human Cells Pupils Learning Outcomes 1.1 Division and Differentiation in Human Cells I can state that cellular differentiation is the process by which a cell develops more
Higher Human Biology Unit 1: Human Cells Pupils Learning Outcomes 1.1 Division and Differentiation in Human Cells I can state that cellular differentiation is the process by which a cell develops more
Ch. 10 From DNA to Protein. AP Biology
 Ch. 10 From DNA to Protein Protein Synthesis Metabolism and Gene Expression n Inheritance of metabolic diseases suggests that genes coded for enzymes n Diseases (phenotypes) caused by non-functional gene
Ch. 10 From DNA to Protein Protein Synthesis Metabolism and Gene Expression n Inheritance of metabolic diseases suggests that genes coded for enzymes n Diseases (phenotypes) caused by non-functional gene
Chapter 14 Active Reading Guide From Gene to Protein
 Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Chapter 14 Active Reading Guide From Gene to Protein This is going to be a very long journey, but it is crucial to your understanding of biology. Work on this chapter a single
Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Chapter 14 Active Reading Guide From Gene to Protein This is going to be a very long journey, but it is crucial to your understanding of biology. Work on this chapter a single
DNA - DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID
 DNA - DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID blueprint of life (has the instructions for making an organism) established by James Watson and Francis Crick codes for your genes shape of a double helix made of repeating
DNA - DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID blueprint of life (has the instructions for making an organism) established by James Watson and Francis Crick codes for your genes shape of a double helix made of repeating
Chapter 8: DNA and RNA
 Chapter 8: DNA and RNA Lecture Outline Enger, E. D., Ross, F. C., & Bailey, D. B. (2012). Concepts in biology (14th ed.). New York: McGraw- Hill. 1 8-1 DNA and the Importance of Proteins Proteins play
Chapter 8: DNA and RNA Lecture Outline Enger, E. D., Ross, F. C., & Bailey, D. B. (2012). Concepts in biology (14th ed.). New York: McGraw- Hill. 1 8-1 DNA and the Importance of Proteins Proteins play
DNA makes RNA makes Proteins. The Central Dogma
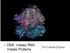 DNA makes RNA makes Proteins The Central Dogma TRANSCRIPTION DNA RNA transcript RNA polymerase RNA PROCESSING Exon RNA transcript (pre-mrna) Intron Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase NUCLEUS CYTOPLASM FORMATION
DNA makes RNA makes Proteins The Central Dogma TRANSCRIPTION DNA RNA transcript RNA polymerase RNA PROCESSING Exon RNA transcript (pre-mrna) Intron Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase NUCLEUS CYTOPLASM FORMATION
CHAPTER 21 LECTURE SLIDES
 CHAPTER 21 LECTURE SLIDES Prepared by Brenda Leady University of Toledo To run the animations you must be in Slideshow View. Use the buttons on the animation to play, pause, and turn audio/text on or off.
CHAPTER 21 LECTURE SLIDES Prepared by Brenda Leady University of Toledo To run the animations you must be in Slideshow View. Use the buttons on the animation to play, pause, and turn audio/text on or off.
What is RNA? Another type of nucleic acid A working copy of DNA Does not matter if it is damaged or destroyed
 RNA Section 3.1 What is RNA? Another type of nucleic acid A working copy of DNA Does not matter if it is damaged or destroyed Used to direct the production of proteins that determines an organisms characteristics
RNA Section 3.1 What is RNA? Another type of nucleic acid A working copy of DNA Does not matter if it is damaged or destroyed Used to direct the production of proteins that determines an organisms characteristics
Introducing new DNA into the genome requires cloning the donor sequence, delivery of the cloned DNA into the cell, and integration into the genome.
 Key Terms Chapter 32: Genetic Engineering Cloning describes propagation of a DNA sequence by incorporating it into a hybrid construct that can be replicated in a host cell. A cloning vector is a plasmid
Key Terms Chapter 32: Genetic Engineering Cloning describes propagation of a DNA sequence by incorporating it into a hybrid construct that can be replicated in a host cell. A cloning vector is a plasmid
Chapter 8 Lecture Outline. Transcription, Translation, and Bioinformatics
 Chapter 8 Lecture Outline Transcription, Translation, and Bioinformatics Replication, Transcription, Translation n Repetitive processes Build polymers of nucleotides or amino acids n All have 3 major steps
Chapter 8 Lecture Outline Transcription, Translation, and Bioinformatics Replication, Transcription, Translation n Repetitive processes Build polymers of nucleotides or amino acids n All have 3 major steps
Bio 101 Sample questions: Chapter 10
 Bio 101 Sample questions: Chapter 10 1. Which of the following is NOT needed for DNA replication? A. nucleotides B. ribosomes C. Enzymes (like polymerases) D. DNA E. all of the above are needed 2 The information
Bio 101 Sample questions: Chapter 10 1. Which of the following is NOT needed for DNA replication? A. nucleotides B. ribosomes C. Enzymes (like polymerases) D. DNA E. all of the above are needed 2 The information
Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes. Dr. Syahril Abdullah Medical Genetics Laboratory
 Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes Dr. Syahril Abdullah Medical Genetics Laboratory syahril@medic.upm.edu.my Lecture Outline 1. The Genome 2. Overview of Gene Control 3. Cellular Differentiation in Higher Eukaryotes
Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes Dr. Syahril Abdullah Medical Genetics Laboratory syahril@medic.upm.edu.my Lecture Outline 1. The Genome 2. Overview of Gene Control 3. Cellular Differentiation in Higher Eukaryotes
Chapter 12. DNA TRANSCRIPTION and TRANSLATION
 Chapter 12 DNA TRANSCRIPTION and TRANSLATION 12-3 RNA and Protein Synthesis WARM UP What are proteins? Where do they come from? From DNA to RNA to Protein DNA in our cells carry the instructions for making
Chapter 12 DNA TRANSCRIPTION and TRANSLATION 12-3 RNA and Protein Synthesis WARM UP What are proteins? Where do they come from? From DNA to RNA to Protein DNA in our cells carry the instructions for making
TRANSCRIPTION AND PROCESSING OF RNA
 TRANSCRIPTION AND PROCESSING OF RNA 1. The steps of gene expression. 2. General characterization of transcription: steps, components of transcription apparatus. 3. Transcription of eukaryotic structural
TRANSCRIPTION AND PROCESSING OF RNA 1. The steps of gene expression. 2. General characterization of transcription: steps, components of transcription apparatus. 3. Transcription of eukaryotic structural
Protein Synthesis: Transcription and Translation
 Protein Synthesis: Transcription and Translation Proteins In living things, proteins are in charge of the expression of our traits (hair/eye color, ability to make insulin, predisposition for cancer, etc.)
Protein Synthesis: Transcription and Translation Proteins In living things, proteins are in charge of the expression of our traits (hair/eye color, ability to make insulin, predisposition for cancer, etc.)
Unit 1 Human cells. 1. Division and differentiation in human cells
 Unit 1 Human cells 1. Division and differentiation in human cells Stem cells Describe the process of differentiation. Explain how differentiation is brought about with reference to genes. Name the two
Unit 1 Human cells 1. Division and differentiation in human cells Stem cells Describe the process of differentiation. Explain how differentiation is brought about with reference to genes. Name the two
MCDB 1041 Class 21 Splicing and Gene Expression
 MCDB 1041 Class 21 Splicing and Gene Expression Learning Goals Describe the role of introns and exons Interpret the possible outcomes of alternative splicing Relate the generation of protein from DNA to
MCDB 1041 Class 21 Splicing and Gene Expression Learning Goals Describe the role of introns and exons Interpret the possible outcomes of alternative splicing Relate the generation of protein from DNA to
Chapter 10: Gene Expression and Regulation
 Chapter 10: Gene Expression and Regulation Fact 1: DNA contains information but is unable to carry out actions Fact 2: Proteins are the workhorses but contain no information THUS Information in DNA must
Chapter 10: Gene Expression and Regulation Fact 1: DNA contains information but is unable to carry out actions Fact 2: Proteins are the workhorses but contain no information THUS Information in DNA must
Molecular Genetics Student Objectives
 Molecular Genetics Student Objectives Exam 1: Enduring understanding 3.A: Heritable information provides for continuity of life. Essential knowledge 3.A.1: DNA, and in some cases RNA, is the primary source
Molecular Genetics Student Objectives Exam 1: Enduring understanding 3.A: Heritable information provides for continuity of life. Essential knowledge 3.A.1: DNA, and in some cases RNA, is the primary source
RNA and Protein Synthesis
 RNA and Protein Synthesis CTE: Agriculture and Natural Resources: C5.3 Understand various cell actions, such as osmosis and cell division. C5.4 Compare and contrast plant and animal cells, bacteria, and
RNA and Protein Synthesis CTE: Agriculture and Natural Resources: C5.3 Understand various cell actions, such as osmosis and cell division. C5.4 Compare and contrast plant and animal cells, bacteria, and
DNA Structure and Replication, and Virus Structure and Replication Test Review
 DNA Structure and Replication, and Virus Structure and Replication Test Review What does DNA stand for? Deoxyribonucleic Acid DNA is what type of macromolecule? DNA is a nucleic acid The building blocks
DNA Structure and Replication, and Virus Structure and Replication Test Review What does DNA stand for? Deoxyribonucleic Acid DNA is what type of macromolecule? DNA is a nucleic acid The building blocks
Chapter 14: Gene Expression: From Gene to Protein
 Chapter 14: Gene Expression: From Gene to Protein This is going to be a very long journey, but it is crucial to your understanding of biology. Work on this chapter a single concept at a time, and expect
Chapter 14: Gene Expression: From Gene to Protein This is going to be a very long journey, but it is crucial to your understanding of biology. Work on this chapter a single concept at a time, and expect
DNA. translation. base pairing rules for DNA Replication. thymine. cytosine. amino acids. The building blocks of proteins are?
 2 strands, has the 5-carbon sugar deoxyribose, and has the nitrogen base Thymine. The actual process of assembling the proteins on the ribosome is called? DNA translation Adenine pairs with Thymine, Thymine
2 strands, has the 5-carbon sugar deoxyribose, and has the nitrogen base Thymine. The actual process of assembling the proteins on the ribosome is called? DNA translation Adenine pairs with Thymine, Thymine
M I C R O B I O L O G Y WITH DISEASES BY TAXONOMY, THIRD EDITION
 M I C R O B I O L O G Y WITH DISEASES BY TAXONOMY, THIRD EDITION Chapter 7 Microbial Genetics Lecture prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, University of Tennessee, Knoxville The Structure and Replication
M I C R O B I O L O G Y WITH DISEASES BY TAXONOMY, THIRD EDITION Chapter 7 Microbial Genetics Lecture prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, University of Tennessee, Knoxville The Structure and Replication
Gene function at the level of traits Gene function at the molecular level
 Gene expression Gene function at the level of traits Gene function at the molecular level Two levels tied together since the molecular level affects the structure and function of cells which determines
Gene expression Gene function at the level of traits Gene function at the molecular level Two levels tied together since the molecular level affects the structure and function of cells which determines
CHAPTER 17 FROM GENE TO PROTEIN. Section C: The Synthesis of Protein
 CHAPTER 17 FROM GENE TO PROTEIN Section C: The Synthesis of Protein 1. Translation is the RNA-directed synthesis of a polypeptide: a closer look 2. Signal peptides target some eukaryotic polypeptides to
CHAPTER 17 FROM GENE TO PROTEIN Section C: The Synthesis of Protein 1. Translation is the RNA-directed synthesis of a polypeptide: a closer look 2. Signal peptides target some eukaryotic polypeptides to
EUKARYOTIC REGULATION C H A P T E R 1 3
 EUKARYOTIC REGULATION C H A P T E R 1 3 EUKARYOTIC REGULATION Every cell in an organism contains a complete set of DNA. But it doesn t use all of the DNA it receives Each cell chooses different DNA sequences
EUKARYOTIC REGULATION C H A P T E R 1 3 EUKARYOTIC REGULATION Every cell in an organism contains a complete set of DNA. But it doesn t use all of the DNA it receives Each cell chooses different DNA sequences
Review Quizzes Chapters 11-16
 Review Quizzes Chapters 11-16 1. In pea plants, the allele for smooth seeds (S) is dominant over the allele for wrinkled seeds (s). In an experiment, when two hybrids are crossed, what percent of the offspring
Review Quizzes Chapters 11-16 1. In pea plants, the allele for smooth seeds (S) is dominant over the allele for wrinkled seeds (s). In an experiment, when two hybrids are crossed, what percent of the offspring
Year III Pharm.D Dr. V. Chitra
 Year III Pharm.D Dr. V. Chitra 1 Genome entire genetic material of an individual Transcriptome set of transcribed sequences Proteome set of proteins encoded by the genome 2 Only one strand of DNA serves
Year III Pharm.D Dr. V. Chitra 1 Genome entire genetic material of an individual Transcriptome set of transcribed sequences Proteome set of proteins encoded by the genome 2 Only one strand of DNA serves
Chapter 17: From Gene to Protein
 Name Period This is going to be a very long journey, but it is crucial to your understanding of biology. Work on this chapter a single concept at a time, and expect to spend at least 6 hours to truly master
Name Period This is going to be a very long journey, but it is crucial to your understanding of biology. Work on this chapter a single concept at a time, and expect to spend at least 6 hours to truly master
Matakuliah Genetika (BIO612206) Jurusan Biologi FMIPA Universitas Lampung. Priyambodo, M.Sc. staff.unila.ac.id/priyambodo
 Matakuliah Genetika (BIO612206) Jurusan Biologi FMIPA Universitas Lampung Priyambodo, M.Sc. staff.unila.ac.id/priyambodo Prokariotik Eukariotik staff.unila.ac.id/priyambodo Regulasi ekspresi gen pada
Matakuliah Genetika (BIO612206) Jurusan Biologi FMIPA Universitas Lampung Priyambodo, M.Sc. staff.unila.ac.id/priyambodo Prokariotik Eukariotik staff.unila.ac.id/priyambodo Regulasi ekspresi gen pada
Regulation of Gene Expression
 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS URRY CAIN WASSERMAN MINORSKY REECE 15 Regulation of Gene Expression Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge, Simon Fraser University SECOND EDITION
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS URRY CAIN WASSERMAN MINORSKY REECE 15 Regulation of Gene Expression Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge, Simon Fraser University SECOND EDITION
Chapter 13. The Nucleus. The nucleus is the hallmark of eukaryotic cells; the very term eukaryotic means having a "true nucleus".
 Chapter 13 The Nucleus The nucleus is the hallmark of eukaryotic cells; the very term eukaryotic means having a "true nucleus". Fig.13.1. The EM of the Nucleus of a Eukaryotic Cell 13.1. The Nuclear Envelope
Chapter 13 The Nucleus The nucleus is the hallmark of eukaryotic cells; the very term eukaryotic means having a "true nucleus". Fig.13.1. The EM of the Nucleus of a Eukaryotic Cell 13.1. The Nuclear Envelope
Keystone Biology Remediation B2: Genetics
 Keystone Biology Remediation B2: Genetics Assessment Anchors: to describe and/or predict observed patterns of inheritance (i.e. dominant, recessive, codominance, incomplete dominance, sex-linked, polygenic,
Keystone Biology Remediation B2: Genetics Assessment Anchors: to describe and/or predict observed patterns of inheritance (i.e. dominant, recessive, codominance, incomplete dominance, sex-linked, polygenic,
KEY CONCEPT DNA was identified as the genetic material through a series of experiments. Found live S with R bacteria and injected
 Section 1: Identifying DNA as the Genetic Material KEY CONCEPT DNA was identified as the genetic material through a series of experiments. VOCABULARY bacteriophage MAIN IDEA: Griffith finds a transforming
Section 1: Identifying DNA as the Genetic Material KEY CONCEPT DNA was identified as the genetic material through a series of experiments. VOCABULARY bacteriophage MAIN IDEA: Griffith finds a transforming
Why are proteins important?
 PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Why are proteins important? proteins help build cell structures some proteins are enzymes that promote biological reactions Proteins are found in muscles, blood, bones, etc.. RNA RNA
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Why are proteins important? proteins help build cell structures some proteins are enzymes that promote biological reactions Proteins are found in muscles, blood, bones, etc.. RNA RNA
Today s lecture: Types of mutations and their impact on protein function
 Today s lecture: Types of mutations and their impact on protein function Mutations can be classified by their effect on the DNA sequence OR the encoded protein 1 From my Lecture 4 (10/1): Classification
Today s lecture: Types of mutations and their impact on protein function Mutations can be classified by their effect on the DNA sequence OR the encoded protein 1 From my Lecture 4 (10/1): Classification
DNA RNA PROTEIN. Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 11 Illustrations 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. unless otherwise noted
 DNA RNA PROTEIN Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 11 Illustrations 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. unless otherwise noted DNA Molecule of heredity Contains all the genetic info our cells inherit Determines
DNA RNA PROTEIN Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 11 Illustrations 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. unless otherwise noted DNA Molecule of heredity Contains all the genetic info our cells inherit Determines
