DNA AND CHROMOSOMES. Genetica per Scienze Naturali a.a prof S. Presciuttini
|
|
|
- Clifford Lyons
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 DNA AND CHROMOSOMES This document is licensed under the Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 2.5 Italy license, available at
2 1. The Building Blocks of DNA DNA has three types of chemical component: Phosphate a sugar called deoxyribose,, and four nitrogenous bases: Adenine (A) Guanine (G) Cytosine (C) Thymine (T). Two of the bases, adenine and guanine, have a double-ring structure characteristic of a type of chemical called a purine.. The other two bases, cytosine and thymine, have a single-ring structure of a type called a pyrimidine. The chemical components of DNA are arranged into groups called nucleotides,, each composed of a phosphate group, a deoxyribose sugar molecule, and any one of the four bases.
3 2. The four nucleotides Chemical structure of the four nucleotides (two with purine bases and two with pyrimidine bases) that are the fundamental building blocks of DNA. The sugar is called deoxyribose because it is a variation of a common sugar, ribose, which has one more oxygen atom
4 DNA is composed of two side-by-side chains ("strands") of nucleotides twisted into the shape of a double helix. The two nucleotide strands are held together by weak associations between the bases of each strand, forming a structure like a spiral staircase 3. The double helix In three dimensions, the bases form rather flat structures, and these flat bases partly stack on top of one another in the twisted structure of the double helix. This stacking of bases adds tremendously to the stability of the molecule by excluding water molecules from the spaces between the base pairs.
5 4. Strand polarity The arrangement of the components of DNA. A segment of the double helix has been unwound to show the structures more clearly. The diagram shows the sugar-phosphate backbone and the hydrogen bonding of bases in the center of the molecule. The sugar-phosphate bonds are called phosphodiester bonds. The carbons of the sugar groups are numbered 1 through 5 (next slide). One part of the phosphodiester bond is between the phosphate and the 5 carbon of deoxyribose, and the other is between the phosphate and the 3 carbon of deoxyribose. Thus, each sugar-phosphate backbone is said to have a 5 - to-3 polarity, and understanding this polarity is essential in understanding DNA properties. In the double-stranded DNA molecule, the two backbones are in opposite, or antiparallel, orientation. One strand is oriented 5 3 ; the other strand, though 5 3, runs in the opposite direction, or, looked at another way, is 3 5
6 5. Base pairing The bases of DNA interact according to a very straightforward rule, namely, that there are only two types of base pairs: A T and G C.. The bases in these two base pairs are said to be complementary. This means that at any "step" of the stair like double-stranded DNA molecule, the only base-to- base associations that can exist between the two strands without substantially distorting the double- stranded DNA molecule are A T and G C. Note that because the G C pair has three hydrogen bonds,, whereas the A T pair has only two, one would predict that DNA containing many G C pairs would be more stable than DNA containing many A T pairs. In fact, this prediction is confirmed. Heat causes the two strands of the DNA double helix to separate (a process called DNA melting or DNA denaturation); it can be shown that DNAs with higher G+C content require higher temperatures to melt them
7 6. DNA forms giant molecules Although hydrogen bonds are individually weak, the two strands of the DNA molecule are held together in a relatively stable manner because there are enormous numbers of these bonds. It is important that the strands be associated through such weak interactions, since they have to be separated during DNA replication and during transcription into RNA The sugar-phosphate backbone, being connected by covalent bonds, is also stable; bacterial DNA form a single giant molecule; in eukaryotes, each chromosome is composed by a single giant molecule of DNA
8 7. How much DNA per genome? Almost all cells of all organisms contain at least one copy of the entire genome of the species (most cell are diploid, i.e. they contains two copies). Genome sizes are measured in units of thousands of nucleotide pairs (called kilobases, kb) or millions of nucleotide pairs (megabases, mb), or sometimes in picograms (10-12 gr) In general, the t total amount of chromosomal DNA in different animals and plants does not vary in a consistent manner with the apparent complexity of the organisms. Yeasts, fruit flies, chickens, and humans have successively larger amounts of DNA in their haploid chromosome sets, in keeping with what we perceive to be the increasing complexity of these organisms. Yet the vertebrates with the greatest amount of DNA per cell are amphibians, which are surely less complex than humans in their structure and behavior.
9 8. Genome sizes Amount of DNA in the genomes of various organisms
10 9. Lenght of a DNA molecule The single chromosome of Escherichia coli is about 1.3 mm of DNA. To enable a macromolecule this large to fit within the bacterium, histone-like proteins bind to the DNA, segregating the DNA molecule into around 50 chromosomal domains and making it more compact. Then an enzyme called DNA gyrase supercoils each domain around itself forming a compacted, supercoiled mass of DNA approximately 0.2 µm in diameter, called nucleoid.
11 10. The nucleoid The nucleoid is one long, single molecule of double stranded, helical, supercoiled DNA. In most bacteria, the two ends of the double- stranded DNA covalently bond together to form both a physical and genetic circle. The chromosome is generally around 1000 µm long and frequently contains as many as 3500 genes. E. coli, that is 2-3 µm in length has a chromosome approximately 1400 µm long.
12 11. Eukaryotic Nuclear Genomes A human cell contains about 2 meters of DNA, packed into 46 chromosomes, all inside a nucleus only 6 µm m in diameter. Thus, in order to pack the DNA into the nucleus, there must be several levels of coiling and supercoiling. Cell wall Nucleus Nucleolus These levels of DNA structure cannot be resolved by the optical microscope, under which interphase nuclei stained with DNA-specific dyes appears composed of a dense, dark-staining material called heterochromatin,, and is scattered throughout the nucleus, and a very light- staining flocculent material which fills the rest of the nucleus, called euchromatin.
13 12. DNA in interphase It is thought that most part of each chromosome in an interphase nucleus (chromatine) has the form of the 30 nm fiber The figure on the left shows the tangled chromatin fibers obtained after disrupting a nucleus. Shearing forces can be used to further uncoil and stretch these fibers and the beaded filaments appear. The strands between the beads are segments of double stranded DNA (right panel).
14 13. The 30 nm fibre Different levels of chromosome uncoiling. The bottom of the figure shows the DNA helix (which is DNA stripped of its histones). In the normal, unstripped chromosome, the double stranded DNA is wrapped around sets of 8 macromolecules of histones (proteins) to form a 10 nm filament. These sets of histones are separated by spacer regions of 4 nm DNA filament. They are the 10 nm nucleoprotein fibrils or "beads on a string" seen in electron micrographs which are called nucleosomes.. The next level of coiling produces the 30 nm nucleoprotein fibers.
15 14. Compacting DNA into eukaryotic chromosomes Stuffing the long strands of chromosomal DNA into a eukaryotic nucleus requires that the DNA be compacted in length approximately 10,000 to 50,000 -fold. Cells achieve this task while still maintaining the chromosomes in a form that allows regulatory proteins to access DNA to turn on (or off) specific genes or to duplicate the chromosome (replication). Model for chromosome structure. On the left is shown tight coiling, representing metaphase: here the loops are so densely packed that only their tips are visible. At the free ends, a solenoid is shown uncoiled to give an approximation of relative scale. On the right is shown a relaxed supercoil, as at interphase
16 15. Compacting factors
1. I can describe the stages of the cell cycle.
 Unit 5 Study Guide Cell Cycle pg. 1 1. I can describe the stages of the cell cycle. Interphase = period in between division G1 = growth phase S = DNA replication G2 = Preparation for division (extra copies
Unit 5 Study Guide Cell Cycle pg. 1 1. I can describe the stages of the cell cycle. Interphase = period in between division G1 = growth phase S = DNA replication G2 = Preparation for division (extra copies
DNA: The Genetic Material. Chapter 10
 DNA: The Genetic Material Chapter 10 DNA as the Genetic Material DNA was first extracted from nuclei in 1870 named nuclein after their source. Chemical analysis determined that DNA was a weak acid rich
DNA: The Genetic Material Chapter 10 DNA as the Genetic Material DNA was first extracted from nuclei in 1870 named nuclein after their source. Chemical analysis determined that DNA was a weak acid rich
DNA STRUCTURE & REPLICATION
 DNA STRUCTURE & REPLICATION A MODEL OF DNA In 1953, two scientists named Watson & Crick built a model of DNA that demonstrates its exact structure and function. They called this model a double helix, which
DNA STRUCTURE & REPLICATION A MODEL OF DNA In 1953, two scientists named Watson & Crick built a model of DNA that demonstrates its exact structure and function. They called this model a double helix, which
translation The building blocks of proteins are? amino acids nitrogen containing bases like A, G, T, C, and U Complementary base pairing links
 The actual process of assembling the proteins on the ribosome is called? translation The building blocks of proteins are? Complementary base pairing links Define and name the Purines amino acids nitrogen
The actual process of assembling the proteins on the ribosome is called? translation The building blocks of proteins are? Complementary base pairing links Define and name the Purines amino acids nitrogen
Types of nucleic acid
 RNA STRUCTURE 1 Types of nucleic acid DNA Deoxyribonucleic acid RNA ribonucleic acid HOCH 2 O OH HOCH 2 O OH OH OH OH (no O) ribose deoxyribose 2 Nucleic acids consist of repeating nucleotide that have
RNA STRUCTURE 1 Types of nucleic acid DNA Deoxyribonucleic acid RNA ribonucleic acid HOCH 2 O OH HOCH 2 O OH OH OH OH (no O) ribose deoxyribose 2 Nucleic acids consist of repeating nucleotide that have
DNA Chapter 12. DNA and RNA B.1.4, B.1.9, B.1.21, B.1.26, B DNA and RNA B.1.4, B.1.9, B.1.21, B.1.26, B Griffith s Experiment
 DNA Chapter 12 DNA and RNA B.1.4, B.1.9, B.1.21, B.1.26, B.1.27 To truly understand genetics, biologists after Mendel had to discover the chemical nature of the gene. In 1928, Frederick Griffith was trying
DNA Chapter 12 DNA and RNA B.1.4, B.1.9, B.1.21, B.1.26, B.1.27 To truly understand genetics, biologists after Mendel had to discover the chemical nature of the gene. In 1928, Frederick Griffith was trying
What Are the Chemical Structures and Functions of Nucleic Acids?
 THE NUCLEIC ACIDS What Are the Chemical Structures and Functions of Nucleic Acids? Nucleic acids are polymers specialized for the storage, transmission, and use of genetic information. DNA = deoxyribonucleic
THE NUCLEIC ACIDS What Are the Chemical Structures and Functions of Nucleic Acids? Nucleic acids are polymers specialized for the storage, transmission, and use of genetic information. DNA = deoxyribonucleic
THE CELLULAR AND MOLECULAR BASIS OF INHERITANCE
 Umm AL Qura University THE CELLULAR AND MOLECULAR BASIS OF INHERITANCE Dr. Neda Bogari www.bogari.net EMERY'S ELEMENTS OF MEDICAL GENETICS Peter Turnpenny and Sian Ellard 13 th edition 2008 COURSE SYLLABUS
Umm AL Qura University THE CELLULAR AND MOLECULAR BASIS OF INHERITANCE Dr. Neda Bogari www.bogari.net EMERY'S ELEMENTS OF MEDICAL GENETICS Peter Turnpenny and Sian Ellard 13 th edition 2008 COURSE SYLLABUS
NUCLEIC ACIDS Genetic material of all known organisms DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid RNA: ribonucleic acid (e.g., some viruses)
 NUCLEIC ACIDS Genetic material of all known organisms DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid RNA: ribonucleic acid (e.g., some viruses) Consist of chemically linked sequences of nucleotides Nitrogenous base Pentose-
NUCLEIC ACIDS Genetic material of all known organisms DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid RNA: ribonucleic acid (e.g., some viruses) Consist of chemically linked sequences of nucleotides Nitrogenous base Pentose-
The structure, type and functions of a cell are all determined by chromosomes:
 DNA Basics The structure, type and functions of a cell are all determined by chromosomes: They are found in the nucleus of a cell. These chromosomes are composed of DNA, the acronym for deoxyribonucleic
DNA Basics The structure, type and functions of a cell are all determined by chromosomes: They are found in the nucleus of a cell. These chromosomes are composed of DNA, the acronym for deoxyribonucleic
Chapter 8 DNA STRUCTURE AND CHROMOSOMAL ORGANIZATION
 Chapter 8 DNA STRUCTURE AND CHROMOSOMAL ORGANIZATION Chapter Summary Even though DNA has been known as a biochemical compound for over 100 years, it was not implicated as the carrier of hereditary information
Chapter 8 DNA STRUCTURE AND CHROMOSOMAL ORGANIZATION Chapter Summary Even though DNA has been known as a biochemical compound for over 100 years, it was not implicated as the carrier of hereditary information
THE COMPONENTS & STRUCTURE OF DNA
 THE COMPONENTS & STRUCTURE OF DNA - How do genes work? - What are they made of, and how do they determine the characteristics of organisms? - Are genes single molecules, or are they longer structures made
THE COMPONENTS & STRUCTURE OF DNA - How do genes work? - What are they made of, and how do they determine the characteristics of organisms? - Are genes single molecules, or are they longer structures made
DNA: An Introduction to structure and function. DNA by the numbers. Why do we study DNA? Chromosomes and DNA
 DA: An Introduction to structure and function Hopefully a review The structure of DA - your job during the PowerPoint: Make a labeled sketch Label the structure of a nucleotide Know which bases pair up
DA: An Introduction to structure and function Hopefully a review The structure of DA - your job during the PowerPoint: Make a labeled sketch Label the structure of a nucleotide Know which bases pair up
DNA Structure & the Genome. Bio160 General Biology
 DNA Structure & the Genome Bio160 General Biology Lecture Outline I. DNA A nucleic acid II. Chromosome Structure III. Chromosomes and Genes IV. DNA vs. RNA I. DNA A Nucleic Acid Structure of DNA: Remember:
DNA Structure & the Genome Bio160 General Biology Lecture Outline I. DNA A nucleic acid II. Chromosome Structure III. Chromosomes and Genes IV. DNA vs. RNA I. DNA A Nucleic Acid Structure of DNA: Remember:
DNA RNA PROTEIN SYNTHESIS -NOTES-
 DNA RNA PROTEIN SYNTHESIS -NOTES- THE COMPONENTS AND STRUCTURE OF DNA DNA is made up of units called nucleotides. Nucleotides are made up of three basic components:, called deoxyribose in DNA In DNA, there
DNA RNA PROTEIN SYNTHESIS -NOTES- THE COMPONENTS AND STRUCTURE OF DNA DNA is made up of units called nucleotides. Nucleotides are made up of three basic components:, called deoxyribose in DNA In DNA, there
Structure of nucleic acids II Biochemistry 302. January 20, 2006
 Structure of nucleic acids II Biochemistry 302 January 20, 2006 Intrinsic structural flexibility of RNA antiparallel A-form Fig. 4.19 High Temp Denaturants In vivo conditions Base stacking w/o base pairing/h-bonds
Structure of nucleic acids II Biochemistry 302 January 20, 2006 Intrinsic structural flexibility of RNA antiparallel A-form Fig. 4.19 High Temp Denaturants In vivo conditions Base stacking w/o base pairing/h-bonds
How do we know what the structure and function of DNA is? - Double helix, base pairs, sugar, and phosphate - Stores genetic information
 DNA: CH 13 How do we know what the structure and function of DNA is? - Double helix, base pairs, sugar, and phosphate - Stores genetic information Discovering DNA s Function 1928: Frederick Griffith studied
DNA: CH 13 How do we know what the structure and function of DNA is? - Double helix, base pairs, sugar, and phosphate - Stores genetic information Discovering DNA s Function 1928: Frederick Griffith studied
Nucleic Acid Structure. Nucleic Acid Sequence Abbreviations. Sequence Abbreviations, con t.
 BC 4054 Spring 2001 Chapter 11 & 12 Review Lecture otes Slide 1 ucleic Acid Structure Linear polymer of nucleotides Phosphodiester linkage between 3 and 5 positions See Figure 11.17 Slide 2 ucleic Acid
BC 4054 Spring 2001 Chapter 11 & 12 Review Lecture otes Slide 1 ucleic Acid Structure Linear polymer of nucleotides Phosphodiester linkage between 3 and 5 positions See Figure 11.17 Slide 2 ucleic Acid
Essential Questions. DNA: The Genetic Material. Copyright McGraw-Hill Education
 Essential Questions Which experiments led to the discovery of DNA as the genetic material? What is the basic structure of DNA? What is the basic structure of eukaryotic chromosomes? Vocabulary Review nucleic
Essential Questions Which experiments led to the discovery of DNA as the genetic material? What is the basic structure of DNA? What is the basic structure of eukaryotic chromosomes? Vocabulary Review nucleic
DNA, Replication and RNA
 DNA, Replication and RNA The structure of DNA DNA, or Deoxyribonucleic Acid, is the blue prints for building all of life. DNA is a long molecule made up of units called NUCLEOTIDES. Each nucleotide is
DNA, Replication and RNA The structure of DNA DNA, or Deoxyribonucleic Acid, is the blue prints for building all of life. DNA is a long molecule made up of units called NUCLEOTIDES. Each nucleotide is
DNA. translation. base pairing rules for DNA Replication. thymine. cytosine. amino acids. The building blocks of proteins are?
 2 strands, has the 5-carbon sugar deoxyribose, and has the nitrogen base Thymine. The actual process of assembling the proteins on the ribosome is called? DNA translation Adenine pairs with Thymine, Thymine
2 strands, has the 5-carbon sugar deoxyribose, and has the nitrogen base Thymine. The actual process of assembling the proteins on the ribosome is called? DNA translation Adenine pairs with Thymine, Thymine
Review of ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
 Nucleic Acids: DNA Review of ORGANIC CHEMISTRY Definition: Contains CARBON (C) and Hydrogen (H) Large polymers can be made of smaller individual monomers. Ex: For carbohydrates, polysaccharides are large
Nucleic Acids: DNA Review of ORGANIC CHEMISTRY Definition: Contains CARBON (C) and Hydrogen (H) Large polymers can be made of smaller individual monomers. Ex: For carbohydrates, polysaccharides are large
DNA and RNA. Chapter 12
 DNA and RNA Chapter 12 Warm Up Exercise Test Corrections Make sure to indicate your new answer and provide an explanation for why this is the correct answer. Do this with a red pen in the margins of your
DNA and RNA Chapter 12 Warm Up Exercise Test Corrections Make sure to indicate your new answer and provide an explanation for why this is the correct answer. Do this with a red pen in the margins of your
What can you tell me about DNA? copyright cmassengale 1
 What can you tell me about DNA? copyright cmassengale 1 DNA and Replication copyright cmassengale 2 Credit for discovery of DNA is given to Watson & Crick 1 DNA DNA stands for deoxyribose nucleic acid
What can you tell me about DNA? copyright cmassengale 1 DNA and Replication copyright cmassengale 2 Credit for discovery of DNA is given to Watson & Crick 1 DNA DNA stands for deoxyribose nucleic acid
Vocabulary. Nucleic Acid Nucleotide Base pairing Complementary Template Strand Semiconservative Replication Polymerase
 DNA and Replication TEKS (6) Science concepts. The student knows the mechanisms of genetics, including the role of nucleic acids and the principles of Mendelian Genetics. The student is expected to: (A)
DNA and Replication TEKS (6) Science concepts. The student knows the mechanisms of genetics, including the role of nucleic acids and the principles of Mendelian Genetics. The student is expected to: (A)
The discovery that DNA is the genetic code involved many experiments.
 Section 1: The discovery that DNA is the genetic code involved many experiments. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Vocabulary Review nucleic acid New double helix nucleosome Discovery
Section 1: The discovery that DNA is the genetic code involved many experiments. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Vocabulary Review nucleic acid New double helix nucleosome Discovery
PowerPoint Notes on Chapter 9 - DNA: The Genetic Material
 PowerPoint Notes on Chapter 9 - DNA: The Genetic Material Section 1 Identifying the Genetic Material Objectives Relate Griffith s conclusions to the observations he made during the transformation experiments.
PowerPoint Notes on Chapter 9 - DNA: The Genetic Material Section 1 Identifying the Genetic Material Objectives Relate Griffith s conclusions to the observations he made during the transformation experiments.
Fig. 16-7a. 5 end Hydrogen bond 3 end. 1 nm. 3.4 nm nm
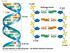 Fig. 16-7a end Hydrogen bond end 1 nm 3.4 nm 0.34 nm (a) Key features of DNA structure end (b) Partial chemical structure end Fig. 16-8 Adenine (A) Thymine (T) Guanine (G) Cytosine (C) Concept 16.2: Many
Fig. 16-7a end Hydrogen bond end 1 nm 3.4 nm 0.34 nm (a) Key features of DNA structure end (b) Partial chemical structure end Fig. 16-8 Adenine (A) Thymine (T) Guanine (G) Cytosine (C) Concept 16.2: Many
DNA is the genetic material. DNA structure. Chapter 7: DNA Replication, Transcription & Translation; Mutations & Ames test
 DNA is the genetic material Chapter 7: DNA Replication, Transcription & Translation; Mutations & Ames test Dr. Amy Rogers Bio 139 General Microbiology Hereditary information is carried by DNA Griffith/Avery
DNA is the genetic material Chapter 7: DNA Replication, Transcription & Translation; Mutations & Ames test Dr. Amy Rogers Bio 139 General Microbiology Hereditary information is carried by DNA Griffith/Avery
A nucleotide consists of: an inorganic phosphate group (attached to carbon 5 of the sugar) a 5C sugar (pentose) a Nitrogenous (N containing) base
 Nucleic Acids! Nucleic acids are found in all living cells and viruses and the two main types are DNA and RNA. They are macromolecules made of chains of nucleotides bonded together. They carry genetic
Nucleic Acids! Nucleic acids are found in all living cells and viruses and the two main types are DNA and RNA. They are macromolecules made of chains of nucleotides bonded together. They carry genetic
Chapter 5 DNA and Chromosomes
 Chapter 5 DNA and Chromosomes DNA as the genetic material Heat-killed bacteria can transform living cells S Smooth R Rough Fred Griffith, 1920 DNA is the genetic material Oswald Avery Colin MacLeod Maclyn
Chapter 5 DNA and Chromosomes DNA as the genetic material Heat-killed bacteria can transform living cells S Smooth R Rough Fred Griffith, 1920 DNA is the genetic material Oswald Avery Colin MacLeod Maclyn
DNA and RNA. Chapter 12
 DNA and RNA Chapter 12 History of DNA Late 1800 s scientists discovered that DNA is in the nucleus of the cell 1902 Walter Sutton proposed that hereditary material resided in the chromosomes in the nucleus
DNA and RNA Chapter 12 History of DNA Late 1800 s scientists discovered that DNA is in the nucleus of the cell 1902 Walter Sutton proposed that hereditary material resided in the chromosomes in the nucleus
How can something so small cause problems so large?
 How can something so small cause problems so large? Objectives Identify the structural components of DNA and relate to its function Create and ask questions about a model of DNA DNA is made of genes. Gene
How can something so small cause problems so large? Objectives Identify the structural components of DNA and relate to its function Create and ask questions about a model of DNA DNA is made of genes. Gene
Chapter 9: DNA: The Molecule of Heredity
 Chapter 9: DNA: The Molecule of Heredity What is DNA? Answer: Molecule that carries the blueprint of life General Features: DNA is packages in chromosomes (DNA + Proteins) Gene = Functional segment of
Chapter 9: DNA: The Molecule of Heredity What is DNA? Answer: Molecule that carries the blueprint of life General Features: DNA is packages in chromosomes (DNA + Proteins) Gene = Functional segment of
Chapter 1 Structure of Nucleic Acids DNA The structure of part of a DNA double helix
 Chapter 1 Structure of Nucleic Acids DNA The structure of part of a DNA double helix Deoxyribonucleic acid ) (DNA) is a nucleic acid that contains the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning
Chapter 1 Structure of Nucleic Acids DNA The structure of part of a DNA double helix Deoxyribonucleic acid ) (DNA) is a nucleic acid that contains the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning
DNA Structure and Replication
 Name: DNA Structure and Replication 1. DNA: Deoxyribonucleic Acid a. Credit for discovery is given to Watson & Crick b. DNA stands for c. This chemical substance is present in the of all cells in all living
Name: DNA Structure and Replication 1. DNA: Deoxyribonucleic Acid a. Credit for discovery is given to Watson & Crick b. DNA stands for c. This chemical substance is present in the of all cells in all living
Structure of nucleic acids II Biochemistry 302. Bob Kelm January 21, 2005
 Structure of nucleic acids II Biochemistry 302 Bob Kelm January 21, 2005 http://biochem.uvm.edu/courses/kelm/302 User: student PW: nucleicacid Secondary structure of RNAs antiparallel A-form Fig. 4.19
Structure of nucleic acids II Biochemistry 302 Bob Kelm January 21, 2005 http://biochem.uvm.edu/courses/kelm/302 User: student PW: nucleicacid Secondary structure of RNAs antiparallel A-form Fig. 4.19
12 2 Chromosomes and DNA Replication
 DNA Replication 12-2 Chromosomes and 1 of 21 DNA and Chromosomes DNA and Chromosomes In prokaryotic cells, DNA is located in the cytoplasm. Most prokaryotes have a single DNA molecule containing nearly
DNA Replication 12-2 Chromosomes and 1 of 21 DNA and Chromosomes DNA and Chromosomes In prokaryotic cells, DNA is located in the cytoplasm. Most prokaryotes have a single DNA molecule containing nearly
Review of Old Information: What is the monomer and polymer of: Macromolecule Monomer Polymer Carbohydrate Lipid Protein
 Section 1.8 Question of the Day: Name: Review of Old Information: What is the monomer and polymer of: Macromolecule Monomer Polymer Carbohydrate Lipid Protein New Information: One of the most important
Section 1.8 Question of the Day: Name: Review of Old Information: What is the monomer and polymer of: Macromolecule Monomer Polymer Carbohydrate Lipid Protein New Information: One of the most important
By the end of today, you will have an answer to: How can 1 strand of DNA serve as a template for replication?
 Name: Period: Date: KIPP NYC College Prep Genetics and Biotech UNIT 9: Introduction to DNA Lecture 4: DNA Modeling and Intro to Replication By the end of today, you will have an answer to: How can 1 strand
Name: Period: Date: KIPP NYC College Prep Genetics and Biotech UNIT 9: Introduction to DNA Lecture 4: DNA Modeling and Intro to Replication By the end of today, you will have an answer to: How can 1 strand
Summary 12 1 DNA RNA and Protein Synthesis Chromosomes and DNA Replication. Name Class Date
 Chapter 12 Summary DNA and RNA 12 1 DNA To understand genetics, biologists had to learn the chemical structure of the gene. Frederick Griffith first learned that some factor from dead, disease-causing
Chapter 12 Summary DNA and RNA 12 1 DNA To understand genetics, biologists had to learn the chemical structure of the gene. Frederick Griffith first learned that some factor from dead, disease-causing
Nucleic Acids: DNA and RNA
 Nucleic Acids: DNA and RNA Living organisms are complex systems. Hundreds of thousands of proteins exist inside each one of us to help carry out our daily functions. These proteins are produced locally,
Nucleic Acids: DNA and RNA Living organisms are complex systems. Hundreds of thousands of proteins exist inside each one of us to help carry out our daily functions. These proteins are produced locally,
Nucleic acids. What important polymer is located in the nucleus? is the instructions for making a cell's.
 Nucleic acids DNA - The Double Helix Recall that the nucleus is a small spherical, dense body in a cell. It is often called the "control center" because it controls all the activities of the cell including
Nucleic acids DNA - The Double Helix Recall that the nucleus is a small spherical, dense body in a cell. It is often called the "control center" because it controls all the activities of the cell including
CHAPTER 11 LECTURE SLIDES
 CHAPTER 11 LECTURE SLIDES Prepared by Brenda Leady University of Toledo To run the animations you must be in Slideshow View. Use the buttons on the animation to play, pause, and turn audio/text on or off.
CHAPTER 11 LECTURE SLIDES Prepared by Brenda Leady University of Toledo To run the animations you must be in Slideshow View. Use the buttons on the animation to play, pause, and turn audio/text on or off.
Nucleic Acids: Structure and Function
 ucleic Acids: Structure and Function Components of ucleotides The building blocks (monomers) of the nucleic acids are called nucleotides. ydrolysis of nucleotides gives phosphoric acid, a pentose sugar,
ucleic Acids: Structure and Function Components of ucleotides The building blocks (monomers) of the nucleic acids are called nucleotides. ydrolysis of nucleotides gives phosphoric acid, a pentose sugar,
DNA - The Double Helix
 DNA - The Double Helix Recall that the nucleus is a small spherical, dense body in a cell. It is often called the "control center" because it controls all the activities of the cell including cell reproduction,
DNA - The Double Helix Recall that the nucleus is a small spherical, dense body in a cell. It is often called the "control center" because it controls all the activities of the cell including cell reproduction,
DNA vs. RNA B-4.1. Compare DNA and RNA in terms of structure, nucleotides and base pairs.
 DNA vs. RNA B-4.1 Compare DNA and RNA in terms of structure, nucleotides and base pairs. Key Concepts l Nucleic Acids: l deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) l ribonucleic acid (RNA) l Nucleotides: l nitrogen base,
DNA vs. RNA B-4.1 Compare DNA and RNA in terms of structure, nucleotides and base pairs. Key Concepts l Nucleic Acids: l deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) l ribonucleic acid (RNA) l Nucleotides: l nitrogen base,
Nucleic acids and protein synthesis
 THE FUNCTIONS OF DNA Nucleic acids and protein synthesis The full name of DNA is deoxyribonucleic acid. Every nucleotide has the same sugar molecule and phosphate group, but each nucleotide contains one
THE FUNCTIONS OF DNA Nucleic acids and protein synthesis The full name of DNA is deoxyribonucleic acid. Every nucleotide has the same sugar molecule and phosphate group, but each nucleotide contains one
DNA - The Double Helix
 Name Date Period DNA - The Double Helix Recall that the nucleus is a small spherical, dense body in a cell. It is often called the "control center" because it controls all the activities of the cell including
Name Date Period DNA - The Double Helix Recall that the nucleus is a small spherical, dense body in a cell. It is often called the "control center" because it controls all the activities of the cell including
BIOB111 - Tutorial activity for Session 13
 BIOB111 - Tutorial activity for Session 13 General topics for week 7 Session 13: Types of nucleic acids, DNA replication Useful links: 1. Visit this website and use its menu to locate information and practice
BIOB111 - Tutorial activity for Session 13 General topics for week 7 Session 13: Types of nucleic acids, DNA replication Useful links: 1. Visit this website and use its menu to locate information and practice
DNA Structure and Replication 1
 Name: # Date: Per: Why? DNA Structure and Replication How is genetic information stored and copied? Deoxyribonucleic acid or DNA is the molecule of heredity. It contains the genetic blueprint for life.
Name: # Date: Per: Why? DNA Structure and Replication How is genetic information stored and copied? Deoxyribonucleic acid or DNA is the molecule of heredity. It contains the genetic blueprint for life.
DNA - The Double Helix
 DNA - The Double Helix Recall that the nucleus is a small spherical, dense body in a cell. It is often called the "control center" because it controls all the activities of the cell including cell reproduction,
DNA - The Double Helix Recall that the nucleus is a small spherical, dense body in a cell. It is often called the "control center" because it controls all the activities of the cell including cell reproduction,
Components of DNA. Components of DNA. Aim: What is the structure of DNA? February 15, DNA_Structure_2011.notebook. Do Now.
 Aim: What is the structure of DNA? Do Now: Explain the Hershey Chase experiment and what was its conclusion? Homework Read pp. 298 299 P.299 3,4,6.7 Do Now Paperclip Combos Material: 8 paperclips, 2 each
Aim: What is the structure of DNA? Do Now: Explain the Hershey Chase experiment and what was its conclusion? Homework Read pp. 298 299 P.299 3,4,6.7 Do Now Paperclip Combos Material: 8 paperclips, 2 each
10-2 Cell Division (Pages )
 10-2 Cell Division (Pages 244-245) What do you think would happen if a cell were simply to split into two, without any advance preparation? Would each daughter cell have everything it needed to survive?
10-2 Cell Division (Pages 244-245) What do you think would happen if a cell were simply to split into two, without any advance preparation? Would each daughter cell have everything it needed to survive?
Name: Date: Pd: Nucleic acids
 Name: Date: Pd: DNA - The Double Helix Nucleic acids Recall that the nucleus is a small spherical, dense body in a cell. It is often called the "control center" because it controls all the activities of
Name: Date: Pd: DNA - The Double Helix Nucleic acids Recall that the nucleus is a small spherical, dense body in a cell. It is often called the "control center" because it controls all the activities of
STUDY GUIDE SECTION 10-1 Discovery of DNA
 STUDY GUIDE SECTION 10-1 Discovery of DNA Name Period Date Multiple Choice-Write the correct letter in the blank. 1. The virulent strain of the bacterium S. pneumoniae causes disease because it a. has
STUDY GUIDE SECTION 10-1 Discovery of DNA Name Period Date Multiple Choice-Write the correct letter in the blank. 1. The virulent strain of the bacterium S. pneumoniae causes disease because it a. has
NUCLEIC ACIDS AND PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
 NUCLEIC ACIDS AND PROTEIN SYNTHESIS DNA Cell Nucleus Chromosomes is a coiled double helix carrying hereditary information of the cell Contains the instructions for making from 20 different amino acids
NUCLEIC ACIDS AND PROTEIN SYNTHESIS DNA Cell Nucleus Chromosomes is a coiled double helix carrying hereditary information of the cell Contains the instructions for making from 20 different amino acids
Genes - DNA - Chromosome. Chutima Talabnin Ph.D. School of Biochemistry,Institute of Science, Suranaree University of Technology
 Genes - DNA - Chromosome Chutima Talabnin Ph.D. School of Biochemistry,Institute of Science, Suranaree University of Technology DNA Cellular DNA contains genes and intragenic regions both of which may
Genes - DNA - Chromosome Chutima Talabnin Ph.D. School of Biochemistry,Institute of Science, Suranaree University of Technology DNA Cellular DNA contains genes and intragenic regions both of which may
Overview: Life s Operating Instructions Concept 16.1: DNA is the genetic material The Search for the Genetic Material: Scientific Inquiry
 Overview: Life s Operating Instructions In 1953, James Watson and Francis Crick introduced an elegant double-helical model for the structure of deoxyribonucleic acid, or DNA DNA, the substance of inheritance,
Overview: Life s Operating Instructions In 1953, James Watson and Francis Crick introduced an elegant double-helical model for the structure of deoxyribonucleic acid, or DNA DNA, the substance of inheritance,
DNA stands for deoxyribose nucleic acid.
 1 DNA stands for deoxyribose nucleic acid. DNA controls the kind of cell which is formed (i.e. muscle, blood, nerve). DNA controls the type of organism which is produced (i.e. buttercup, giraffe, herring,
1 DNA stands for deoxyribose nucleic acid. DNA controls the kind of cell which is formed (i.e. muscle, blood, nerve). DNA controls the type of organism which is produced (i.e. buttercup, giraffe, herring,
DNA - The Double Helix
 DNA - The Double Helix Recall that the nucleus is a small spherical, dense body in a cell. It is often called the "control center" because it controls all the activities of the cell including cell reproduction,
DNA - The Double Helix Recall that the nucleus is a small spherical, dense body in a cell. It is often called the "control center" because it controls all the activities of the cell including cell reproduction,
DNA STRUCTURE AND REPLICATION
 AP BIOLOGY EVOLUTION/HEREDITY UNIT Unit 1 Part 2 Chapter 16 Activity #2 BUILDING BLOCKS OF DNA: Nucleotides: NAME DATE PERIOD DNA STRUCTURE AND REPLICATION 1. 5 carbon sugar (deoxyribose) 2. Nitrogenous
AP BIOLOGY EVOLUTION/HEREDITY UNIT Unit 1 Part 2 Chapter 16 Activity #2 BUILDING BLOCKS OF DNA: Nucleotides: NAME DATE PERIOD DNA STRUCTURE AND REPLICATION 1. 5 carbon sugar (deoxyribose) 2. Nitrogenous
The DNA Molecule: The Molecular Basis of Inheritance
 Slide hapter 6 he DN Molecule: he Molecular Basis of Inheritance PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil ampbell and Jane Reece Lectures by hris Romero, updated by Erin Barley
Slide hapter 6 he DN Molecule: he Molecular Basis of Inheritance PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil ampbell and Jane Reece Lectures by hris Romero, updated by Erin Barley
DNA. Is a molecule that encodes the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms and many viruses.
 Is a molecule that encodes the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms and many viruses. Genetic information is encoded as a sequence of nucleotides (guanine,
Is a molecule that encodes the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms and many viruses. Genetic information is encoded as a sequence of nucleotides (guanine,
Genetic material must be able to:
 Genetic material must be able to: Contain the information necessary to construct an entire organism Pass from parent to offspring and from cell to cell during cell division Be accurately copied Account
Genetic material must be able to: Contain the information necessary to construct an entire organism Pass from parent to offspring and from cell to cell during cell division Be accurately copied Account
Structure and Replication
 Structure and Replication 6.A: Students will identify components of DNA, and describe how information for specifying traits of an organism is carried in the DNA 6.B: Students will recognize that components
Structure and Replication 6.A: Students will identify components of DNA, and describe how information for specifying traits of an organism is carried in the DNA 6.B: Students will recognize that components
The Molecular Basis of Inheritance
 The Molecular Basis of Inheritance Chapter 16 Objectives Describe the contributions of the following people: Griffith; Avery, McCary, and MacLeod; Hershey and Chase; Chargaff; Watson and Crick; Franklin;
The Molecular Basis of Inheritance Chapter 16 Objectives Describe the contributions of the following people: Griffith; Avery, McCary, and MacLeod; Hershey and Chase; Chargaff; Watson and Crick; Franklin;
Multiple choice questions (numbers in brackets indicate the number of correct answers)
 1 Multiple choice questions (numbers in brackets indicate the number of correct answers) February 1, 2013 1. Ribose is found in Nucleic acids Proteins Lipids RNA DNA (2) 2. Most RNA in cells is transfer
1 Multiple choice questions (numbers in brackets indicate the number of correct answers) February 1, 2013 1. Ribose is found in Nucleic acids Proteins Lipids RNA DNA (2) 2. Most RNA in cells is transfer
Nucleic Acids: Structure and Function
 ucleic Acids: Structure and Function Components of ucleotides The building blocks (monomers) of the nucleic acids are called nucleotides. ucleotides are made up of: phosphoric acid, a pentose sugar, and
ucleic Acids: Structure and Function Components of ucleotides The building blocks (monomers) of the nucleic acids are called nucleotides. ucleotides are made up of: phosphoric acid, a pentose sugar, and
Nucleic acids deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) ribonucleic acid (RNA) nucleotide
 Nucleic Acids Nucleic acids are molecules that store information for cellular growth and reproduction There are two types of nucleic acids: - deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) These
Nucleic Acids Nucleic acids are molecules that store information for cellular growth and reproduction There are two types of nucleic acids: - deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) These
Name: Class: Date: ID: A
 Class: _ Date: _ CH 12 Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. How many codons are needed to specify three amino acids? a. 6 c. 3 b. 12
Class: _ Date: _ CH 12 Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. How many codons are needed to specify three amino acids? a. 6 c. 3 b. 12
The Double Helix. DNA and RNA, part 2. Part A. Hint 1. The difference between purines and pyrimidines. Hint 2. Distinguish purines from pyrimidines
 DNA and RNA, part 2 Due: 3:00pm on Wednesday, September 24, 2014 You will receive no credit for items you complete after the assignment is due. Grading Policy The Double Helix DNA, or deoxyribonucleic
DNA and RNA, part 2 Due: 3:00pm on Wednesday, September 24, 2014 You will receive no credit for items you complete after the assignment is due. Grading Policy The Double Helix DNA, or deoxyribonucleic
deoxyribose, and one of the four nitrogenous compounds: adenine (C H N ), cytosine (C H N O),
 Topic Page: DNA Definition: deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) from Processing Water, Wastewater, Residuals, and Excreta for Health and Environmental Protection: An Encyclopedic Dictionary The double-stranded,
Topic Page: DNA Definition: deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) from Processing Water, Wastewater, Residuals, and Excreta for Health and Environmental Protection: An Encyclopedic Dictionary The double-stranded,
Y1 Biology 131 Syllabus - Academic Year
 Y1 Biology 131 Syllabus - Academic Year 2016-2017 Monday 28/11/2016 DNA Packaging Week 11 Tuesday 29/11/2016 Regulation of gene expression Wednesday 22/9/2014 Cell cycle Sunday 4/12/2016 Tutorial Monday
Y1 Biology 131 Syllabus - Academic Year 2016-2017 Monday 28/11/2016 DNA Packaging Week 11 Tuesday 29/11/2016 Regulation of gene expression Wednesday 22/9/2014 Cell cycle Sunday 4/12/2016 Tutorial Monday
Bodies Cells DNA. Bodies are made up of cells All cells run on a set of instructions spelled out in DNA
 What is DNA? Although the environment influences how an organism develops, the genetic information that is held in the molecules of DNA ultimately determines an organism s traits. DNA achieves its control
What is DNA? Although the environment influences how an organism develops, the genetic information that is held in the molecules of DNA ultimately determines an organism s traits. DNA achieves its control
NUCLEIC ACID. Subtitle
 NUCLEIC ACID Subtitle NUCLEIC ACID Building blocks of living organisms One of the four important biomolecule 1 st isolated from the nuclei of white blood cells by Friedrich Miescher (1860) Came from the
NUCLEIC ACID Subtitle NUCLEIC ACID Building blocks of living organisms One of the four important biomolecule 1 st isolated from the nuclei of white blood cells by Friedrich Miescher (1860) Came from the
DNA: Structure and Replication - 1
 DNA: Structure and Replication - 1 We have briefly discussed that DNA is the genetic molecule of life. In eukaryotic organisms DNA (along with its histone proteins) is found in chromosomes. All cell activities
DNA: Structure and Replication - 1 We have briefly discussed that DNA is the genetic molecule of life. In eukaryotic organisms DNA (along with its histone proteins) is found in chromosomes. All cell activities
NUCLEUS. Fig. 2. Various stages in the condensation of chromatin
 NUCLEUS Animal cells contain DNA in nucleus (contains ~ 98% of cell DNA) and mitochondrion. Both compartments are surrounded by an envelope (double membrane). Nuclear DNA represents some linear molecules
NUCLEUS Animal cells contain DNA in nucleus (contains ~ 98% of cell DNA) and mitochondrion. Both compartments are surrounded by an envelope (double membrane). Nuclear DNA represents some linear molecules
Genetics 101. Prepared by: James J. Messina, Ph.D., CCMHC, NCC, DCMHS Assistant Professor, Troy University, Tampa Bay Site
 Genetics 101 Prepared by: James J. Messina, Ph.D., CCMHC, NCC, DCMHS Assistant Professor, Troy University, Tampa Bay Site Before we get started! Genetics 101 Additional Resources http://www.genetichealth.com/
Genetics 101 Prepared by: James J. Messina, Ph.D., CCMHC, NCC, DCMHS Assistant Professor, Troy University, Tampa Bay Site Before we get started! Genetics 101 Additional Resources http://www.genetichealth.com/
DNA Structure and Replication, and Virus Structure and Replication Test Review
 DNA Structure and Replication, and Virus Structure and Replication Test Review What does DNA stand for? Deoxyribonucleic Acid DNA is what type of macromolecule? DNA is a nucleic acid The building blocks
DNA Structure and Replication, and Virus Structure and Replication Test Review What does DNA stand for? Deoxyribonucleic Acid DNA is what type of macromolecule? DNA is a nucleic acid The building blocks
Genome Architecture Structural Subdivisons
 Lecture 4 Hierarchical Organization of the Genome by John R. Finnerty Genome Architecture Structural Subdivisons 1. Nucleotide : monomer building block of DNA 2. DNA : polymer string of nucleotides 3.
Lecture 4 Hierarchical Organization of the Genome by John R. Finnerty Genome Architecture Structural Subdivisons 1. Nucleotide : monomer building block of DNA 2. DNA : polymer string of nucleotides 3.
Replication Review. 1. What is DNA Replication? 2. Where does DNA Replication take place in eukaryotic cells?
 Replication Review 1. What is DNA Replication? 2. Where does DNA Replication take place in eukaryotic cells? 3. Where does DNA Replication take place in the cell cycle? 4. 4. What guides DNA Replication?
Replication Review 1. What is DNA Replication? 2. Where does DNA Replication take place in eukaryotic cells? 3. Where does DNA Replication take place in the cell cycle? 4. 4. What guides DNA Replication?
DNA Structure and Protein synthesis
 DNA Structure and Protein synthesis What is DNA? DNA = deoxyribonucleic acid Chromosomes are made of DNA It carries genetic information: controls the activities of cells by providing instructions for making
DNA Structure and Protein synthesis What is DNA? DNA = deoxyribonucleic acid Chromosomes are made of DNA It carries genetic information: controls the activities of cells by providing instructions for making
Molecular Biology I. The Chemical Nature of DNA. Dr. Obaidur rahman
 Molecular Biology I The Chemical Nature of DNA Dr. Obaidur rahman Characteristics of Genetic Material The coding instructions of all living organisms are written in the same genetic language that of nucleic
Molecular Biology I The Chemical Nature of DNA Dr. Obaidur rahman Characteristics of Genetic Material The coding instructions of all living organisms are written in the same genetic language that of nucleic
DNA Structure and Analysis. Chapter 4: Background
 DNA Structure and Analysis Chapter 4: Background Molecular Biology Three main disciplines of biotechnology Biochemistry Genetics Molecular Biology # Biotechnology: A Laboratory Skills Course explorer.bio-rad.com
DNA Structure and Analysis Chapter 4: Background Molecular Biology Three main disciplines of biotechnology Biochemistry Genetics Molecular Biology # Biotechnology: A Laboratory Skills Course explorer.bio-rad.com
DNA- THE MOLECULE OF LIFE. Link
 DNA- THE MOLECULE OF LIFE Link STRUCTURE OF DNA DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid): DNA is a long, stringy, twisted molecule made up of nucleotides that carries genetic information. DISCOVERIES Rosalind Franklin,
DNA- THE MOLECULE OF LIFE Link STRUCTURE OF DNA DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid): DNA is a long, stringy, twisted molecule made up of nucleotides that carries genetic information. DISCOVERIES Rosalind Franklin,
DNA- THE MOLECULE OF LIFE
 DNA- THE MOLECULE OF LIFE STRUCTURE OF DNA DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid): DNA is a long, stringy, twisted molecule made up of nucleotides that carries genetic information. DISCOVERIES Rosalind Franklin,
DNA- THE MOLECULE OF LIFE STRUCTURE OF DNA DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid): DNA is a long, stringy, twisted molecule made up of nucleotides that carries genetic information. DISCOVERIES Rosalind Franklin,
DNA stands for deoxyribose nucleic acid
 1 DNA 2 DNA stands for deoxyribose nucleic acid This chemical substance is present in the nucleus of all cells in all living organisms DNA controls all the chemical changes which take place in cells The
1 DNA 2 DNA stands for deoxyribose nucleic acid This chemical substance is present in the nucleus of all cells in all living organisms DNA controls all the chemical changes which take place in cells The
Worksheet Structure of DNA and Replication
 Eastern Intermediate High School Honors Biology Name: Period: Date: Worksheet Structure of DN and Replication Directions: Label the diagram below with the following choices: Nucleotide Deoxyribose Phosphate
Eastern Intermediate High School Honors Biology Name: Period: Date: Worksheet Structure of DN and Replication Directions: Label the diagram below with the following choices: Nucleotide Deoxyribose Phosphate
Topic 1 Year 10 Biology
 Topic 1 Year 10 Biology TOPIC 1 STRUCTURE OF DNA Things to cover: 1. History 2. Location 3. Components 4. Base pairing 5. Shape Work to do: 1. Worksheet Nuclear Matter (questions & mind-map) 2. Worksheet
Topic 1 Year 10 Biology TOPIC 1 STRUCTURE OF DNA Things to cover: 1. History 2. Location 3. Components 4. Base pairing 5. Shape Work to do: 1. Worksheet Nuclear Matter (questions & mind-map) 2. Worksheet
LABS 9 AND 10 DNA STRUCTURE AND REPLICATION; RNA AND PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
 LABS 9 AND 10 DNA STRUCTURE AND REPLICATION; RNA AND PROTEIN SYNTHESIS OBJECTIVE 1. OBJECTIVE 2. OBJECTIVE 3. OBJECTIVE 4. Describe the structure of DNA. Explain how DNA replicates. Understand the structure
LABS 9 AND 10 DNA STRUCTURE AND REPLICATION; RNA AND PROTEIN SYNTHESIS OBJECTIVE 1. OBJECTIVE 2. OBJECTIVE 3. OBJECTIVE 4. Describe the structure of DNA. Explain how DNA replicates. Understand the structure
4) separates the DNA strands during replication a. A b. B c. C d. D e. E. 5) covalently connects segments of DNA a. A b. B c. C d. D e.
 1) Chargaff's analysis of the relative base composition of DNA was significant because he was able to show that a. the relative proportion of each of the four bases differs from species to species. b.
1) Chargaff's analysis of the relative base composition of DNA was significant because he was able to show that a. the relative proportion of each of the four bases differs from species to species. b.
Chapter 13 - Concept Mapping
 Chapter 13 - Concept Mapping Using the terms and phrases provided below, complete the concept map showing the discovery of DNA structure. amount of base pairs five-carbon sugar purine DNA polymerases Franklin
Chapter 13 - Concept Mapping Using the terms and phrases provided below, complete the concept map showing the discovery of DNA structure. amount of base pairs five-carbon sugar purine DNA polymerases Franklin
2015 Biology Unit 4 PRACTICE TEST DNA, Structure, Function, Replication Week of December
 Name: Class: Date: 2015 Biology Unit 4 PRACTICE TEST DNA, Structure, Function, Replication Week of 14-18 December 1. Which scientists figured out the three-dimensional structure of DNA by using a model
Name: Class: Date: 2015 Biology Unit 4 PRACTICE TEST DNA, Structure, Function, Replication Week of 14-18 December 1. Which scientists figured out the three-dimensional structure of DNA by using a model
Structural Bioinformatics (C3210) DNA and RNA Structure
 Structural Bioinformatics (C3210) DNA and RNA Structure Importance of DNA/RNA 3D Structure Nucleic acids are essential materials found in all living organisms. Their main function is to maintain and transmit
Structural Bioinformatics (C3210) DNA and RNA Structure Importance of DNA/RNA 3D Structure Nucleic acids are essential materials found in all living organisms. Their main function is to maintain and transmit
Section Outline. Interest Grabber. Figure 12 2 Griffith s Experiment. Frederick Griffith (1928) Figure 12 2 Griffith s Experiment.
 Interest Grabber Section Outline Order! Order! Genes are made of, a large, complex molecule. is composed of individual units called nucleotides. Three of these units form a code. The order, or sequence,
Interest Grabber Section Outline Order! Order! Genes are made of, a large, complex molecule. is composed of individual units called nucleotides. Three of these units form a code. The order, or sequence,
CHAPTER 4, Part 1: LECTURE TOPICS: DNA and RNA - MOLECULES OF HEREDITY
 Chapter 4 Notes: Part 1 Biochemistry 461 Fall 2010 CHAPTER 4, Part 1: LECTURE TOPICS: DNA and RNA - MOLECULES OF HEREDITY 1) DNA/RNA structures, nomenclature, shorthand conventions 2) DNA and RNA as genetic
Chapter 4 Notes: Part 1 Biochemistry 461 Fall 2010 CHAPTER 4, Part 1: LECTURE TOPICS: DNA and RNA - MOLECULES OF HEREDITY 1) DNA/RNA structures, nomenclature, shorthand conventions 2) DNA and RNA as genetic
The Molecul Chapter ar Basis 16: The M of olecular Inheritance Basis of Inheritance Fig. 16-1
 he Chapter Molecular 16: he Basis Molecular of Inheritance Basis of Inheritance Fig. 16-1 dditional Evidence hat DN Is the Genetic Material It was known that DN is a polymer of nucleotides, each consisting
he Chapter Molecular 16: he Basis Molecular of Inheritance Basis of Inheritance Fig. 16-1 dditional Evidence hat DN Is the Genetic Material It was known that DN is a polymer of nucleotides, each consisting
The Nucleus and DNA Replication
 OpenStax-CNX module: m46073 1 The Nucleus and DNA Replication OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section,
OpenStax-CNX module: m46073 1 The Nucleus and DNA Replication OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section,
