Supplemental Information. Phosphorylation by Casein Kinase I Promotes. the Turnover of the Mdm2 Oncoprotein. via the SCF β-trcp Ubiquitin Ligase
|
|
|
- Russell Ferguson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Cancer Cell, Volume 18 Supplemental Information Phosphorylation by Casein Kinase I Promotes the Turnover of the Mdm2 Oncoprotein via the SCF β-trcp Ubiquitin Ligase Hiroyuki Inuzuka, Alan Tseng, Daming Gao, Bo Zhai, Qing Zhang, Shavali Shaik, Lixin Wan, Xiaolu L. Ang, Caroline Mock, Haoqiang Yin, Jayne M. Stommel, Steven Gygi, Galit Lahav, John Asara, Zhi-Xiong Jim Xiao, William G. Kaelin, Jr., J. Wade Harper, and Wenyi Wei SUPPLEMENTAL SECTION INVENTORY SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURES Figure S1 relates to manuscript Figure 1. Figure S2 relates to manuscript Figure 2. Figure S3 relates to manuscript Figure 3. Figure S4 relates to manuscript Figure 4. Figure S5 relates to manuscript Figure 5. Figure S6 relates to manuscript Figure 6. Figure S7 relates to manuscript Figure 7. SUPPLEMENTAL EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES SUPPLEMENTAL REFERENCES
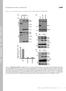
2 Figure S1, related to Figure 1. Mdm2 stability is controlled by β-trcp A. Immunoblot analysis of HeLa cells transfected with the indicated sirna oligos. B. Immunoblot analysis of whole cell lysates (WCL) and immunoprecipitates (IP) derived from 293T cells transfected with Myc-tagged Cullin 1 and the indicated HA-Mdm2 constructs. Twenty hours post-transfection, cells were treated with 10 µm MG132 overnight before harvesting. C. Immunoblot analysis of wild-type and β-trcp1 -/- mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs). D. Immunoblot analysis of 293T cells transfected with the indicated shrna constructs together with HA-Mdm2 and jellyfish GFP (egfp, as transfection controls). Where indicated, Flag-β-TRCP1**, which is engineered to resist the shβ-trcp1+2 effect, was included in the transfection. E. Immunoblot analysis of HeLa cells transfected with the indicated sirna oligos, after synchronization with nocodazole and release.
3 Figure S2, related to Figure 2. Mdm2 C464A binds to β-trcp1 as efficiently as wild-type Mdm2 Immunoblot analysis of whole cell lysates (WCL) and immunoprecipitates (IP) derived from 293T cells transfected with Myc-tagged β-trcp1 and the indicated HA-Mdm2 constructs. Twenty hours posttransfection, cells were treated with 10 µm MG132 overnight before harvesting.
4
5
6 Figure S3, related to Figure 3. Casein Kinase I is involved in regulating Mdm2 stability A. Illustration of the identified major PEST sequences within the Mdm2 primary protein sequence using the PESTfinder program. B. Immunoblot analysis of whole cell lysates (WCL) and immunoprecipitates (IP) derived from 293T cells transfected with HA-Mdm2 and various Myc-tagged CKI constructs. Twenty hours posttransfection, cells were treated with 10 µm MG132 overnight before harvesting. C. Autoradiograms showing various recovered 35 S-labeled CKI isoforms bound to GST-Mdm2 fusion proteins (GST protein as a negative control). IN, input (10% or 2% as indicated). D. Immunoblot analysis of whole cell lysates (WCL) derived from HeLa cells transfected with HA- Mdm2 and various amounts of Myc-tagged CKIδ constructs. E. Immunoblot analysis of whole cell lysates (WCL) derived from HeLa cells transfected with HA- Mdm2 and the indicated Myc-tagged CKIδ constructs. The K38R-CKIδ construct is a kinasedead mutant of CKIδ, which is used as a negative control in this assay. F. Immunoblot analysis of whole cell lysates (WCL) derived from HeLa cells transfected with the indicated Myc-tagged CKIδ constructs to detect the changes in endogenous Mdm2 expression. The K38R-CKIδ construct is a kinase-dead mutant of CKIδ, which is used as a negative control in this assay. G. HeLa cells were transfected with HA-Mdm2 and the indicated Myc-tagged CKIδ constructs. Twenty hours post-transfection, cells were split into 60 mm dishes, and after another 20 hours, cells were treated with 20 μg/ml cycloheximide. At the indicated time points, whole cell lysates were prepared and immunoblots were probed with the indicated antibodies. H. Immunoblot analysis of whole cell lysates (WCL) and immunoprecipitates (IP) derived from 293T cells transfected with HA-Mdm2 and Myc-tagged β-trcp1 constructs. Where indicated, cells were treated with two different CKI inhibitors (25 μm IC261 and 15 μm D4476) for 6 hours
7 before harvesting. Twenty hours post-transfection, cells were treated with 10 µm MG132 overnight before harvesting. I. Immunoblot analysis of HeLa cells transfected with HA-Mdm2 and the indicated shrna constructs. J. HeLa cells were infected with the indicated lentiviral shrna construct and selected with 1 µg /ml puromycin to eliminate non-infected cells. The resulting HeLa cell lines were arrested in the M phase by incubation with nocodazole for 18 hours and then released into the G1 phase. At the indicated time points, cell lysates were collected for immunoblot analysis. K. HeLa cells were transfected with the shgfp or shckiδ plasmid. Twenty hours post-transfection, cells were split into 60 mm dishes. After another 20 hours, cells were treated with 20 μg/ml cycloheximide. At the indicated time points, whole cell lysates were prepared and immunoblots were probed with the indicated antibodies. L. Quantification of the band intensities in K. Mdm2 band intensity was normalized to tubulin, then normalized to the t=0 controls. M. Immunofluorescence and DAPI staining of U2OS cells treated with or without 10 µm doxorubicin for 1 hour. Scale bars: 10 μm. N. Quantitation of the percentage of cells with nuclear CKIδ staining in M. The error bars represent +/- SD.
8
9
10
11
12
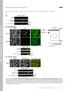
13 Figure S4, related to Figure 4. Casein Kinase I phosphorylates Mdm2 at multiple sites to trigger Mdm2 interaction with β-trcp1 A. Schematic illustration of the Mdm2 protein functional domains and the identified PEST sequences (p1, p2 and p3 region). B. Schematic representation of in vitro phosphorylation of GST-Mdm2 by CKIδ detected by mass spectrometry analysis. Confidentially assigned phosphorylation sites are shown in green while phosphorylation sites shown in red are highly possible phosphorylation sites, but not confidently assigned. C. Schematic representation of in vivo Mdm2 phosphorylation sites in 293T cells treated with the proteasomal inhibitor MG132 (with DMSO as a negative control) detected by mass spectrometry analysis. Confidentially assigned phosphorylation sites are shown in green while phosphorylation sites shown in red are highly possible phosphorylation sites, but not confidently assigned. D. Illustration of the reported CKI phosphorylation sites in Mdm2. E. Illustration of the verified and predicted Mdm2 phosphorylation sites that mimic the β-trcp degron sequence. These potentially critical Ser/Thr phosphorylation sites for individual suboptimal degrons including the putative CKI sites were mutated in a step-wise fashion, and their abilities to be phosphorylated by CKIδ, to interact with and to be degraded by β-trcp1 were analyzed in Figure 4-5. Verified phosphorylation sites are shown in green while predicted phosphorylation sites are shown in blue. The surrounding amino acids, which are possible components of the putative degron sequence are also highlighted in orange. F. Sequence alignment of the putative β-trcp-recognizable non-canonical degron sequence in the p1 region of Mdm2 across different species. G. HeLa cells were transiently transfected with the HA-tagged wild-type or a mutant (S118A/S121A) Mdm2 construct. Thirty hours post-transfection, Mdm2 was recovered by HAimmunoprecipitation, and probed with an antibody that could detect the phosphorylation status of
14 Ser118 or Ser118/Ser121. Where indicated, cells were treated with 15 µm MG132 overnight before harvesting. H. HeLa cells were treated with or without the proteasome inhibitor MG132 to block Mdm2 destruction. Endogenous Mdm2 was immunoprecipitated with anti-mdm2 antibody (with mouse IgG as a negative control). Where indicated, whole cell lysates were treated with λ-phosphatase prior to immunoprecipitation. The recovered Mdm2 immunoprecipitate was separated by SDS- PAGE and immunoblotted with an antibody that could detect the phosphorylation status of Ser118. I. HeLa cells were transiently transfected with the HA-tagged Mdm2 construct. Thirty hours posttransfection, the Mdm2 protein was recovered by HA-immunoprecipitation, and probed with an antibody that could detect the phosphorylation status of Ser118/Ser121. Where indicated, cells were treated with 50 µm etoposide for the indicated times before harvesting. Cells were treated with 10 µm MG132 for 1 hour prior to DNA damage treatment to block Mdm2 destruction. J. HeLa cells were treated with or without the proteasome inhibitor MG132 to block Mdm2 destruction. Endogenous Mdm2 was immunoprecipitated with anti-mdm2 antibody (with mouse IgG as a negative control). Where indicated, cells were treated with the CKI inhibitor D4476 (15 μm) for 3 hours prior to harvesting for immunoprecipitation. The recovered Mdm2 immunoprecipitate was separated by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted with an antibody that could detect the phosphorylation status of Ser118. K. 293T cells were transiently transfected with HA-Mdm2 and the indicated shrna constructs. Thirty hours post-transfection, Mdm2 was recovered by HA-immunoprecipitation, and probed with an antibody that could detect the phosphorylation status of Ser118/Ser121. L. Sequences of the biotinylated Mdm2 peptides used in the β-trcp binding assays. M-N. Autoradiograms showing recovery of 35 S-labeled F-box proteins bound to the indicated biotinylated peptides. IN, input (10%, 5% or 2% as indicated).
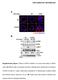
15 O-P. Immunoblot analysis of whole cell lysates (WCL) and immunoprecipitates (IP) derived from 293T cells transfected with Flag-β-TRCP1 and the indicated HA-Mdm2 constructs. Twenty hours post-transfection, cells were treated with 10 µm MG132 overnight before harvesting. Q. Schematic illustration of the various Mdm2 deletion mutants generated for this study. R. Illustration of the various Mdm2 mutants with gradual inactivation of the potentially critical Ser/Thr phosphorylation sites for suboptimal degrons. The abilities of these individual mutants to be phosphorylated by CKIδ and degraded by β-trcp were further analyzed in Figure 4-5. S. CKIδ phosphorylates Mdm2 in vitro at multiple sites. Purified CKIδ protein (from New England Biolabs) was incubated with 5 μg of the indicated GST-Mdm2 proteins in the presence of γ- 32 P- ATP. The kinase reaction products were resolved by SDS-PAGE and phosphorylation was detected by autoradiography. T. Point-mutations in Mdm2 do not affect its interaction with CKIδ in vitro. Whole cell lysates (WCL) derived from 293T cells transfected with Myc-CKIδ were incubated with 3 μg of the indicated GST-Mdm2 proteins. After intensive washing, the recovered GST precipitations were resolved by SDS-PAGE and immunoblot was performed with anti-myc antibody. The PVDF membrane was stained with Ponceau S to indicate equal loading of the indicated GST-proteins on each lane. U. Immunoblot analysis of whole cell lysates (WCL) and immunoprecipitates (IP) derived from 293T cells transfected with the indicated HA-Mdm2 and Myc-tagged CKI constructs. Twenty hours post-transfection, cells were treated with 10 µm MG132 overnight before harvesting. V. Phosphorylation of Mdm2 at multiple sites by CKIδ triggers its interaction with β-trcp1 in vitro. Autoradiograms showing recovery of 35 S-labeled β-trcp1 protein bound to the indicated GST- Mdm2 fusion proteins (GST protein as a negative control) incubated with CKIδ prior to the pulldown assays. IN, input (10% or 2% as indicated).
16 Figure S5, related to Figure 5. GST-p1 and GST-p2 were susceptible to β-trcp1-mediated proteolysis Immunobot analysis of HeLa cells transfected with the indicated GST-Mdm2 and shrna plasmids. A plasmid encoding GFP was used as a negative control for transfection efficiency.
17
18 Figure S6, related to Figure 6. Casein Kinase Iδ phosphorylates Mdm2 at multiple sites to trigger Mdm2 ubiquitination and destruction by β-trcp1 A. HeLa cells were transfected with the indicated HA-Mdm2 constructs. Twenty hours posttransfection, cells were split into 60 mm dishes, and after another 20 hours, treated with 20 μg/ml cycloheximide. At the indicated time points, whole-cell lysates were prepared and immunoblots were probed with the indicated antibodies. B. HeLa cells were transfected with the indicated HA-Mdm2 constructs together with the Flag-β- TRCP1 and Myc-CKIδ plasmids. Twenty hours post-transfection, cells were split into 60 mm dishes, and after another 20 hours, treated with 20 μg/ml cycloheximide. At the indicated time points, whole-cell lysates were prepared and immunoblots were probed with the indicated antibodies. C. Immunoblot analysis of whole cell lysates (WCL) and immunoprecipitates (IP) derived from 293T cells transfected with the indicated HA-Mdm2 and GST-p53 constructs. Twenty hours posttransfection, cells were treated with 10 µm MG132 overnight before harvesting. D. Mutation of the identified major Ser/Thr phosphorylation sites does not affect the ability of Mdm2 to degrade p53 while deletion of the p1, p2 and p3 PEST sequences moderately reduces the E3 ligase activity of Mdm2 towards p53 destruction. HeLa cells were transfected with the indicated HA-Mdm2 constructs. Forty hours post-transfection, whole-cell lysates were prepared and immunoblots were probed with the indicated antibodies. E. Immunoblot analysis of whole cell extracts and anti-ha immunoprecipitates of HeLa cells transfected with the indicated plasmids. Twenty hours post-transfection, cells were treated with the proteasome inhibitor MG132 overnight, and stimulated with 10 μm etoposide for 2 hours before harvesting.
19
20
21 Figure S7, related to Figure 7. β-trcp1 depletion-induced resistance to apoptosis is partially through the p53 pathway and inhibition of Casein Kinase Iδ activity attenuated the p53 pulse in response to continuous DNA damage treatment A. Immunoblot analysis of HeLa cells transfected with HA-Mdm2 and the indicated shrna constructs. Twenty hours post-transfection, cells were treated with etoposide (or with DMSO as a negative control) for 1.5 hours. B. Immunoblot analysis of the indicated HeLa stable cell lines transfected with the indicated shrna constructs. Twenty hours post-transfection, cells were treated with etoposide (or with DMSO as a negative control) for 1.5 hours. The indicated HeLa stable cell lines were generated by infection with the shgfp or shckiδ lentiviral constructs and subsequent selection with 1 μg/ml puromycin to eliminate non-infected cells. C-D. U2OS cells were transfected with the indicated sirna oligos. 20 hours post-transfection, cells were treated with hydroxyurea for 16 hours, and then treated with 1.7 µm doxorubicin for 2 hours before release to normal medium. Twelve hours later, cells were recovered for FACS analysis for detection of the apoptotic (sub-g1) cell population (D) or by Annexin V/7-AAD double straining (C). E. Immunoblot analysis of U2OS cells transfected with the indicated sirna oligos to illustrate the knock down efficiency of the anti-p53 sirna oligo used in the assay. F. HCT116-WT or HCT116-p53 -/- cells were infected with the indicated lentiviral shrna constructs. Forty hours post-infection, cells were selected with 1 µg/ml puromycin to create stable cell lines where the endogenous β-trcp1 is depleted (with shgfp as a negative control). The resulting cell lines were treated with hydroxyurea for 16 hours, and then treated with 1.7 µm doxorubicin for 2 hours before release to normal medium. Twelve hours later, cells were recovered for FACS analysis for detection of the apoptotic (sub-g1) cell population.
22 G. Immunoblot analysis of the various generated HCT116 cell lines to illustrate that Mdm2 upregulation by β-trcp1-depletion is independent of the p53 status. H. Real-time RT-PCR analysis to examine the relative β-trcp1 mrna expression levels in U2OS cells transfected with the indicated sirna oligonucleotides. Three independent sets of experiments were performed to generate the error bar. The error bars represent +/- SD. I. Immunoblot analysis of U2OS cells transfected with the indicated sirna oligos. J. Depletion of endogenous β-trcp1 by shtrcp1 treatment (shgfp as a negative control) in HCT116 cells resulted in elevated BrdU incorporation. The indicated HCT116 cells were arrested in M phase with nocodazole incubation and then released to the cell cycle. At the indicated time points post-nocodazole release, cells were pulsed with BrdU for 20 minutes, fixed with ice-cold Methanol and the percentage of BrdU incorporated cells were analyzed with immunohistochemistry. The error bars represent +/- SD. K. Quantitation of bioluminescent imaging studies of xenografted tumors formed by HCT116 cells as in G that were then superinfected with a retrovirus encoding firefly luciferase. A total of 1.5x10 6 cells were injected subcutaneously into the nude mice (shgfp on the left flank and shtrcp1 on the right flank of the individual nude mice). Bioluminescent images were obtained 1 week later (day 0) and serially after the injection. Error bars represent +/- SEM. See Experimental Procedures for normalization. L. Immunoblot analysis of MCF7 cells treated with the CKI inhibitor D4476 (or with DMSO as a negative control) for 7 hours before cells were treated with NCS. Whole cell lysates were collected at the indicated time points. M. MCF7 cells were infected with the indicated lentiviral shrna constructs. Forty hours postinfection, cells were selected with 1 µg/ml puromycin to create stable cell lines where the endogenous CKIδ is depleted (with shgfp as a negative control). The resulting cell lines were treated with NCS, and whole cell lysates were collected at the indicated time points.
23 SUPPLEMENTAL EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES Plasmids: HA-Mdm2 construct was obtained from Dr. Jiandong Chen. Mdm2, β-trcp1 and CKIδ mutants were generated using the QuikChange XL Site-Directed Mutagenesis Kit (Stratagene) according to the manufacturer s instructions. Various Mdm2 cdna were subcloned using the Pfu polymerase (Stratagene) into the pgex vector to create GST-Mdm2 in frame fusion proteins. Indicated fragments of Mdm2 cdna (Fig. 5D) were subcloned using the Pfu polymerase (Stratagene) into pcmv-gst vector to create constructs that could ectopically overexpress chimera GST-Mdm2 fusion protein in mammalian cells. Flag-β-TRCP1, shrna-β-trcp1+2, shtrcp1, shtrcp2, shrna-gfp and various CKI constructs were described previously (Jin et al., 2003; Shirogane et al., 2005). The Fbw4, Fbw5, Skp2 constructs were described previously (Wei et al., 2005). Myc-β-TRCP1, Myc-β-TRCP2 and Myc-β-TRCP1-R474A constructs were described previously (Jin et al., 2003; Shirogane et al., 2005; Wu et al., 2003). GST-Cullin-1, Myc-Cullin 1, Myc-Cullin 2, Myc-Cullin 3, Myc-Cullin 4A and Myc-Cullin 5 constructs were kind gifts from Dr. James DeCaprio. shrna constructs against various CKI isoforms were obtained from Dr. Jianping Jin. Lentiviral shrna constructs against GFP and CKIδ were obtained from Dr. William Hahn. Antibodies and Reagents: Anti-p21 (sc-397), anti-mdm2 (sc-965), anti c-myc (sc-40), anti-p53 (sc-126), anti-p27 (SC-528), polyclonal anti-ha (SC-805), polyclonal anti-skp2 (SC-7164), anti-cyclin A (SC-751), anti-cyclin B (SC-245), anti- Cdc20 (SC-8358), anti-casein Kinase Iα (SC-6477), anti-casein Kinase Iδ (R-19) (SC-6474), anti-casein Kinase Iδ (H-60) (SC-20709), anti-cullin 1 (SC-17775), anti-plk1 (SC-17783), anti-wee1 (SC-325), anticyclin E (SC-247) antibodies and anti-mdm2 agarose beads (sc-965ac) were purchased from Santa Cruz. Anti-Casein Kinase Iε (610445) was purchased from BD Transduction Laboratory. Anti-tubulin (T-5168), polyclonal anti-flag (F2425), monoclonal anti-flag (F-3165), anti-β-catenin (C7207), anti-vinculin
24 (V4505), peroxidase-conjugated anti-mouse secondary antibody (A4416) and peroxidase-conjugated antirabbit secondary antibody (A4914), anti-flag agarose beads (A2220) and anti-ha agrarose beads (A2095) were purchased from Sigma. Monoclonal anti-ha antibody (MMS-101P) was purchased from Convace. Anti-GFP (632380), monoclonal anti-skp2 ( ) and polyclonal anti-cdh1 ( ) antibodies were purchased from Invitrogen. Monoclonal anti-cdh1 (CC43) was purchased from Oncogene. Anti-Bax (2772), Anti-phospho-Ser317 Chk1 (2344) antibodies were purchased from Cell Signaling. Anti-Mdm2 (Ab1: OP46) and anti-mdm2 (Ab5: OP145) antibodies were purchased from Calbiochem. Anti-Claspin antibody (A267A) was purchased from Bethyl. Polyclonal anit-pser118-mdm2 and anti-pser118pser121-mdm2 antibodies were produced by Proteintech Group, Inc. using synthetic peptides (QESSDSpGTSVSENRC) and (QESSDSpGTSpVSENRC). Oligofectamine, Lipofectamine and Plus reagents were purchased from Invitrogen. Immunoblots and Immunoprecipitation: Cells were lysed in EBC (50 mm Tris ph 8.0, 120 mm NaCl, 0.5% NP-40) buffer supplemented with protease inhibitors (Complete Mini, Roche) and phosphatase inhibitors (phosphatase inhibitor cocktail set I and II, Calbiochem). The protein concentrations of the lysates were measured using the Bio-Rad protein assay reagent on a Beckman Coulter DU-800 spectrophotometer. The lysates were then resolved by SDS- PAGE and immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies. For immunoprecipitation, 800 μg lysates were incubated with the appropriate antibody (1-2 μg) for 3-4 hours at 4 C followed by one hour-incubation with Protein A sepharose beads (GE Healthcare). Immuno-complexes were washed five times with NETN buffer (20 mm Tris, ph 8.0, 100 mm NaCl, 1 mm EDTA and 0.5% NP-40) before being resolved by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted with indicated antibodies. Quantification of the immunoblot band intensity was performed with ImageJ software.
25 Protein Degradation Analysis: Cells were plated into 6 cm tissue-culture dishes 20 hours before transfection. When cells reached an appropriate confluence, they were transfected with 0.4 μg of a plasmid encoding a HA-tagged version of Mdm2 along with 1.0 μg Flag-β-TRCP1, and 0.1 μg of a plasmid encoding GFP as a negative control, in the presence or absence of 0.4 μg of Myc-CKI. For half-life studies, cycloheximide (20 μg/ml, Sigma) was added to the media 40 hours post-transfection. At various time points thereafter, cells were lysed and protein concentration was measured. 30 μg of the indicated whole cell lysates were separated by SDS-PAGE and protein abundances were measured by immunoblot analysis. Detection of Mdm2 phosphorylation sites in vivo: To map Mdm2 phosphorylation status in vivo, 293T cells were transfected with HA-Mdm2 using the calcium phosphate method. Thirty hours post-transfection, 293T cells were treated with 10 μm MG132 for 16 hours to block the 26S proteasome pathway prior to collecting the whole cell lysate for HA-immunoprecipitation. After extensive washing with NETN buffer, the HA-immunoprecipitates were separated by SDS-PAGE and visualized by the Gel-Code Blue reagent. The band containing Mdm2 was excised and treated with DTT to reduce disulfide bonds and iodoacetamide to derivatize cysteine residues. In-gel digestion of the protein was performed with trypsin and chymotrypsin. The resulting peptides were extracted from the gel and analyzed by nanoscale-microcapillary reversed phase liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) essentially as described previously (Villen and Gygi, 2008). All peptide matches were filtered based on mass deviation, tryptic state, XCorr and dcn and confirmed by manual validation. The reliability of sitelocalization of phosphorylation events was evaluated using the Ascore algorithm (Beausoleil et al., 2006). Detection of Mdm2 phosphorylation sites in vitro: GST-Mdm2 protein purified from BL21 E. Coli was incubated with recombinant CKIδ (from New England Biolabs) to perform in vitro kinase reaction as described above. The reaction was stopped by the addition of
26 SDS-containing lysis buffer, and separated using SDS-PAGE. The gel was stained with the Gel-Code Blue reagent, destained and the Mdm2 band was excised. Samples were subjected to reduction with 10mM dithiothreitol (DTT) for 30 minutes, alkylation with 55mM iodoacetamide with 45 minutes, and in-gel digestion with a combination of chymotrypsin and trypsin enzymes. The digested samples were subjected to reversed phase microcapillary/tandem mass spectrometry (LC/MS/MS) as described previously (Dephoure et al., 2008; Villen and Gygi, 2008), or performed using an EASY-nLC splitless nanoflow HPLC (Proxeon Biosciences) with a self-packed 75 μm id x 15 cm C 18 Picofrit column (New Objective) coupled to a LTQ- Orbitrap XL mass spectrometer (Thermo Scientific) in the data-dependent acquisition and positive ion mode at 300 nl/min with one full MS-FT scan followed by six MS/MS spectra. The analysis of the collected MS/MS spectra data was described previously (Beausoleil et al., 2006; Dephoure et al., 2008; Dibble et al., 2009; Gwinn et al.). Half of the digested peptide pool was reserved for enrichment with the Phos-trap Phosphopeptide Enrichment Kit containing titanium dioxide (TiO 2 ) coated magnetic beads (PerkinElmer) according to the vendor s protocol. Briefly, peptide mixtures containing phosphopeptides were acidified with Binding buffer and incubated with 20µL of 20X TiO 2 magnetic beads diluted in 180µL of HPLC grade water for one hour at room temperature (RT) with continuous shaking in a RT incubator followed by washing three times with Binding buffer and one time with Washing buffer. Phosphopeptides were then incubated with 35µL of basic Elution buffer with continuous shaking. Elution buffer was then transferred to a 12x32mm autosampler vial with 50uL of HPLC A buffer and the final solution was concentrated to 5µL using a SpeedVac prior to injection via LC/MS/MS. Real-time RT-PCR Analysis: RNA was extracted using Qiagen RNeasy mini kit, and the reverse transcription reaction was performed using the ABI Taqman Reverse Transcriptional Reagents (N ). After mixing the resulting template with Mdm2 (Hs _m1), β-trcp1 (Hs _m1) or GAPDH (Hs _m1) primers and ABI Taqman Fast Universal PCR Master Mix ( ), the real-time RT-PCR reaction was performed with the ABI-7500 Fast Real-time PCR system.
27 SUPPLEMENTAL REFERENCES Beausoleil, S. A., Villen, J., Gerber, S. A., Rush, J., and Gygi, S. P. (2006). A probability-based approach for high-throughput protein phosphorylation analysis and site localization. Nat Biotechnol 24, Dephoure, N., Zhou, C., Villen, J., Beausoleil, S. A., Bakalarski, C. E., Elledge, S. J., and Gygi, S. P. (2008). A quantitative atlas of mitotic phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105, Dibble, C. C., Asara, J. M., and Manning, B. D. (2009). Characterization of Rictor phosphorylation sites reveals direct regulation of mtor complex 2 by S6K1. Mol Cell Biol 29, Gwinn, D. M., Asara, J. M., and Shaw, R. J. Raptor is phosphorylated by cdc2 during mitosis. PLoS One 5, e9197. Shirogane, T., Jin, J., Ang, X. L., and Harper, J. W. (2005). SCFbeta-TRCP controls clock-dependent transcription via casein kinase 1-dependent degradation of the mammalian period-1 (Per1) protein. J Biol Chem 280, Villen, J., and Gygi, S. P. (2008). The SCX/IMAC enrichment approach for global phosphorylation analysis by mass spectrometry. Nat Protoc 3,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature09732 Supplementary Figure 1: Depletion of Fbw7 results in elevated Mcl-1 abundance. a, Total thymocytes from 8-wk-old Lck-Cre/Fbw7 +/fl (Control) or Lck-Cre/Fbw7 fl/fl (Fbw7 KO) mice
doi:10.1038/nature09732 Supplementary Figure 1: Depletion of Fbw7 results in elevated Mcl-1 abundance. a, Total thymocytes from 8-wk-old Lck-Cre/Fbw7 +/fl (Control) or Lck-Cre/Fbw7 fl/fl (Fbw7 KO) mice
Supplementary Information: Materials and Methods. GST and GST-p53 were purified according to standard protocol after
 Supplementary Information: Materials and Methods Recombinant protein expression and in vitro kinase assay. GST and GST-p53 were purified according to standard protocol after induction with.5mm IPTG for
Supplementary Information: Materials and Methods Recombinant protein expression and in vitro kinase assay. GST and GST-p53 were purified according to standard protocol after induction with.5mm IPTG for
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 The Supplementary Information (SI) Methods Cell culture and transfections H1299, U2OS, 293, HeLa cells were maintained in DMEM medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum. H1299 and 293 cells were
The Supplementary Information (SI) Methods Cell culture and transfections H1299, U2OS, 293, HeLa cells were maintained in DMEM medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum. H1299 and 293 cells were
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Su et al. 10.1073/pnas.1211604110 SI Materials and Methods Cell Culture and Plasmids. Tera-1 and Tera-2 cells (ATCC: HTB- 105/106) were maintained in McCoy s 5A medium with 15% FBS
Supporting Information Su et al. 10.1073/pnas.1211604110 SI Materials and Methods Cell Culture and Plasmids. Tera-1 and Tera-2 cells (ATCC: HTB- 105/106) were maintained in McCoy s 5A medium with 15% FBS
Rictor Forms a Complex with Cullin-1 to Promote SGK1 Ubiquitination and Destruction
 Molecular Cell, Volume 39 Supplemental Information Rictor Forms a Complex with Cullin-1 to Promote SGK1 Ubiquitination and Destruction Daming Gao, Lixin Wan, Hiroyuki Inuzuka, Anders H. Berg, Alan Tseng,
Molecular Cell, Volume 39 Supplemental Information Rictor Forms a Complex with Cullin-1 to Promote SGK1 Ubiquitination and Destruction Daming Gao, Lixin Wan, Hiroyuki Inuzuka, Anders H. Berg, Alan Tseng,
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Han et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201311007/dc1 Figure S1. SIVA1 interacts with PCNA. (A) HEK293T cells were transiently
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Han et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201311007/dc1 Figure S1. SIVA1 interacts with PCNA. (A) HEK293T cells were transiently
Supplementary Information: Materials and Methods. Immunoblot and immunoprecipitation. Cells were washed in phosphate buffered
 Supplementary Information: Materials and Methods Immunoblot and immunoprecipitation. Cells were washed in phosphate buffered saline (PBS) and lysed in TNN lysis buffer (50mM Tris at ph 8.0, 120mM NaCl
Supplementary Information: Materials and Methods Immunoblot and immunoprecipitation. Cells were washed in phosphate buffered saline (PBS) and lysed in TNN lysis buffer (50mM Tris at ph 8.0, 120mM NaCl
Coleman et al., Supplementary Figure 1
 Coleman et al., Supplementary Figure 1 BrdU Merge G1 Early S Mid S Supplementary Figure 1. Sequential destruction of CRL4 Cdt2 targets during the G1/S transition. HCT116 cells were synchronized by sequential
Coleman et al., Supplementary Figure 1 BrdU Merge G1 Early S Mid S Supplementary Figure 1. Sequential destruction of CRL4 Cdt2 targets during the G1/S transition. HCT116 cells were synchronized by sequential
Supplementary information
 Supplementary information The E3 ligase RNF8 regulates KU80 removal and NHEJ repair Lin Feng 1, Junjie Chen 1 1 Department of Experimental Radiation Oncology, The University of Texas M. D. Anderson Cancer
Supplementary information The E3 ligase RNF8 regulates KU80 removal and NHEJ repair Lin Feng 1, Junjie Chen 1 1 Department of Experimental Radiation Oncology, The University of Texas M. D. Anderson Cancer
Supplementary data. sienigma. F-Enigma F-EnigmaSM. a-p53
 Supplementary data Supplemental Figure 1 A sienigma #2 sienigma sicontrol a-enigma - + ++ - - - - - - + ++ - - - - - - ++ B sienigma F-Enigma F-EnigmaSM a-flag HLK3 cells - - - + ++ + ++ - + - + + - -
Supplementary data Supplemental Figure 1 A sienigma #2 sienigma sicontrol a-enigma - + ++ - - - - - - + ++ - - - - - - ++ B sienigma F-Enigma F-EnigmaSM a-flag HLK3 cells - - - + ++ + ++ - + - + + - -
HPV E6 oncoprotein targets histone methyltransferases for modulating specific. Chih-Hung Hsu, Kai-Lin Peng, Hua-Ci Jhang, Chia-Hui Lin, Shwu-Yuan Wu,
 1 HPV E oncoprotein targets histone methyltransferases for modulating specific gene transcription 3 5 Chih-Hung Hsu, Kai-Lin Peng, Hua-Ci Jhang, Chia-Hui Lin, Shwu-Yuan Wu, Cheng-Ming Chiang, Sheng-Chung
1 HPV E oncoprotein targets histone methyltransferases for modulating specific gene transcription 3 5 Chih-Hung Hsu, Kai-Lin Peng, Hua-Ci Jhang, Chia-Hui Lin, Shwu-Yuan Wu, Cheng-Ming Chiang, Sheng-Chung
supplementary information
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2116 Figure S1 CDK phosphorylation of EZH2 in cells. (a) Comparison of candidate CDK phosphorylation sites on EZH2 with known CDK substrates by multiple sequence alignments. (b) CDK1 and
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2116 Figure S1 CDK phosphorylation of EZH2 in cells. (a) Comparison of candidate CDK phosphorylation sites on EZH2 with known CDK substrates by multiple sequence alignments. (b) CDK1 and
ASPP1 Fw GGTTGGGAATCCACGTGTTG ASPP1 Rv GCCATATCTTGGAGCTCTGAGAG
 Supplemental Materials and Methods Plasmids: the following plasmids were used in the supplementary data: pwzl-myc- Lats2 (Aylon et al, 2006), pretrosuper-vector and pretrosuper-shp53 (generous gift of
Supplemental Materials and Methods Plasmids: the following plasmids were used in the supplementary data: pwzl-myc- Lats2 (Aylon et al, 2006), pretrosuper-vector and pretrosuper-shp53 (generous gift of
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 (Supplementary Methods and Materials) GST pull-down assay GST-fusion proteins Fe65 365-533, and Fe65 538-700 were expressed in BL21 bacterial cells and purified with glutathione-agarose beads (Sigma).
(Supplementary Methods and Materials) GST pull-down assay GST-fusion proteins Fe65 365-533, and Fe65 538-700 were expressed in BL21 bacterial cells and purified with glutathione-agarose beads (Sigma).
SANTA CRUZ BIOTECHNOLOGY, INC.
 TECHNICAL SERVICE GUIDE: Western Blotting 2. What size bands were expected and what size bands were detected? 3. Was the blot blank or was a dark background or non-specific bands seen? 4. Did this same
TECHNICAL SERVICE GUIDE: Western Blotting 2. What size bands were expected and what size bands were detected? 3. Was the blot blank or was a dark background or non-specific bands seen? 4. Did this same
Supplemental Information: Phosphorylation of CLIP-170 by Both Plk1 and CK2 Is Involved in the Timely Formation of Kinetochore-microtubule Attachments
 Supplemental Information: Phosphorylation of CLIP-170 by Both Plk1 and CK2 Is Involved in the Timely Formation of Kinetochore-microtubule Attachments Hongchang Li, X. Shawn Liu, Xiaoming Yang, Yingmin
Supplemental Information: Phosphorylation of CLIP-170 by Both Plk1 and CK2 Is Involved in the Timely Formation of Kinetochore-microtubule Attachments Hongchang Li, X. Shawn Liu, Xiaoming Yang, Yingmin
Figure 1: TDP-43 is subject to lysine acetylation within the RNA-binding domain a) QBI-293 cells were transfected with TDP-43 in the presence or
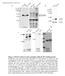 Figure 1: TDP-43 is subject to lysine acetylation within the RNA-binding domain a) QBI-293 cells were transfected with TDP-43 in the presence or absence of the acetyltransferase CBP and acetylated TDP-43
Figure 1: TDP-43 is subject to lysine acetylation within the RNA-binding domain a) QBI-293 cells were transfected with TDP-43 in the presence or absence of the acetyltransferase CBP and acetylated TDP-43
Supplementary Fig. 1 Proteomic analysis of ATR-interacting proteins. ATR, ARID1A and
 Supplementary Figure Legend: Supplementary Fig. 1 Proteomic analysis of ATR-interacting proteins. ATR, ARID1A and ATRIP protein peptides identified from our mass spectrum analysis were shown. Supplementary
Supplementary Figure Legend: Supplementary Fig. 1 Proteomic analysis of ATR-interacting proteins. ATR, ARID1A and ATRIP protein peptides identified from our mass spectrum analysis were shown. Supplementary
supplementary information
 DOI: 1.138/ncb1839 a b Control 1 2 3 Control 1 2 3 Fbw7 Smad3 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 c d IGF-1 IGF-1Rβ IGF-1Rβ-P Control / 1 2 3 4 Real-time RT-PCR Relative quantity (IGF-1/ mrna) 2 1 IGF-1 1 2 3 4 Control /
DOI: 1.138/ncb1839 a b Control 1 2 3 Control 1 2 3 Fbw7 Smad3 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 c d IGF-1 IGF-1Rβ IGF-1Rβ-P Control / 1 2 3 4 Real-time RT-PCR Relative quantity (IGF-1/ mrna) 2 1 IGF-1 1 2 3 4 Control /
Supplementary Material
 Supplementary Material Supplementary Methods Cell synchronization. For synchronized cell growth, thymidine was added to 30% confluent U2OS cells to a final concentration of 2.5mM. Cells were incubated
Supplementary Material Supplementary Methods Cell synchronization. For synchronized cell growth, thymidine was added to 30% confluent U2OS cells to a final concentration of 2.5mM. Cells were incubated
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Nakajima and Tanoue, http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201104118/dc1 Figure S1. DLD-1 cells exhibit the characteristic morphology
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Nakajima and Tanoue, http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201104118/dc1 Figure S1. DLD-1 cells exhibit the characteristic morphology
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1 Effect of ROCK inhibition on lumen abnormality in MDCK cysts. (A) MDCK cells as indicated cultured in Matrigel were treated with and without Y27632 (10
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1 Effect of ROCK inhibition on lumen abnormality in MDCK cysts. (A) MDCK cells as indicated cultured in Matrigel were treated with and without Y27632 (10
Supplementary Materials and Methods
 Supplementary Materials and Methods sirna sequences used in this study The sequences of Stealth Select RNAi for ALK and FLOT-1 were as follows: ALK sense no.1 (ALK): 5 -AAUACUGACAGCCACAGGCAAUGUC-3 ; ALK
Supplementary Materials and Methods sirna sequences used in this study The sequences of Stealth Select RNAi for ALK and FLOT-1 were as follows: ALK sense no.1 (ALK): 5 -AAUACUGACAGCCACAGGCAAUGUC-3 ; ALK
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS SIRTUIN 1 PROMOTES HYPEROXIA-INDUCED LUNG EPITHELIAL DEATH INDEPENDENT OF NRF2 ACTIVATION
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS SIRTUIN PROMOTES HYPEROXIA-INDUCED LUNG EPITHELIAL DEATH INDEPENDENT OF NRF ACTIVATION Haranatha R. Potteti*, Subbiah Rajasekaran*, Senthilkumar B. Rajamohan*, Chandramohan R. Tamatam,
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS SIRTUIN PROMOTES HYPEROXIA-INDUCED LUNG EPITHELIAL DEATH INDEPENDENT OF NRF ACTIVATION Haranatha R. Potteti*, Subbiah Rajasekaran*, Senthilkumar B. Rajamohan*, Chandramohan R. Tamatam,
At E17.5, the embryos were rinsed in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and immersed in
 Supplementary Materials and Methods Barrier function assays At E17.5, the embryos were rinsed in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and immersed in acidic X-gal mix (100 mm phosphate buffer at ph4.3, 3 mm
Supplementary Materials and Methods Barrier function assays At E17.5, the embryos were rinsed in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and immersed in acidic X-gal mix (100 mm phosphate buffer at ph4.3, 3 mm
Supplementary methods Shoc2 In Vitro Ubiquitination Assay
 Supplementary methods Shoc2 In Vitro Ubiquitination Assay 35 S-labelled Shoc2 was prepared using a TNT quick Coupled transcription/ translation System (Promega) as recommended by manufacturer. For the
Supplementary methods Shoc2 In Vitro Ubiquitination Assay 35 S-labelled Shoc2 was prepared using a TNT quick Coupled transcription/ translation System (Promega) as recommended by manufacturer. For the
Supplementary Materials
 Supplementary Materials Supplementary Figure 1. PKM2 interacts with MLC2 in cytokinesis. a, U87, U87/EGFRvIII, and HeLa cells in cytokinesis were immunostained with DAPI and an anti-pkm2 antibody. Thirty
Supplementary Materials Supplementary Figure 1. PKM2 interacts with MLC2 in cytokinesis. a, U87, U87/EGFRvIII, and HeLa cells in cytokinesis were immunostained with DAPI and an anti-pkm2 antibody. Thirty
Supplementary methods
 Supplementary methods Cell culture, infection, transfection, and RNA interference HEK293 cells and its derivatives were grown in DMEM supplemented with 10% FBS. Various constructs were introduced into
Supplementary methods Cell culture, infection, transfection, and RNA interference HEK293 cells and its derivatives were grown in DMEM supplemented with 10% FBS. Various constructs were introduced into
Supplemental Data. LMO4 Controls the Balance between Excitatory. and Inhibitory Spinal V2 Interneurons
 Neuron, Volume 61 Supplemental Data LMO4 Controls the Balance between Excitatory and Inhibitory Spinal V2 Interneurons Kaumudi Joshi, Seunghee Lee, Bora Lee, Jae W. Lee, and Soo-Kyung Lee Supplemental
Neuron, Volume 61 Supplemental Data LMO4 Controls the Balance between Excitatory and Inhibitory Spinal V2 Interneurons Kaumudi Joshi, Seunghee Lee, Bora Lee, Jae W. Lee, and Soo-Kyung Lee Supplemental
Fig. S1. Effect of p120-catenin overexpression on the interaction of SCUBE2 with E-cadherin. The expression plasmid encoding FLAG.
 Fig. S1. Effect of p120-catenin overexpression on the interaction of SCUBE2 with E-cadherin. The expression plasmid encoding FLAG.SCUBE2, E-cadherin.Myc, or HA.p120-catenin was transfected in a combination
Fig. S1. Effect of p120-catenin overexpression on the interaction of SCUBE2 with E-cadherin. The expression plasmid encoding FLAG.SCUBE2, E-cadherin.Myc, or HA.p120-catenin was transfected in a combination
supplementary information
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb1864 Figure S1 Apak specifically inhibits p53 transcriptional activity. Transcription activity of p53 was measured in U2OS (p53 wild-type) and H1299 (p53 deficient) cells which were transfected
DOI: 10.1038/ncb1864 Figure S1 Apak specifically inhibits p53 transcriptional activity. Transcription activity of p53 was measured in U2OS (p53 wild-type) and H1299 (p53 deficient) cells which were transfected
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Dynamic Phosphorylation of HP1 Regulates Mitotic Progression in Human Cells Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. NDR1 interacts with HP1. (a) Immunoprecipitation using
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Dynamic Phosphorylation of HP1 Regulates Mitotic Progression in Human Cells Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. NDR1 interacts with HP1. (a) Immunoprecipitation using
Sarker et al. Supplementary Material. Subcellular Fractionation
 Supplementary Material Subcellular Fractionation Transfected 293T cells were harvested with phosphate buffered saline (PBS) and centrifuged at 2000 rpm (500g) for 3 min. The pellet was washed, re-centrifuged
Supplementary Material Subcellular Fractionation Transfected 293T cells were harvested with phosphate buffered saline (PBS) and centrifuged at 2000 rpm (500g) for 3 min. The pellet was washed, re-centrifuged
Supplemental Information
 Supplemental Information Intrinsic protein-protein interaction mediated and chaperonin assisted sequential assembly of a stable Bardet Biedl syndome protein complex, the BBSome * Qihong Zhang 1#, Dahai
Supplemental Information Intrinsic protein-protein interaction mediated and chaperonin assisted sequential assembly of a stable Bardet Biedl syndome protein complex, the BBSome * Qihong Zhang 1#, Dahai
RheB Activation Assay Kit
 A helping hand for your research Product Manual Configuration-specific Monoclonal Antibody Based RheB Activation Assay Kit Catalog Number: 81201 20 assays NewEast Biosciences 1 FAX: 610-945-2008 Table
A helping hand for your research Product Manual Configuration-specific Monoclonal Antibody Based RheB Activation Assay Kit Catalog Number: 81201 20 assays NewEast Biosciences 1 FAX: 610-945-2008 Table
from Dr. David Livingston. Rabbit anti-myc, V5, and BACH1 were raised by immunizing rabbits with peptides EQKLISEEDI, GKPIPNPLLGLDST, and
 upporting Material Experimental Procedures: Cell culture and antibodies All cell lines were maintained in RPMI 164 medium with 1% fetal calf serum at 37 C in 5% CO 2 (v/v). For HCC 1937-BRCA1 cells and
upporting Material Experimental Procedures: Cell culture and antibodies All cell lines were maintained in RPMI 164 medium with 1% fetal calf serum at 37 C in 5% CO 2 (v/v). For HCC 1937-BRCA1 cells and
Identification of Microprotein-Protein Interactions via APEX Tagging
 Supporting Information Identification of Microprotein-Protein Interactions via APEX Tagging Qian Chu, Annie Rathore,, Jolene K. Diedrich,, Cynthia J. Donaldson, John R. Yates III, and Alan Saghatelian
Supporting Information Identification of Microprotein-Protein Interactions via APEX Tagging Qian Chu, Annie Rathore,, Jolene K. Diedrich,, Cynthia J. Donaldson, John R. Yates III, and Alan Saghatelian
supplementary information
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2172 Figure S1 p53 regulates cellular NADPH and lipid levels via inhibition of G6PD. (a) U2OS cells stably expressing p53 shrna or a control shrna were transfected with control sirna or
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2172 Figure S1 p53 regulates cellular NADPH and lipid levels via inhibition of G6PD. (a) U2OS cells stably expressing p53 shrna or a control shrna were transfected with control sirna or
USP19 modulates autophagy and antiviral immune responses by. deubiquitinating Beclin-1
 USP19 modulates autophagy and antiviral immune responses by deubiquitinating Beclin-1 Shouheng Jin 1,2,, Shuo Tian 1,, Yamei Chen 1,, Chuanxia Zhang 1,2, Weihong Xie, 1 Xiaojun Xia 3,4, Jun Cui 1,3* &
USP19 modulates autophagy and antiviral immune responses by deubiquitinating Beclin-1 Shouheng Jin 1,2,, Shuo Tian 1,, Yamei Chen 1,, Chuanxia Zhang 1,2, Weihong Xie, 1 Xiaojun Xia 3,4, Jun Cui 1,3* &
Cdc42 Activation Assay Kit
 A helping hand for your research Product Manual Configuration-specific Monoclonal Antibody Based Cdc42 Activation Assay Kit Catalog Number: 80701 20 assays 1 Table of Content Product Description 3 Assay
A helping hand for your research Product Manual Configuration-specific Monoclonal Antibody Based Cdc42 Activation Assay Kit Catalog Number: 80701 20 assays 1 Table of Content Product Description 3 Assay
Antibodies against PCNA were previously described [1]. To deplete PCNA from Xenopus egg
![Antibodies against PCNA were previously described [1]. To deplete PCNA from Xenopus egg Antibodies against PCNA were previously described [1]. To deplete PCNA from Xenopus egg](/thumbs/84/90687567.jpg) Supplementary information Supplementary methods PCNA antibody and immunodepletion Antibodies against PCNA were previously described [1]. To deplete PCNA from Xenopus egg extracts, one volume of protein
Supplementary information Supplementary methods PCNA antibody and immunodepletion Antibodies against PCNA were previously described [1]. To deplete PCNA from Xenopus egg extracts, one volume of protein
Supplemental Online Material. The mouse embryonic fibroblast cell line #10 derived from β-arrestin1 -/- -β-arrestin2 -/-
 #1074683s 1 Supplemental Online Material Materials and Methods Cell lines and tissue culture The mouse embryonic fibroblast cell line #10 derived from β-arrestin1 -/- -β-arrestin2 -/- knock-out animals
#1074683s 1 Supplemental Online Material Materials and Methods Cell lines and tissue culture The mouse embryonic fibroblast cell line #10 derived from β-arrestin1 -/- -β-arrestin2 -/- knock-out animals
Supplementary Figure 1 Phosphorylated tau accumulates in Nrf2 (-/-) mice. Hippocampal tissues obtained from Nrf2 (-/-) (10 months old, 4 male; 2
 Supplementary Figure 1 Phosphorylated tau accumulates in Nrf2 (-/-) mice. Hippocampal tissues obtained from Nrf2 (-/-) (10 months old, 4 male; 2 female) or wild-type (5 months old, 1 male; 11 months old,
Supplementary Figure 1 Phosphorylated tau accumulates in Nrf2 (-/-) mice. Hippocampal tissues obtained from Nrf2 (-/-) (10 months old, 4 male; 2 female) or wild-type (5 months old, 1 male; 11 months old,
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1154040/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Selective Blockade of MicroRNA Processing by Lin-28 Srinivas R. Viswanathan, George Q. Daley,* Richard I. Gregory* *To whom
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1154040/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Selective Blockade of MicroRNA Processing by Lin-28 Srinivas R. Viswanathan, George Q. Daley,* Richard I. Gregory* *To whom
Peptide enrichment and fractionation
 Protein sample preparation Successful analysis of low-abundance proteins and/or the identification of posttranslationally modified peptides often require several steps: enrichment, fractionation, and/or
Protein sample preparation Successful analysis of low-abundance proteins and/or the identification of posttranslationally modified peptides often require several steps: enrichment, fractionation, and/or
We performed RT-PCR, cloning, sequencing and qrt-pcr in murine melanoma. cell lines and melanocytic tumors from RET-mice in accordance with the method
 Supplementary Material and Methods Quantitative RT-PCR (qrt-pcr) We performed RT-PCR, cloning, sequencing and qrt-pcr in murine melanoma cell lines and melanocytic tumors from RET-mice in accordance with
Supplementary Material and Methods Quantitative RT-PCR (qrt-pcr) We performed RT-PCR, cloning, sequencing and qrt-pcr in murine melanoma cell lines and melanocytic tumors from RET-mice in accordance with
Supplemental Figure Legends:
 Supplemental Figure Legends: Fig S1. GFP-ABRO1 localization. U2OS cells were infected with retrovirus expressing GFP- ABRO1. The cells were fixed with 3.6% formaldehyde and stained with antibodies against
Supplemental Figure Legends: Fig S1. GFP-ABRO1 localization. U2OS cells were infected with retrovirus expressing GFP- ABRO1. The cells were fixed with 3.6% formaldehyde and stained with antibodies against
Primers used for PCR of conductin, SGK1 and GAPDH have been described in (Dehner et al,
 Supplementary METHODS Flow Cytometry (FACS) For FACS analysis, trypsinized cells were fixed in ethanol, rehydrated in PBS and treated with 40μg/ml propidium iodide and 10μ/ml RNase for 30 min at room temperature.
Supplementary METHODS Flow Cytometry (FACS) For FACS analysis, trypsinized cells were fixed in ethanol, rehydrated in PBS and treated with 40μg/ml propidium iodide and 10μ/ml RNase for 30 min at room temperature.
Supplementary Figure S1 Purification of deubiquitinases HEK293 cells were transfected with the indicated DUB-expressing plasmids.
 Supplementary Figure S1 Purification of deubiquitinases HEK293 cells were transfected with the indicated DUB-expressing plasmids. The cells were harvested 72 h after transfection. FLAG-tagged deubiquitinases
Supplementary Figure S1 Purification of deubiquitinases HEK293 cells were transfected with the indicated DUB-expressing plasmids. The cells were harvested 72 h after transfection. FLAG-tagged deubiquitinases
Attenuation of synaptic toxicity and MARK4/PAR1-mediated Tau phosphorylation by
 Supplementary Methods and Figures Attenuation of synaptic toxicity and MARK4/PAR1-mediated Tau phosphorylation by methylene blue for Alzheimer s disease treatment Wenchao Sun 1, Seongsoo Lee 1,2, Xiaoran
Supplementary Methods and Figures Attenuation of synaptic toxicity and MARK4/PAR1-mediated Tau phosphorylation by methylene blue for Alzheimer s disease treatment Wenchao Sun 1, Seongsoo Lee 1,2, Xiaoran
EPIGENTEK. EpiQuik Tissue Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Kit. Base Catalog # P-2003 PLEASE READ THIS ENTIRE USER GUIDE BEFORE USE
 EpiQuik Tissue Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Kit Base Catalog # P-2003 PLEASE READ THIS ENTIRE USER GUIDE BEFORE USE The EpiQuik Tissue Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Kit is suitable for combining the specificity
EpiQuik Tissue Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Kit Base Catalog # P-2003 PLEASE READ THIS ENTIRE USER GUIDE BEFORE USE The EpiQuik Tissue Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Kit is suitable for combining the specificity
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb.1583
 Acetylation by GCN5 regulates CDC6 phosphorylation in the S-phase of the cell cycle Roberta Paolinelli 1,2, Ramiro Mendoza-Maldonado 2, Anna Cereseto 1 and Mauro Giacca 2 1 Molecular Biology Laboratory,
Acetylation by GCN5 regulates CDC6 phosphorylation in the S-phase of the cell cycle Roberta Paolinelli 1,2, Ramiro Mendoza-Maldonado 2, Anna Cereseto 1 and Mauro Giacca 2 1 Molecular Biology Laboratory,
EPIGENTEK. EpiQuik Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Kit. Base Catalog # P-2002 PLEASE READ THIS ENTIRE USER GUIDE BEFORE USE
 EpiQuik Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Kit Base Catalog # P-2002 PLEASE READ THIS ENTIRE USER GUIDE BEFORE USE The EpiQuik Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Kit is suitable for combining the specificity of
EpiQuik Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Kit Base Catalog # P-2002 PLEASE READ THIS ENTIRE USER GUIDE BEFORE USE The EpiQuik Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Kit is suitable for combining the specificity of
Post-translational modification
 Protein expression Western blotting, is a widely used and accepted technique to detect levels of protein expression in a cell or tissue extract. This technique measures protein levels in a biological sample
Protein expression Western blotting, is a widely used and accepted technique to detect levels of protein expression in a cell or tissue extract. This technique measures protein levels in a biological sample
RNA was isolated using NucleoSpin RNA II (Macherey-Nagel, Bethlehem, PA) according to the
 Supplementary Methods RT-PCR and real-time PCR analysis RNA was isolated using NucleoSpin RNA II (Macherey-Nagel, Bethlehem, PA) according to the manufacturer s protocol and quantified by measuring the
Supplementary Methods RT-PCR and real-time PCR analysis RNA was isolated using NucleoSpin RNA II (Macherey-Nagel, Bethlehem, PA) according to the manufacturer s protocol and quantified by measuring the
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Figure S1 UVRAG amino acid sequence. Bold letters indicate the peptides identified from mass spectrometry analysis. Symbols indicate the prolines in the N-terminal proline-rich sequence (*), the C2 domain
Figure S1 UVRAG amino acid sequence. Bold letters indicate the peptides identified from mass spectrometry analysis. Symbols indicate the prolines in the N-terminal proline-rich sequence (*), the C2 domain
Checkpoint Kinase Activity Immunoblot Kit
 Product Manual Checkpoint Kinase Activity Immunoblot Kit Catalog Number STA- 413 20 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Cdc25C is a protein phosphatase responsible
Product Manual Checkpoint Kinase Activity Immunoblot Kit Catalog Number STA- 413 20 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Cdc25C is a protein phosphatase responsible
Appendix. Table of contents
 Appendix Table of contents 1. Appendix figures 2. Legends of Appendix figures 3. References Appendix Figure S1 -Tub STIL (41) DVFFYQADDEHYIPR (55) (64) AVLLDLEPR (72) 1 451aa (1071) YLNENQLSQLSVTR (1084)
Appendix Table of contents 1. Appendix figures 2. Legends of Appendix figures 3. References Appendix Figure S1 -Tub STIL (41) DVFFYQADDEHYIPR (55) (64) AVLLDLEPR (72) 1 451aa (1071) YLNENQLSQLSVTR (1084)
transcription and the promoter occupancy of Smad proteins. (A) HepG2 cells were co-transfected with the wwp-luc reporter, and FLAG-tagged FHL1,
 Supplementary Data Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Figure 1 FHL-mediated TGFβ-responsive reporter transcription and the promoter occupancy of Smad proteins. (A) HepG2 cells were co-transfected
Supplementary Data Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Figure 1 FHL-mediated TGFβ-responsive reporter transcription and the promoter occupancy of Smad proteins. (A) HepG2 cells were co-transfected
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figures Figure S1. Study of mgtl translation in vitro. (A) Detection of 5 LR RNA using wild-type and anti-sd (91-95) substituted templates in a transcription-translation
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figures Figure S1. Study of mgtl translation in vitro. (A) Detection of 5 LR RNA using wild-type and anti-sd (91-95) substituted templates in a transcription-translation
hours after food deprivation hours after food deprivation
 Figure S.6 protein (fasted / control).2.8.4 p47 p97 Rpt Ufd 3 24 48 hours after food deprivation mrn (fasted / control) C mrn (denervated / control) 2.5 2.5.5 3.5 3 2.5 2.5.5 p97 ** Npl4 Ufd p47 2 3 4
Figure S.6 protein (fasted / control).2.8.4 p47 p97 Rpt Ufd 3 24 48 hours after food deprivation mrn (fasted / control) C mrn (denervated / control) 2.5 2.5.5 3.5 3 2.5 2.5.5 p97 ** Npl4 Ufd p47 2 3 4
Rab5 Activation Assay Kit
 A helping hand for your research Product Manual Configuration-specific Monoclonal Antibody Based Rab5 Activation Assay Kit Catalog Number: 83701 20 assays 24 Whitewoods Lane 1 Table of Content Product
A helping hand for your research Product Manual Configuration-specific Monoclonal Antibody Based Rab5 Activation Assay Kit Catalog Number: 83701 20 assays 24 Whitewoods Lane 1 Table of Content Product
Arf6 Activation Assay Kit
 A helping hand for your research Product Manual Configuration-specific Monoclonal Antibody Based Arf6 Activation Assay Kit Catalog Number: 82401 20 assays NewEast Biosciences 1 Table of Content Product
A helping hand for your research Product Manual Configuration-specific Monoclonal Antibody Based Arf6 Activation Assay Kit Catalog Number: 82401 20 assays NewEast Biosciences 1 Table of Content Product
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 Supplemental material Thompson et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.200909067/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Modification-specific antibodies do not detect unmodified
Supplemental material Thompson et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.200909067/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Modification-specific antibodies do not detect unmodified
Supplemental Data. Wu et al. (2). Plant Cell..5/tpc RGLG Hormonal treatment H2O B RGLG µm ABA µm ACC µm GA Time (hours) µm µm MJ µm IA
 Supplemental Data. Wu et al. (2). Plant Cell..5/tpc..4. A B Supplemental Figure. Immunoblot analysis verifies the expression of the AD-PP2C and BD-RGLG proteins in the Y2H assay. Total proteins were extracted
Supplemental Data. Wu et al. (2). Plant Cell..5/tpc..4. A B Supplemental Figure. Immunoblot analysis verifies the expression of the AD-PP2C and BD-RGLG proteins in the Y2H assay. Total proteins were extracted
Description of supplementary material file
 Description of supplementary material file In the supplementary results we show that the VHL-fibronectin interaction is indirect, mediated by fibronectin binding to COL4A2. This provides additional information
Description of supplementary material file In the supplementary results we show that the VHL-fibronectin interaction is indirect, mediated by fibronectin binding to COL4A2. This provides additional information
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature11070 Supplementary Figure 1 Purification of FLAG-tagged proteins. a, Purification of FLAG-RNF12 by FLAG-affinity from nuclear extracts of wild-type (WT) and two FLAG- RNF12 transgenic
doi:10.1038/nature11070 Supplementary Figure 1 Purification of FLAG-tagged proteins. a, Purification of FLAG-RNF12 by FLAG-affinity from nuclear extracts of wild-type (WT) and two FLAG- RNF12 transgenic
96-well Checkpoint Kinase Activity Assay Kit
 Product Manual 96-well Checkpoint Kinase Activity Assay Kit Catalog Number STA-414 STA-414-5 96 assays 5 x 96 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Cdc25C is a
Product Manual 96-well Checkpoint Kinase Activity Assay Kit Catalog Number STA-414 STA-414-5 96 assays 5 x 96 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Cdc25C is a
Supplementary Fig. 1. Schematic structure of TRAIP and RAP80. The prey line below TRAIP indicates bait and the two lines above RAP80 highlight the
 Supplementary Fig. 1. Schematic structure of TRAIP and RAP80. The prey line below TRAIP indicates bait and the two lines above RAP80 highlight the prey clones identified in the yeast two hybrid screen.
Supplementary Fig. 1. Schematic structure of TRAIP and RAP80. The prey line below TRAIP indicates bait and the two lines above RAP80 highlight the prey clones identified in the yeast two hybrid screen.
Supplementary figures
 Relative intensity Relative intensity Relative intensity Supplementary figures a None Caffeine None Caffeine c None Caffeine 6 6 6 ISG 6 6 6 UBE1L 6 6 6 UBCH8 6 6 6 EFP 1 1 DOX (h) 1 1 CPT (h) 1 1 UV (h)
Relative intensity Relative intensity Relative intensity Supplementary figures a None Caffeine None Caffeine c None Caffeine 6 6 6 ISG 6 6 6 UBE1L 6 6 6 UBCH8 6 6 6 EFP 1 1 DOX (h) 1 1 CPT (h) 1 1 UV (h)
Protein Purification Products. Complete Solutions for All of Your Protein Purification Applications
 Protein Purification Products Complete Solutions for All of Your Protein Purification Applications FLAG-Tagged Protein Products EXPRESS with the pcmv-dykddddk Vector Set Fuse your protein of interest to
Protein Purification Products Complete Solutions for All of Your Protein Purification Applications FLAG-Tagged Protein Products EXPRESS with the pcmv-dykddddk Vector Set Fuse your protein of interest to
used at a final concentration of 5 ng/ml. Rabbit anti-bim and mouse anti-mkp2 antibodies were
 1 Supplemental Methods Reagents and chemicals: TGFβ was a generous gift from Genzyme Inc. (Cambridge, MA) and was used at a final concentration of 5 ng/ml. Rabbit anti-bim and mouse anti-mkp2 antibodies
1 Supplemental Methods Reagents and chemicals: TGFβ was a generous gift from Genzyme Inc. (Cambridge, MA) and was used at a final concentration of 5 ng/ml. Rabbit anti-bim and mouse anti-mkp2 antibodies
Supplementary Fig. 1 Identification of Nedd4 as an IRS-2-associated protein in camp-treated FRTL-5 cells.
 Supplementary Fig. 1 Supplementary Fig. 1 Identification of Nedd4 as an IRS-2-associated protein in camp-treated FRTL-5 cells. (a) FRTL-5 cells were treated with 1 mm dibutyryl camp for 24 h, and the lysates
Supplementary Fig. 1 Supplementary Fig. 1 Identification of Nedd4 as an IRS-2-associated protein in camp-treated FRTL-5 cells. (a) FRTL-5 cells were treated with 1 mm dibutyryl camp for 24 h, and the lysates
Supplemental Experimental Procedures
 Supplemental Experimental Procedures Generation of BLM protein segments and mutants. For immunoprecipitation experiments with topoisomerase IIα, BLM N-terminal segments were generated by PCR amplification
Supplemental Experimental Procedures Generation of BLM protein segments and mutants. For immunoprecipitation experiments with topoisomerase IIα, BLM N-terminal segments were generated by PCR amplification
Supplementary information
 Supplementary information Table of Content: Supplementary Results... 2 Supplementary Figure S1: Experimental validation of AP-MS results by coimmunprecipitation Western blot analysis.... 3 Supplementary
Supplementary information Table of Content: Supplementary Results... 2 Supplementary Figure S1: Experimental validation of AP-MS results by coimmunprecipitation Western blot analysis.... 3 Supplementary
(a) Immunoblotting to show the migration position of Flag-tagged MAVS
 Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of six MAVS isoforms. (a) Immunoblotting to show the migration position of Flag-tagged MAVS isoforms. HEK293T Mavs -/- cells were transfected with constructs expressing
Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of six MAVS isoforms. (a) Immunoblotting to show the migration position of Flag-tagged MAVS isoforms. HEK293T Mavs -/- cells were transfected with constructs expressing
Cell proliferation was measured with Cell Counting Kit-8 (Dojindo Laboratories, Kumamoto, Japan).
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Supplemental Materials and Methods Cell proliferation assay Cell proliferation was measured with Cell Counting Kit-8 (Dojindo Laboratories, Kumamoto, Japan). GCs were plated at 96-well
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Supplemental Materials and Methods Cell proliferation assay Cell proliferation was measured with Cell Counting Kit-8 (Dojindo Laboratories, Kumamoto, Japan). GCs were plated at 96-well
Supplementary Information Alternative splicing of CD44 mrna by ESRP1 enhances lung colonization of metastatic cancer cell
 Supplementary Information Alternative splicing of CD44 mrna by ESRP1 enhances lung colonization of metastatic cancer cell Supplementary Figures S1-S3 Supplementary Methods Supplementary Figure S1. Identification
Supplementary Information Alternative splicing of CD44 mrna by ESRP1 enhances lung colonization of metastatic cancer cell Supplementary Figures S1-S3 Supplementary Methods Supplementary Figure S1. Identification
Quantitative and non-quantitative RT-PCR. cdna was generated from 500ng RNA (iscript;
 Supplemental Methods Quantitative and non-quantitative RT-PCR. cdna was generated from 500ng RNA (iscript; Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA) and standard RT-PCR experiments were carried out using the 2X GoTaq
Supplemental Methods Quantitative and non-quantitative RT-PCR. cdna was generated from 500ng RNA (iscript; Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA) and standard RT-PCR experiments were carried out using the 2X GoTaq
Supplemental Materials and Methods
 Supplemental Materials and Methods Co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP) assay Cells were lysed with NETN buffer (20 mm Tris-HCl, ph 8.0, 0 mm NaCl, 1 mm EDT, 0.5% Nonidet P-40) containing 50 mm β-glycerophosphate,
Supplemental Materials and Methods Co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP) assay Cells were lysed with NETN buffer (20 mm Tris-HCl, ph 8.0, 0 mm NaCl, 1 mm EDT, 0.5% Nonidet P-40) containing 50 mm β-glycerophosphate,
Supplementary Figure 1. GST pull-down analysis of the interaction of GST-cIAP1 (A, B), GSTcIAP1
 Legends Supplementary Figure 1. GST pull-down analysis of the interaction of GST- (A, B), GST mutants (B) or GST- (C) with indicated proteins. A, B, Cell lysate from untransfected HeLa cells were loaded
Legends Supplementary Figure 1. GST pull-down analysis of the interaction of GST- (A, B), GST mutants (B) or GST- (C) with indicated proteins. A, B, Cell lysate from untransfected HeLa cells were loaded
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2743 Figure S1 stabilizes cellular protein level, post-transcriptionally. (a, b) and DDR1 were RNAi-depleted from HEK.293.-CBG cells. Western blots with indicated antibodies (a). RT-PCRs
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2743 Figure S1 stabilizes cellular protein level, post-transcriptionally. (a, b) and DDR1 were RNAi-depleted from HEK.293.-CBG cells. Western blots with indicated antibodies (a). RT-PCRs
Online Supplementary Information
 Online Supplementary Information NLRP4 negatively regulates type I interferon signaling by targeting TBK1 for degradation via E3 ubiquitin ligase DTX4 Jun Cui 1,4,6,7, Yinyin Li 1,5,6,7, Liang Zhu 1, Dan
Online Supplementary Information NLRP4 negatively regulates type I interferon signaling by targeting TBK1 for degradation via E3 ubiquitin ligase DTX4 Jun Cui 1,4,6,7, Yinyin Li 1,5,6,7, Liang Zhu 1, Dan
Supplemental Methods Cell lines and culture
 Supplemental Methods Cell lines and culture AGS, CL5, BT549, and SKBR were propagated in RPMI 64 medium (Mediatech Inc., Manassas, VA) supplemented with % fetal bovine serum (FBS, Atlanta Biologicals,
Supplemental Methods Cell lines and culture AGS, CL5, BT549, and SKBR were propagated in RPMI 64 medium (Mediatech Inc., Manassas, VA) supplemented with % fetal bovine serum (FBS, Atlanta Biologicals,
Schematic representation of the endogenous PALB2 locus and gene-disruption constructs
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of PALB2 -/- and BRCA2 -/- /PALB2 -/- DT40 cells. (A) Schematic representation of the endogenous PALB2 locus and gene-disruption constructs carrying
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of PALB2 -/- and BRCA2 -/- /PALB2 -/- DT40 cells. (A) Schematic representation of the endogenous PALB2 locus and gene-disruption constructs carrying
Mechanism of Induction and Suppression of Antiviral Immunity Directed by Virus-Derived Small RNAs in Drosophila
 Cell Host & Microbe, Volume 4 Supplemental Data Mechanism of Induction and Suppression of Antiviral Immunity Directed by Virus-Derived Small RNAs in Drosophila Roghiyh Aliyari, Qingfa Wu, Hong-Wei Li,
Cell Host & Microbe, Volume 4 Supplemental Data Mechanism of Induction and Suppression of Antiviral Immunity Directed by Virus-Derived Small RNAs in Drosophila Roghiyh Aliyari, Qingfa Wu, Hong-Wei Li,
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURES AND TABLES
 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURES AND TABLES A B Flag-ALDH1A1 IP: α-ac HEK293T WT 91R 128R 252Q 367R 41/ 419R 435R 495R 412R C Flag-ALDH1A1 NAM IP: HEK293T + + - + D NAM - + + E Relative ALDH1A1 activity 1..8.6.4.2
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURES AND TABLES A B Flag-ALDH1A1 IP: α-ac HEK293T WT 91R 128R 252Q 367R 41/ 419R 435R 495R 412R C Flag-ALDH1A1 NAM IP: HEK293T + + - + D NAM - + + E Relative ALDH1A1 activity 1..8.6.4.2
RNA oligonucleotides and 2 -O-methylated oligonucleotides were synthesized by. 5 AGACACAAACACCAUUGUCACACUCCACAGC; Rand-2 OMe,
 Materials and methods Oligonucleotides and DNA constructs RNA oligonucleotides and 2 -O-methylated oligonucleotides were synthesized by Dharmacon Inc. (Lafayette, CO). The sequences were: 122-2 OMe, 5
Materials and methods Oligonucleotides and DNA constructs RNA oligonucleotides and 2 -O-methylated oligonucleotides were synthesized by Dharmacon Inc. (Lafayette, CO). The sequences were: 122-2 OMe, 5
A RRM1 H2AX DAPI. RRM1 H2AX DAPI Merge. Cont. sirna RRM1
 A H2AX DAPI H2AX DAPI Merge Cont sirna Figure S1: Accumulation of RRM1 at DNA damage sites (A) HeLa cells were subjected to in situ detergent extraction without IR irradiation, and immunostained with the
A H2AX DAPI H2AX DAPI Merge Cont sirna Figure S1: Accumulation of RRM1 at DNA damage sites (A) HeLa cells were subjected to in situ detergent extraction without IR irradiation, and immunostained with the
Gα i Activation Assay Kit
 A helping hand for your research Product Manual Configuration-specific Monoclonal Antibody Based Gα i Activation Assay Kit Catalog Number 80301 20 assays NewEast Biosciences, Inc 1 Table of Content Product
A helping hand for your research Product Manual Configuration-specific Monoclonal Antibody Based Gα i Activation Assay Kit Catalog Number 80301 20 assays NewEast Biosciences, Inc 1 Table of Content Product
This is the author's accepted version of the manuscript.
 This is the author's accepted version of the manuscript. The definitive version is published in Nature Communications Online Edition: 2015/4/16 (Japan time), doi:10.1038/ncomms7780. The final version published
This is the author's accepted version of the manuscript. The definitive version is published in Nature Communications Online Edition: 2015/4/16 (Japan time), doi:10.1038/ncomms7780. The final version published
Supplementary Fig. 1
 a FL (1-2266) NL (1-1190) CL (1191-2266) HA-ICE1: - HA-ICE1: - - - FLAG-ICE2: + + + + FLAG-ELL: + + + + + + IP: anti-ha FLAG-ICE2 HA-ICE1-FL HA-ICE1-NL HA-ICE1-CL FLAG-ICE2 b IP: anti-ha FL (1-2266) NL
a FL (1-2266) NL (1-1190) CL (1191-2266) HA-ICE1: - HA-ICE1: - - - FLAG-ICE2: + + + + FLAG-ELL: + + + + + + IP: anti-ha FLAG-ICE2 HA-ICE1-FL HA-ICE1-NL HA-ICE1-CL FLAG-ICE2 b IP: anti-ha FL (1-2266) NL
Ubiquitin (76 aa) UB genes encode linear fusions of UB either to itself (poly-ub genes) or to other proteins these fusions are cleaved by
 Ubiquitin (76 aa) UB genes encode linear fusions of UB either to itself (poly-ub genes) or to other proteins these fusions are cleaved by deubiquitylases (DUBs) yielding mature Ub deubiquitylase FLAG 3
Ubiquitin (76 aa) UB genes encode linear fusions of UB either to itself (poly-ub genes) or to other proteins these fusions are cleaved by deubiquitylases (DUBs) yielding mature Ub deubiquitylase FLAG 3
supplementary information
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb1862 Figure S1 Identification of SCAI as a Dia1 associating factor. (a) Identification of SCAI (Riken cdna 930041I02) as a Dia1-FH3 interacting protein. Mouse brain lysate was incubated
DOI: 10.1038/ncb1862 Figure S1 Identification of SCAI as a Dia1 associating factor. (a) Identification of SCAI (Riken cdna 930041I02) as a Dia1-FH3 interacting protein. Mouse brain lysate was incubated
Gα 13 Activation Assay Kit
 A helping hand for your research Product Manual Configuration-specific Monoclonal Antibody Based Gα 13 Activation Assay Kit Catalog Number: 80401 20 assays NewEast Biosciences 1 Table of Content Product
A helping hand for your research Product Manual Configuration-specific Monoclonal Antibody Based Gα 13 Activation Assay Kit Catalog Number: 80401 20 assays NewEast Biosciences 1 Table of Content Product
Transcriptional regulation of BRCA1 expression by a metabolic switch: Di, Fernandez, De Siervi, Longo, and Gardner. H3K4Me3
 ChIP H3K4Me3 enrichment.25.2.15.1.5 H3K4Me3 H3K4Me3 ctrl H3K4Me3 + E2 NS + E2 1. kb kb +82 kb Figure S1. Estrogen promotes entry of MCF-7 into the cell cycle but does not significantly change activation-associated
ChIP H3K4Me3 enrichment.25.2.15.1.5 H3K4Me3 H3K4Me3 ctrl H3K4Me3 + E2 NS + E2 1. kb kb +82 kb Figure S1. Estrogen promotes entry of MCF-7 into the cell cycle but does not significantly change activation-associated
seminal vesicle thymus kidney lung liver
 a 1 HEK293 1 B 3 3 T GFPSMAD TGFβ (T)/ BMP (B) IB: SMAD1/3TP IB: GFP b wild type mouse tissue kidney thymus seminal vesicle liver lung brain adipose tissue muscle pancreas heart uterus spleen testis IB:
a 1 HEK293 1 B 3 3 T GFPSMAD TGFβ (T)/ BMP (B) IB: SMAD1/3TP IB: GFP b wild type mouse tissue kidney thymus seminal vesicle liver lung brain adipose tissue muscle pancreas heart uterus spleen testis IB:
Supplementary Figure 1. TSA (10 nmol/l), non-class-selective HDAC inhibitor, potentiates
 Supplementary Figure 1. TSA (10 nmol/l), non-class-selective HDAC inhibitor, potentiates vascular calcification (VC). (a) Von Kossa staining shows that TSA potentiated the Pi-induced VC. Scale bar, 100
Supplementary Figure 1. TSA (10 nmol/l), non-class-selective HDAC inhibitor, potentiates vascular calcification (VC). (a) Von Kossa staining shows that TSA potentiated the Pi-induced VC. Scale bar, 100
Stabilization of the Transcription Factor Foxp3 by the Deubiquitinase USP7 Increases Treg-Cell-Suppressive Capacity
 Immunity, Volume 39 Supplemental Information Stabilization of the Transcription Factor Foxp3 by the Deubiquitinase USP7 Increases Treg-Cell-Suppressive Capacity Jorg van Loosdregt, Veerle Fleskens, Juan
Immunity, Volume 39 Supplemental Information Stabilization of the Transcription Factor Foxp3 by the Deubiquitinase USP7 Increases Treg-Cell-Suppressive Capacity Jorg van Loosdregt, Veerle Fleskens, Juan
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb3240 Supplementary Figure 1 GBM cell lines display similar levels of p100 to p52 processing but respond differentially to TWEAK-induced TERT expression according to TERT promoter mutation
DOI: 10.1038/ncb3240 Supplementary Figure 1 GBM cell lines display similar levels of p100 to p52 processing but respond differentially to TWEAK-induced TERT expression according to TERT promoter mutation
