Nucleotide Entry Port. Scaffold Subunits. Polymerase Activity β Sliding Clamp. Clamp Loader. Promoter Recognition
|
|
|
- Mervyn Robertson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Nucleotide Entry ort α (2) Scaffold Subunits olymerase Activity Sliding Clamp σ Clamp Loader romoter Recognition
2 NNAAA AA T A TTTTNNAAAANNN TT T N N17 N6 α α α α α α α α α α α α α α +1
3 α α α α Subunit Function E coli Homologue RB1 polymerase activity CTD - ro-thr-ser- subunit ro-ser-tyr-ser RB2 clamp subunit RB3 scaffold, assembly α subunits RB4 helps to recognizes promoter σ subunit common to all RB5, RB6, RB8, eukaryotic RNA RB10, & RB12 olymerases RB3, RB4, & RB7 unique to ol II RB9, & RB11????
4 GGGCGG GGCCAATC TATAAAA Inr High Mobility Group roteins roximal Initiator Elements (Enhancers) Core romoter Elements or Basal romoter Elements (DNA Sequences) +1 GGGCGG GGCCAATC BRE TATA Inr DE % of 15% of 12.5% of % of Response Element Distal romoter Elements or Enhancers & Silencers TATAAA Inr TB TAF s TFIIA TB TATAAA TFIIA TFIIB TB TATAAA Inr TFIIB TFIIA
5 TFIIH TFIIF RNA ol II TB TATAAA Inr TFIIB TFIIA TFIIF RNA ol II TFIIE TB TATAAA Inr TFIIB TFIIA TFIIF RNA ol II TFIIE TFIIH Closed Complex TFIIF RNA ol II Inr TB TATAAA TFIIB TFIIA TFIIE TFIIH Open Complex hosphorylation of CTD of ol II by TFIIH and/or Other rotein Kinase Initiation Complete romoter Escape TFIIF RNA ol II TFIIA TB TATAAA TFIIB TFIIE TFIIH
6 RNA rocessing RNA rocessing trna rocessing Bacterial trna genes contain 2 to 5 trna s. Eukaryote trna each gene codes for 1 trna. In Bacteria RNase (endonuclease) cuts at mature 5 end. Mature 3 end produced by a combination of RNase & RNaseD (exonuclease) in Bacteria and Eukaryotes. All trna s have a 3 end of CCA. trna Nucleotidyltransferase adds CCA to 3 end of those trna s that do not have the sequence as part of the gene. trna rocessing (continued) Numerous Bases Modified Including 1-Methylguanosine Ribothymidine Inosine 4-Thiouridine Dihydrouridine seudouridine
7 rrna rocessing Bacteria contain 3 pieces of rrna. 5S (120 nucleotides), 16S (1540 nucleotides), & 23S (3200 nucleotides) contained on single gene. Eukaryotes contain 4 pieces of rrna. 5S (120 nucleotides), 5.8S (160 nucleotides) 18S (1900 nucleotides), & 28S (4700 nucleotides). 5S piece a single gene. The other three pieces on one gene. rrna rocessing (continued) Complex process Combination of endonucleases and exonucleases separate the pieces Specific bases methylated using SAM as methyl donor rrna pieces fold into complex three dimensional structures as they interact with / bind to ribosomal proteins
8 GU O O O O O O O CH Base 2 O O O O O O O O Ribonucleic Acid O 3 (1) hosphohydrolase 4 O O O O O CH Base 2 O O O O GT O O O Ribonucleic Acid CA Synthesizing Complex CA Binding Complex O 3 4 O 3 4 (2) Guanylyltransferase O HN N H 2N N N O O O H O CH O 2C O O O Base 2 O O O O O SAM O HN O O O Ribonucleic Acid (3) Guanine-7-methyltransferase adohcy CH 3 N H 2N N N O O O H O CH O 2C O O O Base 2 O O O O O O O O Ribonucleic Acid y-n-y-u-a-y GU Branch oint-binding rotein U1 U1 U1 U1 GU A U2 U1 U1 GU A
9 U1 U1 AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA AAUAAA HO A GU A UG-O U6 U6 U2 U2 GU A U5 U5 U1 U1 U6 U6 U4 U4 U2 U2 GU A U5 U5 GU A U6 U4 U5 U1 U4 Cleavage & olyadenylation Specificity Factor (CSF) olyadenylate olymerase (oly A olymerase) Endonuclease Specificity & Activity Factors AAUAAA AAUAAA A UG-O
10 Why are there Introns? How did Introns arise? TATA1 DNA Exon A GT Intron 1 TATA2 Exon B GT Intron 2 Exon C Transcription hnrna if TATA1 Employed Exon A GU Intron 1 TATA2 Exon B GU Intron 2 Exon C Transcription hnrna if TATA2 Employed Splicing Exon A Exon C Exon B GU Intron 2 Exon C Splicing Exon B Exon C Exon Y GT DNA AATAAA Exon Z AATAAA Transcription Exon Y GU AAUAAA Exon Z AAUAAA If 1st olyadenylation Site Employed Exon Y GU AAUAAA AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA If 2nd olyadenylation Site Employed Exon Y Exon Z AAUAAA AAAAAAAAAAAAAAA
11 cam R R R R CR cam CR
12 R R R R CR R R R R Control of Transcription in Eukaryotes Chromatin Remodeling Heterochromatin vs. Euchromatin Methylated G-C Sequences Z-form DNA Methylation of H3 Acetylation of Core Histones H3 & H4 Histone Acetyltransferases & Histone Deacetylases
13 Some terminology: ROMOTER ELEMENTS are regions of non-coding DNA that regulate the transcription of nearby genes; older nomenclature CIS-REGULATORY ELEMENTS. TRANSCRITION FACTORS are proteins that bind to the promoter elements to bring about the initiation of transcription or the genes that code for these proteins; older nomenclature TRANS- REGULATORY ELEMENTS. High Mobility Group roteins roximal Initiator Elements (Enhancers) Core romoter Elements or Basal romoter Elements (DNA Sequences) GGGCGG GGCCAATC BRE TFIIB TFIIF TATA TFIIATFIIB TB ol II +1 Inr TFIIE DE TFIIH Mediator Basal Transcription Factors {roteins that Bind to Core romoter Elements} DNA Binding Transactivators Signal Response Distal Element Upstream Initiator Elements Enhancers & Silencers Core and roximal Activation Sequences Sequence Module Consensus Sequence Locatio DNA Bound rotein Factor n TATA Box TATAAAA -25 ~10 bp TB BRE G/C G /C G /ACGCC -35?? TFIIB DE A/GG A /T C /T G / A /C +30???? CAAT Box GGCCAATCT -70 ~22 bp CTF/NF1 GC Box GGGCGG -110 ~20 bp S1
14 Distal Upstream or Downstream Activation Sequences Sequence Module Consensus Sequence DNA Bound rotein Factor GC Box GGGCGGG ~20 bp S1 Octamer ATTTGCAT ~20 bp Oct-1 Octamer ATTTGCAT ~23 bp Oct-2 κb GGGACTTTCC ~10 bp NFκB κb GGGACTTTCC ~10 bp H2-TF1 ATF GTGACGT ~10 bp ATF Response Elements to articular hysiological Challenges hysiological Challenge Response Element Consensus Sequence DNA Bound rotein Factor Size (kd) Heat shock HSE CNNGAANNTCCNNG 27 bp HSTF 93 Glucocorticoid GRE TGGTACAAATGTTCT 20 bp Receptor 94 Cadmium MRE CGNCCCGGNCNC??? horbol Esters TRE TGACTCA 22 bp A1 39 Serum SRE CCATATTG 20 bp SrF 52 rotein Kinase A Activation CRE TGACGTCA? CREB 43
15
Differential Gene Expression
 Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Differential Gene Expression September 28, 2006 Chromatin Structure ~140 bp ~60 bp Transcriptional Regulation: 1. Packing prevents access CH 3 2. Acetylation ( C O )
Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Differential Gene Expression September 28, 2006 Chromatin Structure ~140 bp ~60 bp Transcriptional Regulation: 1. Packing prevents access CH 3 2. Acetylation ( C O )
Transcription in Eukaryotes
 Transcription in Eukaryotes Biology I Hayder A Giha Transcription Transcription is a DNA-directed synthesis of RNA, which is the first step in gene expression. Gene expression, is transformation of the
Transcription in Eukaryotes Biology I Hayder A Giha Transcription Transcription is a DNA-directed synthesis of RNA, which is the first step in gene expression. Gene expression, is transformation of the
Differential Gene Expression
 Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Differential Gene Expression June 19, 2008 Differential Gene Expression Overview Chromatin structure Gene anatomy RNA processing and protein production Initiating transcription:
Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Differential Gene Expression June 19, 2008 Differential Gene Expression Overview Chromatin structure Gene anatomy RNA processing and protein production Initiating transcription:
Biochemistry Eukaryotic Transcription
 1 Description of Module Subject Name Paper Name Module Name/Title Dr. Vijaya Khader Dr. MC Varadaraj 2 1. Objectives 1. Understand and have an overview of eucaryotic transcriptional regulation. 2. Explain
1 Description of Module Subject Name Paper Name Module Name/Title Dr. Vijaya Khader Dr. MC Varadaraj 2 1. Objectives 1. Understand and have an overview of eucaryotic transcriptional regulation. 2. Explain
Eukaryotic & Prokaryotic Transcription. RNA polymerases
 Eukaryotic & Prokaryotic Transcription RNA polymerases RNA Polymerases A. E. coli RNA polymerase 1. core enzyme = ββ'(α)2 has catalytic activity but cannot recognize start site of transcription ~500,000
Eukaryotic & Prokaryotic Transcription RNA polymerases RNA Polymerases A. E. coli RNA polymerase 1. core enzyme = ββ'(α)2 has catalytic activity but cannot recognize start site of transcription ~500,000
Transcription Eukaryotic Cells
 Transcription Eukaryotic Cells Packet #20 1 Introduction Transcription is the process in which genetic information, stored in a strand of DNA (gene), is copied into a strand of RNA. Protein-encoding genes
Transcription Eukaryotic Cells Packet #20 1 Introduction Transcription is the process in which genetic information, stored in a strand of DNA (gene), is copied into a strand of RNA. Protein-encoding genes
Eukaryotic Transcription
 Eukaryotic Transcription I. Differences between eukaryotic versus prokaryotic transcription. II. (core vs holoenzyme): RNA polymerase II - Promotor elements. - General Pol II transcription factors (GTF).
Eukaryotic Transcription I. Differences between eukaryotic versus prokaryotic transcription. II. (core vs holoenzyme): RNA polymerase II - Promotor elements. - General Pol II transcription factors (GTF).
Mechanisms of Transcription. School of Life Science Shandong University
 Mechanisms of Transcription School of Life Science Shandong University Ch 12: Mechanisms of Transcription 1. RNA polymerase and the transcription cycle 2. The transcription cycle in bacteria 3. Transcription
Mechanisms of Transcription School of Life Science Shandong University Ch 12: Mechanisms of Transcription 1. RNA polymerase and the transcription cycle 2. The transcription cycle in bacteria 3. Transcription
Chapter 24: Promoters and Enhancers
 Chapter 24: Promoters and Enhancers A typical gene transcribed by RNA polymerase II has a promoter that usually extends upstream from the site where transcription is initiated the (#1) of transcription
Chapter 24: Promoters and Enhancers A typical gene transcribed by RNA polymerase II has a promoter that usually extends upstream from the site where transcription is initiated the (#1) of transcription
SIBC504: TRANSCRIPTION & RNA PROCESSING Assistant Professor Dr. Chatchawan Srisawat
 SIBC504: TRANSCRIPTION & RNA PROCESSING Assistant Professor Dr. Chatchawan Srisawat TRANSCRIPTION: AN OVERVIEW Transcription: the synthesis of a single-stranded RNA from a doublestranded DNA template.
SIBC504: TRANSCRIPTION & RNA PROCESSING Assistant Professor Dr. Chatchawan Srisawat TRANSCRIPTION: AN OVERVIEW Transcription: the synthesis of a single-stranded RNA from a doublestranded DNA template.
TRANSCRIPTION AND PROCESSING OF RNA
 TRANSCRIPTION AND PROCESSING OF RNA 1. The steps of gene expression. 2. General characterization of transcription: steps, components of transcription apparatus. 3. Transcription of eukaryotic structural
TRANSCRIPTION AND PROCESSING OF RNA 1. The steps of gene expression. 2. General characterization of transcription: steps, components of transcription apparatus. 3. Transcription of eukaryotic structural
Differential Gene Expression
 Biology 4361 - Developmental Biology Differential Gene Expression June 18, 2009 Differential Gene Expression Overview Chromatin structure Gene anatomy RNA processing and protein production Initiating transcription:
Biology 4361 - Developmental Biology Differential Gene Expression June 18, 2009 Differential Gene Expression Overview Chromatin structure Gene anatomy RNA processing and protein production Initiating transcription:
DNA Transcription. Dr Aliwaini
 DNA Transcription 1 DNA Transcription-Introduction The synthesis of an RNA molecule from DNA is called Transcription. All eukaryotic cells have five major classes of RNA: ribosomal RNA (rrna), messenger
DNA Transcription 1 DNA Transcription-Introduction The synthesis of an RNA molecule from DNA is called Transcription. All eukaryotic cells have five major classes of RNA: ribosomal RNA (rrna), messenger
CLASS 3.5: 03/29/07 EUKARYOTIC TRANSCRIPTION I: PROMOTERS AND ENHANCERS
 CLASS 3.5: 03/29/07 EUKARYOTIC TRANSCRIPTION I: PROMOTERS AND ENHANCERS A. Promoters and Polymerases (RNA pols): 1. General characteristics - Initiation of transcription requires a. Transcription factors
CLASS 3.5: 03/29/07 EUKARYOTIC TRANSCRIPTION I: PROMOTERS AND ENHANCERS A. Promoters and Polymerases (RNA pols): 1. General characteristics - Initiation of transcription requires a. Transcription factors
Transcription Regulation And Gene Expression in Eukaryotes FS 2016 Graduate Course G2 P Matthias and RG Clerc Pharmazentrum Hörsaal 2 16h15-18h00
 Transcription Regulation And Gene Expression in Eukaryotes FS 2016 Graduate Course G2 P Matthias and RG Clerc Pharmazentrum Hörsaal 2 16h15-18h00 The general problem RG Clerc March 2, 2016 RNA Transcription
Transcription Regulation And Gene Expression in Eukaryotes FS 2016 Graduate Course G2 P Matthias and RG Clerc Pharmazentrum Hörsaal 2 16h15-18h00 The general problem RG Clerc March 2, 2016 RNA Transcription
Transcription & post transcriptional modification
 Transcription & post transcriptional modification Transcription The synthesis of RNA molecules using DNA strands as the templates so that the genetic information can be transferred from DNA to RNA Similarity
Transcription & post transcriptional modification Transcription The synthesis of RNA molecules using DNA strands as the templates so that the genetic information can be transferred from DNA to RNA Similarity
Genomics and Gene Recognition Genes and Blue Genes
 Genomics and Gene Recognition Genes and Blue Genes November 3, 2004 Eukaryotic Gene Structure eukaryotic genomes are considerably more complex than those of prokaryotes eukaryotic cells have organelles
Genomics and Gene Recognition Genes and Blue Genes November 3, 2004 Eukaryotic Gene Structure eukaryotic genomes are considerably more complex than those of prokaryotes eukaryotic cells have organelles
Computational Biology I LSM5191 (2003/4)
 Computational Biology I LSM5191 (2003/4) Aylwin Ng, D.Phil Lecture Notes: Transcriptome: Molecular Biology of Gene Expression I Flow of information: DNA to polypeptide DNA Start Exon1 Intron Exon2 Termination
Computational Biology I LSM5191 (2003/4) Aylwin Ng, D.Phil Lecture Notes: Transcriptome: Molecular Biology of Gene Expression I Flow of information: DNA to polypeptide DNA Start Exon1 Intron Exon2 Termination
Biological information flow
 BCMB 3100 Chapters 36-38 Transcription & RNA Processing Biological information flow Definition of gene RNA Polymerase Gene coding vs template strand Promoter Transcription in E. coli Transcription factors
BCMB 3100 Chapters 36-38 Transcription & RNA Processing Biological information flow Definition of gene RNA Polymerase Gene coding vs template strand Promoter Transcription in E. coli Transcription factors
Biological information flow
 BCMB 3100 Chapters 36-38 Transcription & RNA Processing Biological information flow Definition of gene RNA Polymerase Gene coding vs template strand Promoter Transcription in E. coli Transcription factors
BCMB 3100 Chapters 36-38 Transcription & RNA Processing Biological information flow Definition of gene RNA Polymerase Gene coding vs template strand Promoter Transcription in E. coli Transcription factors
Structure/function relationship in DNA-binding proteins
 PHRM 836 September 22, 2015 Structure/function relationship in DNA-binding proteins Devlin Chapter 8.8-9 u General description of transcription factors (TFs) u Sequence-specific interactions between DNA
PHRM 836 September 22, 2015 Structure/function relationship in DNA-binding proteins Devlin Chapter 8.8-9 u General description of transcription factors (TFs) u Sequence-specific interactions between DNA
Biological information flow
 BCMB 3100 Chapters 36-38 Transcription & RNA Processing Definition of gene RNA Polymerase Gene coding vs template strand Promoter Transcription in E. coli Transcription factors mrna processing Biological
BCMB 3100 Chapters 36-38 Transcription & RNA Processing Definition of gene RNA Polymerase Gene coding vs template strand Promoter Transcription in E. coli Transcription factors mrna processing Biological
Chromatographic Separation of the three forms of RNA Polymerase II.
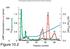 Chromatographic Separation of the three forms of RNA Polymerase II. α-amanitin α-amanitin bound to Pol II Function of the three enzymes. Yeast Pol II. RNA Polymerase Subunit Structures 10-7 Subunit structure.
Chromatographic Separation of the three forms of RNA Polymerase II. α-amanitin α-amanitin bound to Pol II Function of the three enzymes. Yeast Pol II. RNA Polymerase Subunit Structures 10-7 Subunit structure.
RNA metabolism. DNA dependent synthesis of RNA RNA processing RNA dependent synthesis of RNA and DNA.
 RNA metabolism DNA dependent synthesis of RNA RNA processing RNA dependent synthesis of RNA and DNA http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ovc8nxobxmq DNA dependent synthesis of RNA : production of an RNA molecule
RNA metabolism DNA dependent synthesis of RNA RNA processing RNA dependent synthesis of RNA and DNA http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ovc8nxobxmq DNA dependent synthesis of RNA : production of an RNA molecule
Classes of eukaryotic cellular RNAs
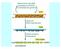 Classes of eukaryotic cellular RNAs ribosomal RNA (rrna) 18S (small subunit) 28S (large subunit) 5.8S (large subunit) 5S (large subunit) transfer RNA (trna) messenger RNA (mrna) heterogeneous nuclear RNA
Classes of eukaryotic cellular RNAs ribosomal RNA (rrna) 18S (small subunit) 28S (large subunit) 5.8S (large subunit) 5S (large subunit) transfer RNA (trna) messenger RNA (mrna) heterogeneous nuclear RNA
RNA: Transcription and Triplet Code
 RNA: Transcription and Triplet Code There are Five Kinds of RNA, All of Which are Templated from DNA. The first type of RNA is trna. The "t" stands for "transfer". This RNA is the RNA that transfers amino
RNA: Transcription and Triplet Code There are Five Kinds of RNA, All of Which are Templated from DNA. The first type of RNA is trna. The "t" stands for "transfer". This RNA is the RNA that transfers amino
Themes: RNA and RNA Processing. Messenger RNA (mrna) What is a gene? RNA is very versatile! RNA-RNA interactions are very important!
 Themes: RNA is very versatile! RNA and RNA Processing Chapter 14 RNA-RNA interactions are very important! Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes have many important differences. Messenger RNA (mrna) Carries genetic
Themes: RNA is very versatile! RNA and RNA Processing Chapter 14 RNA-RNA interactions are very important! Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes have many important differences. Messenger RNA (mrna) Carries genetic
DNA. Is a molecule that encodes the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms and many viruses.
 Is a molecule that encodes the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms and many viruses. Genetic information is encoded as a sequence of nucleotides (guanine,
Is a molecule that encodes the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms and many viruses. Genetic information is encoded as a sequence of nucleotides (guanine,
SSA Signal Search Analysis II
 SSA Signal Search Analysis II SSA other applications - translation In contrast to translation initiation in bacteria, translation initiation in eukaryotes is not guided by a Shine-Dalgarno like motif.
SSA Signal Search Analysis II SSA other applications - translation In contrast to translation initiation in bacteria, translation initiation in eukaryotes is not guided by a Shine-Dalgarno like motif.
Chapter 31. Transcription and RNA processing
 Chapter 31 Transcription and RNA processing RNA polymerase (RNAP) E. coli promoters Components of E. coli RNA Polymerase Holoenzyme (α 2 ββ'ωσ) Structure of prokaryotic RNAP The closed and open state of
Chapter 31 Transcription and RNA processing RNA polymerase (RNAP) E. coli promoters Components of E. coli RNA Polymerase Holoenzyme (α 2 ββ'ωσ) Structure of prokaryotic RNAP The closed and open state of
DNA makes RNA makes Proteins. The Central Dogma
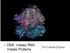 DNA makes RNA makes Proteins The Central Dogma TRANSCRIPTION DNA RNA transcript RNA polymerase RNA PROCESSING Exon RNA transcript (pre-mrna) Intron Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase NUCLEUS CYTOPLASM FORMATION
DNA makes RNA makes Proteins The Central Dogma TRANSCRIPTION DNA RNA transcript RNA polymerase RNA PROCESSING Exon RNA transcript (pre-mrna) Intron Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase NUCLEUS CYTOPLASM FORMATION
Eukaryotic Gene Structure
 Eukaryotic Gene Structure Terminology Genome entire genetic material of an individual Transcriptome set of transcribed sequences Proteome set of proteins encoded by the genome 2 Gene Basic physical and
Eukaryotic Gene Structure Terminology Genome entire genetic material of an individual Transcriptome set of transcribed sequences Proteome set of proteins encoded by the genome 2 Gene Basic physical and
Chapter 13. The Nucleus. The nucleus is the hallmark of eukaryotic cells; the very term eukaryotic means having a "true nucleus".
 Chapter 13 The Nucleus The nucleus is the hallmark of eukaryotic cells; the very term eukaryotic means having a "true nucleus". Fig.13.1. The EM of the Nucleus of a Eukaryotic Cell 13.1. The Nuclear Envelope
Chapter 13 The Nucleus The nucleus is the hallmark of eukaryotic cells; the very term eukaryotic means having a "true nucleus". Fig.13.1. The EM of the Nucleus of a Eukaryotic Cell 13.1. The Nuclear Envelope
The Genetic Code and Transcription. Chapter 12 Honors Genetics Ms. Susan Chabot
 The Genetic Code and Transcription Chapter 12 Honors Genetics Ms. Susan Chabot TRANSCRIPTION Copy SAME language DNA to RNA Nucleic Acid to Nucleic Acid TRANSLATION Copy DIFFERENT language RNA to Amino
The Genetic Code and Transcription Chapter 12 Honors Genetics Ms. Susan Chabot TRANSCRIPTION Copy SAME language DNA to RNA Nucleic Acid to Nucleic Acid TRANSLATION Copy DIFFERENT language RNA to Amino
REGULATION OF PROTEIN SYNTHESIS. II. Eukaryotes
 REGULATION OF PROTEIN SYNTHESIS II. Eukaryotes Complexities of eukaryotic gene expression! Several steps needed for synthesis of mrna! Separation in space of transcription and translation! Compartmentation
REGULATION OF PROTEIN SYNTHESIS II. Eukaryotes Complexities of eukaryotic gene expression! Several steps needed for synthesis of mrna! Separation in space of transcription and translation! Compartmentation
Year III Pharm.D Dr. V. Chitra
 Year III Pharm.D Dr. V. Chitra 1 Genome entire genetic material of an individual Transcriptome set of transcribed sequences Proteome set of proteins encoded by the genome 2 Only one strand of DNA serves
Year III Pharm.D Dr. V. Chitra 1 Genome entire genetic material of an individual Transcriptome set of transcribed sequences Proteome set of proteins encoded by the genome 2 Only one strand of DNA serves
Protein Synthesis Notes
 Protein Synthesis Notes Protein Synthesis: Overview Transcription: synthesis of mrna under the direction of DNA. Translation: actual synthesis of a polypeptide under the direction of mrna. Transcription
Protein Synthesis Notes Protein Synthesis: Overview Transcription: synthesis of mrna under the direction of DNA. Translation: actual synthesis of a polypeptide under the direction of mrna. Transcription
Fig Ch 17: From Gene to Protein
 Fig. 17-1 Ch 17: From Gene to Protein Basic Principles of Transcription and Translation RNA is the intermediate between genes and the proteins for which they code Transcription is the synthesis of RNA
Fig. 17-1 Ch 17: From Gene to Protein Basic Principles of Transcription and Translation RNA is the intermediate between genes and the proteins for which they code Transcription is the synthesis of RNA
CHAPTER 13 LECTURE SLIDES
 CHAPTER 13 LECTURE SLIDES Prepared by Brenda Leady University of Toledo To run the animations you must be in Slideshow View. Use the buttons on the animation to play, pause, and turn audio/text on or off.
CHAPTER 13 LECTURE SLIDES Prepared by Brenda Leady University of Toledo To run the animations you must be in Slideshow View. Use the buttons on the animation to play, pause, and turn audio/text on or off.
Regulatory Dynamics in Engineered Gene Networks
 Regulatory Dynamics in Engineered Gene Networks The Physico-chemical Foundation of Transcriptional Regulation with Applications to Systems Biology Mads Kærn Boston University Center for BioDynamics Center
Regulatory Dynamics in Engineered Gene Networks The Physico-chemical Foundation of Transcriptional Regulation with Applications to Systems Biology Mads Kærn Boston University Center for BioDynamics Center
RNA synthesis/transcription I Biochemistry 302. February 6, 2004 Bob Kelm
 RNA synthesis/transcription I Biochemistry 302 February 6, 2004 Bob Kelm Overview of RNA classes Messenger RNA (mrna) Encodes protein Relatively short half-life ( 3 min in E. coli, 30 min in eukaryotic
RNA synthesis/transcription I Biochemistry 302 February 6, 2004 Bob Kelm Overview of RNA classes Messenger RNA (mrna) Encodes protein Relatively short half-life ( 3 min in E. coli, 30 min in eukaryotic
TRANSCRIPTION COMPARISON OF DNA & RNA TRANSCRIPTION. Umm AL Qura University. Sugar Ribose Deoxyribose. Bases AUCG ATCG. Strand length Short Long
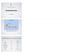 Umm AL Qura University TRANSCRIPTION Dr Neda Bogari TRANSCRIPTION COMPARISON OF DNA & RNA RNA DNA Sugar Ribose Deoxyribose Bases AUCG ATCG Strand length Short Long No. strands One Two Helix Single Double
Umm AL Qura University TRANSCRIPTION Dr Neda Bogari TRANSCRIPTION COMPARISON OF DNA & RNA RNA DNA Sugar Ribose Deoxyribose Bases AUCG ATCG Strand length Short Long No. strands One Two Helix Single Double
Differential Gene Expression
 IBS 8102 Cell, Molecular, and Developmental Biology Differential Gene Expression January 22, 2008 Differential Gene Expression Chromatin structure Gene anatomy Gene sequences Control of gene transcription
IBS 8102 Cell, Molecular, and Developmental Biology Differential Gene Expression January 22, 2008 Differential Gene Expression Chromatin structure Gene anatomy Gene sequences Control of gene transcription
Spring 2006 Biochemistry 302 Exam 2
 Name Spring 2006 Biochemistry 302 Exam 2 Directions: This exam has 45 questions/problems totaling 110 points. Check to make sure you have seven pages. Some questions have multiple parts so read each one
Name Spring 2006 Biochemistry 302 Exam 2 Directions: This exam has 45 questions/problems totaling 110 points. Check to make sure you have seven pages. Some questions have multiple parts so read each one
Chapter 18: Regulation of Gene Expression. 1. Gene Regulation in Bacteria 2. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes 3. Gene Regulation & Cancer
 Chapter 18: Regulation of Gene Expression 1. Gene Regulation in Bacteria 2. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes 3. Gene Regulation & Cancer Gene Regulation Gene regulation refers to all aspects of controlling
Chapter 18: Regulation of Gene Expression 1. Gene Regulation in Bacteria 2. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes 3. Gene Regulation & Cancer Gene Regulation Gene regulation refers to all aspects of controlling
DNA Transcription. Visualizing Transcription. The Transcription Process
 DNA Transcription By: Suzanne Clancy, Ph.D. 2008 Nature Education Citation: Clancy, S. (2008) DNA transcription. Nature Education 1(1) If DNA is a book, then how is it read? Learn more about the DNA transcription
DNA Transcription By: Suzanne Clancy, Ph.D. 2008 Nature Education Citation: Clancy, S. (2008) DNA transcription. Nature Education 1(1) If DNA is a book, then how is it read? Learn more about the DNA transcription
Chapter 8 Lecture Outline. Transcription, Translation, and Bioinformatics
 Chapter 8 Lecture Outline Transcription, Translation, and Bioinformatics Replication, Transcription, Translation n Repetitive processes Build polymers of nucleotides or amino acids n All have 3 major steps
Chapter 8 Lecture Outline Transcription, Translation, and Bioinformatics Replication, Transcription, Translation n Repetitive processes Build polymers of nucleotides or amino acids n All have 3 major steps
Protein Synthesis & Gene Expression
 DNA provides the instructions for how to build proteins Each gene dictates how to build a single protein in prokaryotes The sequence of nucleotides (AGCT) in DNA dictates the order of amino acids that
DNA provides the instructions for how to build proteins Each gene dictates how to build a single protein in prokaryotes The sequence of nucleotides (AGCT) in DNA dictates the order of amino acids that
GENE REGULATION slide shows by Kim Foglia modified Slides with blue edges are Kim s
 GENE REGULATION slide shows by Kim Foglia modified Slides with blue edges are Kim s 2007-2008 Bacterial metabolism Bacteria need to respond quickly to changes in their environment STOP GO if they have
GENE REGULATION slide shows by Kim Foglia modified Slides with blue edges are Kim s 2007-2008 Bacterial metabolism Bacteria need to respond quickly to changes in their environment STOP GO if they have
Matakuliah Genetika (BIO612206) Jurusan Biologi FMIPA Universitas Lampung. Priyambodo, M.Sc. staff.unila.ac.id/priyambodo
 Matakuliah Genetika (BIO612206) Jurusan Biologi FMIPA Universitas Lampung Priyambodo, M.Sc. staff.unila.ac.id/priyambodo Prokariotik Eukariotik staff.unila.ac.id/priyambodo Regulasi ekspresi gen pada
Matakuliah Genetika (BIO612206) Jurusan Biologi FMIPA Universitas Lampung Priyambodo, M.Sc. staff.unila.ac.id/priyambodo Prokariotik Eukariotik staff.unila.ac.id/priyambodo Regulasi ekspresi gen pada
Division Ave. High School AP Biology
 Control of Eukaryotic Genes 2007-2008 The BIG Questions n How are genes turned on & off in eukaryotes? n How do cells with the same genes differentiate to perform completely different, specialized functions?
Control of Eukaryotic Genes 2007-2008 The BIG Questions n How are genes turned on & off in eukaryotes? n How do cells with the same genes differentiate to perform completely different, specialized functions?
Nucleic acids deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) ribonucleic acid (RNA) nucleotide
 Nucleic Acids Nucleic acids are molecules that store information for cellular growth and reproduction There are two types of nucleic acids: - deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) These
Nucleic Acids Nucleic acids are molecules that store information for cellular growth and reproduction There are two types of nucleic acids: - deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) These
36. The double bonds in naturally-occuring fatty acids are usually isomers. A. cis B. trans C. both cis and trans D. D- E. L-
 36. The double bonds in naturally-occuring fatty acids are usually isomers. A. cis B. trans C. both cis and trans D. D- E. L- 37. The essential fatty acids are A. palmitic acid B. linoleic acid C. linolenic
36. The double bonds in naturally-occuring fatty acids are usually isomers. A. cis B. trans C. both cis and trans D. D- E. L- 37. The essential fatty acids are A. palmitic acid B. linoleic acid C. linolenic
Transcription in Prokaryotes. Jörg Bungert, PhD Phone:
 Transcription in Prokaryotes Jörg Bungert, PhD Phone: 352-273-8098 Email: jbungert@ufl.edu Objectives Understand the basic mechanism of transcription. Know the function of promoter elements and associating
Transcription in Prokaryotes Jörg Bungert, PhD Phone: 352-273-8098 Email: jbungert@ufl.edu Objectives Understand the basic mechanism of transcription. Know the function of promoter elements and associating
Chapter 9-II - Transcriptional Control of Gene Expression
 Chapter 9-II - Transcriptional Control of Gene Expression Transcriptional Control of Gene Expression 9.3 RNA Polymerase II Promoters and General Transcription Factors Three types of promoter sequences
Chapter 9-II - Transcriptional Control of Gene Expression Transcriptional Control of Gene Expression 9.3 RNA Polymerase II Promoters and General Transcription Factors Three types of promoter sequences
Chapter 16: Gene Expression from Biology by OpenStax College is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported license.
 Chapter 16: Gene Expression from Biology by OpenStax College is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported license. 2013, Rice University. CHAPTER 16 GENE EXPRESSION 429 16 GENE EXPRESSION
Chapter 16: Gene Expression from Biology by OpenStax College is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported license. 2013, Rice University. CHAPTER 16 GENE EXPRESSION 429 16 GENE EXPRESSION
Information Readout: Transcription and Post-transcriptional Processing Translation
 Information Readout: Transcription and Post-transcriptional Processing Translation Copyright 2013 Pearson Canada Inc. 27-1 DNA as the Template for RNA Synthesis Enzymology of RNA Synthesis: RNA Polymerase
Information Readout: Transcription and Post-transcriptional Processing Translation Copyright 2013 Pearson Canada Inc. 27-1 DNA as the Template for RNA Synthesis Enzymology of RNA Synthesis: RNA Polymerase
Protein Synthesis. DNA to RNA to Protein
 Protein Synthesis DNA to RNA to Protein From Genes to Proteins Processing the information contained in DNA into proteins involves a sequence of events known as gene expression and results in protein synthesis.
Protein Synthesis DNA to RNA to Protein From Genes to Proteins Processing the information contained in DNA into proteins involves a sequence of events known as gene expression and results in protein synthesis.
BEADLE & TATUM EXPERIMENT
 FROM DNA TO PROTEINS: gene expression Chapter 14 LECTURE OBJECTIVES What Is the Evidence that Genes Code for Proteins? How Does Information Flow from Genes to Proteins? How Is the Information Content in
FROM DNA TO PROTEINS: gene expression Chapter 14 LECTURE OBJECTIVES What Is the Evidence that Genes Code for Proteins? How Does Information Flow from Genes to Proteins? How Is the Information Content in
Genomics and Gene Recognition Genes and Blue Genes
 Genomics and Gene Recognition Genes and Blue Genes November 1, 2004 Prokaryotic Gene Structure prokaryotes are simplest free-living organisms studying prokaryotes can give us a sense what is the minimum
Genomics and Gene Recognition Genes and Blue Genes November 1, 2004 Prokaryotic Gene Structure prokaryotes are simplest free-living organisms studying prokaryotes can give us a sense what is the minimum
Transcription. DNA to RNA
 Transcription from DNA to RNA The Central Dogma of Molecular Biology replication DNA RNA Protein transcription translation Why call it transcription and translation? transcription is such a direct copy
Transcription from DNA to RNA The Central Dogma of Molecular Biology replication DNA RNA Protein transcription translation Why call it transcription and translation? transcription is such a direct copy
CHAPTERS , 17: Eukaryotic Genetics
 CHAPTERS 14.1 14.6, 17: Eukaryotic Genetics 1. Review the levels of DNA packing within the eukaryote nucleus. Label each level. (A similar diagram is on pg 188 of your textbook.) 2. How do the coding regions
CHAPTERS 14.1 14.6, 17: Eukaryotic Genetics 1. Review the levels of DNA packing within the eukaryote nucleus. Label each level. (A similar diagram is on pg 188 of your textbook.) 2. How do the coding regions
RNA Processing. Voet-Voet 1254 RNA molecules. Post-transcriptional processing. Enzymes. Most bacterial RNA molecules All eukaryotic RNA molecules
 RNA Processing Voet-Voet 1254 RNA molecules Post-transcriptional processing Most bacterial RNA molecules All eukaryotic RNA molecules Enzymes Catalytic RNA Ribozymes Catalytic protein Summary RNA processing
RNA Processing Voet-Voet 1254 RNA molecules Post-transcriptional processing Most bacterial RNA molecules All eukaryotic RNA molecules Enzymes Catalytic RNA Ribozymes Catalytic protein Summary RNA processing
Make the protein through the genetic dogma process.
 Make the protein through the genetic dogma process. Coding Strand 5 AGCAATCATGGATTGGGTACATTTGTAACTGT 3 Template Strand mrna Protein Complete the table. DNA strand DNA s strand G mrna A C U G T A T Amino
Make the protein through the genetic dogma process. Coding Strand 5 AGCAATCATGGATTGGGTACATTTGTAACTGT 3 Template Strand mrna Protein Complete the table. DNA strand DNA s strand G mrna A C U G T A T Amino
Gene Expression and Heritable Phenotype. CBS520 Eric Nabity
 Gene Expression and Heritable Phenotype CBS520 Eric Nabity DNA is Just the Beginning DNA was determined to be the genetic material, and the structure was identified as a (double stranded) double helix.
Gene Expression and Heritable Phenotype CBS520 Eric Nabity DNA is Just the Beginning DNA was determined to be the genetic material, and the structure was identified as a (double stranded) double helix.
Review of Protein (one or more polypeptide) A polypeptide is a long chain of..
 Gene expression Review of Protein (one or more polypeptide) A polypeptide is a long chain of.. In a protein, the sequence of amino acid determines its which determines the protein s A protein with an enzymatic
Gene expression Review of Protein (one or more polypeptide) A polypeptide is a long chain of.. In a protein, the sequence of amino acid determines its which determines the protein s A protein with an enzymatic
RNA. Ribonucleotidi monofosfato uniti a. formare una catena polinucleotidica
 RNA Ribonucleotidi monofosfato uniti a formare una catena polinucleotidica Formazione del legame fosfodiesterico I precursori della sintesi sono i ribonucleotidi trifosfato. L energia che occorre per la
RNA Ribonucleotidi monofosfato uniti a formare una catena polinucleotidica Formazione del legame fosfodiesterico I precursori della sintesi sono i ribonucleotidi trifosfato. L energia che occorre per la
DNA Binding Domains: Structural Motifs. Effector Domain. Zinc Fingers. Zinc Fingers, continued. Zif268
 DNA Binding Domains: Structural Motifs Studies of known transcription factors have found several motifs of protein design to allow sequence-specific binding of DNA. We will cover only three of these motifs:
DNA Binding Domains: Structural Motifs Studies of known transcription factors have found several motifs of protein design to allow sequence-specific binding of DNA. We will cover only three of these motifs:
RNA Structure and the Versatility of RNA. Mitesh Shrestha
 RNA Structure and the Versatility of RNA Mitesh Shrestha Ribonucleic Acid (RNA) Nitrogenous Bases (Adenine, Uracil, Guanine, Cytosine) Ribose Sugar Ribonucleic Acid (RNA) Phosphate Group RNA world Hypothesis
RNA Structure and the Versatility of RNA Mitesh Shrestha Ribonucleic Acid (RNA) Nitrogenous Bases (Adenine, Uracil, Guanine, Cytosine) Ribose Sugar Ribonucleic Acid (RNA) Phosphate Group RNA world Hypothesis
Chapter 11: Regulation of Gene Expression
 Chapter Review 1. It has long been known that there is probably a genetic link for alcoholism. Researchers studying rats have begun to elucidate this link. Briefly describe the genetic mechanism found
Chapter Review 1. It has long been known that there is probably a genetic link for alcoholism. Researchers studying rats have begun to elucidate this link. Briefly describe the genetic mechanism found
Ch. 10 Notes DNA: Transcription and Translation
 Ch. 10 Notes DNA: Transcription and Translation GOALS Compare the structure of RNA with that of DNA Summarize the process of transcription Relate the role of codons to the sequence of amino acids that
Ch. 10 Notes DNA: Transcription and Translation GOALS Compare the structure of RNA with that of DNA Summarize the process of transcription Relate the role of codons to the sequence of amino acids that
RNA : functional role
 RNA : functional role Hamad Yaseen, PhD MLS Department, FAHS Hamad.ali@hsc.edu.kw RNA mrna rrna trna 1 From DNA to Protein -Outline- From DNA to RNA From RNA to Protein From DNA to RNA Transcription: Copying
RNA : functional role Hamad Yaseen, PhD MLS Department, FAHS Hamad.ali@hsc.edu.kw RNA mrna rrna trna 1 From DNA to Protein -Outline- From DNA to RNA From RNA to Protein From DNA to RNA Transcription: Copying
Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes
 12 Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes WORKING WITH THE FIGURES 1. In Figure 12-4, certain mutations decrease the relative transcription rate of the -globin gene. Where are these mutations located,
12 Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes WORKING WITH THE FIGURES 1. In Figure 12-4, certain mutations decrease the relative transcription rate of the -globin gene. Where are these mutations located,
Chapter 12. DNA TRANSCRIPTION and TRANSLATION
 Chapter 12 DNA TRANSCRIPTION and TRANSLATION 12-3 RNA and Protein Synthesis WARM UP What are proteins? Where do they come from? From DNA to RNA to Protein DNA in our cells carry the instructions for making
Chapter 12 DNA TRANSCRIPTION and TRANSLATION 12-3 RNA and Protein Synthesis WARM UP What are proteins? Where do they come from? From DNA to RNA to Protein DNA in our cells carry the instructions for making
NUCLEUS. Fig. 2. Various stages in the condensation of chromatin
 NUCLEUS Animal cells contain DNA in nucleus (contains ~ 98% of cell DNA) and mitochondrion. Both compartments are surrounded by an envelope (double membrane). Nuclear DNA represents some linear molecules
NUCLEUS Animal cells contain DNA in nucleus (contains ~ 98% of cell DNA) and mitochondrion. Both compartments are surrounded by an envelope (double membrane). Nuclear DNA represents some linear molecules
Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes
 Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes The latest estimates are that a human cell, a eukaryotic cell, contains 20,000 25,000 genes. Some of these are expressed in all cells all the time. These so-called housekeeping
Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes The latest estimates are that a human cell, a eukaryotic cell, contains 20,000 25,000 genes. Some of these are expressed in all cells all the time. These so-called housekeeping
Chapter 13. From DNA to Protein
 Chapter 13 From DNA to Protein Proteins All proteins consist of polypeptide chains A linear sequence of amino acids Each chain corresponds to the nucleotide base sequenceof a gene The Path From Genes to
Chapter 13 From DNA to Protein Proteins All proteins consist of polypeptide chains A linear sequence of amino acids Each chain corresponds to the nucleotide base sequenceof a gene The Path From Genes to
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Flow of Genetic Information The flow of genetic information can be symbolized as: DNA RNA Protein
 PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Flow of Genetic Information The flow of genetic information can be symbolized as: DNA RNA Protein This is also known as: The central dogma of molecular biology Protein Proteins are made
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Flow of Genetic Information The flow of genetic information can be symbolized as: DNA RNA Protein This is also known as: The central dogma of molecular biology Protein Proteins are made
From Gene to Protein transcription, messenger RNA (mrna) translation, RNA processing triplet code, template strand, codons,
 From Gene to Protein I. Transcription and translation are the two main processes linking gene to protein. A. RNA is chemically similar to DNA, except that it contains ribose as its sugar and substitutes
From Gene to Protein I. Transcription and translation are the two main processes linking gene to protein. A. RNA is chemically similar to DNA, except that it contains ribose as its sugar and substitutes
DNA Topoisomerases relieve the supercoiling stress ahead of the fork
 DNA Topoisomerases relieve the supercoiling stress ahead of the fork Tw 1) T w : # of turns around the central axis 2) W r : # of times the double helix crosses itself 3) Linking Number: L k = T w + W
DNA Topoisomerases relieve the supercoiling stress ahead of the fork Tw 1) T w : # of turns around the central axis 2) W r : # of times the double helix crosses itself 3) Linking Number: L k = T w + W
Lecture 14. Eukaryotic gene regulation: Regulation of trna and 5S rrna synthesis by RNA polymerase III
 Lecture 14 Eukaryotic gene regulation: Regulation of trna and 5S rrna synthesis by RNA polymerase III So far.. Regulation of mrna synthesis Regulation of rrna synthesis Regulation of trna & 5S rrna synthesis
Lecture 14 Eukaryotic gene regulation: Regulation of trna and 5S rrna synthesis by RNA polymerase III So far.. Regulation of mrna synthesis Regulation of rrna synthesis Regulation of trna & 5S rrna synthesis
Chapter 15: Genes and Proteins from Biology by OpenStax College is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported license.
 Chapter 15: Genes and Proteins from Biology by OpenStax College is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported license. 2013, Rice University CHAPTER 15 GENES AND PROTEINS 403 15 GENES AND
Chapter 15: Genes and Proteins from Biology by OpenStax College is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported license. 2013, Rice University CHAPTER 15 GENES AND PROTEINS 403 15 GENES AND
Chromatin Structure and its Effects on Transcription
 Chromatin Structure and its Effects on Transcription Epigenetics 2014 by Nigel Atkinson The University of Texas at Austin From Weaver 4th edition and Armstrong 1st edition What is the point? DNA is not
Chromatin Structure and its Effects on Transcription Epigenetics 2014 by Nigel Atkinson The University of Texas at Austin From Weaver 4th edition and Armstrong 1st edition What is the point? DNA is not
BIOLOGY. Chapter 16 GenesExpression
 BIOLOGY Chapter 16 GenesExpression CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 18 Gene Expression 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 16.1 Differential Gene Expression results
BIOLOGY Chapter 16 GenesExpression CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 18 Gene Expression 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 16.1 Differential Gene Expression results
GENE EXPRESSION AT THE MOLECULAR LEVEL. Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
 GENE EXPRESSION AT THE MOLECULAR LEVEL Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Gene expression Gene function at the level of traits Gene function
GENE EXPRESSION AT THE MOLECULAR LEVEL Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Gene expression Gene function at the level of traits Gene function
RNA and Protein Synthesis
 Harriet Wilson, Lecture Notes Bio. Sci. 4 - Microbiology Sierra College RNA and Protein Synthesis Considerable evidence suggests that RNA molecules evolved prior to DNA molecules and proteins, and that
Harriet Wilson, Lecture Notes Bio. Sci. 4 - Microbiology Sierra College RNA and Protein Synthesis Considerable evidence suggests that RNA molecules evolved prior to DNA molecules and proteins, and that
Chromosomes. Chromosomes. Genes. Strands of DNA that contain all of the genes an organism needs to survive and reproduce
 Chromosomes Chromosomes Strands of DNA that contain all of the genes an organism needs to survive and reproduce Genes Segments of DNA that specify how to build a protein genes may specify more than one
Chromosomes Chromosomes Strands of DNA that contain all of the genes an organism needs to survive and reproduce Genes Segments of DNA that specify how to build a protein genes may specify more than one
MCDB 1041 Class 21 Splicing and Gene Expression
 MCDB 1041 Class 21 Splicing and Gene Expression Learning Goals Describe the role of introns and exons Interpret the possible outcomes of alternative splicing Relate the generation of protein from DNA to
MCDB 1041 Class 21 Splicing and Gene Expression Learning Goals Describe the role of introns and exons Interpret the possible outcomes of alternative splicing Relate the generation of protein from DNA to
DNA RNA PROTEIN SYNTHESIS -NOTES-
 DNA RNA PROTEIN SYNTHESIS -NOTES- THE COMPONENTS AND STRUCTURE OF DNA DNA is made up of units called nucleotides. Nucleotides are made up of three basic components:, called deoxyribose in DNA In DNA, there
DNA RNA PROTEIN SYNTHESIS -NOTES- THE COMPONENTS AND STRUCTURE OF DNA DNA is made up of units called nucleotides. Nucleotides are made up of three basic components:, called deoxyribose in DNA In DNA, there
Chapter 10: Gene Expression and Regulation
 Chapter 10: Gene Expression and Regulation Fact 1: DNA contains information but is unable to carry out actions Fact 2: Proteins are the workhorses but contain no information THUS Information in DNA must
Chapter 10: Gene Expression and Regulation Fact 1: DNA contains information but is unable to carry out actions Fact 2: Proteins are the workhorses but contain no information THUS Information in DNA must
Chapter 8: DNA and RNA
 Chapter 8: DNA and RNA Lecture Outline Enger, E. D., Ross, F. C., & Bailey, D. B. (2012). Concepts in biology (14th ed.). New York: McGraw- Hill. 1 8-1 DNA and the Importance of Proteins Proteins play
Chapter 8: DNA and RNA Lecture Outline Enger, E. D., Ross, F. C., & Bailey, D. B. (2012). Concepts in biology (14th ed.). New York: McGraw- Hill. 1 8-1 DNA and the Importance of Proteins Proteins play
Bundle 5 Test Review
 Bundle 5 Test Review DNA vs. RNA DNA Replication Gene Mutations- Protein Synthesis 1. Label the different components and complete the complimentary base pairing. What is this molecule called? _Nucleic
Bundle 5 Test Review DNA vs. RNA DNA Replication Gene Mutations- Protein Synthesis 1. Label the different components and complete the complimentary base pairing. What is this molecule called? _Nucleic
The information provided below may be useful in answering some questions.
 Molecular Exam 1 More Tutorial at www.dumblittledoctor.com The information provided below may be useful in answering some questions. INFORMATION ON COMPONENTS OF RIBOSOMES I. Prokaryotes (e.g. E. coli)
Molecular Exam 1 More Tutorial at www.dumblittledoctor.com The information provided below may be useful in answering some questions. INFORMATION ON COMPONENTS OF RIBOSOMES I. Prokaryotes (e.g. E. coli)
Transcriptional Regulation in Eukaryotes
 Transcriptional Regulation in Eukaryotes Concepts, Strategies, and Techniques Michael Carey Stephen T. Smale COLD SPRING HARBOR LABORATORY PRESS NEW YORK 2000 Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, 0-87969-537-4
Transcriptional Regulation in Eukaryotes Concepts, Strategies, and Techniques Michael Carey Stephen T. Smale COLD SPRING HARBOR LABORATORY PRESS NEW YORK 2000 Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, 0-87969-537-4
7.2 Protein Synthesis. From DNA to Protein Animation
 7.2 Protein Synthesis From DNA to Protein Animation Proteins Why are proteins so important? They break down your food They build up muscles They send signals through your brain that control your body They
7.2 Protein Synthesis From DNA to Protein Animation Proteins Why are proteins so important? They break down your food They build up muscles They send signals through your brain that control your body They
Module 7: The Central Dogma. CSE590: Molecular programming and neural computation. All slides by Eric Klavins.
 Module 7: The Central Dogma CSE590: Molecular programming and neural computation. All slides by Eric Klavins. 1 The Central Dogma RNA Polymerase The Ribosome m Note: We will look mainly at prokaryo=c (e.g.
Module 7: The Central Dogma CSE590: Molecular programming and neural computation. All slides by Eric Klavins. 1 The Central Dogma RNA Polymerase The Ribosome m Note: We will look mainly at prokaryo=c (e.g.
PART THREE - ANSWERS. ANSWERS to Questions from Part Three
 ANSWERS to Questions from Part Three Answers, Chapter 10. Transcription: RNA polymerases 10.1 The sigma factor (σ) causes RNA polymerase to bind to the correct sites on DNA to initiate transcription (i.e.
ANSWERS to Questions from Part Three Answers, Chapter 10. Transcription: RNA polymerases 10.1 The sigma factor (σ) causes RNA polymerase to bind to the correct sites on DNA to initiate transcription (i.e.
Lecture 21: Epigenetics Nurture or Nature? Chromatin DNA methylation Histone Code Twin study X-chromosome inactivation Environemnt and epigenetics
 Lecture 21: Epigenetics Nurture or Nature? Chromatin DNA methylation Histone Code Twin study X-chromosome inactivation Environemnt and epigenetics Epigenetics represents the science for the studying heritable
Lecture 21: Epigenetics Nurture or Nature? Chromatin DNA methylation Histone Code Twin study X-chromosome inactivation Environemnt and epigenetics Epigenetics represents the science for the studying heritable
1. DNA, RNA structure. 2. DNA replication. 3. Transcription, translation
 1. DNA, RNA structure 2. DNA replication 3. Transcription, translation DNA and RNA are polymers of nucleotides DNA is a nucleic acid, made of long chains of nucleotides Nucleotide Phosphate group Nitrogenous
1. DNA, RNA structure 2. DNA replication 3. Transcription, translation DNA and RNA are polymers of nucleotides DNA is a nucleic acid, made of long chains of nucleotides Nucleotide Phosphate group Nitrogenous
Einführung in die Genetik
 Einführung in die Genetik Prof. Dr. Kay Schneitz (EBio Pflanzen) http://plantdev.bio.wzw.tum.de schneitz@wzw.tum.de Twitter: @PlantDevTUM, #genetiktum FB: Plant Development TUM Prof. Dr. Claus Schwechheimer
Einführung in die Genetik Prof. Dr. Kay Schneitz (EBio Pflanzen) http://plantdev.bio.wzw.tum.de schneitz@wzw.tum.de Twitter: @PlantDevTUM, #genetiktum FB: Plant Development TUM Prof. Dr. Claus Schwechheimer
