RNA. Ribonucleotidi monofosfato uniti a. formare una catena polinucleotidica
|
|
|
- Allen Quinn
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2
3 RNA Ribonucleotidi monofosfato uniti a formare una catena polinucleotidica
4 Formazione del legame fosfodiesterico
5 I precursori della sintesi sono i ribonucleotidi trifosfato. L energia che occorre per la formazione del legame fosfodiesterico è data dall eliminazione del pirofosfato per idrolisi del legame.
6 La direzione di sintesi è 5-3
7 La sequenza nucleotidica dell RNA è dettata dalla sequenza nucleotidica del DNA
8 L enzima che catalizza l unione dei ribonucleotidi è l RNA polimerasi
9 RNA polimerasi sintetizza RNA in direzione 5 3 E in grado di iniziare la sintesi. Non necessita di un innesco Utilizza ribonucleosidi 5 -trifosfato (ATP, GTP, UTP e CTP) e richiede Mg++ Il 3 OH agisce da nucleofilo sul gruppo fosfato in 5 del ribonucleoside trifosfato entrante e si ha liberazione di PPi (NMP)n + NTP = (NMP)n+1+ PPi Ppi 2Pi Ogni nucleotide è selezionato in base alle regole della complementarietà A:U e G:C
10 closed promoter complex Transcription RNA polymerase open promoter complex initiation elongation termination RNA product
11 Legame al promotore della RNA polimerasi Apertura della doppia elica Inizio della sintesi Allungamento Terminazione
12 Direzione della sintesi Filamento senso Filamento antisenso
13 5' G C A G T A C A T G T C 3' coding strand 3' C G T C A T G T A C A G 5' template strand transcription 5' G C A G U A C A U G U C 3' RNA
14 5..AGAAGATGTCGGGCCAAACGCTCACGGATCGGATCGCCGCCGCTCAGTACAGCGTTACAGGCTCTGCTGT AGCAAGAGCGGTCTGCAAAGCCACTACTCATGAAGTAATGGGCCCCAAGAAAAAGCACCTGGACTATTTGATCCAGGC TACCAACGAGACCAATGTTAATATTCCTCAGATGGCCGACACTCTCTTTGAGCGGGCAACAAACAGTAGCTGGGTGGTT GTGTTTAAGGCTTTAGTGACAACACATCATCTCATGGTGCATGGAAATGAGAGATTTATTCAATATTTGGCTTCTAGAAA TACACTATTCAATCTCAGCAATTTTTTGGACAAAAGTGGATCCCATGGTTATGATATGTCTACCTTCATAAGGCGCTATA GTAGATATTTGAATGAAAAGGCTTTTTCTTACAGACAGATGGCCTTTGATTTTGCCAGGGTGAAGAAAGGGGCCGATGG TGTAATGAGGACAATGGCTCCCGAAAAGCTGCTAAAGAGTATGCCAATACTACAGGGACAAATTGATGCACTGCTTGAA TTTGATGTGCATCCAAATGAACTAACAAATGGTGTCATAAATGCAGCATTTATGCTTCTTTTCAAAGATCTTATCAAACTT TTTGCTTGCTACAATGATGGTGTTATTAACTTACTCGAAAAGTTTTTTGAAATGAAGAAAGGACAATGTAAAGATGCTCTA GAAATTTACAAACGATTTCTAACTAGAATGACACGAGTGTCTGAATTTCTCAAGGTTGCAGAGCAAGTTGGTATTGATAA AGGTGACATTCCTGACCTCACACAGGCTCCCAGCAGTCTTATGGAGACGCTTGAACAGCATCTAAATACATTAGAAGGA AAGAAACCTGGAAACAATGAAGGATCTGGTGCTCCCTCTCCATTAAGTAAGTCTTCTCCAGCCACAACTGTTACGTCTC CTAATTCTACACCAGCTAAAACTATTGACACATCCCCACCGGTTGATTTATTTGCAACTGCATCTGCGGCTGTCCCAGTC AGCACTTCTAAACCATCTAGTGATCTCCTGGACCTCCAGCCAGACTTTTCCTCTGGAGGGGCAGCAGCAGCCGCAGCA CCAGCACCACCACCACCTGCTGGAGGAGCCACTGCATGGGGAGACCTTTTGGGAGAGGATTCTTTGGCTGCACTTTCC TCTGTTCCCTCTGAAGCACAGATTTCAGATCCATTTGCACCAGAACCTACCCCTCCTACTACAACTGCTGAAATTGCAAC CACTACTGCTGCCACCGCCGCTGCCACCACCACTACCATTCATCTCTTGCCAGCTTAGTAGGCAATCTTGGAATTTCTG GTACCACAACAAAAAAGGGAGATCTTCAGTGGAATGCTGGAGAGAAAAAGTTGACTGGTGGAGCCAACTGGCAGCCTA AAGTAGCTCCAGCAACCTGGTCAGCAGGCGTTCCACCAAGTGCACCTTTGCAAGGAGCTGTACCTCCAACCAGTTCAG TTCCTCCTGTTGCCGGGGCCCCATCGGTTGGACAACCTGGAGCAGGATTTGGAATGCCTCCTGCTGGGACAGGCATG CCCATGATGCCTCAGCAGCCGGTCATGTTTGCACAGCCCATGATGAGGCCCCCCTTTGGAGCTGCCGCTGTACCTGGC ACGCAGCTTTCTCCAAGCCCTACACCTGCCAGTCAGAGTCCCAAGAAACCTCCAGCAAAGGACCCATTAGCGGATCTTA ACATCAAGGATTTCTTGTAAACAATTTAAGCTGCAATATTTGTGACTGAATAGGAAAATAAATGAGTTTGGAGACTTCAAA TAAGATTGATGCTGAGTTTCAAAGGGAGCCACCAGTACCAAACCCAATACTTACTCATAACTTCTCTTCCAAAATGTGTA ACACAGCCGTGAAAGTGAACATTAGGAATATGTACTACCTTAGCTGTTATCCCTACTCTTGAAATTGTAGTGTATTTGGA TTATTTGTGTATTGTACGATGTAAACAATGAATGGATGTTACTGATGCCGTTAGTGCTTTTTTGGACTTCACCTGAGGAC AGATGATGCAGCTGTTGTGTGGCGAGCTATTTGGAAAGACGTCTGTGTTTTTGAAGGTTTCAATGTACATATAACTTTTG AACAAACCCCAAACTCTTCCCATAAATTATCTTTTCTTCTGTATCTCTGTTACAAGCGTAGTGTGATAATACCAGATAATA AGGAAAACACTCATAAATATACAAAACTTTTTCAGTGTGGAGTACATTTTTCCAATCACAGGAACTTCAACTGTTGTGAGA AATGTTTATTTTTGTGGCACTGTATATGTTAA..3
15
16 Holoenzyme The holoenzyme of RNA-pol in E.coli consists of 5 different subunits: 2. holoenzyme core
17
18
19
20 The human RNA polymerases Polymerase Location Product RNA polymerase I nucleolus 18S, 28S, 5.8S rrna RNA polymerase II nucleoplasm hnrna/mrna, U1, U2, U4, U5 snrna RNA polymerase III nucleoplasm trna, 5S RNA, U6 snrna, 7SL RNA mitochondrial RNA polymerase mitochondrion all mitochondrial RNA
21
22 b). Gene structure promoter region exons (filled and unfilled boxed regions) +1 introns (between exons) transcribed region mrna structure 5 3 translated region
23
24 TATA box (TATAAAA) located approximately bp upstream of the +1 start site determines the exact start site (not in all promoters) binds the TATA binding protein (TBP) which is a subunit of TFIID GC box (CCGCCC) binds Sp1 (Specificity factor 1) CAAT box (GGCCAATCT) binds CTF (CAAT box transcription factor) Octamer (ATTTGCAT) binds OTF (Octamer transcription factor) Sequence elements within a typical eukaryotic gene 1 1 based on the thymidine kinase gene octamer transcription element promoter +1 ATTTGCAT GC CAAT GC TATA
25 Proteins regulating eukaryotic mrna synthesis General transcription factors TFIID (a multisubunit protein) binds to the TATA box to begin the assembly of the transcription apparatus the TATA binding protein (TBP) directly binds the TATA box TBP associated factors (TAFs) bind to TBP TFIIA, TFIIB, TFIIE, TFIIF, TFIIH 1, TFIIJ assemble with TFIID RNA polymerase II binds the promoter region via the TFII s Transcription factors binding to other promoter elements and transcription elements interact with proteins at the promoter and further stabilize (or inhibit) formation of a functional preinitiation complex 1 TFIIH is also involved in phosphorylation of RNA polymerase II, DNA repair (Cockayne syndrome mutations), and cell cycle regulation
26 Binding of the general transcription factors E F TAFs B TFIID H A TBP J TFIID (a multisubunit protein) binds to the TATA box to begin the assembly of the transcription apparatus the TATA binding protein (TBP) directly binds the TATA box TBP associated factors (TAFs) bind to TBP TFIIA, TFIIB, TFIIE, TFIIF, TFIIH, TFIIJ assemble with TFIID
27 Binding of RNA polymerase II E F B TFIID H A TBP J RNA pol II RNA polymerase II (a multisubunit protein) binds to the promoter region by interacting with the TFII s TFs recruit histone acetylase to the promoter
28 TATA BOX BINDING PROTEIN TBP Saddle-like domain TATA BOX DNA BINDING
29 TAF5 stabilizes TAFs interaction, specially histonelike ones (TAF6, TAF9) TAF1: Acetyl transferase activity Interaction with TFIIF TAF6 TAF11 TAF4 TAF12 TAF9 TAF13 TAF3 TAF12 TAF8 TAF4 TAF10 TBP TAF7 TAF5 TAF5 TAF11 TAF8 TAF3 TATA BOX TAF13 TAF6 TAF9 TAF10
30 DNA BENDING
31 TFIID
32 Pre-initiation complex (PIC) RNA pol II TF II A TBP TAF TATA TF II F TF II B TF II E TF II H DNA
33 Pre-initiation complex (PIC) TBP of TFII D binds TATA TFII A and TFII B bind TFII D TFII F-RNA-pol complex binds TFII B TFII F and TFII E open the dsdna (helicase and ATPase) TFII H: completion of PIC
34 c. Termination The termination sequence is AATAAA followed by GT repeats. The termination is closely related to the post-transcriptional modification.
35
36 Structure of eukaryotic mrna 5 Cap 7mGppp 5 untranslated region initiation AUG translated region 3 untranslated region UGA termination polyadenylation signal AAUAAA (A) ~200 poly(a) tail all mrnas have a 5 cap and all mrnas (with the exception of the histone mrnas) contain a poly(a) tail the 5 cap and 3 poly(a) tail prevent mrna degradation loss of the cap and poly(a) tail results in mrna degradation 3
37 Steps in mrna processing (hnrna is the precursor of mrna) capping (occurs co-transcriptionally) cleavage and polyadenylation (forms the 3 end) splicing (occurs in the nucleus prior to transport) exon 1 intron 1 exon 2 cap Transcription of pre-mrna and capping at the 5 end Cleavage of the 3 end and polyadenylation cap cap poly(a) Splicing to remove intron sequences cap poly(a) Transport of mature mrna to the cytoplasm
38
39 The 5 - cap structure is found on hnrna too. The capping process occurs in nuclei. The cap structure of mrna will be recognized by the cap-binding protein required for translation. The capping occurs prior to the splicing.
40 b. Poly-A tailing at 3 - end There is no poly(dt) sequence on the DNA template. The tailing process dose not depend on the template. The tailing process occurs prior to the splicing. The tailing process takes place in the nuclei.
41 Polyadenylation cleavage of the primary transcript occurs approximately nucleotides 3 -ward of the AAUAAA consensus site polyadenylation catalyzed by poly(a) polymerase approximately 200 adenylate residues are added cleavage AAUAAA mgpppnmpnm mgpppnmpnm AAUAAA A A A polyadenylation A A A 3 poly(a) is associated with poly(a) binding protein (PBP) function of poly(a) tail is to stabilize mrna
42
43
44
45 Splicing Rimozione di un introne attraverso due reazioni sequenziali di trasferimento di fosfato, note come transesterificazioni. Queste uniscono due esoni rimuovendo l introne come un cappio
46
47
48 Recognition of splice sites invariant GU and AG dinucleotides at intron ends donor (upstream) and acceptor (downstream) splice sites are within conserved consensus sequences donor (5 ) splice site branch site acceptor (3 ) splice site G/GUAAGU... A... YYYYYNYAG/G U1 U2 small nuclear RNA (snrna) U1 recognizes the donor splice site sequence (base-pairing interaction) U2 snrna binds to the branch site (base-pairing interaction) Y= U or C for pyrimidine; N= any nucleotide
49 intron 1 Step 2: binding of U4, U5, U6 2 OH-A exon 1 exon 2 U5 5 G-p-G-U - A-G-p-G 3 U1 U2 U4 U6 intron 1 Step 3: U1 is released, then U4 is released 2 OH-A exon 1 exon 2 U5 U6 U2 5 G-p-G-U - A-G-p-G 3
50 Step 4: U6 binds the 5 splice site and the two splicing reactions occur, catalyzed by U2 and U6 snrnps intron 1 mrna 3 G-A U6 2 OH-A U-G-5 -p-2 -A U5 U2 5 G-p-G 3
51
52
53 Differenti molecole di mrna dallo stesso gene Splicing alternativo Uso di promotori alternativi Uso di segnali di poliadenilazione alternativi
54
55
56 Structure of prokaryotic messenger RNA 5 Shine-Dalgarno sequence PuPuPuPuPuPuPuPu 3 AAU termination translated region initiation AUG The Shine-Dalgarno (SD) sequence base-pairs with a pyrimidine-rich sequence in 16S rrna to facilitate the initiation of protein synthesis
57 Il gene dei procarioti è policistronico
58 Enhancers Nei geni degli eucarioti gli enhancers possono distare dalla regione codificante anche più di 50 Kb.
59 Regolazione dell espressione genica Organizzazione della cromatina Punto 1 Inizio della trascrizione
60 Meccanismi di Regolazione dell espressione genica Fase Nucleare Scelta del gene che deve essere espresso Maturazione dell RNA Trasferimento Nucleo Citoplasma Fase Citoplasmatica Sintesi delle catene polipeptidiche Modificazioni post-traduzionali Trasferimento delle proteine nelle sedi di competenza
61 Il differenziamento cellulare dipende da meccanismi di regolazione dell espressione genica
62
63 Trascrizione sintesi di tutti gli RNA cellulari
Classes of eukaryotic cellular RNAs
 Classes of eukaryotic cellular RNAs ribosomal RNA (rrna) 18S (small subunit) 28S (large subunit) 5.8S (large subunit) 5S (large subunit) transfer RNA (trna) messenger RNA (mrna) heterogeneous nuclear RNA
Classes of eukaryotic cellular RNAs ribosomal RNA (rrna) 18S (small subunit) 28S (large subunit) 5.8S (large subunit) 5S (large subunit) transfer RNA (trna) messenger RNA (mrna) heterogeneous nuclear RNA
Il differenziamento cellulare dipende da meccanismi di regolazione
 Il differenziamento cellulare dipende da meccanismi di regolazione dell espressione genica Trascrizione sintesi di tutti gli RNA cellulari RNA Ribonucleotidi monofosfato uniti a formare una catena polinucleotidica
Il differenziamento cellulare dipende da meccanismi di regolazione dell espressione genica Trascrizione sintesi di tutti gli RNA cellulari RNA Ribonucleotidi monofosfato uniti a formare una catena polinucleotidica
Il differenziamento cellulare dipende da meccanismi di regolazione dell espressione genica
 Il differenziamento cellulare dipende da meccanismi di regolazione dell espressione genica RNA Ribonucleotidi monofosfato uniti a formare una catena polinucleotidica I precursori della sintesi sono
Il differenziamento cellulare dipende da meccanismi di regolazione dell espressione genica RNA Ribonucleotidi monofosfato uniti a formare una catena polinucleotidica I precursori della sintesi sono
Trascrizione sintesi di tutti gli RNA cellulari
 Trascrizione sintesi di tutti gli RNA cellulari RNA Ribonucleotidi monofosfato uniti a formare una catena polinucleotidica Formazione del legame fosfodiesterico I precursori della sintesi sono i ribonucleotidi
Trascrizione sintesi di tutti gli RNA cellulari RNA Ribonucleotidi monofosfato uniti a formare una catena polinucleotidica Formazione del legame fosfodiesterico I precursori della sintesi sono i ribonucleotidi
Transcription in Eukaryotes
 Transcription in Eukaryotes Biology I Hayder A Giha Transcription Transcription is a DNA-directed synthesis of RNA, which is the first step in gene expression. Gene expression, is transformation of the
Transcription in Eukaryotes Biology I Hayder A Giha Transcription Transcription is a DNA-directed synthesis of RNA, which is the first step in gene expression. Gene expression, is transformation of the
SIBC504: TRANSCRIPTION & RNA PROCESSING Assistant Professor Dr. Chatchawan Srisawat
 SIBC504: TRANSCRIPTION & RNA PROCESSING Assistant Professor Dr. Chatchawan Srisawat TRANSCRIPTION: AN OVERVIEW Transcription: the synthesis of a single-stranded RNA from a doublestranded DNA template.
SIBC504: TRANSCRIPTION & RNA PROCESSING Assistant Professor Dr. Chatchawan Srisawat TRANSCRIPTION: AN OVERVIEW Transcription: the synthesis of a single-stranded RNA from a doublestranded DNA template.
TRANSCRIPTION AND PROCESSING OF RNA
 TRANSCRIPTION AND PROCESSING OF RNA 1. The steps of gene expression. 2. General characterization of transcription: steps, components of transcription apparatus. 3. Transcription of eukaryotic structural
TRANSCRIPTION AND PROCESSING OF RNA 1. The steps of gene expression. 2. General characterization of transcription: steps, components of transcription apparatus. 3. Transcription of eukaryotic structural
Chapter 11. Transcription. The biochemistry and molecular biology department of CMU
 Chapter 11 Transcription The biochemistry and molecular biology department of CMU Transcription The synthesis of RNA molecules using DNA strands as the templates so that the genetic information can be
Chapter 11 Transcription The biochemistry and molecular biology department of CMU Transcription The synthesis of RNA molecules using DNA strands as the templates so that the genetic information can be
30 Gene expression: Transcription
 30 Gene expression: Transcription Gene structure. o Exons coding region of DNA. o Introns non-coding region of DNA. o Introns are interspersed between exons of a single gene. o Promoter region helps enzymes
30 Gene expression: Transcription Gene structure. o Exons coding region of DNA. o Introns non-coding region of DNA. o Introns are interspersed between exons of a single gene. o Promoter region helps enzymes
GENETICS - CLUTCH CH.10 TRANSCRIPTION.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: OVERVIEW OF TRANSCRIPTION Transcription is the process of using DNA as a template to RNA RNA polymerase is the enzyme that transcribes DNA - There are many different types
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: OVERVIEW OF TRANSCRIPTION Transcription is the process of using DNA as a template to RNA RNA polymerase is the enzyme that transcribes DNA - There are many different types
Transcription Eukaryotic Cells
 Transcription Eukaryotic Cells Packet #20 1 Introduction Transcription is the process in which genetic information, stored in a strand of DNA (gene), is copied into a strand of RNA. Protein-encoding genes
Transcription Eukaryotic Cells Packet #20 1 Introduction Transcription is the process in which genetic information, stored in a strand of DNA (gene), is copied into a strand of RNA. Protein-encoding genes
Biochemistry Eukaryotic Transcription
 1 Description of Module Subject Name Paper Name Module Name/Title Dr. Vijaya Khader Dr. MC Varadaraj 2 1. Objectives 1. Understand and have an overview of eucaryotic transcriptional regulation. 2. Explain
1 Description of Module Subject Name Paper Name Module Name/Title Dr. Vijaya Khader Dr. MC Varadaraj 2 1. Objectives 1. Understand and have an overview of eucaryotic transcriptional regulation. 2. Explain
Transcription & post transcriptional modification
 Transcription & post transcriptional modification Transcription The synthesis of RNA molecules using DNA strands as the templates so that the genetic information can be transferred from DNA to RNA Similarity
Transcription & post transcriptional modification Transcription The synthesis of RNA molecules using DNA strands as the templates so that the genetic information can be transferred from DNA to RNA Similarity
Chapter 3. DNA, RNA, and Protein Synthesis
 Chapter 3. DNA, RNA, and Protein Synthesis 4. Transcription Gene Expression Regulatory region (promoter) 5 flanking region Upstream region Coding region 3 flanking region Downstream region Transcription
Chapter 3. DNA, RNA, and Protein Synthesis 4. Transcription Gene Expression Regulatory region (promoter) 5 flanking region Upstream region Coding region 3 flanking region Downstream region Transcription
Lecture 11. Initiation of RNA Pol II transcription. Transcription Initiation Complex
 Lecture 11 *Eukaryotic Transcription Gene Organization RNA Processing 5 cap 3 polyadenylation splicing Translation Initiation of RNA Pol II transcription Consensus sequence of promoter TATA Transcription
Lecture 11 *Eukaryotic Transcription Gene Organization RNA Processing 5 cap 3 polyadenylation splicing Translation Initiation of RNA Pol II transcription Consensus sequence of promoter TATA Transcription
Eukaryotic Transcription
 Eukaryotic Transcription I. Differences between eukaryotic versus prokaryotic transcription. II. (core vs holoenzyme): RNA polymerase II - Promotor elements. - General Pol II transcription factors (GTF).
Eukaryotic Transcription I. Differences between eukaryotic versus prokaryotic transcription. II. (core vs holoenzyme): RNA polymerase II - Promotor elements. - General Pol II transcription factors (GTF).
Eukaryotic & Prokaryotic Transcription. RNA polymerases
 Eukaryotic & Prokaryotic Transcription RNA polymerases RNA Polymerases A. E. coli RNA polymerase 1. core enzyme = ββ'(α)2 has catalytic activity but cannot recognize start site of transcription ~500,000
Eukaryotic & Prokaryotic Transcription RNA polymerases RNA Polymerases A. E. coli RNA polymerase 1. core enzyme = ββ'(α)2 has catalytic activity but cannot recognize start site of transcription ~500,000
DNA Transcription. Dr Aliwaini
 DNA Transcription 1 DNA Transcription-Introduction The synthesis of an RNA molecule from DNA is called Transcription. All eukaryotic cells have five major classes of RNA: ribosomal RNA (rrna), messenger
DNA Transcription 1 DNA Transcription-Introduction The synthesis of an RNA molecule from DNA is called Transcription. All eukaryotic cells have five major classes of RNA: ribosomal RNA (rrna), messenger
Gene Expression: Transcription, Translation, RNAs and the Genetic Code
 Lecture 28-29 Gene Expression: Transcription, Translation, RNAs and the Genetic Code Central dogma of molecular biology During transcription, the information in a DNA sequence (a gene) is copied into a
Lecture 28-29 Gene Expression: Transcription, Translation, RNAs and the Genetic Code Central dogma of molecular biology During transcription, the information in a DNA sequence (a gene) is copied into a
Computational Biology I LSM5191 (2003/4)
 Computational Biology I LSM5191 (2003/4) Aylwin Ng, D.Phil Lecture Notes: Transcriptome: Molecular Biology of Gene Expression I Flow of information: DNA to polypeptide DNA Start Exon1 Intron Exon2 Termination
Computational Biology I LSM5191 (2003/4) Aylwin Ng, D.Phil Lecture Notes: Transcriptome: Molecular Biology of Gene Expression I Flow of information: DNA to polypeptide DNA Start Exon1 Intron Exon2 Termination
Lecture Summary: Regulation of transcription. General mechanisms-what are the major regulatory points?
 BCH 401G Lecture 37 Andres Lecture Summary: Regulation of transcription. General mechanisms-what are the major regulatory points? RNA processing: Capping, polyadenylation, splicing. Why process mammalian
BCH 401G Lecture 37 Andres Lecture Summary: Regulation of transcription. General mechanisms-what are the major regulatory points? RNA processing: Capping, polyadenylation, splicing. Why process mammalian
TRANSCRIPTION COMPARISON OF DNA & RNA TRANSCRIPTION. Umm AL Qura University. Sugar Ribose Deoxyribose. Bases AUCG ATCG. Strand length Short Long
 Umm AL Qura University TRANSCRIPTION Dr Neda Bogari TRANSCRIPTION COMPARISON OF DNA & RNA RNA DNA Sugar Ribose Deoxyribose Bases AUCG ATCG Strand length Short Long No. strands One Two Helix Single Double
Umm AL Qura University TRANSCRIPTION Dr Neda Bogari TRANSCRIPTION COMPARISON OF DNA & RNA RNA DNA Sugar Ribose Deoxyribose Bases AUCG ATCG Strand length Short Long No. strands One Two Helix Single Double
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 08: Transcription, Translation and the Genetic Code
 Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 08: Transcription, Translation and the Genetic Code Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about how genes function is correct? Question #1 (A)
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 08: Transcription, Translation and the Genetic Code Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about how genes function is correct? Question #1 (A)
M1 - Biochemistry. Nucleic Acid Structure II/Transcription I
 M1 - Biochemistry Nucleic Acid Structure II/Transcription I PH Ratz, PhD (Resources: Lehninger et al., 5th ed., Chapters 8, 24 & 26) 1 Nucleic Acid Structure II/Transcription I Learning Objectives: 1.
M1 - Biochemistry Nucleic Acid Structure II/Transcription I PH Ratz, PhD (Resources: Lehninger et al., 5th ed., Chapters 8, 24 & 26) 1 Nucleic Acid Structure II/Transcription I Learning Objectives: 1.
CLASS 3.5: 03/29/07 EUKARYOTIC TRANSCRIPTION I: PROMOTERS AND ENHANCERS
 CLASS 3.5: 03/29/07 EUKARYOTIC TRANSCRIPTION I: PROMOTERS AND ENHANCERS A. Promoters and Polymerases (RNA pols): 1. General characteristics - Initiation of transcription requires a. Transcription factors
CLASS 3.5: 03/29/07 EUKARYOTIC TRANSCRIPTION I: PROMOTERS AND ENHANCERS A. Promoters and Polymerases (RNA pols): 1. General characteristics - Initiation of transcription requires a. Transcription factors
Eukaryotic Gene Expression John O. Thomas
 Eukaryotic Gene Expression John O. Thomas I) RNA polymerases A) There are four RNA polymerases in human cells. 1) RNA polymerase I, located in the nucleolar region of the nucleus, is responsible for the
Eukaryotic Gene Expression John O. Thomas I) RNA polymerases A) There are four RNA polymerases in human cells. 1) RNA polymerase I, located in the nucleolar region of the nucleus, is responsible for the
Transcription. The sugar molecule found in RNA is ribose, rather than the deoxyribose found in DNA.
 Transcription RNA (ribonucleic acid) is a key intermediary between a DNA sequence and a polypeptide. RNA is an informational polynucleotide similar to DNA, but it differs from DNA in three ways: RNA generally
Transcription RNA (ribonucleic acid) is a key intermediary between a DNA sequence and a polypeptide. RNA is an informational polynucleotide similar to DNA, but it differs from DNA in three ways: RNA generally
Themes: RNA and RNA Processing. Messenger RNA (mrna) What is a gene? RNA is very versatile! RNA-RNA interactions are very important!
 Themes: RNA is very versatile! RNA and RNA Processing Chapter 14 RNA-RNA interactions are very important! Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes have many important differences. Messenger RNA (mrna) Carries genetic
Themes: RNA is very versatile! RNA and RNA Processing Chapter 14 RNA-RNA interactions are very important! Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes have many important differences. Messenger RNA (mrna) Carries genetic
Transcription and Post Transcript Modification
 Transcription and Post Transcript Modification You Should Be Able To 1. Describe transcription. 2. Compare and contrast eukaryotic + prokaryotic transcription. 3. Explain mrna processing in eukaryotes.
Transcription and Post Transcript Modification You Should Be Able To 1. Describe transcription. 2. Compare and contrast eukaryotic + prokaryotic transcription. 3. Explain mrna processing in eukaryotes.
DNA Prokaryote Transcription Steps (updated February 2013)
 URS AACTGT ATATTA - 35-10 transcription Pribnow Box discriminator +1 AGGAGGT TTA TCCTCCA ATT Gene C TGA TAG ACT ATC rho or GC hairpin loop transcription termination DNA Prokaryote Transcription Steps (updated
URS AACTGT ATATTA - 35-10 transcription Pribnow Box discriminator +1 AGGAGGT TTA TCCTCCA ATT Gene C TGA TAG ACT ATC rho or GC hairpin loop transcription termination DNA Prokaryote Transcription Steps (updated
Transcription is the first stage of gene expression
 Transcription is the first stage of gene expression RNA synthesis is catalyzed by RNA polymerase, which pries the DNA strands apart and hooks together the RNA nucleotides The RNA is complementary to the
Transcription is the first stage of gene expression RNA synthesis is catalyzed by RNA polymerase, which pries the DNA strands apart and hooks together the RNA nucleotides The RNA is complementary to the
BIOCHEMISTRY REVIEW. Overview of Biomolecules. Chapter 12 Transcription
 BIOCHEMISTRY REVIEW Overview of Biomolecules Chapter 12 Transcription 2 3 4 5 Are You Getting It?? Which are general characteristics of transcription? (multiple answers) a) An entire DNA molecule is transcribed
BIOCHEMISTRY REVIEW Overview of Biomolecules Chapter 12 Transcription 2 3 4 5 Are You Getting It?? Which are general characteristics of transcription? (multiple answers) a) An entire DNA molecule is transcribed
Transcription. Manzur Ali PP, DBT,M.E.S College,Marampally
 Transcription Manzur Ali PP, DBT,M.E.S College,Marampally manzursir@gmail.com RNA transcription is actively regulated Not all DNA is transcribed in a given cell (less than 50% even in prokaryotes) For
Transcription Manzur Ali PP, DBT,M.E.S College,Marampally manzursir@gmail.com RNA transcription is actively regulated Not all DNA is transcribed in a given cell (less than 50% even in prokaryotes) For
Mechanisms of Transcription. School of Life Science Shandong University
 Mechanisms of Transcription School of Life Science Shandong University Ch 12: Mechanisms of Transcription 1. RNA polymerase and the transcription cycle 2. The transcription cycle in bacteria 3. Transcription
Mechanisms of Transcription School of Life Science Shandong University Ch 12: Mechanisms of Transcription 1. RNA polymerase and the transcription cycle 2. The transcription cycle in bacteria 3. Transcription
BIO 311C Spring Lecture 36 Wednesday 28 Apr.
 BIO 311C Spring 2010 1 Lecture 36 Wednesday 28 Apr. Synthesis of a Polypeptide Chain 5 direction of ribosome movement along the mrna 3 ribosome mrna NH 2 polypeptide chain direction of mrna movement through
BIO 311C Spring 2010 1 Lecture 36 Wednesday 28 Apr. Synthesis of a Polypeptide Chain 5 direction of ribosome movement along the mrna 3 ribosome mrna NH 2 polypeptide chain direction of mrna movement through
Bis2A 12.2 Eukaryotic Transcription
 OpenStax-CNX module: m56061 1 Bis2A 12.2 Eukaryotic Transcription Mitch Singer Based on Eukaryotic Transcription by OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative
OpenStax-CNX module: m56061 1 Bis2A 12.2 Eukaryotic Transcription Mitch Singer Based on Eukaryotic Transcription by OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative
BEADLE & TATUM EXPERIMENT
 FROM DNA TO PROTEINS: gene expression Chapter 14 LECTURE OBJECTIVES What Is the Evidence that Genes Code for Proteins? How Does Information Flow from Genes to Proteins? How Is the Information Content in
FROM DNA TO PROTEINS: gene expression Chapter 14 LECTURE OBJECTIVES What Is the Evidence that Genes Code for Proteins? How Does Information Flow from Genes to Proteins? How Is the Information Content in
Initiation and termination of transcription, Post transcription modification of the RNA. Mitesh Shrestha
 Initiation and termination of transcription, Post transcription modification of the RNA Mitesh Shrestha Transcription: overview In prokaryotes transcription and translation are coupled. Proteins are synthesized
Initiation and termination of transcription, Post transcription modification of the RNA Mitesh Shrestha Transcription: overview In prokaryotes transcription and translation are coupled. Proteins are synthesized
Make the protein through the genetic dogma process.
 Make the protein through the genetic dogma process. Coding Strand 5 AGCAATCATGGATTGGGTACATTTGTAACTGT 3 Template Strand mrna Protein Complete the table. DNA strand DNA s strand G mrna A C U G T A T Amino
Make the protein through the genetic dogma process. Coding Strand 5 AGCAATCATGGATTGGGTACATTTGTAACTGT 3 Template Strand mrna Protein Complete the table. DNA strand DNA s strand G mrna A C U G T A T Amino
Transcription steps. Transcription steps. Eukaryote RNA processing
 Transcription steps Initiation at 5 end of gene binding of RNA polymerase to promoter unwinding of DNA Elongation addition of nucleotides to 3 end rules of base pairing requires Mg 2+ energy from NTP substrates
Transcription steps Initiation at 5 end of gene binding of RNA polymerase to promoter unwinding of DNA Elongation addition of nucleotides to 3 end rules of base pairing requires Mg 2+ energy from NTP substrates
Transcription. By : Lucia Dhiantika Witasari M.Biotech., Apt
 Transcription By : Lucia Dhiantika Witasari M.Biotech., Apt REGULATION OF GENE EXPRESSION 11/26/2010 2 RNA Messenger RNAs (mrnas) encode the amino acid sequence of one or more polypeptides specified by
Transcription By : Lucia Dhiantika Witasari M.Biotech., Apt REGULATION OF GENE EXPRESSION 11/26/2010 2 RNA Messenger RNAs (mrnas) encode the amino acid sequence of one or more polypeptides specified by
There are four major types of introns. Group I introns, found in some rrna genes, are self-splicing: they can catalyze their own removal.
 1 2 Continuous genes - Intron: Many eukaryotic genes contain coding regions called exons and noncoding regions called intervening sequences or introns. The average human gene contains from eight to nine
1 2 Continuous genes - Intron: Many eukaryotic genes contain coding regions called exons and noncoding regions called intervening sequences or introns. The average human gene contains from eight to nine
Chapter 17. From Gene to Protein
 Chapter 17 From Gene to Protein One Gene One Enzyme Hypothesis Archibald Garrod 1 st to suggest that genes dictate phenotypes through enzymes that catalyze specific chemical reactions ; alkaptonuria Beadle
Chapter 17 From Gene to Protein One Gene One Enzyme Hypothesis Archibald Garrod 1 st to suggest that genes dictate phenotypes through enzymes that catalyze specific chemical reactions ; alkaptonuria Beadle
Chapter 3 Gene Function. Transcription Prokaroyotes Eukaryotes Transcript processing Proteins Translation Genetic nomenclature
 Chapter 3 Gene Function Transcription Prokaroyotes Eukaryotes Transcript processing Proteins Translation Genetic nomenclature Transcription RNA composition ATP, GTP, UTP, CTP are substrates for RNA polymerase.
Chapter 3 Gene Function Transcription Prokaroyotes Eukaryotes Transcript processing Proteins Translation Genetic nomenclature Transcription RNA composition ATP, GTP, UTP, CTP are substrates for RNA polymerase.
FROM GENE TO PROTEIN. One Gene One Enzyme Hypothesis 3/12/2013. Basic Principles of Transcription & Translation
 One Gene One Enzyme Hypothesis FROM GENE TO PROTEIN C H A P T E R 1 7 Archibald Garrod 1 st to suggest that genes dictate phenotypes through enzymes that catalyze specific chemical reactions ; alkaptonuria
One Gene One Enzyme Hypothesis FROM GENE TO PROTEIN C H A P T E R 1 7 Archibald Garrod 1 st to suggest that genes dictate phenotypes through enzymes that catalyze specific chemical reactions ; alkaptonuria
The discovery of the role of RNA RNA structure, synthesis and function
 Central Dogma The discovery of the role of RNA RNA structure, synthesis and function! Fundamental observations in genetics!! Genes are located in nuclei (in eukaryotes)!! Polypeptides are synthesised in
Central Dogma The discovery of the role of RNA RNA structure, synthesis and function! Fundamental observations in genetics!! Genes are located in nuclei (in eukaryotes)!! Polypeptides are synthesised in
Fig Ch 17: From Gene to Protein
 Fig. 17-1 Ch 17: From Gene to Protein Basic Principles of Transcription and Translation RNA is the intermediate between genes and the proteins for which they code Transcription is the synthesis of RNA
Fig. 17-1 Ch 17: From Gene to Protein Basic Principles of Transcription and Translation RNA is the intermediate between genes and the proteins for which they code Transcription is the synthesis of RNA
DNA Evolution of knowledge about gene. Contains information about RNAs and proteins. Polynucleotide chains; Double stranded molecule;
 Evolution of knowledge about gene G. Mendel Hereditary factors W.Johannsen, 1909 G.W.Beadle, E.L.Tatum, 1945 Ingram, 1957 Actual concepts The gene hereditary unit located in chromosomes Hypotheses One
Evolution of knowledge about gene G. Mendel Hereditary factors W.Johannsen, 1909 G.W.Beadle, E.L.Tatum, 1945 Ingram, 1957 Actual concepts The gene hereditary unit located in chromosomes Hypotheses One
BS 50 Genetics and Genomics Week of Oct 24
 BS 50 Genetics and Genomics Week of Oct 24 Additional Practice Problems for Section Question 1: The following table contains a list of statements that apply to replication, transcription, both, or neither.
BS 50 Genetics and Genomics Week of Oct 24 Additional Practice Problems for Section Question 1: The following table contains a list of statements that apply to replication, transcription, both, or neither.
Transcription. DNA to RNA
 Transcription from DNA to RNA The Central Dogma of Molecular Biology replication DNA RNA Protein transcription translation Why call it transcription and translation? transcription is such a direct copy
Transcription from DNA to RNA The Central Dogma of Molecular Biology replication DNA RNA Protein transcription translation Why call it transcription and translation? transcription is such a direct copy
RNA metabolism. DNA dependent synthesis of RNA RNA processing RNA dependent synthesis of RNA and DNA.
 RNA metabolism DNA dependent synthesis of RNA RNA processing RNA dependent synthesis of RNA and DNA http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ovc8nxobxmq DNA dependent synthesis of RNA : production of an RNA molecule
RNA metabolism DNA dependent synthesis of RNA RNA processing RNA dependent synthesis of RNA and DNA http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ovc8nxobxmq DNA dependent synthesis of RNA : production of an RNA molecule
DNA. Is a molecule that encodes the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms and many viruses.
 Is a molecule that encodes the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms and many viruses. Genetic information is encoded as a sequence of nucleotides (guanine,
Is a molecule that encodes the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms and many viruses. Genetic information is encoded as a sequence of nucleotides (guanine,
CH 17 :From Gene to Protein
 CH 17 :From Gene to Protein Defining a gene gene gene Defining a gene is problematic because one gene can code for several protein products, some genes code only for RNA, two genes can overlap, and there
CH 17 :From Gene to Protein Defining a gene gene gene Defining a gene is problematic because one gene can code for several protein products, some genes code only for RNA, two genes can overlap, and there
Analyzed Fungi Neurospora crassa mutants. Mutants were UNABLE to grow without Arginine (an amino acid) Other biochemical experiments indicated:
 From Gene to Protein Beadle and Tatum Analyzed Fungi Neurospora crassa mutants Mutants were UNABLE to grow without Arginine (an amino acid) Other biochemical experiments indicated: Precursor Ornithine
From Gene to Protein Beadle and Tatum Analyzed Fungi Neurospora crassa mutants Mutants were UNABLE to grow without Arginine (an amino acid) Other biochemical experiments indicated: Precursor Ornithine
Nucleotide Entry Port. Scaffold Subunits. Polymerase Activity β Sliding Clamp. Clamp Loader. Promoter Recognition
 Nucleotide Entry ort α (2) Scaffold Subunits olymerase Activity Sliding Clamp σ Clamp Loader romoter Recognition -35-10 NNAAA AA T A TTTTNNAAAANNN TT T N N17 N6 α α α α α α α α α α α α α α +1 α α α α Subunit
Nucleotide Entry ort α (2) Scaffold Subunits olymerase Activity Sliding Clamp σ Clamp Loader romoter Recognition -35-10 NNAAA AA T A TTTTNNAAAANNN TT T N N17 N6 α α α α α α α α α α α α α α +1 α α α α Subunit
We can now identify three major pathways of information flow in the cell (in replication, information passes from one DNA molecule to other DNA
 1 We can now identify three major pathways of information flow in the cell (in replication, information passes from one DNA molecule to other DNA molecules; in transcription, information passes from DNA
1 We can now identify three major pathways of information flow in the cell (in replication, information passes from one DNA molecule to other DNA molecules; in transcription, information passes from DNA
RNA : functional role
 RNA : functional role Hamad Yaseen, PhD MLS Department, FAHS Hamad.ali@hsc.edu.kw RNA mrna rrna trna 1 From DNA to Protein -Outline- From DNA to RNA From RNA to Protein From DNA to RNA Transcription: Copying
RNA : functional role Hamad Yaseen, PhD MLS Department, FAHS Hamad.ali@hsc.edu.kw RNA mrna rrna trna 1 From DNA to Protein -Outline- From DNA to RNA From RNA to Protein From DNA to RNA Transcription: Copying
Resources. This lecture Campbell and Farrell's Biochemistry, Chapter 11
 Transcription Resources This lecture Campbell and Farrell's Biochemistry, Chapter 11 2 Definition of a gene The entire nucleic acid sequence that is necessary for the synthesis of a functional polypeptide
Transcription Resources This lecture Campbell and Farrell's Biochemistry, Chapter 11 2 Definition of a gene The entire nucleic acid sequence that is necessary for the synthesis of a functional polypeptide
DIFFERENT ASPECTS OF GENE REGULATION
 TARTU UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF BILOGY AND GEOGRAPHY DIFFERENT ASPECTS OF GENE REGULATION TARTU 2005 Sten Ilmjärv 2 TABLE OF CONTENT TABLE OF CONTENT...2 GLOSSARY...3 INTRODUCTION...4 1. THE GENE...5 2. GENE
TARTU UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF BILOGY AND GEOGRAPHY DIFFERENT ASPECTS OF GENE REGULATION TARTU 2005 Sten Ilmjärv 2 TABLE OF CONTENT TABLE OF CONTENT...2 GLOSSARY...3 INTRODUCTION...4 1. THE GENE...5 2. GENE
Molecular Biology (BIOL 4320) Exam #1 March 12, 2002
 Molecular Biology (BIOL 4320) Exam #1 March 12, 2002 Name KEY SS# This exam is worth a total of 100 points. The number of points each question is worth is shown in parentheses after the question number.
Molecular Biology (BIOL 4320) Exam #1 March 12, 2002 Name KEY SS# This exam is worth a total of 100 points. The number of points each question is worth is shown in parentheses after the question number.
Protein Synthesis Notes
 Protein Synthesis Notes Protein Synthesis: Overview Transcription: synthesis of mrna under the direction of DNA. Translation: actual synthesis of a polypeptide under the direction of mrna. Transcription
Protein Synthesis Notes Protein Synthesis: Overview Transcription: synthesis of mrna under the direction of DNA. Translation: actual synthesis of a polypeptide under the direction of mrna. Transcription
Chapter 24: Promoters and Enhancers
 Chapter 24: Promoters and Enhancers A typical gene transcribed by RNA polymerase II has a promoter that usually extends upstream from the site where transcription is initiated the (#1) of transcription
Chapter 24: Promoters and Enhancers A typical gene transcribed by RNA polymerase II has a promoter that usually extends upstream from the site where transcription is initiated the (#1) of transcription
DNA REPLICATION. DNA structure. Semiconservative replication. DNA structure. Origin of replication. Replication bubbles and forks.
 DNA REPLICATION 5 4 Phosphate 3 DNA structure Nitrogenous base 1 Deoxyribose 2 Nucleotide DNA strand = DNA polynucleotide 2004 Biology Olympiad Preparation Program 2 2004 Biology Olympiad Preparation Program
DNA REPLICATION 5 4 Phosphate 3 DNA structure Nitrogenous base 1 Deoxyribose 2 Nucleotide DNA strand = DNA polynucleotide 2004 Biology Olympiad Preparation Program 2 2004 Biology Olympiad Preparation Program
DNA Replication and Repair
 DNA Replication and Repair http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/organic/imgorg/cendog.gif Overview of DNA Replication SWYK CNs 1, 2, 30 Explain how specific base pairing enables existing DNA strands
DNA Replication and Repair http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/organic/imgorg/cendog.gif Overview of DNA Replication SWYK CNs 1, 2, 30 Explain how specific base pairing enables existing DNA strands
Differential Gene Expression
 Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Differential Gene Expression June 19, 2008 Differential Gene Expression Overview Chromatin structure Gene anatomy RNA processing and protein production Initiating transcription:
Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Differential Gene Expression June 19, 2008 Differential Gene Expression Overview Chromatin structure Gene anatomy RNA processing and protein production Initiating transcription:
Information Readout: Transcription and Post-transcriptional Processing Translation
 Information Readout: Transcription and Post-transcriptional Processing Translation Copyright 2013 Pearson Canada Inc. 27-1 DNA as the Template for RNA Synthesis Enzymology of RNA Synthesis: RNA Polymerase
Information Readout: Transcription and Post-transcriptional Processing Translation Copyright 2013 Pearson Canada Inc. 27-1 DNA as the Template for RNA Synthesis Enzymology of RNA Synthesis: RNA Polymerase
BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH.17 - GENE EXPRESSION.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: GENES Beadle and Tatum develop the one gene one enzyme hypothesis through their work with Neurospora (bread mold). This idea was later revised as the one gene one polypeptide
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: GENES Beadle and Tatum develop the one gene one enzyme hypothesis through their work with Neurospora (bread mold). This idea was later revised as the one gene one polypeptide
Gene function at the level of traits Gene function at the molecular level
 Gene expression Gene function at the level of traits Gene function at the molecular level Two levels tied together since the molecular level affects the structure and function of cells which determines
Gene expression Gene function at the level of traits Gene function at the molecular level Two levels tied together since the molecular level affects the structure and function of cells which determines
Molecular Genetics Principles of Gene Expression: Transcription
 Paper No. : 16 Module : 12 Principles of gene expression: Transcription Development Team Principal Investigator: Prof. Neeta Sehgal Head, Department of Zoology, University of Delhi Paper Coordinator: Prof.
Paper No. : 16 Module : 12 Principles of gene expression: Transcription Development Team Principal Investigator: Prof. Neeta Sehgal Head, Department of Zoology, University of Delhi Paper Coordinator: Prof.
Genes and How They Work. Chapter 15
 Genes and How They Work Chapter 15 The Nature of Genes They proposed the one gene one enzyme hypothesis. Today we know this as the one gene one polypeptide hypothesis. 2 The Nature of Genes The central
Genes and How They Work Chapter 15 The Nature of Genes They proposed the one gene one enzyme hypothesis. Today we know this as the one gene one polypeptide hypothesis. 2 The Nature of Genes The central
Transcription & RNA Processing
 Chapter 10. Transcription & RNA Processing 1. Transfer of Genetic Information: the Central Dogma 2. The Process of Gene Expression 3. Transcription & RNA Processing in Eukaryotes 4. Interrupted Genes in
Chapter 10. Transcription & RNA Processing 1. Transfer of Genetic Information: the Central Dogma 2. The Process of Gene Expression 3. Transcription & RNA Processing in Eukaryotes 4. Interrupted Genes in
DNA Function: Information Transmission
 DNA Function: Information Transmission DNA is called the code of life. What does it code for? *the information ( code ) to make proteins! Why are proteins so important? Nearly every function of a living
DNA Function: Information Transmission DNA is called the code of life. What does it code for? *the information ( code ) to make proteins! Why are proteins so important? Nearly every function of a living
The Flow of Genetic Information
 Chapter 17 The Flow of Genetic Information The DNA inherited by an organism leads to specific traits by dictating the synthesis of proteins and of RNA molecules involved in protein synthesis. Proteins
Chapter 17 The Flow of Genetic Information The DNA inherited by an organism leads to specific traits by dictating the synthesis of proteins and of RNA molecules involved in protein synthesis. Proteins
Differential Gene Expression
 Developmental Biology Biology 4361 Differential Gene Expression October 13, 2005 core transcription initiation site 5 promoter 3 TATAT +1 upstream downstream Basal transcription factors (eukaryotes) TFIID
Developmental Biology Biology 4361 Differential Gene Expression October 13, 2005 core transcription initiation site 5 promoter 3 TATAT +1 upstream downstream Basal transcription factors (eukaryotes) TFIID
Wednesday, November 22, 17. Exons and Introns
 Exons and Introns Introns and Exons Exons: coded regions of DNA that get transcribed and translated into proteins make up 5% of the genome Introns and Exons Introns: non-coded regions of DNA Must be removed
Exons and Introns Introns and Exons Exons: coded regions of DNA that get transcribed and translated into proteins make up 5% of the genome Introns and Exons Introns: non-coded regions of DNA Must be removed
Chapter 13. From DNA to Protein
 Chapter 13 From DNA to Protein Proteins All proteins consist of polypeptide chains A linear sequence of amino acids Each chain corresponds to the nucleotide base sequenceof a gene The Path From Genes to
Chapter 13 From DNA to Protein Proteins All proteins consist of polypeptide chains A linear sequence of amino acids Each chain corresponds to the nucleotide base sequenceof a gene The Path From Genes to
B. Incorrect! Centromeric DNA is largely heterochromatin, which is inactive DNA.
 MCAT Biology - Problem Drill 06: Molecular Biology of Eukaryotes Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which type of DNA would have the highest level of expression? Question #01 (A) Heterochromatin. (B) Centromeric
MCAT Biology - Problem Drill 06: Molecular Biology of Eukaryotes Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which type of DNA would have the highest level of expression? Question #01 (A) Heterochromatin. (B) Centromeric
A. Incorrect! This feature does help with it suitability as genetic material.
 College Biology - Problem Drill 08: Gene Structures and Functions No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the statements below is NOT true in explaining why DNA is a suitable genetic material? #01 (A) Its double helix
College Biology - Problem Drill 08: Gene Structures and Functions No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the statements below is NOT true in explaining why DNA is a suitable genetic material? #01 (A) Its double helix
Biochemistry 302. Exam 2. March 10, Answer Key
 1 Biochemistry 302 Exam 2 March 10, 2004 Answer Key 2 Biochemistry 302, Spring 2004 Exam 2 (100 points) Name I. Short answer 1. Identify the 5 end, 3 end, amino acid acceptor nucleoside, and bases comprising
1 Biochemistry 302 Exam 2 March 10, 2004 Answer Key 2 Biochemistry 302, Spring 2004 Exam 2 (100 points) Name I. Short answer 1. Identify the 5 end, 3 end, amino acid acceptor nucleoside, and bases comprising
Ch. 10 From DNA to Protein. AP Biology
 Ch. 10 From DNA to Protein Protein Synthesis Metabolism and Gene Expression n Inheritance of metabolic diseases suggests that genes coded for enzymes n Diseases (phenotypes) caused by non-functional gene
Ch. 10 From DNA to Protein Protein Synthesis Metabolism and Gene Expression n Inheritance of metabolic diseases suggests that genes coded for enzymes n Diseases (phenotypes) caused by non-functional gene
I. Gene Expression Figure 1: Central Dogma of Molecular Biology
 I. Gene Expression Figure 1: Central Dogma of Molecular Biology Central Dogma: Gene Expression: RNA Structure RNA nucleotides contain the pentose sugar Ribose instead of deoxyribose. Contain the bases
I. Gene Expression Figure 1: Central Dogma of Molecular Biology Central Dogma: Gene Expression: RNA Structure RNA nucleotides contain the pentose sugar Ribose instead of deoxyribose. Contain the bases
Fermentation. Lesson Overview. Lesson Overview 13.1 RNA
 13.1 RNA THINK ABOUT IT DNA is the genetic material of cells. The sequence of nucleotide bases in the strands of DNA carries some sort of code. In order for that code to work, the cell must be able to
13.1 RNA THINK ABOUT IT DNA is the genetic material of cells. The sequence of nucleotide bases in the strands of DNA carries some sort of code. In order for that code to work, the cell must be able to
Chapter 2. An Introduction to Genes and Genomes
 PowerPoint Lectures for Introduction to Biotechnology, Second Edition William J.Thieman and Michael A.Palladino Chapter 2 An Introduction to Genes and Genomes Lectures by Lara Dowland Chapter Contents
PowerPoint Lectures for Introduction to Biotechnology, Second Edition William J.Thieman and Michael A.Palladino Chapter 2 An Introduction to Genes and Genomes Lectures by Lara Dowland Chapter Contents
The Genetic Code and Transcription. Chapter 12 Honors Genetics Ms. Susan Chabot
 The Genetic Code and Transcription Chapter 12 Honors Genetics Ms. Susan Chabot TRANSCRIPTION Copy SAME language DNA to RNA Nucleic Acid to Nucleic Acid TRANSLATION Copy DIFFERENT language RNA to Amino
The Genetic Code and Transcription Chapter 12 Honors Genetics Ms. Susan Chabot TRANSCRIPTION Copy SAME language DNA to RNA Nucleic Acid to Nucleic Acid TRANSLATION Copy DIFFERENT language RNA to Amino
Biological information flow
 BCMB 3100 Chapters 36-38 Transcription & RNA Processing Definition of gene RNA Polymerase Gene coding vs template strand Promoter Transcription in E. coli Transcription factors mrna processing Biological
BCMB 3100 Chapters 36-38 Transcription & RNA Processing Definition of gene RNA Polymerase Gene coding vs template strand Promoter Transcription in E. coli Transcription factors mrna processing Biological
Chapters 31-32: Ribonucleic Acid (RNA)
 Chapters 31-32: Ribonucleic Acid (RNA) Short segments from the transcription, processing and translation sections of each chapter Slide 1 RNA In comparison with DNA RNA utilizes uracil in place of thymine
Chapters 31-32: Ribonucleic Acid (RNA) Short segments from the transcription, processing and translation sections of each chapter Slide 1 RNA In comparison with DNA RNA utilizes uracil in place of thymine
Chapter 17 Lecture. Concepts of Genetics. Tenth Edition. Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes
 Chapter 17 Lecture Concepts of Genetics Tenth Edition Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes Chapter Contents 17.1 Eukaryotic Gene Regulation Can Occur at Any of the Steps Leading from DNA to Protein
Chapter 17 Lecture Concepts of Genetics Tenth Edition Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes Chapter Contents 17.1 Eukaryotic Gene Regulation Can Occur at Any of the Steps Leading from DNA to Protein
Biology. Biology. Slide 1 of 39. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology Biology 1 of 39 12-3 RNA and Protein Synthesis 2 of 39 Essential Question What is transcription and translation and how do they take place? 3 of 39 12 3 RNA and Protein Synthesis Genes are coded
Biology Biology 1 of 39 12-3 RNA and Protein Synthesis 2 of 39 Essential Question What is transcription and translation and how do they take place? 3 of 39 12 3 RNA and Protein Synthesis Genes are coded
Biology. Biology. Slide 1 of 39. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology Biology 1 of 39 12-3 RNA and Protein Synthesis 2 of 39 12 3 RNA and Protein Synthesis Genes are coded DNA instructions that control the production of proteins. Genetic messages can be decoded by
Biology Biology 1 of 39 12-3 RNA and Protein Synthesis 2 of 39 12 3 RNA and Protein Synthesis Genes are coded DNA instructions that control the production of proteins. Genetic messages can be decoded by
Lecture for Wednesday. Dr. Prince BIOL 1408
 Lecture for Wednesday Dr. Prince BIOL 1408 THE FLOW OF GENETIC INFORMATION FROM DNA TO RNA TO PROTEIN Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Genes are expressed as proteins A gene is a segment of DNA that
Lecture for Wednesday Dr. Prince BIOL 1408 THE FLOW OF GENETIC INFORMATION FROM DNA TO RNA TO PROTEIN Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Genes are expressed as proteins A gene is a segment of DNA that
Feedback D. Incorrect! No, although this is a correct characteristic of RNA, this is not the best response to the questions.
 Biochemistry - Problem Drill 23: RNA No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements best describes the structural highlights of RNA? (A) RNA can be single or double stranded. (B) G-C pairs have 3 hydrogen
Biochemistry - Problem Drill 23: RNA No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements best describes the structural highlights of RNA? (A) RNA can be single or double stranded. (B) G-C pairs have 3 hydrogen
From Gene to Protein. Chapter 17
 From Gene to Protein Chapter 17 What you need to know: The key terms: gene expression, transcription, and translation. The major events of transcription. How eukaryotic cells modify RNA after transcription.
From Gene to Protein Chapter 17 What you need to know: The key terms: gene expression, transcription, and translation. The major events of transcription. How eukaryotic cells modify RNA after transcription.
The RNA Polymerase II General Transcription Machinery Prof. Michael Hampsey
 The RNA Polymerase II General Transcription Machinery Michael Hampsey, PhD Robert Wood Johnson Medical School Piscataway, New Jersey 1 Central Dogma of Molecular Biology DNA Stores genetic information
The RNA Polymerase II General Transcription Machinery Michael Hampsey, PhD Robert Wood Johnson Medical School Piscataway, New Jersey 1 Central Dogma of Molecular Biology DNA Stores genetic information
Chapter 8 Lecture Outline. Transcription, Translation, and Bioinformatics
 Chapter 8 Lecture Outline Transcription, Translation, and Bioinformatics Replication, Transcription, Translation n Repetitive processes Build polymers of nucleotides or amino acids n All have 3 major steps
Chapter 8 Lecture Outline Transcription, Translation, and Bioinformatics Replication, Transcription, Translation n Repetitive processes Build polymers of nucleotides or amino acids n All have 3 major steps
Proofreading, post-replication modification of DNA. Mitesh Shrestha
 Proofreading, post-replication modification of DNA Mitesh Shrestha Proofreading During DNA replication (copying), most DNA polymerases can check their work with each base that they add. This process is
Proofreading, post-replication modification of DNA Mitesh Shrestha Proofreading During DNA replication (copying), most DNA polymerases can check their work with each base that they add. This process is
Matakuliah Genetika (BIO612206) Jurusan Biologi FMIPA Universitas Lampung. Priyambodo, M.Sc. staff.unila.ac.id/priyambodo
 Matakuliah Genetika (BIO612206) Jurusan Biologi FMIPA Universitas Lampung Priyambodo, M.Sc. staff.unila.ac.id/priyambodo Prokariotik Eukariotik staff.unila.ac.id/priyambodo Regulasi ekspresi gen pada
Matakuliah Genetika (BIO612206) Jurusan Biologi FMIPA Universitas Lampung Priyambodo, M.Sc. staff.unila.ac.id/priyambodo Prokariotik Eukariotik staff.unila.ac.id/priyambodo Regulasi ekspresi gen pada
RNA Expression of the information in a gene generally involves production of an RNA molecule transcribed from a DNA template. RNA differs from DNA
 RNA Expression of the information in a gene generally involves production of an RNA molecule transcribed from a DNA template. RNA differs from DNA that it has a hydroxyl group at the 2 position of the
RNA Expression of the information in a gene generally involves production of an RNA molecule transcribed from a DNA template. RNA differs from DNA that it has a hydroxyl group at the 2 position of the
Chromatographic Separation of the three forms of RNA Polymerase II.
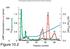 Chromatographic Separation of the three forms of RNA Polymerase II. α-amanitin α-amanitin bound to Pol II Function of the three enzymes. Yeast Pol II. RNA Polymerase Subunit Structures 10-7 Subunit structure.
Chromatographic Separation of the three forms of RNA Polymerase II. α-amanitin α-amanitin bound to Pol II Function of the three enzymes. Yeast Pol II. RNA Polymerase Subunit Structures 10-7 Subunit structure.
Videos. Lesson Overview. Fermentation
 Lesson Overview Fermentation Videos Bozeman Transcription and Translation: https://youtu.be/h3b9arupxzg Drawing transcription and translation: https://youtu.be/6yqplgnjr4q Objectives 29a) I can contrast
Lesson Overview Fermentation Videos Bozeman Transcription and Translation: https://youtu.be/h3b9arupxzg Drawing transcription and translation: https://youtu.be/6yqplgnjr4q Objectives 29a) I can contrast
Genetics Biology 331 Exam 3B Spring 2015
 Genetics Biology 331 Exam 3B Spring 2015 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) DNA methylation may be a significant mode of genetic regulation
Genetics Biology 331 Exam 3B Spring 2015 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) DNA methylation may be a significant mode of genetic regulation
