Supplemental Data. Polycomb Silencing of KNOX Genes Confines. Shoot Stem Cell Niches in Arabidopsis Current Biology, Volume 18
|
|
|
- Grant Sparks
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Supplemental Data Polycomb Silencing of KNOX Genes Confines Shoot Stem Cell Niches in Arabidopsis Lin Xu and Wen-Hui Shen - 1 -
2 Figure S1. Phylogram of RING1, BMI1 and RAD18 homologues in several organisms The phylogenic analysis was performed using MEGA3.0 package with bootstrapping set at 500 replicates
3 Figure S2. Alignment of AtRING1a and AtRING1b amino acid sequences Consensus symbols below the alignments indicate: identical residues (*), conserved (:) and semi-conserved (.) substitutions. The alignment was generated using CLUSTALW program
4 Figure S3. RT-PCR analysis of AtRING1a and AtRING1b expression in different organs of the wild-type Col plants - 4 -
5 Figure S4. Production and mature plant phenotype of Atring1a -/- Atring1b -/- mutant (A) A schematic representation of procedures in obtaining the double mutant Atring1a -/- Atring1b -/-. The two homozygous mutant alleles Atring1a -/- and Atring1b -/- were combined together by crossing. Then through selfing and genotyping by PCR, Line-29 with genotype Atring1a -/- AtRING1b +/- and Line-22 with genotype AtRING1a +/- Atring1b -/- were obtained. (B) Comparison of a 35-day-old wild-type Col plant and a 50-day-old mutant Atring1a -/- Atring1b - /- plant. Note that the mutant plant is sterile and cannot set siliques
6 Figure S5. Rescue of the Atring1a -/- Atring1b -/- mutant phenotype by transformation with AtRING1a or AtRING1b gene (A) Diagram of genomic organization at the AtRING1a and AtRING1b gene regions in two BAC clones. The XbaI-SalI fragment containing AtRING1a (patring1a) and the SalI-SacI fragment containing AtRING1b (patring1b) are used to rescue the Atring1a -/- Atring1b -/- mutant. (B) Comparison of 23-day-old plants and inflorescences of the Atring1a -/- Atring1b -/- mutant with the same mutant rescued by patring1a or patring1b. Bars = 5 mm
7 Figure S6. ChIP analysis of H3K27 trimethylation at STM, KNAT2, KNAT6 and AG in the mutants Atring1a -/- Atring1b -/- and cl f-/- compared with the wild-type Col (A) Diagram of STM, KNAT2, KNAT6 and AG gene structure indicating the regions examined by ChIP. Black boxes represent exons; lines represent promoter and introns; bars labed I-III represent regions amplified by PCR. (B) ChIP analysis with antibodies specific to trimethyl-h3k day-old plants of the wildtype Col and the mutants Atring1a -/- Atring1b -/- and clf -/- were analyzed. Input and no antibody (-) are shown as positive and negative controls
8 Table S1. List of primers used in this study. Name Sequence AGI ID Gene name Position (ATG or ACG= +1~+3) RT-PCR primers AtRING1a-F1 5 gactagtatgtctgtcaagaat AATAG At5g44280 AtRING1a +1~+21 AtRING1a-R1 5 AGAACCTGTGGAGACATTC At5g44280 AtRING1a +1192~+1173 AtRING1b-F1 5 cgggatccatgccttccttgaa GAGCTT At1g03770 AtRING1b +1~+21 AtRING1b-R1 5 CAGATATCCGCTAGATCAA CAAC At1g03770 AtRING1b +730~+707 STM-F4 5 AAGCTGAGGATAGAGAG At1g62360 STM +1920~+1937 STM-R3 5 GGATCGATCAAAGCATGG At1g62360 STM +2934~+2917 KNAT1-F1 5 TGTCAGAGTCCCATTCA At4g08150 KNAT1 +915~+932 KNAT1-R1 5 GCAACGAGAGGTTGTTATT3 At4g08150 KNAT ~+2667 KNAT2-F1 5 TGACGAGGAACTGAGAGAA G At1g70510 KNAT ~+5061 KNAT2-R1 5 GGTTCCATTCATTCGCGATG At1g70510 KNAT ~+5605 KNAT6-F1 5 GGTGTAATATCATCTGACG3 At1g23380 KNAT ~+4528 KNAT6-R1 5 TGTCGTCCATGCTTCACT At1g23380 KNAT ~+5083 WUS-F1 5 TAACAAGCCATATCCCAGC3 At2g17950 WUS +468~+486 WUS-R1 5 GCTTTAATCCCGAGCGA At2g17950 WUS +1603~+1586 CLV3-F1 5 TGTACTCATTAAGGCCTCTC At2g27250 CLV3-46~-27 CLV3-R1 5 CATGAAACTACAAGCTTAC At2g27250 CLV3 +408~+389 AG-F1 5 AATCAGCCAAATTGCGTCA A At4g18960 AG +3427~+3447 AG-R1 5 GCTTTATATTGCTTGCTCAA C At4g18960 AG +4423~+4402 AP3-F1 5 GAGACAAATAGAAATCTCC G At3g54340 AP3 +470~+489 AP3-R1 5 TAGACAATGATGGCACCAG At3g54340 AP ~+1679 AS1-F1 5 GAAGTTGCTCTTGAGTTTGG G At2g37630 AS1-426~+-406 AS1-R1 5 GCTCAACTCTCTTGTTACTC At2g37630 AS1 +358~+339 AS2-F1 5 CCTCTGAGCAACAGAAGCC At1g65620 AS2-371~-353 AS2-R1 5 CCGAGGCTTTGGTACTTAG3 At1g65620 AS2 +347~+329 ACTIN-F1 AAGTCATAACCATCGGAGCT G At5g09810 ACTIN +923~+943 ACTIN-R1 ACCAGATAAGACAAGACACA C At5g09810 ACTIN +1433~+1413 Genomic PCR primers AtRING1a-F2 5 CCAGATGTGTTTAGCTTGTG At5g44280 AtRING1a +502~+521 AtRING1a-R1 5 AGAACCTGTGGAGACATTC At5g44280 AtRING1a +1192~
9 AtRING1b-F1 AtRING1b-R1 Cloning primers AtRING1a-F1 AtRING1a-R2 AtRING1b-F1 AtRING1b-R2 AtRING1a- FLAG-F LHP1-F1 LHP1-R1 CLF-F1 CLF-R1 5 cgggatccatgccttccttgaa GAGCTT 5 CAGATATCCGCTAGATCAA CAAC 5 gactagtatgtctgtcaagaat AATAG 5 ccgctcgagcacgtccattaggc TCCAAGTTT 5 cgggatccatgccttccttgaa GAGCTT 5 ccgctcgagtcacactgtttgaa TTACTTG 5 agatctatggactacaaagacc ATGACGGTGATTATAAAGATC ATGATATCGATTACAAGGATG ACGATGACAAGggatccATGTCT GTCAAGAATAATAG 5 gaagatctatgaaaggggcaag TGGTG 5 ccgctcgagttaaggcgttcgat TGTACT 5 cgggatccatggcgtcagaagc TTCGC 5 ggaattcgcgttcttccacctgt AAC At1g03770 AtRING1b +1~+21 At1g03770 AtRING1b +730~+707 At5g44280 AtRING1a +1~+21 At5g44280 AtRING1a +3026~+3002 At1g03770 AtRING1b +1~+21 At1g03770 AtRING1b +2693~+2673 At5g44280 AtRING1a +1~+21 At5g17690 LHP1 +1~+20 At5g17690 LHP ~+2015 At2g23380 CLF +1~+20 At2g23380 CLF +4604~+4585 ChIP PCR primers STM-F1 5 CCTTAGATTTATCTTCCTGG At1g62360 STM (I) -362~-343 STM-R1 5 GGCTTTGCTATATAGCTATG At1g62360 STM (I) -36~-55 STM-F2 5 CATAGCTATATAGCAAAGC At1g62360 STM (II) -55~-36 STM-R2 5 AGAATAGGCAGGAGCACAA G At1g62360 STM (II) +285~+266 STM-F3 5 GAGAGAACACTTGATGATT G At1g62360 STM (III) +2667~+2686 STM-R3 5 GGATCGATCAAAGCATGG At1g62360 STM (III) +2934~+2917 KNAT2-F2 5 GATATTATACGCGACTAAC AG At1g70510 KNAT2 (I) -967~-947 KNAT2-R2 5 TTACGGTGGCCGACACCTA At1g70510 KNAT2 (I) -676~-695 KNAT6-F2 5 ACAAGTTTCATTTCCATAGC At1g23380 KNAT6 (I) +1087~+1106 KNAT6-R2 5 CATTCAGTACGCAACAAGC At1g23380 KNAT6 (I) +1425~+1406 AG-F2 5 AAGCTAGATTTGATTCTCTT At4g18960 AG (I) +353~+373 AG-R2 5 CTCAGATCTCCTTTAACTTT G At4g18960 AG (I) +646~+626 The lowercase letters in the primer sequences represent additional nucleotides to introduce restriction sites
10 Supplemental Experimental Procedures Plant materials and growth conditions All Arabidopsis alleles were derived from the Columbia (Col) ecotype. Seeds of mutants Atring1a -/- (AL_945948), Atring1b -/- (SALK_117958), clf -/- (CLF-29) and lhp1 -/- (tlf2-2) were obtained from the Arabidopsis Biological Resource Center (ABRC) and Nottingham Arabidopsis Stock Centre (NASC) ( Double and triple mutants and GUS-reporter constructs, described in the text, were obtained by crossing appropriate plant lines. Plants were grown in the greenhouse under 16h light and 8h dark at 22 C. RT-PCR analysis Total RNA was prepared from plant tissues using TRI Reagent (Invitrogen, After treatment with DNase (Promega, complementary DNA was synthesized using a reverse transcription kit according to the manufacturer s recommendation (Promega). PCR amplification from the cdna template was performed using gene-specific primers (see Supplemental Table S1). Complementation of mutant plants The genomic fragments containing AtRING1a and AtRING1b were isolated from BAC K9L2 and BAC F21M11 by digestion with the restriction enzyme couples XbaI-SalI and SalI-SacI, respectively. They were cloned into the pcambia1300 vector (Cambia, and the resulting constructs were used to transform [26] the Atring1a - /- AtRING1b +/- and AtRING1a +/- Atring1b -/- plants, respectively. In the T1-generation of transformed plants, progeny with the mutant Atring1a -/- Atring1b -/- background containing a transgene were identified by genomic PCR analysis using gene-specific primers (see Supplemental Table S1). Histology and microscopy Small organs or seedlings of wild-type and mutant plants were examined using a LEICA MZ12 dissecting microscope (Leica France, Rueil-Malmaison, France). Higher magnification photographs were taken using a Nikon Eclipse 800 microscope (Nikon France, Champigny sur Marne, France), which was also used for examination of histology sections prepared as
11 described in Yu et al. [26]. Confocal microscopy images were taken using a ZEISS LSM510 microscope (Carl Zeiss, Jena, Germany). Scanning electron microscopy images were taken using a Hitachi S-2460 (Hittachi, Japan). Preparation of thin section specimens and scanning electron microscopy were as described in Chen et al. [27]. Histochemical GUS activity assay Plant material for GUS activity assay was freshly collected and immersed in the GUS staining buffer [26]. After incubation under vacuum for 15min, to facilitate entry of the substrate, the enzymatic reaction was maintained by incubation at 37 C for 14h. Plant material was cleared by 70% ethanol, and observed directly under the dissecting microscope or fixed, sectioned and observed under the Nikon Eclipse 800 microscope. Protein subcellular localization Subcellular localization of AtRING1a and AtRING1b was investigated with GFP- or YFPfused proteins as described previously [26, 28]. The entire coding regions of AtRING1a and AtRING1b cdnas were obtained by RT-PCR from the wild-type Col inflorescences using the primer pairs AtRING1a-F1 with AtRING1a-R2 and AtRING1b-F1 with AtRING1b-R2 (see Supplemental Table S1), respectively. They were fused with the end of GFP or YFP cdna and subcloned under the control of the CaMV 35S promoter. Transgenic plants expressing GFP-fused AtRING1a or YFP-fused AtRING1b were obtained. The GFP and YFP fluorescence images of cells from transgenic plants were taken using the ZEISS LSM510 microscope. Yeast two-hybrid assays CLF and LHP1 cdnas were obtained by RT-PCR from the wild-type Col inflorescences using the primer pairs CLF-F1 with CLF-R1 and LHP1-F1 with LHP1-R1 (see Supplemental Table S1), respectively. These cdnas, as well as the AtRING1a and AtRING1b cdnas, were cloned into the pgbkt7 and pgadt7 vectors (Clontech, AS1 and AS2 constructs were described previously [29]. Construct combinations of a pgadt7- based and a pgbkt7-based expression vector were co-transformed into the yeast strain PHA69-4A, and transformants were selected for growth on media lacking tryptophan and leucine. The interaction between proteins was tested by growth of the transformants on media lacking tryptophan, leucine and adenine
12 Pulldown assays The AtRING1a cdna fused to 3xFLAG tag sequences was obtained by PCR amplification using primers AtRING1a-FLAG-F and AtRING1a-R2 (see Supplemental Table S1), and cloned under the control of the CaMV 35S promoter. Transgenic plants expressing FLAG- AtRING1a were obtained. The CLF and LHP1 cdnas were cloned into the BamHI-XhoI sites of pgex-4t-1 for production of GST-fused proteins. Production and purification of GST- CLF and GST-LHP1 proteins were performed according to the manufacturer s recommendation (Amersham-Pharmacia Biotech, Pulldown experiments were performed according to the previously described protocol [30]. Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP) ChIP was performed as previously described [28] using 15-day-old seedlings. Antibodies against H3 trimethyl-lys 27 (Upstate Catalogue no , and gene specific PCR-primers (see Supplemental Table S1) were used in the analysis. Supplemental References 26. Yu, Y., Steinmetz, A., Meyer, D., Brown, S., and Shen, W.H. (2003). The tobacco A- type cyclin, Nicta;CYCA3;2, at the nexus of cell division and differentiation. Plant Cell 15, Chen, C., Wang, S., and Huang, H. (2000). LEUNIG has multiple functions in gynoecium development in Arabidopsis. Genesis 26, Xu, L., Zhao, Z., Dong, A., Soubigou-Taconnat, L., Renou, J.P., Steinmetz, A., and Shen, W.H. (2008). Di- and tri- but not monomethylation on histone H3 lysine 36 marks active transcription of genes involved in flowering time regulation and other processes in Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol Cell Biol 28, Xu, L., Xu, Y., Dong, A., Sun, Y., Pi, L., Xu, Y., and Huang, H. (2003). Novel as1 and as2 defects in leaf adaxial-abaxial polarity reveal the requirement for ASYMMETRIC LEAVES1 and 2 and ERACTA functions in specifying leaf adaxial identity. Development 130, Yu, Y., Dong, A., and Shen, W. (2004). Molecular characterization of the tobacco SET domain protein NtSET1 unravels its role in histone methylation, chromatin binding, and segregation. Plant J. 40,
Construction of plant complementation vector and generation of transgenic plants
 MATERIAL S AND METHODS Plant materials and growth conditions Arabidopsis ecotype Columbia (Col0) was used for this study. SALK_072009, SALK_076309, and SALK_027645 were obtained from the Arabidopsis Biological
MATERIAL S AND METHODS Plant materials and growth conditions Arabidopsis ecotype Columbia (Col0) was used for this study. SALK_072009, SALK_076309, and SALK_027645 were obtained from the Arabidopsis Biological
Jung-Nam Cho, Jee-Youn Ryu, Young-Min Jeong, Jihye Park, Ji-Joon Song, Richard M. Amasino, Bosl Noh, and Yoo-Sun Noh
 Developmental Cell, Volume 22 Supplemental Information Control of Seed Germination by Light-Induced Histone Arginine Demethylation Activity Jung-Nam Cho, Jee-Youn Ryu, Young-Min Jeong, Jihye Park, Ji-Joon
Developmental Cell, Volume 22 Supplemental Information Control of Seed Germination by Light-Induced Histone Arginine Demethylation Activity Jung-Nam Cho, Jee-Youn Ryu, Young-Min Jeong, Jihye Park, Ji-Joon
Supplementary information, Figure S1
 Supplementary information, Figure S1 (A) Schematic diagram of the sgrna and hspcas9 expression cassettes in a single binary vector designed for Agrobacterium-mediated stable transformation of Arabidopsis
Supplementary information, Figure S1 (A) Schematic diagram of the sgrna and hspcas9 expression cassettes in a single binary vector designed for Agrobacterium-mediated stable transformation of Arabidopsis
A subclass of HSP70s regulate development and abiotic stress responses in Arabidopsis thaliana
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 Journal of Plant Research A subclass of HSP70s regulate development and abiotic stress responses in Arabidopsis thaliana Linna Leng 1 Qianqian Liang
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 Journal of Plant Research A subclass of HSP70s regulate development and abiotic stress responses in Arabidopsis thaliana Linna Leng 1 Qianqian Liang
Supplemental Data. Lee et al. Plant Cell. (2010) /tpc Supplemental Figure 1. Protein and Gene Structures of DWA1 and DWA2.
 Supplemental Figure 1. Protein and Gene Structures of DWA1 and DWA2. (A) Protein structures of DWA1 and DWA2. WD40 region was determined based on the NCBI conserved domain databases (B, C) Schematic representation
Supplemental Figure 1. Protein and Gene Structures of DWA1 and DWA2. (A) Protein structures of DWA1 and DWA2. WD40 region was determined based on the NCBI conserved domain databases (B, C) Schematic representation
Supplemental Data. Osakabe et al. (2013). Plant Cell /tpc
 Supplemental Figure 1. Phylogenetic analysis of KUP in various species. The amino acid sequences of KUPs from green algae and land plants were identified with a BLAST search and aligned using ClustalW
Supplemental Figure 1. Phylogenetic analysis of KUP in various species. The amino acid sequences of KUPs from green algae and land plants were identified with a BLAST search and aligned using ClustalW
Alternative Cleavage and Polyadenylation of RNA
 Developmental Cell 18 Supplemental Information The Spen Family Protein FPA Controls Alternative Cleavage and Polyadenylation of RNA Csaba Hornyik, Lionel C. Terzi, and Gordon G. Simpson Figure S1, related
Developmental Cell 18 Supplemental Information The Spen Family Protein FPA Controls Alternative Cleavage and Polyadenylation of RNA Csaba Hornyik, Lionel C. Terzi, and Gordon G. Simpson Figure S1, related
Enhancers mutations that make the original mutant phenotype more extreme. Suppressors mutations that make the original mutant phenotype less extreme
 Interactomics and Proteomics 1. Interactomics The field of interactomics is concerned with interactions between genes or proteins. They can be genetic interactions, in which two genes are involved in the
Interactomics and Proteomics 1. Interactomics The field of interactomics is concerned with interactions between genes or proteins. They can be genetic interactions, in which two genes are involved in the
Candidate region (0.74 Mb) ATC TCT GGG ACT CAT GAG CAG GAG GCT AGC ATC TCT GGG ACT CAT TAG CAG GAG GCT AGC
 A idm-3 idm-3 B Physical distance (Mb) 4.6 4.86.6 8.4 C Chr.3 Recom. Rate (%) ATG 3.9.9.9 9.74 Candidate region (.74 Mb) n=4 TAA D idm-3 G3T(E4) G4A(W988) WT idm-3 ATC TCT GGG ACT CAT GAG CAG GAG GCT AGC
A idm-3 idm-3 B Physical distance (Mb) 4.6 4.86.6 8.4 C Chr.3 Recom. Rate (%) ATG 3.9.9.9 9.74 Candidate region (.74 Mb) n=4 TAA D idm-3 G3T(E4) G4A(W988) WT idm-3 ATC TCT GGG ACT CAT GAG CAG GAG GCT AGC
Supplemental Data Supplemental Figure 1.
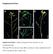 Supplemental Data Supplemental Figure 1. Silique arrangement in the wild-type, jhs, and complemented lines. Wild-type (WT) (A), the jhs1 mutant (B,C), and the jhs1 mutant complemented with JHS1 (Com) (D)
Supplemental Data Supplemental Figure 1. Silique arrangement in the wild-type, jhs, and complemented lines. Wild-type (WT) (A), the jhs1 mutant (B,C), and the jhs1 mutant complemented with JHS1 (Com) (D)
Supplemental Data. Steiner et al. Plant Cell. (2012) /tpc
 Supplemental Figure 1. SPY does not interact with free GST. Invitro pull-down assay using E. coli-expressed MBP-SPY and GST, GST-TCP14 and GST-TCP15. MBP-SPY was used as bait and incubated with equal amount
Supplemental Figure 1. SPY does not interact with free GST. Invitro pull-down assay using E. coli-expressed MBP-SPY and GST, GST-TCP14 and GST-TCP15. MBP-SPY was used as bait and incubated with equal amount
Using mutants to clone genes
 Using mutants to clone genes Objectives 1. What is positional cloning? 2. What is insertional tagging? 3. How can one confirm that the gene cloned is the same one that is mutated to give the phenotype
Using mutants to clone genes Objectives 1. What is positional cloning? 2. What is insertional tagging? 3. How can one confirm that the gene cloned is the same one that is mutated to give the phenotype
Gene Expression Technology
 Gene Expression Technology Bing Zhang Department of Biomedical Informatics Vanderbilt University bing.zhang@vanderbilt.edu Gene expression Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene
Gene Expression Technology Bing Zhang Department of Biomedical Informatics Vanderbilt University bing.zhang@vanderbilt.edu Gene expression Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene
7 Gene Isolation and Analysis of Multiple
 Genetic Techniques for Biological Research Corinne A. Michels Copyright q 2002 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd ISBNs: 0-471-89921-6 (Hardback); 0-470-84662-3 (Electronic) 7 Gene Isolation and Analysis of Multiple
Genetic Techniques for Biological Research Corinne A. Michels Copyright q 2002 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd ISBNs: 0-471-89921-6 (Hardback); 0-470-84662-3 (Electronic) 7 Gene Isolation and Analysis of Multiple
Supplementary Figure S1. Immunodetection of full-length XA21 and the XA21 C-terminal cleavage product.
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure S1. Immunodetection of full-length XA21 and the XA21 C-terminal cleavage product. Total protein extracted from Kitaake wild type and rice plants carrying
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure S1. Immunodetection of full-length XA21 and the XA21 C-terminal cleavage product. Total protein extracted from Kitaake wild type and rice plants carrying
Supplemental Information. Boundary Formation through a Direct. Threshold-Based Readout. of Mobile Small RNA Gradients
 Developmental Cell, Volume 43 Supplemental Information Boundary Formation through a Direct Threshold-Based Readout of Mobile Small RNA Gradients Damianos S. Skopelitis, Anna H. Benkovics, Aman Y. Husbands,
Developmental Cell, Volume 43 Supplemental Information Boundary Formation through a Direct Threshold-Based Readout of Mobile Small RNA Gradients Damianos S. Skopelitis, Anna H. Benkovics, Aman Y. Husbands,
Multiple choice questions (numbers in brackets indicate the number of correct answers)
 1 Multiple choice questions (numbers in brackets indicate the number of correct answers) February 1, 2013 1. Ribose is found in Nucleic acids Proteins Lipids RNA DNA (2) 2. Most RNA in cells is transfer
1 Multiple choice questions (numbers in brackets indicate the number of correct answers) February 1, 2013 1. Ribose is found in Nucleic acids Proteins Lipids RNA DNA (2) 2. Most RNA in cells is transfer
Supplemental Data. Wu et al. (2). Plant Cell..5/tpc RGLG Hormonal treatment H2O B RGLG µm ABA µm ACC µm GA Time (hours) µm µm MJ µm IA
 Supplemental Data. Wu et al. (2). Plant Cell..5/tpc..4. A B Supplemental Figure. Immunoblot analysis verifies the expression of the AD-PP2C and BD-RGLG proteins in the Y2H assay. Total proteins were extracted
Supplemental Data. Wu et al. (2). Plant Cell..5/tpc..4. A B Supplemental Figure. Immunoblot analysis verifies the expression of the AD-PP2C and BD-RGLG proteins in the Y2H assay. Total proteins were extracted
CHAPTER 9 DNA Technologies
 CHAPTER 9 DNA Technologies Recombinant DNA Artificially created DNA that combines sequences that do not occur together in the nature Basis of much of the modern molecular biology Molecular cloning of genes
CHAPTER 9 DNA Technologies Recombinant DNA Artificially created DNA that combines sequences that do not occur together in the nature Basis of much of the modern molecular biology Molecular cloning of genes
Supplemental Figure 1
 Supplemental Data. Breuer et al. 2007. BIN4, a novel component of the plant DNA topoisomerase VI complex, is required for endoreduplication in Arabidopsis. Supplemental Figure 1 Endoreduplication stalls
Supplemental Data. Breuer et al. 2007. BIN4, a novel component of the plant DNA topoisomerase VI complex, is required for endoreduplication in Arabidopsis. Supplemental Figure 1 Endoreduplication stalls
INTRODUCTION TO REVERSE TRANSCRIPTION PCR (RT-PCR) ABCF 2016 BecA-ILRI Hub, Nairobi 21 st September 2016 Roger Pelle Principal Scientist
 INTRODUCTION TO REVERSE TRANSCRIPTION PCR (RT-PCR) ABCF 2016 BecA-ILRI Hub, Nairobi 21 st September 2016 Roger Pelle Principal Scientist Objective of PCR To provide a solution to one of the most pressing
INTRODUCTION TO REVERSE TRANSCRIPTION PCR (RT-PCR) ABCF 2016 BecA-ILRI Hub, Nairobi 21 st September 2016 Roger Pelle Principal Scientist Objective of PCR To provide a solution to one of the most pressing
Contents... vii. List of Figures... xii. List of Tables... xiv. Abbreviatons... xv. Summary... xvii. 1. Introduction In vitro evolution...
 vii Contents Contents... vii List of Figures... xii List of Tables... xiv Abbreviatons... xv Summary... xvii 1. Introduction...1 1.1 In vitro evolution... 1 1.2 Phage Display Technology... 3 1.3 Cell surface
vii Contents Contents... vii List of Figures... xii List of Tables... xiv Abbreviatons... xv Summary... xvii 1. Introduction...1 1.1 In vitro evolution... 1 1.2 Phage Display Technology... 3 1.3 Cell surface
Supplemental Data. mir156-regulated SPL Transcription. Factors Define an Endogenous Flowering. Pathway in Arabidopsis thaliana
 Cell, Volume 138 Supplemental Data mir156-regulated SPL Transcription Factors Define an Endogenous Flowering Pathway in Arabidopsis thaliana Jia-Wei Wang, Benjamin Czech, and Detlef Weigel Table S1. Interaction
Cell, Volume 138 Supplemental Data mir156-regulated SPL Transcription Factors Define an Endogenous Flowering Pathway in Arabidopsis thaliana Jia-Wei Wang, Benjamin Czech, and Detlef Weigel Table S1. Interaction
Figure S1. Figure S2. Figure S3 HB Anti-FSP27 (COOH-terminal peptide) Ab. Anti-GST-FSP27(45-127) Ab.
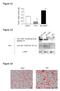 / 36B4 mrna ratio Figure S1 * 2. 1.6 1.2.8 *.4 control TNFα BRL49653 Figure S2 Su bw AT p iw Anti- (COOH-terminal peptide) Ab Blot : Anti-GST-(45-127) Ab β-actin Figure S3 HB2 HW AT BA T Figure S4 A TAG
/ 36B4 mrna ratio Figure S1 * 2. 1.6 1.2.8 *.4 control TNFα BRL49653 Figure S2 Su bw AT p iw Anti- (COOH-terminal peptide) Ab Blot : Anti-GST-(45-127) Ab β-actin Figure S3 HB2 HW AT BA T Figure S4 A TAG
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 11: Recombinant DNA
 Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 11: Recombinant DNA Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the sources of DNA used for molecular cloning is correct? Question #1 (A) cdna
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 11: Recombinant DNA Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the sources of DNA used for molecular cloning is correct? Question #1 (A) cdna
Fatchiyah
 Fatchiyah Email: fatchiya@yahoo.co.id RNAs: mrna trna rrna RNAi DNAs: Protein: genome DNA cdna mikro-makro mono-poly single-multi Analysis: Identification human and animal disease Finger printing Sexing
Fatchiyah Email: fatchiya@yahoo.co.id RNAs: mrna trna rrna RNAi DNAs: Protein: genome DNA cdna mikro-makro mono-poly single-multi Analysis: Identification human and animal disease Finger printing Sexing
Supplemental Figure 1. Mutation in NLA Causes Increased Pi Uptake Activity and
 Supplemental Figure 1. Mutation in NLA Causes Increased Pi Uptake Activity and PHT1 Protein Amounts. (A) Shoot morphology of 19-day-old nla mutants under Pi-sufficient conditions. (B) [ 33 P]Pi uptake
Supplemental Figure 1. Mutation in NLA Causes Increased Pi Uptake Activity and PHT1 Protein Amounts. (A) Shoot morphology of 19-day-old nla mutants under Pi-sufficient conditions. (B) [ 33 P]Pi uptake
GTTCGGGTTCC TTTTGAGCAG
 Supplementary Figures Splice variants of the SIP1 transcripts play a role in nodule organogenesis in Lotus japonicus. Wang C, Zhu H, Jin L, Chen T, Wang L, Kang H, Hong Z, Zhang Z. 5 UTR CDS 3 UTR TCTCAACCATCCTTTGTCTGCTTCCGCCGCATGGGTGAGGTCATTTTGTCTAGATGACGTGCAATTTACAATGA
Supplementary Figures Splice variants of the SIP1 transcripts play a role in nodule organogenesis in Lotus japonicus. Wang C, Zhu H, Jin L, Chen T, Wang L, Kang H, Hong Z, Zhang Z. 5 UTR CDS 3 UTR TCTCAACCATCCTTTGTCTGCTTCCGCCGCATGGGTGAGGTCATTTTGTCTAGATGACGTGCAATTTACAATGA
including, but not limited to:
 *This Section is part of the original Request for Proposal # P08 080. The Contractor should provide the following eligible Scientific Biomedical Research Equipment, Reagents & Supplies including, but not
*This Section is part of the original Request for Proposal # P08 080. The Contractor should provide the following eligible Scientific Biomedical Research Equipment, Reagents & Supplies including, but not
Activation of a Floral Homeotic Gene in Arabidopsis
 Activation of a Floral Homeotic Gene in Arabidopsis By Maximiliam A. Busch, Kirsten Bomblies, and Detlef Weigel Presentation by Lis Garrett and Andrea Stevenson http://ucsdnews.ucsd.edu/archive/graphics/images/image5.jpg
Activation of a Floral Homeotic Gene in Arabidopsis By Maximiliam A. Busch, Kirsten Bomblies, and Detlef Weigel Presentation by Lis Garrett and Andrea Stevenson http://ucsdnews.ucsd.edu/archive/graphics/images/image5.jpg
Supplementary Figure 1 qrt-pcr expression analysis of NLP8 with and without KNO 3 during germination.
 Supplementary Figure 1 qrt-pcr expression analysis of NLP8 with and without KNO 3 during germination. Seeds of Col-0 were harvested from plants grown at 16 C, stored for 2 months, imbibed for indicated
Supplementary Figure 1 qrt-pcr expression analysis of NLP8 with and without KNO 3 during germination. Seeds of Col-0 were harvested from plants grown at 16 C, stored for 2 months, imbibed for indicated
3 Designing Primers for Site-Directed Mutagenesis
 3 Designing Primers for Site-Directed Mutagenesis 3.1 Learning Objectives During the next two labs you will learn the basics of site-directed mutagenesis: you will design primers for the mutants you designed
3 Designing Primers for Site-Directed Mutagenesis 3.1 Learning Objectives During the next two labs you will learn the basics of site-directed mutagenesis: you will design primers for the mutants you designed
HiPer RT-PCR Teaching Kit
 HiPer RT-PCR Teaching Kit Product Code: HTBM024 Number of experiments that can be performed: 5 Duration of Experiment: Protocol: 4 hours Agarose Gel Electrophoresis: 45 minutes Storage Instructions: The
HiPer RT-PCR Teaching Kit Product Code: HTBM024 Number of experiments that can be performed: 5 Duration of Experiment: Protocol: 4 hours Agarose Gel Electrophoresis: 45 minutes Storage Instructions: The
PrimePCR Assay Validation Report
 Gene Information Gene Name Gene Symbol Organism Gene Summary Gene Aliases RefSeq Accession No. UniGene ID Ensembl Gene ID sema domain, immunoglobulin domain (Ig), short basic domain, secreted, (semaphorin)
Gene Information Gene Name Gene Symbol Organism Gene Summary Gene Aliases RefSeq Accession No. UniGene ID Ensembl Gene ID sema domain, immunoglobulin domain (Ig), short basic domain, secreted, (semaphorin)
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Yuan et al. 10.1073/pnas.0906869106 Fig. S1. Heat map showing that Populus ICS is coregulated with orthologs of Arabidopsis genes involved in PhQ biosynthesis and PSI function, but
Supporting Information Yuan et al. 10.1073/pnas.0906869106 Fig. S1. Heat map showing that Populus ICS is coregulated with orthologs of Arabidopsis genes involved in PhQ biosynthesis and PSI function, but
MIT Department of Biology 7.013: Introductory Biology - Spring 2005 Instructors: Professor Hazel Sive, Professor Tyler Jacks, Dr.
 MIT Department of Biology 7.01: Introductory Biology - Spring 2005 Instructors: Professor Hazel Sive, Professor Tyler Jacks, Dr. Claudette Gardel iv) Would Xba I be useful for cloning? Why or why not?
MIT Department of Biology 7.01: Introductory Biology - Spring 2005 Instructors: Professor Hazel Sive, Professor Tyler Jacks, Dr. Claudette Gardel iv) Would Xba I be useful for cloning? Why or why not?
Figure S1. Characterization of the irx9l-1 mutant. (A) Diagram of the Arabidopsis IRX9L gene drawn based on information from TAIR (the Arabidopsis
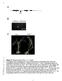 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Figure S1. Characterization of the irx9l-1 mutant. (A) Diagram of the Arabidopsis IRX9L gene drawn based on information from TAIR (the Arabidopsis Information Research). Exons
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Figure S1. Characterization of the irx9l-1 mutant. (A) Diagram of the Arabidopsis IRX9L gene drawn based on information from TAIR (the Arabidopsis Information Research). Exons
scgem Workflow Experimental Design Single cell DNA methylation primer design
 scgem Workflow Experimental Design Single cell DNA methylation primer design The scgem DNA methylation assay uses qpcr to measure digestion of target loci by the methylation sensitive restriction endonuclease
scgem Workflow Experimental Design Single cell DNA methylation primer design The scgem DNA methylation assay uses qpcr to measure digestion of target loci by the methylation sensitive restriction endonuclease
Percent survival. Supplementary fig. S3 A.
 Supplementary fig. S3 A. B. 100 Percent survival 80 60 40 20 Ml 0 0 100 C. Fig. S3 Comparison of leukaemia incidence rate in the triple targeted chimaeric mice and germline-transmission translocator mice
Supplementary fig. S3 A. B. 100 Percent survival 80 60 40 20 Ml 0 0 100 C. Fig. S3 Comparison of leukaemia incidence rate in the triple targeted chimaeric mice and germline-transmission translocator mice
Confocal immunofluorescence microscopy
 Confocal immunofluorescence microscopy HL-6 and cells were cultured and cytospun onto glass slides. The cells were double immunofluorescence stained for Mt NPM1 and fibrillarin (nucleolar marker). Briefly,
Confocal immunofluorescence microscopy HL-6 and cells were cultured and cytospun onto glass slides. The cells were double immunofluorescence stained for Mt NPM1 and fibrillarin (nucleolar marker). Briefly,
Unit 6: Molecular Genetics & DNA Technology Guided Reading Questions (100 pts total)
 Name: AP Biology Biology, Campbell and Reece, 7th Edition Adapted from chapter reading guides originally created by Lynn Miriello Chapter 16 The Molecular Basis of Inheritance Unit 6: Molecular Genetics
Name: AP Biology Biology, Campbell and Reece, 7th Edition Adapted from chapter reading guides originally created by Lynn Miriello Chapter 16 The Molecular Basis of Inheritance Unit 6: Molecular Genetics
Genetic Engineering & Recombinant DNA
 Genetic Engineering & Recombinant DNA Chapter 10 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc) Permission required for reproduction or display. Applications of Genetic Engineering Basic science vs. Applied
Genetic Engineering & Recombinant DNA Chapter 10 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc) Permission required for reproduction or display. Applications of Genetic Engineering Basic science vs. Applied
The GeneEditor TM in vitro Mutagenesis System: Site- Directed Mutagenesis Using Altered Beta-Lactamase Specificity
 Promega Notes Magazine Number 62, 1997, p. 02 The GeneEditor TM in vitro Mutagenesis System: Site- Directed Mutagenesis Using Altered Beta-Lactamase Specificity By Christine Andrews and Scott Lesley Promega
Promega Notes Magazine Number 62, 1997, p. 02 The GeneEditor TM in vitro Mutagenesis System: Site- Directed Mutagenesis Using Altered Beta-Lactamase Specificity By Christine Andrews and Scott Lesley Promega
SuperScript IV Reverse Transcriptase as a better alternative to AMV-based enzymes
 WHITE PAPER SuperScript IV Reverse Transcriptase SuperScript IV Reverse Transcriptase as a better alternative to AMV-based enzymes Abstract Reverse transcriptases (RTs) from avian myeloblastosis virus
WHITE PAPER SuperScript IV Reverse Transcriptase SuperScript IV Reverse Transcriptase as a better alternative to AMV-based enzymes Abstract Reverse transcriptases (RTs) from avian myeloblastosis virus
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL AND METHODS
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL AND METHODS Amplification of HEV ORF1, ORF2 and ORF3 genome regions Total RNA was extracted from 200 µl EDTA plasma using Cobas AmpliPrep total nucleic acid isolation kit (Roche,
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL AND METHODS Amplification of HEV ORF1, ORF2 and ORF3 genome regions Total RNA was extracted from 200 µl EDTA plasma using Cobas AmpliPrep total nucleic acid isolation kit (Roche,
A 5 P degradation hot spot influences molecular farming of anticancerogenic nuclease TBN1 in tobacco cells
 Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture (PCTOC) A 5 P degradation hot spot influences molecular farming of anticancerogenic nuclease TBN1 in tobacco cells Anna Týcová a,b, Rajen J. J. Piernikarczyk c, Michael
Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture (PCTOC) A 5 P degradation hot spot influences molecular farming of anticancerogenic nuclease TBN1 in tobacco cells Anna Týcová a,b, Rajen J. J. Piernikarczyk c, Michael
PrimePCR Assay Validation Report
 Gene Information Gene Name SRY (sex determining region Y)-box 6 Gene Symbol Organism Gene Summary Gene Aliases RefSeq Accession No. UniGene ID Ensembl Gene ID SOX6 Human This gene encodes a member of the
Gene Information Gene Name SRY (sex determining region Y)-box 6 Gene Symbol Organism Gene Summary Gene Aliases RefSeq Accession No. UniGene ID Ensembl Gene ID SOX6 Human This gene encodes a member of the
sides of the aleurone (Al) but it is excluded from the basal endosperm transfer layer
 Supplemental Data. Gómez et al. (2009). The maize transcription factor MRP-1 (Myb-Related-Protein-1) is a key regulator of the differentiation of transfer cells. Supplemental Figure 1. Expression analyses
Supplemental Data. Gómez et al. (2009). The maize transcription factor MRP-1 (Myb-Related-Protein-1) is a key regulator of the differentiation of transfer cells. Supplemental Figure 1. Expression analyses
Heme utilization in the Caenorhabditis elegans hypodermal cells is facilitated by hemeresponsive
 Supplemental Data Heme utilization in the Caenorhabditis elegans hypodermal cells is facilitated by hemeresponsive gene-2 Caiyong Chen 1, Tamika K. Samuel 1, Michael Krause 2, Harry A. Dailey 3, and Iqbal
Supplemental Data Heme utilization in the Caenorhabditis elegans hypodermal cells is facilitated by hemeresponsive gene-2 Caiyong Chen 1, Tamika K. Samuel 1, Michael Krause 2, Harry A. Dailey 3, and Iqbal
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:.38/nature899 Supplementary Figure Suzuki et al. a c p7 -/- / WT ratio (+)/(-) p7 -/- / WT ratio Log X 3. Fold change by treatment ( (+)/(-)) Log X.5 3-3. -. b Fold change by treatment ( (+)/(-)) 8
doi:.38/nature899 Supplementary Figure Suzuki et al. a c p7 -/- / WT ratio (+)/(-) p7 -/- / WT ratio Log X 3. Fold change by treatment ( (+)/(-)) Log X.5 3-3. -. b Fold change by treatment ( (+)/(-)) 8
a. Primers were purchased from Display Systems Biotech and are listed numerically to differentiate them
 Table 2-1. Random upstream primers used in fluorescence differential display. Upstream primer a Sequence 1 5 GATCATAGCC 2 5 CTGCTTGATG 3 5 GATCCAGTAC 4 5 GATCGCATTG 5 5 AAACTCCGTC 6 5 TGGTAAAGGG 7 5 GATCATGGTC
Table 2-1. Random upstream primers used in fluorescence differential display. Upstream primer a Sequence 1 5 GATCATAGCC 2 5 CTGCTTGATG 3 5 GATCCAGTAC 4 5 GATCGCATTG 5 5 AAACTCCGTC 6 5 TGGTAAAGGG 7 5 GATCATGGTC
Activation of a Floral Homeotic Gene in Arabidopsis
 Activation of a Floral Homeotic Gene in Arabidopsis Busch, M.A., Bomblies, K., Weigel, D. kuleuven-kortrijk.be Simon Olthof Louie Christodoulidis 1 In Arabidopsis flowers, appearance is based, in part,
Activation of a Floral Homeotic Gene in Arabidopsis Busch, M.A., Bomblies, K., Weigel, D. kuleuven-kortrijk.be Simon Olthof Louie Christodoulidis 1 In Arabidopsis flowers, appearance is based, in part,
Recombinant DNA Technology
 History of recombinant DNA technology Recombinant DNA Technology (DNA cloning) Majid Mojarrad Recombinant DNA technology is one of the recent advances in biotechnology, which was developed by two scientists
History of recombinant DNA technology Recombinant DNA Technology (DNA cloning) Majid Mojarrad Recombinant DNA technology is one of the recent advances in biotechnology, which was developed by two scientists
Computational Biology I LSM5191
 Computational Biology I LSM5191 Lecture 5 Notes: Genetic manipulation & Molecular Biology techniques Broad Overview of: Enzymatic tools in Molecular Biology Gel electrophoresis Restriction mapping DNA
Computational Biology I LSM5191 Lecture 5 Notes: Genetic manipulation & Molecular Biology techniques Broad Overview of: Enzymatic tools in Molecular Biology Gel electrophoresis Restriction mapping DNA
Lecture 25 (11/15/17)
 Lecture 25 (11/15/17) Reading: Ch9; 328-332 Ch25; 990-995, 1005-1012 Problems: Ch9 (study-guide: applying); 1,2 Ch9 (study-guide: facts); 7,8 Ch25 (text); 1-3,5-7,9,10,13-15 Ch25 (study-guide: applying);
Lecture 25 (11/15/17) Reading: Ch9; 328-332 Ch25; 990-995, 1005-1012 Problems: Ch9 (study-guide: applying); 1,2 Ch9 (study-guide: facts); 7,8 Ch25 (text); 1-3,5-7,9,10,13-15 Ch25 (study-guide: applying);
Supplementary Table 1. The Q-PCR primer sequence is summarized in the following table.
 Supplementary Table 1. The Q-PCR primer sequence is summarized in the following table. Name Sequence (5-3 ) Application Flag-u ggactacaaggacgacgatgac Shared upstream primer for all the amplifications of
Supplementary Table 1. The Q-PCR primer sequence is summarized in the following table. Name Sequence (5-3 ) Application Flag-u ggactacaaggacgacgatgac Shared upstream primer for all the amplifications of
Recent technology allow production of microarrays composed of 70-mers (essentially a hybrid of the two techniques)
 Microarrays and Transcript Profiling Gene expression patterns are traditionally studied using Northern blots (DNA-RNA hybridization assays). This approach involves separation of total or polya + RNA on
Microarrays and Transcript Profiling Gene expression patterns are traditionally studied using Northern blots (DNA-RNA hybridization assays). This approach involves separation of total or polya + RNA on
Translation of HTT mrna with expanded CAG repeats is regulated by
 Supplementary Information Translation of HTT mrna with expanded CAG repeats is regulated by the MID1-PP2A protein complex Sybille Krauß 1,*, Nadine Griesche 1, Ewa Jastrzebska 2,3, Changwei Chen 4, Désiree
Supplementary Information Translation of HTT mrna with expanded CAG repeats is regulated by the MID1-PP2A protein complex Sybille Krauß 1,*, Nadine Griesche 1, Ewa Jastrzebska 2,3, Changwei Chen 4, Désiree
Chemical hijacking of auxin signaling with an engineered auxin-tir1
 1 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Chemical hijacking of auxin signaling with an engineered auxin-tir1 pair Naoyuki Uchida 1,2*, Koji Takahashi 2*, Rie Iwasaki 1, Ryotaro Yamada 2, Masahiko Yoshimura 2, Takaho
1 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Chemical hijacking of auxin signaling with an engineered auxin-tir1 pair Naoyuki Uchida 1,2*, Koji Takahashi 2*, Rie Iwasaki 1, Ryotaro Yamada 2, Masahiko Yoshimura 2, Takaho
HeLa cells stably transfected with an empty pcdna3 vector (HeLa Neo) or with a plasmid
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS AND METHODS Cell culture, transfection and treatments. HeLa cells stably transfected with an empty pcdna3 vector (HeLa Neo) or with a plasmid encoding vmia (HeLa vmia) 1 were cultured
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS AND METHODS Cell culture, transfection and treatments. HeLa cells stably transfected with an empty pcdna3 vector (HeLa Neo) or with a plasmid encoding vmia (HeLa vmia) 1 were cultured
Materials and methods. by University of Washington Yeast Resource Center) from several promoters, including
 Supporting online material for Elowitz et al. report Materials and methods Strains and plasmids. Plasmids expressing CFP or YFP (wild-type codons, developed by University of Washington Yeast Resource Center)
Supporting online material for Elowitz et al. report Materials and methods Strains and plasmids. Plasmids expressing CFP or YFP (wild-type codons, developed by University of Washington Yeast Resource Center)
Methods of Biomaterials Testing Lesson 3-5. Biochemical Methods - Molecular Biology -
 Methods of Biomaterials Testing Lesson 3-5 Biochemical Methods - Molecular Biology - Chromosomes in the Cell Nucleus DNA in the Chromosome Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) DNA has double-helix structure The
Methods of Biomaterials Testing Lesson 3-5 Biochemical Methods - Molecular Biology - Chromosomes in the Cell Nucleus DNA in the Chromosome Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) DNA has double-helix structure The
PrimePCR Assay Validation Report
 Gene Information Gene Name transforming growth factor, beta 1 Gene Symbol Organism Gene Summary Gene Aliases RefSeq Accession No. UniGene ID Ensembl Gene ID TGFB1 Human This gene encodes a member of the
Gene Information Gene Name transforming growth factor, beta 1 Gene Symbol Organism Gene Summary Gene Aliases RefSeq Accession No. UniGene ID Ensembl Gene ID TGFB1 Human This gene encodes a member of the
RNA oligonucleotides and 2 -O-methylated oligonucleotides were synthesized by. 5 AGACACAAACACCAUUGUCACACUCCACAGC; Rand-2 OMe,
 Materials and methods Oligonucleotides and DNA constructs RNA oligonucleotides and 2 -O-methylated oligonucleotides were synthesized by Dharmacon Inc. (Lafayette, CO). The sequences were: 122-2 OMe, 5
Materials and methods Oligonucleotides and DNA constructs RNA oligonucleotides and 2 -O-methylated oligonucleotides were synthesized by Dharmacon Inc. (Lafayette, CO). The sequences were: 122-2 OMe, 5
supplementary information
 DOI: 1.138/ncb1839 a b Control 1 2 3 Control 1 2 3 Fbw7 Smad3 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 c d IGF-1 IGF-1Rβ IGF-1Rβ-P Control / 1 2 3 4 Real-time RT-PCR Relative quantity (IGF-1/ mrna) 2 1 IGF-1 1 2 3 4 Control /
DOI: 1.138/ncb1839 a b Control 1 2 3 Control 1 2 3 Fbw7 Smad3 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 c d IGF-1 IGF-1Rβ IGF-1Rβ-P Control / 1 2 3 4 Real-time RT-PCR Relative quantity (IGF-1/ mrna) 2 1 IGF-1 1 2 3 4 Control /
PrimePCR Assay Validation Report
 Gene Information Gene Name collagen, type IV, alpha 1 Gene Symbol Organism Gene Summary Gene Aliases RefSeq Accession No. UniGene ID Ensembl Gene ID COL4A1 Human This gene encodes the major type IV alpha
Gene Information Gene Name collagen, type IV, alpha 1 Gene Symbol Organism Gene Summary Gene Aliases RefSeq Accession No. UniGene ID Ensembl Gene ID COL4A1 Human This gene encodes the major type IV alpha
Gateway Vectors for BiFC
 Gateway Vectors for BiFC 1. The enhanced YFP (EYFP) are used (Split EYFP). 2. The Fusion fusion gene is expressed by CaMV35S promoter. 3. The N- or C-terminal fragments of EYFP are fused subsequent to
Gateway Vectors for BiFC 1. The enhanced YFP (EYFP) are used (Split EYFP). 2. The Fusion fusion gene is expressed by CaMV35S promoter. 3. The N- or C-terminal fragments of EYFP are fused subsequent to
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL. Supplemental Methods. Cumate solution was from System Biosciences. Human complement C1q and complement
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplemental Methods Reagents Cumate solution was from System Biosciences. Human complement Cq and complement C-esterase inhibitor (C-INH) were from Calbiochem. C-INH (Berinert) for
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplemental Methods Reagents Cumate solution was from System Biosciences. Human complement Cq and complement C-esterase inhibitor (C-INH) were from Calbiochem. C-INH (Berinert) for
Efficient Multi-site-directed Mutagenesis directly from Genomic Template.
 Efficient Multi-site-directed Mutagenesis directly from Genomic Template. Fengtao Luo 1, Xiaolan Du 1, Tujun Weng 1, Xuan Wen 1, Junlan Huang 1, Lin Chen 1 Running title: Multi-site-directed Mutagenesis
Efficient Multi-site-directed Mutagenesis directly from Genomic Template. Fengtao Luo 1, Xiaolan Du 1, Tujun Weng 1, Xuan Wen 1, Junlan Huang 1, Lin Chen 1 Running title: Multi-site-directed Mutagenesis
Trasposable elements: Uses of P elements Problem set B at the end
 Trasposable elements: Uses of P elements Problem set B at the end P-elements have revolutionized the way Drosophila geneticists conduct their research. Here, we will discuss just a few of the approaches
Trasposable elements: Uses of P elements Problem set B at the end P-elements have revolutionized the way Drosophila geneticists conduct their research. Here, we will discuss just a few of the approaches
M Keramatipour 2. M Keramatipour 1. M Keramatipour 4. M Keramatipour 3. M Keramatipour 5. M Keramatipour
 Molecular Cloning Methods Mohammad Keramatipour MD, PhD keramatipour@tums.ac.ir Outline DNA recombinant technology DNA cloning co Cell based PCR PCR-based Some application of DNA cloning Genomic libraries
Molecular Cloning Methods Mohammad Keramatipour MD, PhD keramatipour@tums.ac.ir Outline DNA recombinant technology DNA cloning co Cell based PCR PCR-based Some application of DNA cloning Genomic libraries
Protocol for Genome Editing via the RNA-guided Cas9 Nuclease in. Zebrafish Embryos 1
 Protocol for Genome Editing via the RNA-guided Cas9 Nuclease in Zebrafish Embryos 1 1. In vitro synthesis of capped Cas9 mrna The full length of humanized Cas9 cdnas with double NLS were cloned into pxt7
Protocol for Genome Editing via the RNA-guided Cas9 Nuclease in Zebrafish Embryos 1 1. In vitro synthesis of capped Cas9 mrna The full length of humanized Cas9 cdnas with double NLS were cloned into pxt7
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Marty et al. 10.1073/pnas.0900206106 SI Materials and Methods Semiquantitative RT-PCR. Total RNA was extracted from Arabidopsis leaf material ground in liquid N 2. RNA was extracted
Supporting Information Marty et al. 10.1073/pnas.0900206106 SI Materials and Methods Semiquantitative RT-PCR. Total RNA was extracted from Arabidopsis leaf material ground in liquid N 2. RNA was extracted
Recombinant DNA Technology. The Role of Recombinant DNA Technology in Biotechnology. yeast. Biotechnology. Recombinant DNA technology.
 PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, North Carolina State University C H A P T E R 8 Recombinant DNA Technology The Role of Recombinant DNA Technology in Biotechnology Biotechnology?
PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, North Carolina State University C H A P T E R 8 Recombinant DNA Technology The Role of Recombinant DNA Technology in Biotechnology Biotechnology?
Supplementary Figure 1. BES1 specifically inhibits ABA responses in early seedling
 Supplementary Figure 1. BES1 specifically inhibits ABA responses in early seedling development. a. Exogenous BR application overcomes the hypersensitivity of bzr1-1d seedlings to ABA. Seed germination
Supplementary Figure 1. BES1 specifically inhibits ABA responses in early seedling development. a. Exogenous BR application overcomes the hypersensitivity of bzr1-1d seedlings to ABA. Seed germination
Supplemental Data. LMO4 Controls the Balance between Excitatory. and Inhibitory Spinal V2 Interneurons
 Neuron, Volume 61 Supplemental Data LMO4 Controls the Balance between Excitatory and Inhibitory Spinal V2 Interneurons Kaumudi Joshi, Seunghee Lee, Bora Lee, Jae W. Lee, and Soo-Kyung Lee Supplemental
Neuron, Volume 61 Supplemental Data LMO4 Controls the Balance between Excitatory and Inhibitory Spinal V2 Interneurons Kaumudi Joshi, Seunghee Lee, Bora Lee, Jae W. Lee, and Soo-Kyung Lee Supplemental
Genome Sequence Assembly
 Genome Sequence Assembly Learning Goals: Introduce the field of bioinformatics Familiarize the student with performing sequence alignments Understand the assembly process in genome sequencing Introduction:
Genome Sequence Assembly Learning Goals: Introduce the field of bioinformatics Familiarize the student with performing sequence alignments Understand the assembly process in genome sequencing Introduction:
Genetics - Problem Drill 19: Dissection of Gene Function: Mutational Analysis of Model Organisms
 Genetics - Problem Drill 19: Dissection of Gene Function: Mutational Analysis of Model Organisms No. 1 of 10 1. The mouse gene knockout is based on. (A) Homologous recombination (B) Site-specific recombination
Genetics - Problem Drill 19: Dissection of Gene Function: Mutational Analysis of Model Organisms No. 1 of 10 1. The mouse gene knockout is based on. (A) Homologous recombination (B) Site-specific recombination
BIO303, Genetics Study Guide II for Spring 2007 Semester
 BIO303, Genetics Study Guide II for Spring 2007 Semester 1 Questions from F05 1. Tryptophan (Trp) is encoded by the codon UGG. Suppose that a cell was treated with high levels of 5- Bromouracil such that
BIO303, Genetics Study Guide II for Spring 2007 Semester 1 Questions from F05 1. Tryptophan (Trp) is encoded by the codon UGG. Suppose that a cell was treated with high levels of 5- Bromouracil such that
Molecular Markers CRITFC Genetics Workshop December 9, 2014
 Molecular Markers CRITFC Genetics Workshop December 9, 2014 Molecular Markers Tools that allow us to collect information about an individual, a population, or a species Application in fisheries mating
Molecular Markers CRITFC Genetics Workshop December 9, 2014 Molecular Markers Tools that allow us to collect information about an individual, a population, or a species Application in fisheries mating
Molecular Genetics Techniques. BIT 220 Chapter 20
 Molecular Genetics Techniques BIT 220 Chapter 20 What is Cloning? Recombinant DNA technologies 1. Producing Recombinant DNA molecule Incorporate gene of interest into plasmid (cloning vector) 2. Recombinant
Molecular Genetics Techniques BIT 220 Chapter 20 What is Cloning? Recombinant DNA technologies 1. Producing Recombinant DNA molecule Incorporate gene of interest into plasmid (cloning vector) 2. Recombinant
Supplemental Information
 Supplemental Information Itemized List Materials and Methods, Related to Supplemental Figures S5A-C and S6. Supplemental Figure S1, Related to Figures 1 and 2. Supplemental Figure S2, Related to Figure
Supplemental Information Itemized List Materials and Methods, Related to Supplemental Figures S5A-C and S6. Supplemental Figure S1, Related to Figures 1 and 2. Supplemental Figure S2, Related to Figure
EPIGENTEK. EpiQuik Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Kit. Base Catalog # P-2002 PLEASE READ THIS ENTIRE USER GUIDE BEFORE USE
 EpiQuik Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Kit Base Catalog # P-2002 PLEASE READ THIS ENTIRE USER GUIDE BEFORE USE The EpiQuik Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Kit is suitable for combining the specificity of
EpiQuik Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Kit Base Catalog # P-2002 PLEASE READ THIS ENTIRE USER GUIDE BEFORE USE The EpiQuik Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Kit is suitable for combining the specificity of
Impact of Retinoic acid induced-1 (Rai1) on Regulators of Metabolism and Adipogenesis
 Impact of Retinoic acid induced-1 (Rai1) on Regulators of Metabolism and Adipogenesis The mammalian system undergoes ~24 hour cycles known as circadian rhythms that temporally orchestrate metabolism, behavior,
Impact of Retinoic acid induced-1 (Rai1) on Regulators of Metabolism and Adipogenesis The mammalian system undergoes ~24 hour cycles known as circadian rhythms that temporally orchestrate metabolism, behavior,
BIOLOGY Dr.Locke Lecture# 27 An Introduction to Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
 BIOLOGY 207 - Dr.Locke Lecture# 27 An Introduction to Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Required readings and problems: Reading: Open Genetics, Chapter 8.1 Problems: Chapter 8 Optional Griffiths (2008) 9
BIOLOGY 207 - Dr.Locke Lecture# 27 An Introduction to Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Required readings and problems: Reading: Open Genetics, Chapter 8.1 Problems: Chapter 8 Optional Griffiths (2008) 9
Technical Review. Real time PCR
 Technical Review Real time PCR Normal PCR: Analyze with agarose gel Normal PCR vs Real time PCR Real-time PCR, also known as quantitative PCR (qpcr) or kinetic PCR Key feature: Used to amplify and simultaneously
Technical Review Real time PCR Normal PCR: Analyze with agarose gel Normal PCR vs Real time PCR Real-time PCR, also known as quantitative PCR (qpcr) or kinetic PCR Key feature: Used to amplify and simultaneously
4/26/2015. Cut DNA either: Cut DNA either:
 Ch.20 Enzymes that cut DNA at specific sequences (restriction sites) resulting in segments of DNA (restriction fragments) Typically 4-8 bp in length & often palindromic Isolated from bacteria (Hundreds
Ch.20 Enzymes that cut DNA at specific sequences (restriction sites) resulting in segments of DNA (restriction fragments) Typically 4-8 bp in length & often palindromic Isolated from bacteria (Hundreds
CHAPTER 20 DNA TECHNOLOGY AND GENOMICS. Section A: DNA Cloning
 Section A: DNA Cloning 1. DNA technology makes it possible to clone genes for basic research and commercial applications: an overview 2. Restriction enzymes are used to make recombinant DNA 3. Genes can
Section A: DNA Cloning 1. DNA technology makes it possible to clone genes for basic research and commercial applications: an overview 2. Restriction enzymes are used to make recombinant DNA 3. Genes can
Biotechnology. Explorer Program. Serious About Science Education 5/17/09 1
 Biotechnology Explorer Program Serious About Science Education 5/17/09 1 Chromosome 8: PCR TM PCR Workshop Kirk Brown,, Tracy High School; Tracy, Ca Stan Hitomi,, Monte Vista High School; Danville, CA
Biotechnology Explorer Program Serious About Science Education 5/17/09 1 Chromosome 8: PCR TM PCR Workshop Kirk Brown,, Tracy High School; Tracy, Ca Stan Hitomi,, Monte Vista High School; Danville, CA
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature09937 a Name Position Primersets 1a 1b 2 3 4 b2 Phenotype Genotype b Primerset 1a D T C R I E 10000 8000 6000 5000 4000 3000 2500 2000 1500 1000 800 Donor (D)
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature09937 a Name Position Primersets 1a 1b 2 3 4 b2 Phenotype Genotype b Primerset 1a D T C R I E 10000 8000 6000 5000 4000 3000 2500 2000 1500 1000 800 Donor (D)
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/317/5837/477/dc1 Supporting Online Material for AAV Vector Integration Sites in Mouse Hepatocellular Carcinoma Anthony Donsante, Daniel G. Miller, Yi Li, Carole Vogler,
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/317/5837/477/dc1 Supporting Online Material for AAV Vector Integration Sites in Mouse Hepatocellular Carcinoma Anthony Donsante, Daniel G. Miller, Yi Li, Carole Vogler,
Lecture 3 (FW) January 28, 2009 Cloning of DNA; PCR amplification Reading assignment: Cloning, ; ; 330 PCR, ; 329.
 Lecture 3 (FW) January 28, 2009 Cloning of DNA; PCR amplification Reading assignment: Cloning, 240-245; 286-87; 330 PCR, 270-274; 329. Take Home Lesson(s) from Lecture 2: 1. DNA is a double helix of complementary
Lecture 3 (FW) January 28, 2009 Cloning of DNA; PCR amplification Reading assignment: Cloning, 240-245; 286-87; 330 PCR, 270-274; 329. Take Home Lesson(s) from Lecture 2: 1. DNA is a double helix of complementary
pgbkt7 Anti- Myc AH109 strain (KDa) 50
 pgbkt7 (KDa) 50 37 Anti- Myc AH109 strain Supplementary Figure 1. Protein expression of CRN and TDR in yeast. To analyse the protein expression of CRNKD and TDRKD, total proteins extracted from yeast culture
pgbkt7 (KDa) 50 37 Anti- Myc AH109 strain Supplementary Figure 1. Protein expression of CRN and TDR in yeast. To analyse the protein expression of CRNKD and TDRKD, total proteins extracted from yeast culture
Reverse transcription-pcr (rt-pcr) Dr. Hani Alhadrami
 Reverse transcription-pcr (rt-pcr) Dr. Hani Alhadrami hanialhadrami@kau.edu.sa www.hanialhadrami.kau.edu.sa Overview Several techniques are available to detect and analyse RNA. Examples of these techniques
Reverse transcription-pcr (rt-pcr) Dr. Hani Alhadrami hanialhadrami@kau.edu.sa www.hanialhadrami.kau.edu.sa Overview Several techniques are available to detect and analyse RNA. Examples of these techniques
PCR. CSIBD Molecular Genetics Course July 12, 2011 Michael Choi, M.D.
 PCR CSIBD Molecular Genetics Course July 12, 2011 Michael Choi, M.D. General Outline of the Lecture I. Background II. Basic Principles III. Detection and Analysis of PCR Products IV. Common Applications
PCR CSIBD Molecular Genetics Course July 12, 2011 Michael Choi, M.D. General Outline of the Lecture I. Background II. Basic Principles III. Detection and Analysis of PCR Products IV. Common Applications
Quiz Submissions Quiz 4
 Quiz Submissions Quiz 4 Attempt 1 Written: Nov 1, 2015 17:35 Nov 1, 2015 22:19 Submission View Released: Nov 4, 2015 20:24 Question 1 0 / 1 point Three RNA polymerases synthesize most of the RNA present
Quiz Submissions Quiz 4 Attempt 1 Written: Nov 1, 2015 17:35 Nov 1, 2015 22:19 Submission View Released: Nov 4, 2015 20:24 Question 1 0 / 1 point Three RNA polymerases synthesize most of the RNA present
Contents. 1 Basic Molecular Microbiology of Bacteria... 1 Exp. 1.1 Isolation of Genomic DNA Introduction Principle...
 Contents 1 Basic Molecular Microbiology of Bacteria... 1 Exp. 1.1 Isolation of Genomic DNA... 1 Introduction... 1 Principle... 1 Reagents Required and Their Role... 2 Procedure... 3 Observation... 4 Result
Contents 1 Basic Molecular Microbiology of Bacteria... 1 Exp. 1.1 Isolation of Genomic DNA... 1 Introduction... 1 Principle... 1 Reagents Required and Their Role... 2 Procedure... 3 Observation... 4 Result
Some types of Mutagenesis
 Mutagenesis What Is a Mutation? Genetic information is encoded by the sequence of the nucleotide bases in DNA of the gene. The four nucleotides are: adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine
Mutagenesis What Is a Mutation? Genetic information is encoded by the sequence of the nucleotide bases in DNA of the gene. The four nucleotides are: adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine
Introduction. Technical Note
 DNA and RNA quantification: fast and simple with PicoGreen dsdna and RiboGreen RNA quantification reagents Fluorescence intensity on Infinite F2 and Infinite M2 Introduction DNA quantification Detection
DNA and RNA quantification: fast and simple with PicoGreen dsdna and RiboGreen RNA quantification reagents Fluorescence intensity on Infinite F2 and Infinite M2 Introduction DNA quantification Detection
Antisense RNA Insert Design for Plasmid Construction to Knockdown Target Gene Expression
 Vol. 1:7-15 Antisense RNA Insert Design for Plasmid Construction to Knockdown Target Gene Expression Ji, Tom, Lu, Aneka, Wu, Kaylee Department of Microbiology and Immunology, University of British Columbia
Vol. 1:7-15 Antisense RNA Insert Design for Plasmid Construction to Knockdown Target Gene Expression Ji, Tom, Lu, Aneka, Wu, Kaylee Department of Microbiology and Immunology, University of British Columbia
