Supplemental Data. Wu et al. (2). Plant Cell..5/tpc RGLG Hormonal treatment H2O B RGLG µm ABA µm ACC µm GA Time (hours) µm µm MJ µm IA
|
|
|
- Everett Phillips
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Supplemental Data. Wu et al. (2). Plant Cell..5/tpc..4. A B Supplemental Figure. Immunoblot analysis verifies the expression of the AD-PP2C and BD-RGLG proteins in the Y2H assay. Total proteins were extracted from the yeast cells for immunoblot analysis. α-ha was used to detect AD-PP2Cs and α-myc was used to detect BDRGLGs GAPDH was used as a loading control. RGLGs. control The RING domain of RGLG was deleted to avoid autoactivation and accordingly, accordingly its molecular mass is lower than the rest of RGLGs.
2 Supplemental Data. Wu et al. (2). Plant Cell..5/tpc RGLG Hormonal treatment H2O B RGLG µm ABA µm ACC µm GA Time (hours) µm µm MJ µm IAA zeatin RGLG RGLG mock Abiotic stress root tissue 2 Abiotic stress aerial tissue cold osmotic nm BL C RGLG5 4 2 RGLG5 Relative expresssion (a.u.). AtGenExpress m A microarray data a A salt mock cold osmotic Time (hours) salt Supplemental Figure 2. Relative expression of RGLG and RGLG5 in seedlings. Seedlings g were treated with different hormones ((A)) or submitted to cold ((4ºC), ), osmotic (( mm mannitol)) or salt ((5 mm NaCl)) stress ((B,, C). ) Expression data were obtained from Affymetrix microarrays for Arabidopsis deposited in AtGenExpress public database (Goda et al., 28) and visualized using the AtGenExpress Visualization Tool located in Goda,H., et al., (28). The AtGenExpress hormone and chemical treatment data set: experimental design, data evaluation, model data analysis and data access. Plant J. 55,
3 Supplemental Data. Wu et al. (2). Plant Cell..5/tpc..4. Supplemental pp Figure g. RGLG5 transcript p levels were reduced in amirna transgenic g plants compared p p to wild type. yp (A) Diagram showing location and target sequence of the designed amirna in RGLG5. (B) Decreased RGLG5 transcript level in amirna transgenic lines compared to the wild type detected. Four-week-old Arabidopsis leaves were used for RNA extraction. Gene expression was examined using RT-qPCR. UBQ was used as the internal control, and expression levels were normalized to that examined in Col-. Data represent the mean ± SD of four technical replicas. (C) Relative expression levels of five RGLG genes in selected RGLG5 amirna transgenic lines. No significant effect on other RGLGs expression indicates specific downregulation of RGLG5 in the checked amirna transgenic lines, and line 4 (4#) was chosen for use in this work. Four-week-old Arabidopsis leaves were used for RNA extraction. Gene expression was examined using RT-qPCR. UBQ was used as the internal control, and expression levels were normalized to that examined in Col-. Data represent the mean ± SD of four technical replicas. (D) Photographs of 4-week-old plants under short-day conditions used in the phenotype analysis.
4 Supplemental Data. Wu et al. (2). Plant Cell..5/tpc..4.
5 Supplemental Data. Wu et al. (2). Plant Cell..5/tpc..4. Supplemental Figure 4. ABA hypersensitivity in Arabidopsis transgenic lines overexpressing (OX) either RGLG or RGLG5. (A) Germination (radicle emergence) of wild type (Col-), transgenic plants overexpressing RGLG or RGLG5, and pp2ca- mutants after 72-h growth on MS plates containing the indicated concentrations of ABA. Bars are SD of three replications. Asterisks indicate a significant difference from wild type (Student s t-test: *, P <.5; **, P <.). ((B)) Percentage g of seeds that developed p fullyy g green expanded p cotyledons y ((seedling g establishment)) after 7-dayy g growth on MS p plates containing g the indicated concentrations of ABA. Bars are SD of three replications. Asterisks indicate a significant difference from wild type (Student s t-test: *, P <.5; **, P <.). (C) Photographs of representative seedlings taken 7 days after sowing on MS plates with or without µm ABA. (D) Enhanced sensitivity to salt-mediated inhibition of germination and seedling establishment. Germination and postgermination growth of Arabidopsis transgenic lines overexpressing RGLG or RGLG5 compared to Col- wt. Seeds were sown on MS plates containing the indicated concentrations of NaCl and photographs were taken after 7 days. days (E) Enhanced ABA-mediated inhibition of primary root growth in RGLG or RGLG5 OX seedlings compared to the wild type. Photographs were taken days after transferring 5-day-old seedlings to MS plates supplemented without or with 5 µm ABA. (F) Root length quantification of previous experiment. Bars indicate mean ± SD of thirty seedlings. Asterisks indicate a significant difference from wild type (Student s t-test: *, P <.5; **, P <.). (G) Enhanced induction of ABA-responsive genes is observed in Arabidopsis transgenic lines overexpressing either RGLG or RGLG5. 7-day-old Arabidopsis seedlings were transferred to liquid MS medium containing 5 µm ABA and sampled at the indicated time points. Gene expression was examined using RT-qPCR. UBQ was used as the internal control, and expression levels were normalized to that examined at time point h. Data represent the mean ± SD of four technical replicates.
6 Supplemental Data. Wu et al. (2). Plant Cell..5/tpc..4. Supplemental Figure 5. E ligase activity of RGLG5 and in vitro ubiquitination of PP2CA by RGLG and RGLG5. ( ) Self-ubiquitination (A) q of GST-RGLG5 indicating g ubiquitin q ligase g activityy of RGLG5. The ubiquitination q assayy was p performed in the p presence of E,, E2 ATP and FLAG-ubiquitin, and sampled at the indicated time points. Ubiquitinated bands were detected using FLAG antibody. (B) Loss of ubiquitination activities of GST-RGLG5 by deleting or mutating its RING-domain. Ubiquitination assay was carried out as in (A). FLAG antibody was used to detect the ubiquitinated bands. (C) In vitro ubiquitination of PP2CA by RGLG (left) and RGLG5 (right). Purified GST-PP2CA was incubated with ATP, FLAG-Ubiquitin, E, E2 and serial concentrations of MBP-RGLG or RGLG5. The ubiquitinated products were examined by anti-gst or anti-mbp antibodies. IB using anti-mbp detects self-ubiquitination self ubiquitination of MBP-RGLG MBP RGLG and MBP-RGLG5. MBP RGLG5
7 Supplemental Data. Wu et al. (2). Plant Cell..5/tpc..4. Supplemental Figure. In vitro ubiquitination of PP2CA by RGLG and RGLG5 is not affected by ABA and PYL4. (A) In vitro ubiquitination of PP2CA in the presence of serial concentrations of ABA. Ubiquitination assay was performed as described in Figure 5A., 2 and 4 µm ABA was added together with other reaction components, respectively. The ubiquitination of PP2CA was analyzed by western blot using anti-gst antibody. (B) In vitro ubiquitination of PP2CA in the presence of ABA, PYL4 or both. The ubiquitination level of PP2CA was not influenced by addition of µm ABA, ABA PYL4 or ABA plus serial concentrations of PYL4, PYL4 respectively. respectively
8 Supplemental Data. Wu et al. (2). Plant Cell..5/tpc..4. Supplemental Figure 7. Expression of the PP2CA promoter is strongly induced by ABA. (A) Photographs showing GUS expression driven by PP2CApro in roots and cotyledons of 5-d-old seedlings. ABA treatment ( µm for h) strongly induces expression of GUS. (B) Immunoblot analysis using anti-gus antibody was performed to quantify GUS protein levels. (C) Transcriptional profiles of PP2C genes in response to ABA. Seven-day-old Arabidopsis seedlings were transferred in liquid MS medium containing 5 µm ABA and sampled at the indicated time points. Gene expression was examined using RT-qPCR. ABA-responsive RD29a expression indicated the effectiveness of ABA treatment. UBQ was used as the internal control, and expression levels of the indicated transcripts were normalized to those measured at time point. Data represent the mean ± SD of four technical replicates.
9 Supplemental Data. Wu et al. (2). Plant Cell..5/tpc..4. Supplemental Figure 8. α-e2 is a specific antibody for PP2CA. 2-week-old Col- and pp2ca- etiolated seedlings were treated without (-) or with (+) 5 µm ABA for h in darkness. Then total proteins were extracted and equal amounts of each treatment were subjected to western blot analysis. α-e2 was used to detect endogenous PP2CA with a dilution of :5. α-actin was analyzed as a loading control. Endogenous PP2CA (arrow) was detected in Col- and it was markedly induced by ABA t t treatment, t whereas h it was absent b t in i pp2ca- 2 mutant t t (-/+ABA). ( / ABA)
10 Supplemental Data. Wu et al. (2). Plant Cell..5/tpc..4. Supplemental Figure 9. GUS staining of seedlings expressing PP2CA-GUS or HAB2-GUS reveals ABA-induced degradation of the phosphatases via the 2S proteasome pathway. Representative photographs of transgenic Arabidopsis seedlings constitutively expressing PP2CA-GUS, HAB2-GUS or GUS (negative control). For drug treatment, 7-day-old seedlings were transferred to liquid MS medium supplemented without (Mock) or with µm CHX, 5 µm ABA, or the indicated combinations lacking or containing 5 µm MG2. Samples were taken at the indicated time points after treatment and subjected to GUS staining. Bars = mm.
11 Supplemental Data. Wu et al. (2). Plant Cell..5/tpc..4. Supplemental S l t l Figure Fi Overexpression. O i off RGLG or RGLG5 enhances h ABA ABA-promoted t d degradation d d ti off FLAG-PP2CA. FLAG PP2CA ABA-promoted ABA t d degradation of His-PP2CA in cell-free assays is enhanced in protein extracts prepared from RGLG or RGLG5 overexpressing plants. (A) FLAG-PP2CA protein dynamics in Col- versus RGLG or RGLG5 overexpressing (ox) backgrounds in response to ABA. Assays were performed as described in Figure 7C. (B) The signal intensity in (A) was measured by Image J software. The relative protein levels of FLAG-PP2CA in different genetic backgrounds at time point h were set as. Bars indicate the mean ± SD from three replications replications. Student s Student s t tests were used to determine significant levels of the indicated comparisons. **, P <.; *, P <.5. (C) In vitro cell-free degradation of PP2CA in Col- versus RGLGox extracts. Purified His-PP2CA was incubated for the indicated time period in the presence of ABA or ABA+MG2 with protein extracts prepared from 7-day-old wild type (Col-) or RGLGox seedlings. Actin was analyzed as a loading control. (D) Three-independent experiments as in (C) were performed and the signal intensity was determined by Image J software. The protein levels of His-PP2CA at min were defined as. Bars indicate SD calculated from three replicas. (E) In vitro cell-free degradation of PP2CA in Col- versus RGLG5ox extracts. Assays were performed as in (C). (F) Three-independent experiments as in (E) were performed and the signal intensity was determined by Image J software. Bars indicate SD calculated from three replicas.
12 Supplemental Data. Wu et al. (2). Plant Cell..5/tpc..4. Treatment Mock Protein name PP2CA PP2CA ABA + MG2 RGLG Peptides identified by MS Peptide score/ p VLGVLAMSR VLGVLAMSR VLGVLAMSR VIYWDGAR RLDLLPSIK QSSDNVSVVVVDLR QSSDNVSVVVVDLR QSSDNVSVVVVDLR VLGVLAMSR VLGVLAMSR VLGVLAMSR VIYWDGAR RLDLLPSIK RLDLLPSIK ECNLVVNGATR IVADSAVAPPLENCR QSSDNVSVVVVDLRK DMEDAVSIHPSFLQR DMEDAVSIHPSFLQR MDKEVSQRECNLVVNGATR GAGAGDDSDAAHNACSDAALLLTK GAGAGDDSDAAHNACSDAALLLTK IPNFEPSVPPYPFESK IPNFEPSVPPYPFESK IPNFEPSVPPYPFESK IPNFEPSVPPYPFESK ISDNYSSLLQVSEALGR 45.5/ /. 47/.5 4.8/ / / /.2 2.9/ /5.8E /2.E / 2E /.2E-5 4.7/.8.8/.55.99/.22.59/ /8.8E /2.E-5 2.5/ / / /.89 2./.7 7.4/ /4.9E-7.87/.2 7 5/ 4 7.5/.4 22./.42./ /.4E-5 Supplemental S l t l Table T bl. List Li t off peptides tid identified id tifi d for f PP2CA and d RGLG in i anti-flag ti FLAG immunoprecipitates i i it t obtained bt i d from f 5Spro: FLAG-PP2CA FLAG PP2CA Arabidopsis seedlings mock-treated or treated with ABA and MG2. For mock treatment, two-week-old seedlings were transferred to liquid MS medium for h. For MG and ABA treatment, 5 μm MG2 was added for h and then 5 μm ABA was added for additional h.
Supplemental Data. Lee et al. Plant Cell. (2010) /tpc Supplemental Figure 1. Protein and Gene Structures of DWA1 and DWA2.
 Supplemental Figure 1. Protein and Gene Structures of DWA1 and DWA2. (A) Protein structures of DWA1 and DWA2. WD40 region was determined based on the NCBI conserved domain databases (B, C) Schematic representation
Supplemental Figure 1. Protein and Gene Structures of DWA1 and DWA2. (A) Protein structures of DWA1 and DWA2. WD40 region was determined based on the NCBI conserved domain databases (B, C) Schematic representation
Jung-Nam Cho, Jee-Youn Ryu, Young-Min Jeong, Jihye Park, Ji-Joon Song, Richard M. Amasino, Bosl Noh, and Yoo-Sun Noh
 Developmental Cell, Volume 22 Supplemental Information Control of Seed Germination by Light-Induced Histone Arginine Demethylation Activity Jung-Nam Cho, Jee-Youn Ryu, Young-Min Jeong, Jihye Park, Ji-Joon
Developmental Cell, Volume 22 Supplemental Information Control of Seed Germination by Light-Induced Histone Arginine Demethylation Activity Jung-Nam Cho, Jee-Youn Ryu, Young-Min Jeong, Jihye Park, Ji-Joon
Supplementary Figure 1 qrt-pcr expression analysis of NLP8 with and without KNO 3 during germination.
 Supplementary Figure 1 qrt-pcr expression analysis of NLP8 with and without KNO 3 during germination. Seeds of Col-0 were harvested from plants grown at 16 C, stored for 2 months, imbibed for indicated
Supplementary Figure 1 qrt-pcr expression analysis of NLP8 with and without KNO 3 during germination. Seeds of Col-0 were harvested from plants grown at 16 C, stored for 2 months, imbibed for indicated
Supplemental Data. Steiner et al. Plant Cell. (2012) /tpc
 Supplemental Figure 1. SPY does not interact with free GST. Invitro pull-down assay using E. coli-expressed MBP-SPY and GST, GST-TCP14 and GST-TCP15. MBP-SPY was used as bait and incubated with equal amount
Supplemental Figure 1. SPY does not interact with free GST. Invitro pull-down assay using E. coli-expressed MBP-SPY and GST, GST-TCP14 and GST-TCP15. MBP-SPY was used as bait and incubated with equal amount
Supplementary Figure S1. Immunodetection of full-length XA21 and the XA21 C-terminal cleavage product.
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure S1. Immunodetection of full-length XA21 and the XA21 C-terminal cleavage product. Total protein extracted from Kitaake wild type and rice plants carrying
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure S1. Immunodetection of full-length XA21 and the XA21 C-terminal cleavage product. Total protein extracted from Kitaake wild type and rice plants carrying
Hossain_Supplemental Figure 1
 Hossain_Supplemental Figure 1 GFP-PACT GFP-PACT Motif I GFP-PACT Motif II A. MG132 (1µM) GFP Tubulin GFP-PACT Pericentrin GFP-PACT GFP-PACT Pericentrin Fig. S1. Expression and localization of Orc1 PACT
Hossain_Supplemental Figure 1 GFP-PACT GFP-PACT Motif I GFP-PACT Motif II A. MG132 (1µM) GFP Tubulin GFP-PACT Pericentrin GFP-PACT GFP-PACT Pericentrin Fig. S1. Expression and localization of Orc1 PACT
A subclass of HSP70s regulate development and abiotic stress responses in Arabidopsis thaliana
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 Journal of Plant Research A subclass of HSP70s regulate development and abiotic stress responses in Arabidopsis thaliana Linna Leng 1 Qianqian Liang
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 Journal of Plant Research A subclass of HSP70s regulate development and abiotic stress responses in Arabidopsis thaliana Linna Leng 1 Qianqian Liang
Figure 1: TDP-43 is subject to lysine acetylation within the RNA-binding domain a) QBI-293 cells were transfected with TDP-43 in the presence or
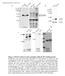 Figure 1: TDP-43 is subject to lysine acetylation within the RNA-binding domain a) QBI-293 cells were transfected with TDP-43 in the presence or absence of the acetyltransferase CBP and acetylated TDP-43
Figure 1: TDP-43 is subject to lysine acetylation within the RNA-binding domain a) QBI-293 cells were transfected with TDP-43 in the presence or absence of the acetyltransferase CBP and acetylated TDP-43
Online Supplementary Information
 Online Supplementary Information NLRP4 negatively regulates type I interferon signaling by targeting TBK1 for degradation via E3 ubiquitin ligase DTX4 Jun Cui 1,4,6,7, Yinyin Li 1,5,6,7, Liang Zhu 1, Dan
Online Supplementary Information NLRP4 negatively regulates type I interferon signaling by targeting TBK1 for degradation via E3 ubiquitin ligase DTX4 Jun Cui 1,4,6,7, Yinyin Li 1,5,6,7, Liang Zhu 1, Dan
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:.38/nature899 Supplementary Figure Suzuki et al. a c p7 -/- / WT ratio (+)/(-) p7 -/- / WT ratio Log X 3. Fold change by treatment ( (+)/(-)) Log X.5 3-3. -. b Fold change by treatment ( (+)/(-)) 8
doi:.38/nature899 Supplementary Figure Suzuki et al. a c p7 -/- / WT ratio (+)/(-) p7 -/- / WT ratio Log X 3. Fold change by treatment ( (+)/(-)) Log X.5 3-3. -. b Fold change by treatment ( (+)/(-)) 8
Enhancers mutations that make the original mutant phenotype more extreme. Suppressors mutations that make the original mutant phenotype less extreme
 Interactomics and Proteomics 1. Interactomics The field of interactomics is concerned with interactions between genes or proteins. They can be genetic interactions, in which two genes are involved in the
Interactomics and Proteomics 1. Interactomics The field of interactomics is concerned with interactions between genes or proteins. They can be genetic interactions, in which two genes are involved in the
ASPP1 Fw GGTTGGGAATCCACGTGTTG ASPP1 Rv GCCATATCTTGGAGCTCTGAGAG
 Supplemental Materials and Methods Plasmids: the following plasmids were used in the supplementary data: pwzl-myc- Lats2 (Aylon et al, 2006), pretrosuper-vector and pretrosuper-shp53 (generous gift of
Supplemental Materials and Methods Plasmids: the following plasmids were used in the supplementary data: pwzl-myc- Lats2 (Aylon et al, 2006), pretrosuper-vector and pretrosuper-shp53 (generous gift of
Construction of plant complementation vector and generation of transgenic plants
 MATERIAL S AND METHODS Plant materials and growth conditions Arabidopsis ecotype Columbia (Col0) was used for this study. SALK_072009, SALK_076309, and SALK_027645 were obtained from the Arabidopsis Biological
MATERIAL S AND METHODS Plant materials and growth conditions Arabidopsis ecotype Columbia (Col0) was used for this study. SALK_072009, SALK_076309, and SALK_027645 were obtained from the Arabidopsis Biological
pgbkt7 Anti- Myc AH109 strain (KDa) 50
 pgbkt7 (KDa) 50 37 Anti- Myc AH109 strain Supplementary Figure 1. Protein expression of CRN and TDR in yeast. To analyse the protein expression of CRNKD and TDRKD, total proteins extracted from yeast culture
pgbkt7 (KDa) 50 37 Anti- Myc AH109 strain Supplementary Figure 1. Protein expression of CRN and TDR in yeast. To analyse the protein expression of CRNKD and TDRKD, total proteins extracted from yeast culture
Supplementary Table 1. The Q-PCR primer sequence is summarized in the following table.
 Supplementary Table 1. The Q-PCR primer sequence is summarized in the following table. Name Sequence (5-3 ) Application Flag-u ggactacaaggacgacgatgac Shared upstream primer for all the amplifications of
Supplementary Table 1. The Q-PCR primer sequence is summarized in the following table. Name Sequence (5-3 ) Application Flag-u ggactacaaggacgacgatgac Shared upstream primer for all the amplifications of
* ** ** * IB: p-p90rsk. p90rsk (Ser380) (arbitrary units) (Ser380) p90rsk. IB: p90rsk. Tubulin. IB: Tubulin. Ang II (200 nm) Ang II (200 nm)
 I: p-p9rsk I: p9rsk I: C I: p-p9rsk I: p9rsk 5 (ka) 5 5 (min) Ang II ( nm) p-p9rsk (Ser8) p9rsk p-p9rsk (Ser8) p9rsk (h) Mannitol 5 mm -Glucose 5 mm p9rsk (Ser8) (arbitrary units) p-p9rsk (Ser8) (arbitrary
I: p-p9rsk I: p9rsk I: C I: p-p9rsk I: p9rsk 5 (ka) 5 5 (min) Ang II ( nm) p-p9rsk (Ser8) p9rsk p-p9rsk (Ser8) p9rsk (h) Mannitol 5 mm -Glucose 5 mm p9rsk (Ser8) (arbitrary units) p-p9rsk (Ser8) (arbitrary
GTTCGGGTTCC TTTTGAGCAG
 Supplementary Figures Splice variants of the SIP1 transcripts play a role in nodule organogenesis in Lotus japonicus. Wang C, Zhu H, Jin L, Chen T, Wang L, Kang H, Hong Z, Zhang Z. 5 UTR CDS 3 UTR TCTCAACCATCCTTTGTCTGCTTCCGCCGCATGGGTGAGGTCATTTTGTCTAGATGACGTGCAATTTACAATGA
Supplementary Figures Splice variants of the SIP1 transcripts play a role in nodule organogenesis in Lotus japonicus. Wang C, Zhu H, Jin L, Chen T, Wang L, Kang H, Hong Z, Zhang Z. 5 UTR CDS 3 UTR TCTCAACCATCCTTTGTCTGCTTCCGCCGCATGGGTGAGGTCATTTTGTCTAGATGACGTGCAATTTACAATGA
Alternative Cleavage and Polyadenylation of RNA
 Developmental Cell 18 Supplemental Information The Spen Family Protein FPA Controls Alternative Cleavage and Polyadenylation of RNA Csaba Hornyik, Lionel C. Terzi, and Gordon G. Simpson Figure S1, related
Developmental Cell 18 Supplemental Information The Spen Family Protein FPA Controls Alternative Cleavage and Polyadenylation of RNA Csaba Hornyik, Lionel C. Terzi, and Gordon G. Simpson Figure S1, related
Coleman et al., Supplementary Figure 1
 Coleman et al., Supplementary Figure 1 BrdU Merge G1 Early S Mid S Supplementary Figure 1. Sequential destruction of CRL4 Cdt2 targets during the G1/S transition. HCT116 cells were synchronized by sequential
Coleman et al., Supplementary Figure 1 BrdU Merge G1 Early S Mid S Supplementary Figure 1. Sequential destruction of CRL4 Cdt2 targets during the G1/S transition. HCT116 cells were synchronized by sequential
sides of the aleurone (Al) but it is excluded from the basal endosperm transfer layer
 Supplemental Data. Gómez et al. (2009). The maize transcription factor MRP-1 (Myb-Related-Protein-1) is a key regulator of the differentiation of transfer cells. Supplemental Figure 1. Expression analyses
Supplemental Data. Gómez et al. (2009). The maize transcription factor MRP-1 (Myb-Related-Protein-1) is a key regulator of the differentiation of transfer cells. Supplemental Figure 1. Expression analyses
Figure S1. Figure S2. Figure S3 HB Anti-FSP27 (COOH-terminal peptide) Ab. Anti-GST-FSP27(45-127) Ab.
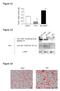 / 36B4 mrna ratio Figure S1 * 2. 1.6 1.2.8 *.4 control TNFα BRL49653 Figure S2 Su bw AT p iw Anti- (COOH-terminal peptide) Ab Blot : Anti-GST-(45-127) Ab β-actin Figure S3 HB2 HW AT BA T Figure S4 A TAG
/ 36B4 mrna ratio Figure S1 * 2. 1.6 1.2.8 *.4 control TNFα BRL49653 Figure S2 Su bw AT p iw Anti- (COOH-terminal peptide) Ab Blot : Anti-GST-(45-127) Ab β-actin Figure S3 HB2 HW AT BA T Figure S4 A TAG
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Su et al. 10.1073/pnas.1211604110 SI Materials and Methods Cell Culture and Plasmids. Tera-1 and Tera-2 cells (ATCC: HTB- 105/106) were maintained in McCoy s 5A medium with 15% FBS
Supporting Information Su et al. 10.1073/pnas.1211604110 SI Materials and Methods Cell Culture and Plasmids. Tera-1 and Tera-2 cells (ATCC: HTB- 105/106) were maintained in McCoy s 5A medium with 15% FBS
Figure S1. Immunoblotting showing proper expression of tagged R and AVR proteins in N. benthamiana.
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Figure S1. Immunoblotting showing proper expression of tagged R and AVR proteins in N. benthamiana. YFP:, :CFP, HA: and (A) and HA, CFP and YFPtagged and AVR1-CO39 (B) were expressed
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Figure S1. Immunoblotting showing proper expression of tagged R and AVR proteins in N. benthamiana. YFP:, :CFP, HA: and (A) and HA, CFP and YFPtagged and AVR1-CO39 (B) were expressed
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
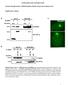 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Dynamic Phosphorylation of HP1 Regulates Mitotic Progression in Human Cells Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. NDR1 interacts with HP1. (a) Immunoprecipitation using
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Dynamic Phosphorylation of HP1 Regulates Mitotic Progression in Human Cells Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. NDR1 interacts with HP1. (a) Immunoprecipitation using
GFP CCD2 GFP IP:GFP
 D1 D2 1 75 95 148 178 492 GFP CCD1 CCD2 CCD2 GFP D1 D2 GFP D1 D2 Beclin 1 IB:GFP IP:GFP Supplementary Figure 1: Mapping domains required for binding to HEK293T cells are transfected with EGFP-tagged mutant
D1 D2 1 75 95 148 178 492 GFP CCD1 CCD2 CCD2 GFP D1 D2 GFP D1 D2 Beclin 1 IB:GFP IP:GFP Supplementary Figure 1: Mapping domains required for binding to HEK293T cells are transfected with EGFP-tagged mutant
Table S1 A list of primers used in the study
 Table S1 A list of primers used in the study Gene Forward primer (5-3 ) Reverse primer (5-3 ) T3 ATTAACCCTCACTAAAGGGA T7 TAATACGACTCACTATAGGG PvSPX2-5 GGAAGAATGACGTTGAGA PvSPX3-5 CAGCCCTTCTATGAAATTGA PvSPX3-3
Table S1 A list of primers used in the study Gene Forward primer (5-3 ) Reverse primer (5-3 ) T3 ATTAACCCTCACTAAAGGGA T7 TAATACGACTCACTATAGGG PvSPX2-5 GGAAGAATGACGTTGAGA PvSPX3-5 CAGCCCTTCTATGAAATTGA PvSPX3-3
Parthanatos mediates AIMP2-activated age-dependent dopaminergic neuronal loss
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Parthanatos mediates AIMP2-activated age-dependent dopaminergic neuronal loss Yunjong Lee, Senthilkumar S. Karuppagounder, Joo-Ho Shin, Yun-Il Lee, Han Seok Ko, Debbie Swing,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Parthanatos mediates AIMP2-activated age-dependent dopaminergic neuronal loss Yunjong Lee, Senthilkumar S. Karuppagounder, Joo-Ho Shin, Yun-Il Lee, Han Seok Ko, Debbie Swing,
PHT1;2-CFP YFP-PHF + PHT1;2-CFP YFP-PHF
 YFP-PHF1 CFP-PHT1;2 PHT1;2-CFP YFP-PHF + PHT1;2-CFP YFP-PHF + CFP-PHT1;2 Negative control!-gfp Supplemental Figure 1: PHT1;2 accumulation is PHF1 dependent. Immunoblot analysis on total protein extract
YFP-PHF1 CFP-PHT1;2 PHT1;2-CFP YFP-PHF + PHT1;2-CFP YFP-PHF + CFP-PHT1;2 Negative control!-gfp Supplemental Figure 1: PHT1;2 accumulation is PHF1 dependent. Immunoblot analysis on total protein extract
Supplemental Data. mir156-regulated SPL Transcription. Factors Define an Endogenous Flowering. Pathway in Arabidopsis thaliana
 Cell, Volume 138 Supplemental Data mir156-regulated SPL Transcription Factors Define an Endogenous Flowering Pathway in Arabidopsis thaliana Jia-Wei Wang, Benjamin Czech, and Detlef Weigel Table S1. Interaction
Cell, Volume 138 Supplemental Data mir156-regulated SPL Transcription Factors Define an Endogenous Flowering Pathway in Arabidopsis thaliana Jia-Wei Wang, Benjamin Czech, and Detlef Weigel Table S1. Interaction
Supplementary Material
 Fig S1. Interactions of OsDof24 with the OsC4PPDK promoter in rice protoplasts (a) Loss-of-function analysis of the OsC4PPDK promoter Effects of OsDof24 overexpression and the mapping of OsDof24-binding
Fig S1. Interactions of OsDof24 with the OsC4PPDK promoter in rice protoplasts (a) Loss-of-function analysis of the OsC4PPDK promoter Effects of OsDof24 overexpression and the mapping of OsDof24-binding
Supplemental Data Supplemental Figure 1.
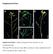 Supplemental Data Supplemental Figure 1. Silique arrangement in the wild-type, jhs, and complemented lines. Wild-type (WT) (A), the jhs1 mutant (B,C), and the jhs1 mutant complemented with JHS1 (Com) (D)
Supplemental Data Supplemental Figure 1. Silique arrangement in the wild-type, jhs, and complemented lines. Wild-type (WT) (A), the jhs1 mutant (B,C), and the jhs1 mutant complemented with JHS1 (Com) (D)
Arabidopsis TF genes
 Expression profiling of Arabidopsis TF genes by qpcr Tomasz Czechowski Tomasz Czechowski MPI of Molecular Plant Physiology (MPI-MP) MP) Molecular Plant Nutrition Group Nitrogen metabolism in plants Nitrogenous
Expression profiling of Arabidopsis TF genes by qpcr Tomasz Czechowski Tomasz Czechowski MPI of Molecular Plant Physiology (MPI-MP) MP) Molecular Plant Nutrition Group Nitrogen metabolism in plants Nitrogenous
supplementary information
 DOI: 1.138/ncb1839 a b Control 1 2 3 Control 1 2 3 Fbw7 Smad3 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 c d IGF-1 IGF-1Rβ IGF-1Rβ-P Control / 1 2 3 4 Real-time RT-PCR Relative quantity (IGF-1/ mrna) 2 1 IGF-1 1 2 3 4 Control /
DOI: 1.138/ncb1839 a b Control 1 2 3 Control 1 2 3 Fbw7 Smad3 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 c d IGF-1 IGF-1Rβ IGF-1Rβ-P Control / 1 2 3 4 Real-time RT-PCR Relative quantity (IGF-1/ mrna) 2 1 IGF-1 1 2 3 4 Control /
Short hairpin RNA (shrna) against MMP14. Lentiviral plasmids containing shrna
 Supplemental Materials and Methods Short hairpin RNA (shrna) against MMP14. Lentiviral plasmids containing shrna (Mission shrna, Sigma) against mouse MMP14 were transfected into HEK293 cells using FuGene6
Supplemental Materials and Methods Short hairpin RNA (shrna) against MMP14. Lentiviral plasmids containing shrna (Mission shrna, Sigma) against mouse MMP14 were transfected into HEK293 cells using FuGene6
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization and high expression of Lnc-β-Catm in liver CSCs. (a) Heatmap of differently expressed lncrnas in Liver CSCs (CD13 + CD133 + ) and non-cscs (CD13 - CD133 - ) according
Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization and high expression of Lnc-β-Catm in liver CSCs. (a) Heatmap of differently expressed lncrnas in Liver CSCs (CD13 + CD133 + ) and non-cscs (CD13 - CD133 - ) according
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Legends for Supplementary Tables. Supplementary Table 1. An excel file containing primary screen data. Worksheet 1, Normalized quantification data from a duplicated screen: valid
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Legends for Supplementary Tables. Supplementary Table 1. An excel file containing primary screen data. Worksheet 1, Normalized quantification data from a duplicated screen: valid
Activation of a Floral Homeotic Gene in Arabidopsis
 Activation of a Floral Homeotic Gene in Arabidopsis By Maximiliam A. Busch, Kirsten Bomblies, and Detlef Weigel Presentation by Lis Garrett and Andrea Stevenson http://ucsdnews.ucsd.edu/archive/graphics/images/image5.jpg
Activation of a Floral Homeotic Gene in Arabidopsis By Maximiliam A. Busch, Kirsten Bomblies, and Detlef Weigel Presentation by Lis Garrett and Andrea Stevenson http://ucsdnews.ucsd.edu/archive/graphics/images/image5.jpg
Supplemental Figure 1. Mutation in NLA Causes Increased Pi Uptake Activity and
 Supplemental Figure 1. Mutation in NLA Causes Increased Pi Uptake Activity and PHT1 Protein Amounts. (A) Shoot morphology of 19-day-old nla mutants under Pi-sufficient conditions. (B) [ 33 P]Pi uptake
Supplemental Figure 1. Mutation in NLA Causes Increased Pi Uptake Activity and PHT1 Protein Amounts. (A) Shoot morphology of 19-day-old nla mutants under Pi-sufficient conditions. (B) [ 33 P]Pi uptake
ENCODE RBP Antibody Characterization Guidelines
 ENCODE RBP Antibody Characterization Guidelines Approved on November 18, 2016 Background An integral part of the ENCODE Project is to characterize the antibodies used in the experiments. This document
ENCODE RBP Antibody Characterization Guidelines Approved on November 18, 2016 Background An integral part of the ENCODE Project is to characterize the antibodies used in the experiments. This document
Journal of Cell Science Supplementary Material
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE LEGENDS Figure S1: Eps8 is localized at focal adhesions and binds directly to FAK (A) Focal
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE LEGENDS Figure S1: Eps8 is localized at focal adhesions and binds directly to FAK (A) Focal
Supplemental Material for Xue et al. List. Supplemental Figure legends. Figure S1. Related to Figure 1. Figure S2. Related to Figure 3
 Supplemental Material for Xue et al List Supplemental Figure legends Figure S1. Related to Figure 1 Figure S. Related to Figure 3 Figure S3. Related to Figure 4 Figure S4. Related to Figure 4 Figure S5.
Supplemental Material for Xue et al List Supplemental Figure legends Figure S1. Related to Figure 1 Figure S. Related to Figure 3 Figure S3. Related to Figure 4 Figure S4. Related to Figure 4 Figure S5.
42 fl organelles = 34.5 fl (1) 3.5X X 0.93 = 78,000 (2)
 SUPPLEMENTAL DATA Supplementary Experimental Procedures Fluorescence Microscopy - A Zeiss Axiovert 200M microscope equipped with a Zeiss 100x Plan- Apochromat (1.40 NA) DIC objective and Hamamatsu Orca
SUPPLEMENTAL DATA Supplementary Experimental Procedures Fluorescence Microscopy - A Zeiss Axiovert 200M microscope equipped with a Zeiss 100x Plan- Apochromat (1.40 NA) DIC objective and Hamamatsu Orca
HCT116 SW48 Nutlin: p53
 Figure S HCT6 SW8 Nutlin: - + - + p GAPDH Figure S. Nutlin- treatment induces p protein. HCT6 and SW8 cells were left untreated or treated for 8 hr with Nutlin- ( µm) to up-regulate p. Whole cell lysates
Figure S HCT6 SW8 Nutlin: - + - + p GAPDH Figure S. Nutlin- treatment induces p protein. HCT6 and SW8 cells were left untreated or treated for 8 hr with Nutlin- ( µm) to up-regulate p. Whole cell lysates
Figure S1: NUN preparation yields nascent, unadenylated RNA with a different profile from Total RNA.
 Summary of Supplemental Information Figure S1: NUN preparation yields nascent, unadenylated RNA with a different profile from Total RNA. Figure S2: rrna removal procedure is effective for clearing out
Summary of Supplemental Information Figure S1: NUN preparation yields nascent, unadenylated RNA with a different profile from Total RNA. Figure S2: rrna removal procedure is effective for clearing out
Microbially Mediated Plant Salt Tolerance and Microbiome based Solutions for Saline Agriculture
 Microbially Mediated Plant Salt Tolerance and Microbiome based Solutions for Saline Agriculture Contents Introduction Abiotic Tolerance Approaches Reasons for failure Roots, microorganisms and soil-interaction
Microbially Mediated Plant Salt Tolerance and Microbiome based Solutions for Saline Agriculture Contents Introduction Abiotic Tolerance Approaches Reasons for failure Roots, microorganisms and soil-interaction
ab Ubiquitylation Assay Kit
 ab139467 Ubiquitylation Assay Kit Instructions for Use For the activation of ubiquitin for use in ubiquitylation experiments This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic use.
ab139467 Ubiquitylation Assay Kit Instructions for Use For the activation of ubiquitin for use in ubiquitylation experiments This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic use.
Candidate region (0.74 Mb) ATC TCT GGG ACT CAT GAG CAG GAG GCT AGC ATC TCT GGG ACT CAT TAG CAG GAG GCT AGC
 A idm-3 idm-3 B Physical distance (Mb) 4.6 4.86.6 8.4 C Chr.3 Recom. Rate (%) ATG 3.9.9.9 9.74 Candidate region (.74 Mb) n=4 TAA D idm-3 G3T(E4) G4A(W988) WT idm-3 ATC TCT GGG ACT CAT GAG CAG GAG GCT AGC
A idm-3 idm-3 B Physical distance (Mb) 4.6 4.86.6 8.4 C Chr.3 Recom. Rate (%) ATG 3.9.9.9 9.74 Candidate region (.74 Mb) n=4 TAA D idm-3 G3T(E4) G4A(W988) WT idm-3 ATC TCT GGG ACT CAT GAG CAG GAG GCT AGC
Kwon et al., Supplemental Figure 1
 Kwon et al., Supplemental Figure 1 Mock, 14 dpi AvrRpm1, 14 dpi RabG3bDN RabG3bRNAi Supplemental Figure S1. Cell death phenotypes of leaves inoculated with Pst DC3000 (AvrRpm1) in 5-week-old young plants.
Kwon et al., Supplemental Figure 1 Mock, 14 dpi AvrRpm1, 14 dpi RabG3bDN RabG3bRNAi Supplemental Figure S1. Cell death phenotypes of leaves inoculated with Pst DC3000 (AvrRpm1) in 5-week-old young plants.
Transfection of CRISPR/Cas9 Nuclease NLS ribonucleoprotein (RNP) into adherent mammalian cells using Lipofectamine RNAiMAX
 Transfection of CRISPR/Cas9 Nuclease NLS ribonucleoprotein (RNP) into adherent mammalian cells using Lipofectamine RNAiMAX INTRODUCTION The CRISPR/Cas genome editing system consists of a single guide RNA
Transfection of CRISPR/Cas9 Nuclease NLS ribonucleoprotein (RNP) into adherent mammalian cells using Lipofectamine RNAiMAX INTRODUCTION The CRISPR/Cas genome editing system consists of a single guide RNA
Khaled_Fig. S MITF TYROSINASE R²= MITF PDE4D R²= Variance from mean mrna expression
 Khaled_Fig. S Variance from mean mrna expression.8 2 MITF.6 TYROSINASE.4 R²=.73.2.8.6.4.2.8.6.4.2.8.6.4.2 MALME3M SKMEL28 UACC257 MITF PDE4D R²=.63 4.5 5 MITF 3.5 4 PDE4B 2.5 3 R²=.2.5 2.5.8.6.4.2.8.6.4.2
Khaled_Fig. S Variance from mean mrna expression.8 2 MITF.6 TYROSINASE.4 R²=.73.2.8.6.4.2.8.6.4.2.8.6.4.2 MALME3M SKMEL28 UACC257 MITF PDE4D R²=.63 4.5 5 MITF 3.5 4 PDE4B 2.5 3 R²=.2.5 2.5.8.6.4.2.8.6.4.2
Polyclonal ARHGAP25 antibody was prepared from rabbit serum after intracutaneous
 Preparation and purification of polyclonal antibodies Polyclonal ARHGAP25 antibody was prepared from rabbit serum after intracutaneous injections of glutathione S-transferase-ARHGAP25-(509-619) (GST-coiled
Preparation and purification of polyclonal antibodies Polyclonal ARHGAP25 antibody was prepared from rabbit serum after intracutaneous injections of glutathione S-transferase-ARHGAP25-(509-619) (GST-coiled
Activation of a Floral Homeotic Gene in Arabidopsis
 Activation of a Floral Homeotic Gene in Arabidopsis Busch, M.A., Bomblies, K., Weigel, D. kuleuven-kortrijk.be Simon Olthof Louie Christodoulidis 1 In Arabidopsis flowers, appearance is based, in part,
Activation of a Floral Homeotic Gene in Arabidopsis Busch, M.A., Bomblies, K., Weigel, D. kuleuven-kortrijk.be Simon Olthof Louie Christodoulidis 1 In Arabidopsis flowers, appearance is based, in part,
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/323/5910/124/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Regulation of Neuronal Survival Factor MEF2D by Chaperone-Mediated Autophagy Qian Yang, Hua She, Marla Gearing, Emanuela
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/323/5910/124/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Regulation of Neuronal Survival Factor MEF2D by Chaperone-Mediated Autophagy Qian Yang, Hua She, Marla Gearing, Emanuela
Thyroid peroxidase gene expression is induced by lipopolysaccharide involving Nuclear Factor (NF)-κB p65 subunit phosphorylation
 1 2 3 4 5 SUPPLEMENTAL DATA Thyroid peroxidase gene expression is induced by lipopolysaccharide involving Nuclear Factor (NF)-κB p65 subunit phosphorylation Magalí Nazar, Juan Pablo Nicola, María Laura
1 2 3 4 5 SUPPLEMENTAL DATA Thyroid peroxidase gene expression is induced by lipopolysaccharide involving Nuclear Factor (NF)-κB p65 subunit phosphorylation Magalí Nazar, Juan Pablo Nicola, María Laura
Supplementary Fig. S1. SAMHD1c has a more potent dntpase activity than. SAMHD1c. Purified recombinant SAMHD1c and SAMHD1c proteins (with
 Supplementary Fig. S1. SAMHD1c has a more potent dntpase activity than SAMHD1c. Purified recombinant SAMHD1c and SAMHD1c proteins (with concentration of 800nM) were incubated with 1mM dgtp for the indicated
Supplementary Fig. S1. SAMHD1c has a more potent dntpase activity than SAMHD1c. Purified recombinant SAMHD1c and SAMHD1c proteins (with concentration of 800nM) were incubated with 1mM dgtp for the indicated
Supplemental Information. HEXIM1 and NEAT1 Long Non-coding RNA Form. a Multi-subunit Complex that Regulates. DNA-Mediated Innate Immune Response
 Molecular Cell, Volume 67 Supplemental Information HEXIM1 and NEAT1 Long Non-coding RNA Form a Multi-subunit Complex that Regulates DNA-Mediated Innate Immune Response Mehdi Morchikh, Alexandra Cribier,
Molecular Cell, Volume 67 Supplemental Information HEXIM1 and NEAT1 Long Non-coding RNA Form a Multi-subunit Complex that Regulates DNA-Mediated Innate Immune Response Mehdi Morchikh, Alexandra Cribier,
mirna Purification from Plant Tissues: Corn, Soybean and Arabidopsis
 mirna Purification from Plant Tissues: Corn, Soybean and Arabidopsis A Maxwell RSC mirna Tissue Kit Application Note Materials Required: Maxwell RSC mirna Tissue Kit (Cat.# AS1480) QuantiFluor RNA System
mirna Purification from Plant Tissues: Corn, Soybean and Arabidopsis A Maxwell RSC mirna Tissue Kit Application Note Materials Required: Maxwell RSC mirna Tissue Kit (Cat.# AS1480) QuantiFluor RNA System
Supplemental Data. Aung et al. (2011). Plant Cell /tpc
 35S pro:pmd1-yfp 10 µm Supplemental Figure 1. -terminal YFP fusion of PMD1 (PMD1-YFP, in green) is localized to the cytosol. grobacterium cells harboring 35S pro :PMD1-YFP were infiltrated into tobacco
35S pro:pmd1-yfp 10 µm Supplemental Figure 1. -terminal YFP fusion of PMD1 (PMD1-YFP, in green) is localized to the cytosol. grobacterium cells harboring 35S pro :PMD1-YFP were infiltrated into tobacco
Supplemental Information. Role of phosphatase of regenerating liver 1 (PRL1) in spermatogenesis
 Supplemental Information Role of phosphatase of regenerating liver 1 (PRL1) in spermatogenesis Yunpeng Bai ;, Lujuan Zhang #, Hongming Zhou #, Yuanshu Dong #, Qi Zeng, Weinian Shou, and Zhong-Yin Zhang
Supplemental Information Role of phosphatase of regenerating liver 1 (PRL1) in spermatogenesis Yunpeng Bai ;, Lujuan Zhang #, Hongming Zhou #, Yuanshu Dong #, Qi Zeng, Weinian Shou, and Zhong-Yin Zhang
Supplementary information, Figure S1
 Supplementary information, Figure S1 (A) Schematic diagram of the sgrna and hspcas9 expression cassettes in a single binary vector designed for Agrobacterium-mediated stable transformation of Arabidopsis
Supplementary information, Figure S1 (A) Schematic diagram of the sgrna and hspcas9 expression cassettes in a single binary vector designed for Agrobacterium-mediated stable transformation of Arabidopsis
Supplemental Information. PARP1 Represses PAP and Inhibits Polyadenylation during Heat Shock
 Molecular Cell, Volume 49 Supplemental Information PARP1 Represses PAP and Inhibits Polyadenylation during Heat Shock Dafne Campigli Di Giammartino, Yongsheng Shi, and James L. Manley Supplemental Information
Molecular Cell, Volume 49 Supplemental Information PARP1 Represses PAP and Inhibits Polyadenylation during Heat Shock Dafne Campigli Di Giammartino, Yongsheng Shi, and James L. Manley Supplemental Information
Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture
 Supplementary materials for Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture Article tile: Agrobacterium mediated Genetic Transformation of Miscanthus sinensis Authors: Ok-Jin Hwang 1, Mi-Ae Cho 1, Yun-Jeong Han 1,
Supplementary materials for Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture Article tile: Agrobacterium mediated Genetic Transformation of Miscanthus sinensis Authors: Ok-Jin Hwang 1, Mi-Ae Cho 1, Yun-Jeong Han 1,
Department of Molecular, Cellular, and Developmental Biology, Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut c
 The Plant Cell, Vol. 22: 108 123, January 2010, www.plantcell.org ã 2010 American Society of Plant Biologists Arabidopsis CULLIN4-Damaged DNA Binding Protein 1 Interacts with CONSTITUTIVELY PHOTOMORPHOGENIC1-SUPPRESSOR
The Plant Cell, Vol. 22: 108 123, January 2010, www.plantcell.org ã 2010 American Society of Plant Biologists Arabidopsis CULLIN4-Damaged DNA Binding Protein 1 Interacts with CONSTITUTIVELY PHOTOMORPHOGENIC1-SUPPRESSOR
The microtubule-associated tau protein has intrinsic acetyltransferase activity. Todd J. Cohen, Dave Friedmann, Andrew W. Hwang, Ronen Marmorstein and
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION: The microtubule-associated tau protein has intrinsic acetyltransferase activity Todd J. Cohen, Dave Friedmann, Andrew W. Hwang, Ronen Marmorstein and Virginia M.Y. Lee Cohen
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION: The microtubule-associated tau protein has intrinsic acetyltransferase activity Todd J. Cohen, Dave Friedmann, Andrew W. Hwang, Ronen Marmorstein and Virginia M.Y. Lee Cohen
Integration of Light- and Brassinosteroid-Signaling Pathways by a GATA Transcription Factor in Arabidopsis
 Article Integration of Light- and Brassinosteroid-Signaling Pathways by a GATA Transcription Factor in Arabidopsis Xiao-Min Luo, 1,5,6 Wen-Hui Lin, 1,2,6 Shengwei Zhu, 1,2,6 Jia-Ying Zhu, 1,5,6 Yu Sun,
Article Integration of Light- and Brassinosteroid-Signaling Pathways by a GATA Transcription Factor in Arabidopsis Xiao-Min Luo, 1,5,6 Wen-Hui Lin, 1,2,6 Shengwei Zhu, 1,2,6 Jia-Ying Zhu, 1,5,6 Yu Sun,
Supplementary Material and Methods
 Supplementary Material and Methods Microarray Total RNA was extracted from three independent batches of plants using Tri-Reagent (Ambion, Austin, TX, USA). From each batch of wild type (Col- 0) and wrky33
Supplementary Material and Methods Microarray Total RNA was extracted from three independent batches of plants using Tri-Reagent (Ambion, Austin, TX, USA). From each batch of wild type (Col- 0) and wrky33
Supplementary Figure 1: Expression of RNF8, HERC2 and NEURL4 in the cerebellum and knockdown of RNF8 by RNAi (a) Lysates of the cerebellum from rat
 Supplementary Figure 1: Expression of RNF8, HERC2 and NEURL4 in the cerebellum and knockdown of RNF8 by RNAi (a) Lysates of the cerebellum from rat pups at P6, P14, P22, P30 and adult (A) rats were subjected
Supplementary Figure 1: Expression of RNF8, HERC2 and NEURL4 in the cerebellum and knockdown of RNF8 by RNAi (a) Lysates of the cerebellum from rat pups at P6, P14, P22, P30 and adult (A) rats were subjected
Cooperative Research Centre for Tropical Plant Protection, University of Queensland, St. Lucia, Queensland, 4072, Australia
 The Plant Cell, Vol. 16, 3460 3479, December 2004, www.plantcell.org ª 2004 American Society of Plant Biologists Antagonistic Interaction between Abscisic Acid and Jasmonate-Ethylene Signaling Pathways
The Plant Cell, Vol. 16, 3460 3479, December 2004, www.plantcell.org ª 2004 American Society of Plant Biologists Antagonistic Interaction between Abscisic Acid and Jasmonate-Ethylene Signaling Pathways
- NaCr. + NaCr. α H3K4me2 α H3K4me3 α H3K9me3 α H3K27me3 α H3K36me3 H3 H2A-2B H4 H3 H2A-2B H4 H3 H2A-2B H4. α Kcr. (rabbit) α Kac.
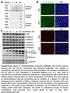 + NaCr NaCr + NaCr NaCr Peptides 10ng 50ng 250ng K α Pan (mouse) Pan (mouse) 10ng 50ng 250ng α Pan (rabbit) C 10ng 50ng 250ng α Pan (mouse) 0 1.25 2.5 5 10 20 40 (mm) NaCr 24h α Pan (rabbit) α K4me2 α
+ NaCr NaCr + NaCr NaCr Peptides 10ng 50ng 250ng K α Pan (mouse) Pan (mouse) 10ng 50ng 250ng α Pan (rabbit) C 10ng 50ng 250ng α Pan (mouse) 0 1.25 2.5 5 10 20 40 (mm) NaCr 24h α Pan (rabbit) α K4me2 α
Anti-Aging Skin Care Regimen. What is Phyto Stem Cell Plant Cell Callus?
 Anti-Aging Skin Care Regimen What is Phyto Stem Cell Plant Cell Callus? 01 Plant Cell Culture Technology for Anti-Aging Actives Phytochemicals are non-nutritive plant chemicals that have protective or
Anti-Aging Skin Care Regimen What is Phyto Stem Cell Plant Cell Callus? 01 Plant Cell Culture Technology for Anti-Aging Actives Phytochemicals are non-nutritive plant chemicals that have protective or
FRAUNHOFER IME SCREENINGPORT
 FRAUNHOFER IME SCREENINGPORT Detection technologies used in drug discovery Introduction Detection technologies in drug discovery is unlimited only a biased snapshot can be presented Differences can presented
FRAUNHOFER IME SCREENINGPORT Detection technologies used in drug discovery Introduction Detection technologies in drug discovery is unlimited only a biased snapshot can be presented Differences can presented
Heme utilization in the Caenorhabditis elegans hypodermal cells is facilitated by hemeresponsive
 Supplemental Data Heme utilization in the Caenorhabditis elegans hypodermal cells is facilitated by hemeresponsive gene-2 Caiyong Chen 1, Tamika K. Samuel 1, Michael Krause 2, Harry A. Dailey 3, and Iqbal
Supplemental Data Heme utilization in the Caenorhabditis elegans hypodermal cells is facilitated by hemeresponsive gene-2 Caiyong Chen 1, Tamika K. Samuel 1, Michael Krause 2, Harry A. Dailey 3, and Iqbal
sirna Transfection Into Primary Neurons Using Fuse-It-siRNA
 sirna Transfection Into Primary Neurons Using Fuse-It-siRNA This Application Note describes a protocol for sirna transfection into sensitive, primary cortical neurons using Fuse-It-siRNA. This innovative
sirna Transfection Into Primary Neurons Using Fuse-It-siRNA This Application Note describes a protocol for sirna transfection into sensitive, primary cortical neurons using Fuse-It-siRNA. This innovative
SureSilencing sirna Array Technology Overview
 SureSilencing sirna Array Technology Overview Pathway-Focused sirna-based RNA Interference Topics to be Covered Who is SuperArray? Brief Introduction to RNA Interference Challenges Facing RNA Interference
SureSilencing sirna Array Technology Overview Pathway-Focused sirna-based RNA Interference Topics to be Covered Who is SuperArray? Brief Introduction to RNA Interference Challenges Facing RNA Interference
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Chakrabarty et al. 10.1073/pnas.1018001108 SI Materials and Methods Cell Lines. All cell lines were purchased from the American Type Culture Collection. Media and FBS were purchased
Supporting Information Chakrabarty et al. 10.1073/pnas.1018001108 SI Materials and Methods Cell Lines. All cell lines were purchased from the American Type Culture Collection. Media and FBS were purchased
MATERIAL DATA SHEET. NOTE: Kit contains reagents sufficient for 10 x 30 μl reactions and 5 Western Blots (minigel. Reagents Provided in Kit
 Lot # XXXXX ITCH/AIP4 Ubiquitin Ligase Kit Cat. # K-270 MATERIAL DATA SHEET The mammalian Itchy homolog, or ITCH, (also known as Atrophin-1-interacting protein 4 or AIP4) is a HECT domain class ubiquitin
Lot # XXXXX ITCH/AIP4 Ubiquitin Ligase Kit Cat. # K-270 MATERIAL DATA SHEET The mammalian Itchy homolog, or ITCH, (also known as Atrophin-1-interacting protein 4 or AIP4) is a HECT domain class ubiquitin
Supplemental Data Supplementary Figure Legends and Scheme Figure S1.
 Supplemental Data Supplementary Figure Legends and Scheme Figure S1. UTK1 inhibits the second EGF-induced wave of lamellipodia formation in TT cells. A and B, EGF-induced lamellipodia formation in TT cells,
Supplemental Data Supplementary Figure Legends and Scheme Figure S1. UTK1 inhibits the second EGF-induced wave of lamellipodia formation in TT cells. A and B, EGF-induced lamellipodia formation in TT cells,
Supplemental Materials. Matrix Proteases Contribute to Progression of Pelvic Organ Prolapse in Mice and Humans
 Supplemental Materials Matrix Proteases Contribute to Progression of Pelvic Organ Prolapse in Mice and Humans Madhusudhan Budatha, Shayzreen Roshanravan, Qian Zheng, Cecilia Weislander, Shelby L. Chapman,
Supplemental Materials Matrix Proteases Contribute to Progression of Pelvic Organ Prolapse in Mice and Humans Madhusudhan Budatha, Shayzreen Roshanravan, Qian Zheng, Cecilia Weislander, Shelby L. Chapman,
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information MLL histone methylases regulate expression of HDLR- in presence of estrogen and control plasma cholesterol in vivo Khairul I. Ansari 1, Sahba Kasiri 1, Imran Hussain 1, Samara
Supplementary Information MLL histone methylases regulate expression of HDLR- in presence of estrogen and control plasma cholesterol in vivo Khairul I. Ansari 1, Sahba Kasiri 1, Imran Hussain 1, Samara
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 PCR-genotyping of the three mouse models used in this study and controls for behavioral experiments after semi-chronic Pten inhibition. a-c. DNA from App/Psen1 (a), Pten tg (b) and
Supplementary Figure 1 PCR-genotyping of the three mouse models used in this study and controls for behavioral experiments after semi-chronic Pten inhibition. a-c. DNA from App/Psen1 (a), Pten tg (b) and
BR-dependent phosphorylation modulates PIF4 transcriptional activity and shapes diurnal hypocotyl growth
 BR-dependent phosphorylation modulates PIF4 transcriptional activity and shapes diurnal hypocotyl growth Stella Bernardo-Garcıa, 1 Miguel de Lucas, 1 Cristina Martınez, Ana Espinosa-Ruiz, Jean-Michel Daviere,
BR-dependent phosphorylation modulates PIF4 transcriptional activity and shapes diurnal hypocotyl growth Stella Bernardo-Garcıa, 1 Miguel de Lucas, 1 Cristina Martınez, Ana Espinosa-Ruiz, Jean-Michel Daviere,
The plant hormone abscisic acid (ABA) plays essential roles
 Integration of light and abscisic acid signaling during seed germination and early seedling development Hao Chen*, Jingyu Zhang, Michael M. Neff, Suk-Whan Hong, Huiyong Zhang, Xing-Wang Deng, and Liming
Integration of light and abscisic acid signaling during seed germination and early seedling development Hao Chen*, Jingyu Zhang, Michael M. Neff, Suk-Whan Hong, Huiyong Zhang, Xing-Wang Deng, and Liming
AP Biology Gene Expression/Biotechnology REVIEW
 AP Biology Gene Expression/Biotechnology REVIEW Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Gene expression can be a. regulated before transcription.
AP Biology Gene Expression/Biotechnology REVIEW Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Gene expression can be a. regulated before transcription.
Supplemental Information. Boundary Formation through a Direct. Threshold-Based Readout. of Mobile Small RNA Gradients
 Developmental Cell, Volume 43 Supplemental Information Boundary Formation through a Direct Threshold-Based Readout of Mobile Small RNA Gradients Damianos S. Skopelitis, Anna H. Benkovics, Aman Y. Husbands,
Developmental Cell, Volume 43 Supplemental Information Boundary Formation through a Direct Threshold-Based Readout of Mobile Small RNA Gradients Damianos S. Skopelitis, Anna H. Benkovics, Aman Y. Husbands,
Supplemental Information
 Supplemental Information Itemized List Materials and Methods, Related to Supplemental Figures S5A-C and S6. Supplemental Figure S1, Related to Figures 1 and 2. Supplemental Figure S2, Related to Figure
Supplemental Information Itemized List Materials and Methods, Related to Supplemental Figures S5A-C and S6. Supplemental Figure S1, Related to Figures 1 and 2. Supplemental Figure S2, Related to Figure
SANTA CRUZ BIOTECHNOLOGY, INC.
 TECHNICAL SERVICE GUIDE: Western Blotting 2. What size bands were expected and what size bands were detected? 3. Was the blot blank or was a dark background or non-specific bands seen? 4. Did this same
TECHNICAL SERVICE GUIDE: Western Blotting 2. What size bands were expected and what size bands were detected? 3. Was the blot blank or was a dark background or non-specific bands seen? 4. Did this same
Materials and Methods: All strains were derivatives of SK1 and are listed in Supplemental Table 1.
 Supplemental Online Material: Materials and Methods: All strains were derivatives of SK1 and are listed in Supplemental Table 1. Constructs: pclb2-3ha-cdc5 and pclb2-3ha-cdc2 strains were constructed by
Supplemental Online Material: Materials and Methods: All strains were derivatives of SK1 and are listed in Supplemental Table 1. Constructs: pclb2-3ha-cdc5 and pclb2-3ha-cdc2 strains were constructed by
Impact of Retinoic acid induced-1 (Rai1) on Regulators of Metabolism and Adipogenesis
 Impact of Retinoic acid induced-1 (Rai1) on Regulators of Metabolism and Adipogenesis The mammalian system undergoes ~24 hour cycles known as circadian rhythms that temporally orchestrate metabolism, behavior,
Impact of Retinoic acid induced-1 (Rai1) on Regulators of Metabolism and Adipogenesis The mammalian system undergoes ~24 hour cycles known as circadian rhythms that temporally orchestrate metabolism, behavior,
A Dual Pathogenic Mechanism Links Tau Acetylation to Sporadic Tauopathy
 A Dual Pathogenic Mechanism Links Tau Acetylation to Sporadic Tauopathy Hanna Trzeciakiewicz, Jui-Heng Tseng, Connor M. Wander, Victoria Madden, Ashutosh Tripathy, Chao-Xing Yuan, and Todd J. Cohen Supplementary
A Dual Pathogenic Mechanism Links Tau Acetylation to Sporadic Tauopathy Hanna Trzeciakiewicz, Jui-Heng Tseng, Connor M. Wander, Victoria Madden, Ashutosh Tripathy, Chao-Xing Yuan, and Todd J. Cohen Supplementary
by Neurobasal medium (supplemented with B27, 0.5mM glutamine, and 100 U/mL
 Supplementary Materials and methods Neuronal cultures and transfection The hippocampus was dissected from E8 rat embryos, dissociated, and neurons plated onto glass coverslips coated with poly-ornithine
Supplementary Materials and methods Neuronal cultures and transfection The hippocampus was dissected from E8 rat embryos, dissociated, and neurons plated onto glass coverslips coated with poly-ornithine
Blot: a spot or stain, especially of ink on paper.
 Blotting technique Blot: a spot or stain, especially of ink on paper. 2/27 In molecular biology and genetics, a blot is a method of transferring proteins, DNA or RNA, onto a carrier (for example, a nitrocellulose,pvdf
Blotting technique Blot: a spot or stain, especially of ink on paper. 2/27 In molecular biology and genetics, a blot is a method of transferring proteins, DNA or RNA, onto a carrier (for example, a nitrocellulose,pvdf
A) B) Ladder. Supplementary Figure 1. Recombinant calpain 14 purification analysis. A) The general domain structure of classical
 A) B) Ladder C) r4 r4 Nt- -Ct 78 kda Supplementary Figure 1. Recombinant calpain 14 purification analysis. A) The general domain structure of classical calpains is shown. The protease core consists of
A) B) Ladder C) r4 r4 Nt- -Ct 78 kda Supplementary Figure 1. Recombinant calpain 14 purification analysis. A) The general domain structure of classical calpains is shown. The protease core consists of
ab Hypoxic Response Human Flow Cytometry Kit
 ab126585 Hypoxic Response Human Flow Cytometry Kit Instructions for Use For measuring protein levels by flow cytometry: hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha (HIF1A) and BCL2/adenovirus E1B 19 kda proteininteracting
ab126585 Hypoxic Response Human Flow Cytometry Kit Instructions for Use For measuring protein levels by flow cytometry: hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha (HIF1A) and BCL2/adenovirus E1B 19 kda proteininteracting
This Document Contains:
 This Document Contains: 1. In-Cell Western Protocol II. Cell Seeding and Stimulation Supplemental Protocol III. Complete Assay Example: Detailing the Seeding, Stimulation and Detection of the A431 Cellular
This Document Contains: 1. In-Cell Western Protocol II. Cell Seeding and Stimulation Supplemental Protocol III. Complete Assay Example: Detailing the Seeding, Stimulation and Detection of the A431 Cellular
Protocol for induction of expression and cell lysate production
 Protocol for induction of expression and cell lysate production AV-04 Doxycyclin induction and cell lysate 1.0 Introduction / Description This method is intended for the treatment of the previously transfected
Protocol for induction of expression and cell lysate production AV-04 Doxycyclin induction and cell lysate 1.0 Introduction / Description This method is intended for the treatment of the previously transfected
ab SUMOylation Assay Kit
 ab139470 SUMOylation Assay Kit Instructions for Use For the generation and detection of SUMOylated proteins in vitro. This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic use. Version
ab139470 SUMOylation Assay Kit Instructions for Use For the generation and detection of SUMOylated proteins in vitro. This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic use. Version
Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1259; doi: /ijms
 S1 of S5 Supplementary Materials: Fibroblast-Derived Extracellular Matrix Induces Chondrogenic Differentiation in Human Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal/Stem Cells in Vitro Kevin Dzobo, Taegyn Turnley,
S1 of S5 Supplementary Materials: Fibroblast-Derived Extracellular Matrix Induces Chondrogenic Differentiation in Human Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal/Stem Cells in Vitro Kevin Dzobo, Taegyn Turnley,
Toll Receptor-Mediated Hippo Signaling Controls Innate Immunity in Drosophila
 Cell Supplemental Information Toll Receptor-Mediated Hippo Signaling Controls Innate Immunity in Drosophila Bo Liu, Yonggang Zheng, Feng Yin, Jianzhong Yu, Neal Silverman, and Duojia Pan Supplemental Experimental
Cell Supplemental Information Toll Receptor-Mediated Hippo Signaling Controls Innate Immunity in Drosophila Bo Liu, Yonggang Zheng, Feng Yin, Jianzhong Yu, Neal Silverman, and Duojia Pan Supplemental Experimental
Small-Molecule Drug Target Identification/Deconvolution Technologies
 Small-Molecule Drug Target Identification/Deconvolution Technologies Case-Studies Shantani Target ID Technology Tool Box Target Deconvolution is not Trivial = A single Tool / Technology May Not necessarily
Small-Molecule Drug Target Identification/Deconvolution Technologies Case-Studies Shantani Target ID Technology Tool Box Target Deconvolution is not Trivial = A single Tool / Technology May Not necessarily
% Viability. isw2 ino isw2 ino isw2 ino isw2 ino mM HU 4-NQO CPT
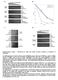 a Drug concentration b 1.3% MMS nhp1 nhp1 8 nhp1 mag1.5% MMS.3% MMS nhp1 nhp1 ino8 9 ino8 9 % Viability 4.5% MMS ino8 9 ino8 9 2.5.1.15 % MMS c d nhp1 nhp1 nhp1 nhp1 nhp1 nhp1 Control (YPD) γ IR (1 gy)
a Drug concentration b 1.3% MMS nhp1 nhp1 8 nhp1 mag1.5% MMS.3% MMS nhp1 nhp1 ino8 9 ino8 9 % Viability 4.5% MMS ino8 9 ino8 9 2.5.1.15 % MMS c d nhp1 nhp1 nhp1 nhp1 nhp1 nhp1 Control (YPD) γ IR (1 gy)
