SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND VIDEOS
|
|
|
- Kory Richardson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
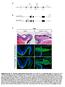
1 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND VIDEOS Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of Human Intestinal Organoids (HIOs). (a) Method for generating HIOs through directed differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells. (b) Temporal expression of differentiation markers at each stage of HIO development. Activin A mediated efficient differentiation into definitive endoderm
2 (FOXA2 + and SOX17 + ) and WNT activation in combination with FGF4 induced CDX2 expression in monolayers and free-floating spheroids. Data representative of 3 independent experiments. (c) Growth of spheroids in Matrigel for 4 weeks resulted in the formation of HIOs expressing CDX2 + epithelium. Data representative of 6 independent experiments. HIOs were engrafted into the kidney subcapsular space of mice, where after 6 weeks they grew and matured to form intestinal tissue with crypts and villi. The human-specific antibody HuNu shows that intestinal epithelium and mesenchyme are human in origin. Data representative of 3 independent experiments. Scale bars, 100 µm (d) Schematic for generating and incorporating vagal NCCs into HIOs (to accompany figure 1). HIOs and NCCs are generated separately, combined by low-speed centrifugation, embedded in Matrigel and grown for 4 weeks in vitro. 2
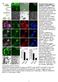
3 Supplementary Figure 2. Generation of vagal-like Neural Crest Cells (NCCs). 3
4 (a) Day 6 free-floating neurospheres are roughly 500 µm in diameter and positive for PAX6, Vimentin, and SOX9, characteristic of neural stem cells and the lateral neural plate where neural crest cells form. (b) Neurospheres attached to a fibronectin substrate and formed neural rosettes visible with bright field microscopy. Attached neurospheres broadly expressed PAX6 whereas Vimentin staining was observed at the edge of neural rosettes where NCCs were delaminating. As NCCs migrated away from rosettes, PAX6 was down regulated whereas SOX2 expression was maintained. Scale bars, 500 µm (left panels), 100 µm (middle and right panels). (c) NCCs displayed stellate morphology and were positive for surface markers HNK-1, p75 NTR, and RET. Scale bars, 50 µm (left panel), 100 µm (middle and right panels). (d) Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of neural plate border genes and regulators of neural crest cell specification. (e) Treatment of neurospheres for 48 hours with RA results in the formation of NCCs that express Vagallevel HOX genes. Values in graphs represent mean ± s.e.m.; * P < 0.01, ** P < 0.001; Student s t-test (two-tailed, unpaired); n=3 (cell culture replicates) per condition; data representative of 3 independent experiments. 4
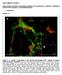
5 Supplementary Figure 3. Comparison of human and chick NCC behavior. (a and b) Isolation and culturing of cranial (Hox-negative) and trunk (Hox-positive) NCCs from chick embryos and analysis of Hox gene expression. NCCs isolated from anterior chicken neural tube do not express Hox genes while those isolated from posterior neural tube are HoxB7 positive. (c) Chicken cranial NCCs express vagal-level Hox genes HoxB3 and HoxB7 when treated with 2 µm RA for 48 hours. A different posteriorizing factor, FGF4, had no effect on Hox gene expression. (d) Schematic describing engraftment of human PSC-derived NCCs into chicken embryos. GFPlabeled human NCCs were injected intersomitically into HH10-12 chick embryos in ovo. (e) Embryos were analyzed at ~HH23. GFP-labeled cells had migrated laterally along the neural tube (NT) and could be found colonizing the foregut (FG). Scale bar, 100 µm. (f) Differentiation of GFP-labeled cells into peripheral neurons (Peripherin) (dorsal, right; anterior, up). Scale bar, 500 µm. Data representative of 5 independent experiments injecting human NCCs into chick embryos. 5
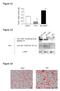
6 6
7 Supplementary Figure 4. Differentiation potential of cranial (- RA) and vagal-like (- RA) NCCs and expression of NCC migratory cues. (a) In vitro differentiation of human PSC-derived NCCs into neuroglial lineages and mesenchymal lineages (osteocytes and chondrocytes). Cranial and RA-treated NCCs were equally competent to form neuroglial lineages (Peripherin and GFAP), osteocytes (alizarin red), and chondrocytes (alcian blue) in vitro. Scale bars, 50 µm (left panels), 500 µm (middle and right panels). Data representative of 2 independent experiments. (b) NCCs were generated from H9-GAPDH-GFP human ESCs, which ubiquitously express GFP, and combined with HIOs generated from H1 ESCs. HIOs were co-stained for GFP and pan-neuronal marker PGP9.5 or glial marker S100β. Neuroglial cells in HIOs+ENS are NCC-derived as is evidenced by co-expression of GFP and neuroglial markers. Scale bars, 100 µm. Data representative of 3 independent experiments. (c) Small intestine of E11.5 mouse embryo showed a similar distribution of neurons compared to HIOs+ENS in vitro. Although glial progenitors are present in the gut of E11.5 mouse embryos, S100β is not expressed until E14.5 suggesting that HIOs+ENS are slightly more mature than E11.5 intestine. Scale bars, 100 µm. (d) HIOs formed in vitro expressed GDNF and EDN3. Values in graphs represent mean ± s.e.m.; * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01; t-test (two-tailed, unpaired); n=3 (cell culture replicates). Data are representative of 2 independent experiments. 7
8 Supplementary Figure 5. Differential gene expression in HIOs+ENS in vitro. (a) Heatmap was generated clustering on both gene and condition, using the Euclidean distance metric and Average linkage rule. HIOs and HIOs+ENS clustered separately according to their gene expression pattern. (b) Spearman correlation matrix confirmed that HIOs and HIOs+ENS presented separate and distinct cluster patterns based on gene expression. (c) Barplots of top 15 ontological enrichments in HIOs+ENS. 8
9 a. in vitro 4 Week HIOs + NCCs b. in vivo engrafted HIOs + NCCs HIOs + Cranial-like NCCs (No RA) 10/11 4/5 HIOs + Vagal-like NCCs (2 M RA) 11/11 5/5 Supplementary Figure 6. HIOs + human cranial- and vagal-like NCCs engrafted in vivo. (a and b) PSC-derived cranial/hox-negative (no RA) and vagal/hox-positive (2 µm RA) NCCs were both competent to engraft and form ENS neuroglial cells. Cranial-like NCCs formed pigmented epithelium (arrowhead) in vitro (a) and in vivo (b) suggesting a retained competence to form neuroepithelium. Scale bars, 1 mm (left panels), 2 mm (right panels) 9
10 Supplementary Figure 7. HIOs+ENS grown in vivo form a neuroglial plexus and ganglia-like structures. (a) Whole mount immunostaining for neurons (TUBB3, en face view) and muscle (DES, Desmin, en face view) shows neuronal network organized above the muscular layer in HIO+ENS (right panel, n=6), reminiscent of the human ENS plexus organization (left panel, n=5). Lower panel shows whole mount immunostaining of developing neurons and smooth muscle in the ENS of adult and perinatal (e18.5) mouse jejunum (n=3). Scale bars, 100 µm (upper panels), 50 µm (lower panels). (b) Whole mount immunostaining for glia (S100β, en face view) shows glial network organized similarly in 10
11 both human (left panel, n=5) and HIOs+ENS (right panel, n=5). Lower panel shows whole mount immunostaining of developing glia in the ENS of adult and perinatal (e18.5) mouse jejunum (n=3). Scale bar, 100 µm (upper panels), 50 µm (lower panels). (c) In immunostained sections (upper panels), Neurons (NF220) were spread throughout a myenteric-like plexus and contained neuronal cell bodies (HuC/D) in clusters, similar to human myenteric plexus (n=3). Scale bars, 50 µm. Whole mount (lower panel) immunostaining for neurons (TUBB3, en face view) and neural cell bodies (HuC/D, lateral view) shows neuronal cell bodies organized into a ganglion-like clusters in HIOs+ENS (n=5). Scale bars, 100 µm. Data representative of 3 independent experiments. (d) Following engraftment in vivo, dopaminergic neurons (TH), interneurons (ChAT, 5-HT), sensory neurons (CALB1), excitatory neurons (Calretinin) and inhibitory neurons (nnos) were all found in HIOs+ENS. Scale bar, 100µm. 11
12 Supplementary Figure 8. Neuronal cells express GCaMP6f +. Following days in culture, HIOs+ GCaMP6f-derived ENS were stained for GFP (GCaMP6f) and TUBB3. GFP is expressed in TUBB3+ cells suggesting that neuronal cells are expressing calcium transients. Scale bar, 50 µm. Data shown is a representative example from 4 independent experiments. 12
13 Supplementary Figure 9. Neuromuscular coupling in HIOs+ENS. 13
14 (a) Recordings of spontaneous contractions in transplanted HIOs and HIOs+ENS. (b) Left panel shows representative recording of Veratridine stimulation in HIOs (n=3) and HIOs+ENS (n=5). Right panel represents area under the curve (AUC) during Veratridine (3 µm) stimulation measured for 2 minutes before and after stimulation. (c) Area under the curve during Dimethylphenylpiperazinium (DMPP; 10 µm) stimulation measured for 2 minutes before and after stimulation, followed by tetrodotoxin (TTX; 10µM) treatment (n=3). (d) Area under the curve during DMPP stimulation measured for 2 minutes after stimulation, followed by NG-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME) treatment (n=3). (e) Left panel representative recordings following Sodium Nitroprusside (SNP) stimulation of both HIOs (n=4) and HIO+ENS tissues (n=14). Right panel area under the curve during SNP stimulation measured for 2 minutes before and after stimulation. Values in graphs represent mean ± s.e.m; Mann & Whitney test. 14
15 Supplementary Figure 10. PHOX2B expression and analysis of HIOs+PHOX2B mutant NCCs. (a) Schematic depicting the PHOX2B gene, indicating the homeobox domain and the downstream polyalanine sites. Arrow points to the targeted mutation, Y14X, present in the isogenic ips cells used to generate neural crest cells. (b) Quantitative reversetranscription PCR (qrt-pcr) data of HOXB genes in day 6 neurospheres and early passage neural crest cells suggesting similar patterning along the anterior-posterior axis between different PHOX2B genotypes at early stages. (c) Confocal imaging of in vitro cultures of HIOs±NCCs, demonstrating the absence of PHOX2B transcripts in the Y14X homozygous knockout. (d) Extended lists of gene ontology categories from RNA-seq analysis of expression differences in HIOs that were recombined with homozygous and heterozygous PHOX2B mutations compared to wild-type NCCs. 15
16 Supplementary Video 1. 3-dimensional image of human intestine showing enteric nerves in association with smooth muscle. Nerves were stained with TUBB3 (green) and smooth muscle was stained with Desmin (red). Nerves were tightly integrated into the layers of smooth muscle. Video corresponds to Supplementary Fig. 7a, top left panel. Supplementary Video 2. 3-dimensional image of HIOs+ENS tissue grown in vivo showing human enteric nerves in association with smooth muscle. Nerves were stained with TUBB3 (green) and smooth muscle was stained with Desmin (red). NCC-derived nerves were embedded within the layers of smooth muscle both in the myenteric and submucosal layers. Video corresponds to Supplementary Fig. 7a, top right panel. Supplementary Video 3. Time-lapse video of HIOs+ENS in vitro where the ENS was derived from neural crest cells containing a GCaMP6f reporter. Twenty-minute timelapse video of HIOs+ENS showing Ca 2+ flux specifically in NCC-derived cells. HIOs were generated with H1 cells, which do not have a Ca 2+ indicator. Single neurons have regular periodicity of depolarization. Video corresponds to Supplementary Fig. 3a. Supplementary Video 4. KCl stimulation of HIOs+ENS in vitro. Time-lapse video of HIOs+ENS showing broad depolarization of NCC-derived ENS cells in response to KCl addition. NCCs were generated from GCaMP6f expressing ipscs. Video corresponds to Supplementary Fig. 3b. Supplementary Video 5. Time-lapse video of explanted HIOs+ENS grown in vivo using GCaMP6f neural crest cells. A large nerve fiber was imaged where calcium oscillation was observed. NCCs were generated from GCaMP6f expressing ipscs. Video corresponds to Fig. 3c (left panel). Supplementary Video 6. KCl stimulation of explanted HIOs+ENS grown in vivo using GCaMP6f neural crest cells. Time-lapse video of transplanted HIOs+ENS showing depolarization of NCC-derived ENS cells in response to KCl addition. NCCs were generated from GCaMP6f expressing ipscs. Video corresponds to Fig. 3c, right panel. Supplementary Video 7-9. Time-lapse videos of electrically stimulated HIOs grown in vivo. Video 7 corresponds to the left panel of Fig. 4a (HIO) and shows an HIO lacking enteric nerves. Video 8 corresponds to the middle panel of Fig. 4a (HIO+ENS) and shows an HIO containing engrafted neural crest cells. Video 9 corresponds to the right panel of Fig. 4a (HIO+ENS) and shows an HIO containing engrafted neural crest cells that were stimulated in the presence of tetrodotoxin (HIO+ENS + TTX). Videos are played at 16X play speed. 16
17 TABLES Primary Antibody Source Dilution at RT Dilution at 4C Goat anti-e-cadherin R&D #AF648 1:250 Rat anti-e-cadherin R&D #MAB7481 1:1000 Mouse anti-e-cadherin BD # :500 Rabbit anti-βiii-tubulin (TUBB3) Abcam #ab :2000 Chicken anti-βiii-tubulin (TUBB3) Abcam #ab :1000 Rabbit anti-c-kit/cd117 (YR145) Abcam #ab :400 Mouse anti-huc/d Invitrogen #A :200 Rabbit anti-pgp9.5 Dako #Z :1000 Mouse anti-hnk-1 DSHB #1C10 1:50 Mouse anti-p75 NTR ATS #AB-N07 1:200 Rabbit anti-ret Aviva #ARP :200 Goat anti-peripherin Santa Cruz #sc :200 Mouse anti-gfap Millipore #MAB360 1:500 Rabbit anti-s100β Dako #Z :1000 Rabbit anti-nnos Abcam #ab :1000 Goat anti-desmin Santa Cruz #sc :100 Goat anti-calretinin Millipore #Ab1550 1:2000 Rabbit anti-calbindin Gift from K. Campbell 1:4000 Chicken anti-th Aves #TYH 1:500 Mouse anti-human Nuclei Chemicon #MAB1281 1:200 Chicken anti-nf220 Ab-online #ABIN :2000 Rabbit anti-syn1 Abcam #AB8 1:500 Mouse anti-chga DHSB #CPTC-CHGA-1 1:500 Rabbit anti-chat Millipore 1:200 Rabbit anti-ki67 Thermo #RM :500 Goat anti-gfp Abcam #ab6673 1:200 Secondary Antibody Source Dilution at RT Dilution at 4C Donkey anti-mouse 488 Jackson Immuno 1:500 1:1000 Donkey anti-mouse 546 Invitrogen 1:500 1:1000 Donkey anti-goat 568 Invitrogen 1:500 1:1000 Donkey anti-rabbit 546 Invitrogen 1:500 1:1000 Donkey anti-rabbit 647 Jackson Immuno 1:500 1:1000 Donkey anti-chicken 549 Invitrogen 1:500 1:1000 Goat anti-rabbit biotin Vector 1:500 1:1000
18 Horse anti-mouse biotin Vector 1:500 1:1000 Supplementary Table 1 Antibodies and dilutions for immunohistochemistry Gene Orientation Primer Sequence AP2α Sense ATGCTTTGGAAATTGACGGA Anti-sense ATTGACCTACAGTGCCCAGC Edn3 Sense GCACGTGCTTCACCTACAAG Anti-sense GGACAGTCCATAGGGCACC GAPDH Sense CCCATCACCATCTTCCAGGAG Anti-sense CTTCTCCATGGTGGTGAAGACG GDNF Sense TCCATGACATCATCGAACTGA Anti-sense GTCTGCCTGGTGCTGCTC HoxA2 Sense CCAAGAAAACCGCACTTCTG Anti-sense CATCGGCGATTTCCAGG HoxB3 Sense CGTCATGAATGGGATCTGC Anti-sense ATATTCACATCGAGCCCCAG HoxB5 Sense GGAAGCTTCACATCAGCCAT Anti-sense GGAACTCCTTTTCCAGCTCC HoxB7 Sense AACTTCCGGATCTACCCCTG Anti-sense CTTTCTCCAGCTCCAGGGTC Pax3 Sense GCCGCATCCTGAGAAGTAAA Anti-sense CTTCATCTGATTGGGGTGCT Pax7 Sense CAAACACAGCATCGACGG Anti-sense CTTCAGTGGGAGGTCAGGTT Snail2 Sense TGACCTGTCTGCAAATGCTC Anti-sense CAGACCCTGGTTGCTTCAA Sox10 Sense AGCTCAGCAAGACGCTGG Anti-sense CTTTCTTGTGCTGCATACGG
19 Sox9 Sense GTAATCCGGGTGGTCCTTCT Anti-sense GTACCCGCACTTGCACAAC Zic1 Sense AAGATCCACAAAAGGACGCA Anti-sense CACGTGCATGTGCTTCTTG Supplementary Table 2 Primers for qpcr.
Supplementary Figure 1: Derivation and characterization of RN ips cell lines. (a) RN ips cells maintain expression of pluripotency markers OCT4 and
 Supplementary Figure 1: Derivation and characterization of RN ips cell lines. (a) RN ips cells maintain expression of pluripotency markers OCT4 and SSEA4 after 10 passages in mtesr 1 medium. (b) Schematic
Supplementary Figure 1: Derivation and characterization of RN ips cell lines. (a) RN ips cells maintain expression of pluripotency markers OCT4 and SSEA4 after 10 passages in mtesr 1 medium. (b) Schematic
GENESDEV/2007/ Supplementary Figure 1 Elkabetz et al.,
 GENESDEV/2007/089581 Supplementary Figure 1 Elkabetz et al., GENESDEV/2007/089581 Supplementary Figure 2 Elkabetz et al., GENESDEV/2007/089581 Supplementary Figure 3 Elkabetz et al., GENESDEV/2007/089581
GENESDEV/2007/089581 Supplementary Figure 1 Elkabetz et al., GENESDEV/2007/089581 Supplementary Figure 2 Elkabetz et al., GENESDEV/2007/089581 Supplementary Figure 3 Elkabetz et al., GENESDEV/2007/089581
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 a before amputation regeneration regenerated limb DERMIS SKELETON MUSCLE SCHWANN CELLS EPIDERMIS DERMIS SKELETON MUSCLE SCHWANN CELLS EPIDERMIS developmental origin: lateral plate mesoderm presomitic mesoderm
a before amputation regeneration regenerated limb DERMIS SKELETON MUSCLE SCHWANN CELLS EPIDERMIS DERMIS SKELETON MUSCLE SCHWANN CELLS EPIDERMIS developmental origin: lateral plate mesoderm presomitic mesoderm
Guided differentiation of ES cell into mesenchymal stem cell
 Guided differentiation of ES cell into mesenchymal stem cell Takumi Era Division of Molecular Neurobiology Institute of Molecular Embryology and Genetics, Kumamoto University Differentiation pathways of
Guided differentiation of ES cell into mesenchymal stem cell Takumi Era Division of Molecular Neurobiology Institute of Molecular Embryology and Genetics, Kumamoto University Differentiation pathways of
Supplementary Fig. S1. Schematic representation of mouse lines Pax6 fl/fl and mrx-cre used in this study. (A) To generate Pax6 fl/ fl
 Supplementary Fig. S1. Schematic representation of mouse lines Pax6 fl/fl and mrx-cre used in this study. (A) To generate Pax6 fl/ fl, loxp sites flanking exons 3-6 (red arrowheads) were introduced into
Supplementary Fig. S1. Schematic representation of mouse lines Pax6 fl/fl and mrx-cre used in this study. (A) To generate Pax6 fl/ fl, loxp sites flanking exons 3-6 (red arrowheads) were introduced into
ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION Figure 1. METHODS ipsc culture ATCC No. Initial Cell Type Description Reprogramming Method Table 1.
 THE ESSENTIALS OF LIFE SCIENCE RESEARCH GLOBALLY DELIVERED DIRECTED DIFFERENTIATION OF GASTROINTESTINAL EPITHELIAL ORGANOIDS USING ATCC CELLMATRIX BASEMENT MEMBRANE FROM MULTIPLE HUMAN ATCC ipsc LINES
THE ESSENTIALS OF LIFE SCIENCE RESEARCH GLOBALLY DELIVERED DIRECTED DIFFERENTIATION OF GASTROINTESTINAL EPITHELIAL ORGANOIDS USING ATCC CELLMATRIX BASEMENT MEMBRANE FROM MULTIPLE HUMAN ATCC ipsc LINES
Cycles of vascular plexus formation within the nephrogenic zone of the developing mouse kidney
 1 Supplementary text and data for: 2 3 4 5 Cycles of vascular plexus formation within the nephrogenic zone of the developing mouse kidney Authors: David A. D. Munro 1*, Peter Hohenstein 2, and Jamie A.
1 Supplementary text and data for: 2 3 4 5 Cycles of vascular plexus formation within the nephrogenic zone of the developing mouse kidney Authors: David A. D. Munro 1*, Peter Hohenstein 2, and Jamie A.
Supplemental Information
 Supplemental Information Itemized List Materials and Methods, Related to Supplemental Figures S5A-C and S6. Supplemental Figure S1, Related to Figures 1 and 2. Supplemental Figure S2, Related to Figure
Supplemental Information Itemized List Materials and Methods, Related to Supplemental Figures S5A-C and S6. Supplemental Figure S1, Related to Figures 1 and 2. Supplemental Figure S2, Related to Figure
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. ZBTB20 expression in the developing DRG. ZBTB20 expression in the developing DRG was detected by immunohistochemistry using anti-zbtb20 antibody 9A10 on
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. ZBTB20 expression in the developing DRG. ZBTB20 expression in the developing DRG was detected by immunohistochemistry using anti-zbtb20 antibody 9A10 on
Directed Differentiation of Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells. into Fallopian Tube Epithelium
 Directed Differentiation of Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells into Fallopian Tube Epithelium Nur Yucer 1,2, Marie Holzapfel 2, Tilley Jenkins Vogel 2, Lindsay Lenaeus 1, Loren Ornelas 1, Anna Laury
Directed Differentiation of Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells into Fallopian Tube Epithelium Nur Yucer 1,2, Marie Holzapfel 2, Tilley Jenkins Vogel 2, Lindsay Lenaeus 1, Loren Ornelas 1, Anna Laury
A cost-effective system for differentiation of intestinal epithelium from human induced pluripotent stem cells
 A cost-effective system for differentiation of intestinal epithelium from human induced pluripotent stem cells Soichiro Ogaki 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, *, ayu orooka 1,*, Kaito Otera 1, 1, 3 and Shoen Kume Supplementary
A cost-effective system for differentiation of intestinal epithelium from human induced pluripotent stem cells Soichiro Ogaki 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, *, ayu orooka 1,*, Kaito Otera 1, 1, 3 and Shoen Kume Supplementary
Xeno-Free Systems for hesc & hipsc. Facilitating the shift from Stem Cell Research to Clinical Applications
 Xeno-Free Systems for hesc & hipsc Facilitating the shift from Stem Cell Research to Clinical Applications NutriStem Defined, xeno-free (XF), serum-free media (SFM) specially formulated for growth and
Xeno-Free Systems for hesc & hipsc Facilitating the shift from Stem Cell Research to Clinical Applications NutriStem Defined, xeno-free (XF), serum-free media (SFM) specially formulated for growth and
Supporting Figure 1: Meis2 and Pax6 transcripts in the adult murine brain detected by in situ
 DEVELOP2013097295_supplementary figures Supporting Figure 1: Meis2 and Pax6 transcripts in the adult murine brain detected by in situ hybridization on vibratome sections. (A) Meis2-specific transcripts
DEVELOP2013097295_supplementary figures Supporting Figure 1: Meis2 and Pax6 transcripts in the adult murine brain detected by in situ hybridization on vibratome sections. (A) Meis2-specific transcripts
Supplementary Table 1. Primary antibodies used in this study.
 Supplementary Table 1. Primary antibodies used in this study. Antibodies Mouse monoclonal Antibody(Ab) Working dilution Oct4 1:2 Pax6 1:1 Company Notes 1 Santa Cruz Biotechnology Use only Cy3 2nd antibody
Supplementary Table 1. Primary antibodies used in this study. Antibodies Mouse monoclonal Antibody(Ab) Working dilution Oct4 1:2 Pax6 1:1 Company Notes 1 Santa Cruz Biotechnology Use only Cy3 2nd antibody
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 BALB/c LYVE1-deficient mice exhibited reduced lymphatic trafficking of all DC subsets after oxazolone-induced sensitization. (a) Schematic overview of the mouse skin oxazolone contact
Supplementary Figure 1 BALB/c LYVE1-deficient mice exhibited reduced lymphatic trafficking of all DC subsets after oxazolone-induced sensitization. (a) Schematic overview of the mouse skin oxazolone contact
 Supplemental Tables Supplemental Table 1. Phenotypic profile of different HSC lines. Marker d0 mhsc d7 mhsc 8B LX2 CD11b 3.61% 2.21% 2.16% 3.77% F4/80 4.54% 2.05% 0.127% 1.44% Elastin 3.90% 2.95% 4.23%
Supplemental Tables Supplemental Table 1. Phenotypic profile of different HSC lines. Marker d0 mhsc d7 mhsc 8B LX2 CD11b 3.61% 2.21% 2.16% 3.77% F4/80 4.54% 2.05% 0.127% 1.44% Elastin 3.90% 2.95% 4.23%
Figure S2. Response of mouse ES cells to GSK3 inhibition. Mentioned in discussion
 Stem Cell Reports, Volume 1 Supplemental Information Robust Self-Renewal of Rat Embryonic Stem Cells Requires Fine-Tuning of Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3 Inhibition Yaoyao Chen, Kathryn Blair, and Austin
Stem Cell Reports, Volume 1 Supplemental Information Robust Self-Renewal of Rat Embryonic Stem Cells Requires Fine-Tuning of Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3 Inhibition Yaoyao Chen, Kathryn Blair, and Austin
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Integrin alpha 11 in regulation of myofibroblasts phenotype: Implication for fibrotic diseases
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Integrin alpha 11 in regulation of myofibroblasts phenotype: Implication for fibrotic diseases Ruchi Bansal 1, Shigeki Nakagawa 2, Saleh Yazdani 1, Joop van Baarlen 3, Anu Venkatesh
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Integrin alpha 11 in regulation of myofibroblasts phenotype: Implication for fibrotic diseases Ruchi Bansal 1, Shigeki Nakagawa 2, Saleh Yazdani 1, Joop van Baarlen 3, Anu Venkatesh
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2239 Hepatocytes (Endoderm) Foreskin fibroblasts (Mesoderm) Melanocytes (Ectoderm) +Dox rtta TetO CMV O,S,M,K & N H1 hes H7 hes H9 hes H1 hes-derived EBs H7 hes-derived EBs H9 hes-derived
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2239 Hepatocytes (Endoderm) Foreskin fibroblasts (Mesoderm) Melanocytes (Ectoderm) +Dox rtta TetO CMV O,S,M,K & N H1 hes H7 hes H9 hes H1 hes-derived EBs H7 hes-derived EBs H9 hes-derived
SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION
 UTX/KDM6A demethylase activity is required for satellite cell-mediated muscle regeneration Hervé Faralli 1,2, Chaochen Wang 3, Kiran Nakka 1,2, Soji Sebastian 1,, Aissa Benyoucef 1,2, Lenan Zhuang 3, Alphonse
UTX/KDM6A demethylase activity is required for satellite cell-mediated muscle regeneration Hervé Faralli 1,2, Chaochen Wang 3, Kiran Nakka 1,2, Soji Sebastian 1,, Aissa Benyoucef 1,2, Lenan Zhuang 3, Alphonse
Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Analyst. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Seidel et al. 2016 Page 1 of 13 In vitro field potential monitoring on multi-micro electrode array
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Analyst. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Seidel et al. 2016 Page 1 of 13 In vitro field potential monitoring on multi-micro electrode array
Isolation, culture, and transfection of primary mammary epithelial organoids
 Supplementary Experimental Procedures Isolation, culture, and transfection of primary mammary epithelial organoids Primary mammary epithelial organoids were prepared from 8-week-old CD1 mice (Charles River)
Supplementary Experimental Procedures Isolation, culture, and transfection of primary mammary epithelial organoids Primary mammary epithelial organoids were prepared from 8-week-old CD1 mice (Charles River)
Supplemental Materials. Matrix Proteases Contribute to Progression of Pelvic Organ Prolapse in Mice and Humans
 Supplemental Materials Matrix Proteases Contribute to Progression of Pelvic Organ Prolapse in Mice and Humans Madhusudhan Budatha, Shayzreen Roshanravan, Qian Zheng, Cecilia Weislander, Shelby L. Chapman,
Supplemental Materials Matrix Proteases Contribute to Progression of Pelvic Organ Prolapse in Mice and Humans Madhusudhan Budatha, Shayzreen Roshanravan, Qian Zheng, Cecilia Weislander, Shelby L. Chapman,
To assess the localization of Citrine fusion proteins, we performed antibody staining to
 Trinh et al 1 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL FlipTraps recapitulate endogenous protein localization To assess the localization of Citrine fusion proteins, we performed antibody staining to compare the expression
Trinh et al 1 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL FlipTraps recapitulate endogenous protein localization To assess the localization of Citrine fusion proteins, we performed antibody staining to compare the expression
Supplementary information to accompany: A novel role for the DNA repair gene Rad51 in Netrin-1 signalling
 Supplementary information to accompany: A novel role for the DNA repair gene Rad51 in Netrin-1 signalling Glendining KA 1, Markie D 2, Gardner RJM 4, Franz EA 3, Robertson SP 4, Jasoni CL 1 Supplementary
Supplementary information to accompany: A novel role for the DNA repair gene Rad51 in Netrin-1 signalling Glendining KA 1, Markie D 2, Gardner RJM 4, Franz EA 3, Robertson SP 4, Jasoni CL 1 Supplementary
Supplementary Figure S1. Non-SMCs in rat carotid artery.
 Supplementary Figure S1. Non-SMCs in rat carotid artery. L M A Cross sections of carotid artery were stained for SM-MHC (red) and SMA (Green). Nuclei were stained with DAPI. L: lumen, M: media, A: adventitia.
Supplementary Figure S1. Non-SMCs in rat carotid artery. L M A Cross sections of carotid artery were stained for SM-MHC (red) and SMA (Green). Nuclei were stained with DAPI. L: lumen, M: media, A: adventitia.
Supplementary Figure 1 qrt-pcr expression analysis of NLP8 with and without KNO 3 during germination.
 Supplementary Figure 1 qrt-pcr expression analysis of NLP8 with and without KNO 3 during germination. Seeds of Col-0 were harvested from plants grown at 16 C, stored for 2 months, imbibed for indicated
Supplementary Figure 1 qrt-pcr expression analysis of NLP8 with and without KNO 3 during germination. Seeds of Col-0 were harvested from plants grown at 16 C, stored for 2 months, imbibed for indicated
Supplemental Information Inventory
 Cell Stem Cell, Volume 6 Supplemental Information Distinct Hematopoietic Stem Cell Subtypes Are Differentially Regulated by TGF-β1 Grant A. Challen, Nathan C. Boles, Stuart M. Chambers, and Margaret A.
Cell Stem Cell, Volume 6 Supplemental Information Distinct Hematopoietic Stem Cell Subtypes Are Differentially Regulated by TGF-β1 Grant A. Challen, Nathan C. Boles, Stuart M. Chambers, and Margaret A.
Post-expansion antibody delivery, after epitope-preserving homogenization.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Post-expansion antibody delivery, after epitope-preserving homogenization. (a, b) Wide-field fluorescence images of Thy1-YFP-expressing mouse brain hemisphere slice before expansion
Supplementary Figure 1 Post-expansion antibody delivery, after epitope-preserving homogenization. (a, b) Wide-field fluorescence images of Thy1-YFP-expressing mouse brain hemisphere slice before expansion
Supplementary Material. Levels of S100B protein drive the reparative process in acute muscle injury and muscular dystrophy
 Supplementary Material Levels of protein drive the reparative process in acute muscle injury and muscular dystrophy Francesca Riuzzi 1,4 *, Sara Beccafico 1,4 *, Roberta Sagheddu 1,4, Sara Chiappalupi
Supplementary Material Levels of protein drive the reparative process in acute muscle injury and muscular dystrophy Francesca Riuzzi 1,4 *, Sara Beccafico 1,4 *, Roberta Sagheddu 1,4, Sara Chiappalupi
IKK is a therapeutic target in KRAS-induced lung cancer with disrupted p53 activity
 IKK is a therapeutic target in KRAS-induced lung cancer with disrupted p5 activity H6 5 5 H58 A59 H6 H58 A59 anti-ikkα anti-ikkβ anti-panras anti-gapdh anti-ikkα anti-ikkβ anti-panras anti-gapdh anti-ikkα
IKK is a therapeutic target in KRAS-induced lung cancer with disrupted p5 activity H6 5 5 H58 A59 H6 H58 A59 anti-ikkα anti-ikkβ anti-panras anti-gapdh anti-ikkα anti-ikkβ anti-panras anti-gapdh anti-ikkα
Solution Key Problem Set
 Solution Key- 7.013 Problem Set 5-2013 Question 1 During a summer hike you suddenly spot a huge grizzly bear. This emergency situation triggers a fight or flight response through a signaling pathway as
Solution Key- 7.013 Problem Set 5-2013 Question 1 During a summer hike you suddenly spot a huge grizzly bear. This emergency situation triggers a fight or flight response through a signaling pathway as
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 PCR-genotyping of the three mouse models used in this study and controls for behavioral experiments after semi-chronic Pten inhibition. a-c. DNA from App/Psen1 (a), Pten tg (b) and
Supplementary Figure 1 PCR-genotyping of the three mouse models used in this study and controls for behavioral experiments after semi-chronic Pten inhibition. a-c. DNA from App/Psen1 (a), Pten tg (b) and
Contents. The Right Surface for Every Cell Extracellular Matrices and Biologically Coated Surfaces ECM Mimetic and Advanced Surfaces...
 Contents The Right Surface for Every Cell... 1 Extracellular Matrices and Biologically Coated Surfaces... 2 Corning Matrigel Matrix... 2 Corning BioCoat Cultureware... 3 ECM Mimetic and Advanced Surfaces...
Contents The Right Surface for Every Cell... 1 Extracellular Matrices and Biologically Coated Surfaces... 2 Corning Matrigel Matrix... 2 Corning BioCoat Cultureware... 3 ECM Mimetic and Advanced Surfaces...
Supplementary Figure 1: Expression of RNF8, HERC2 and NEURL4 in the cerebellum and knockdown of RNF8 by RNAi (a) Lysates of the cerebellum from rat
 Supplementary Figure 1: Expression of RNF8, HERC2 and NEURL4 in the cerebellum and knockdown of RNF8 by RNAi (a) Lysates of the cerebellum from rat pups at P6, P14, P22, P30 and adult (A) rats were subjected
Supplementary Figure 1: Expression of RNF8, HERC2 and NEURL4 in the cerebellum and knockdown of RNF8 by RNAi (a) Lysates of the cerebellum from rat pups at P6, P14, P22, P30 and adult (A) rats were subjected
Chemically defined conditions for human ipsc derivation and culture
 Nature Methods Chemically defined conditions for human ipsc derivation and culture Guokai Chen, Daniel R Gulbranson, Zhonggang Hou, Jennifer M Bolin, Victor Ruotti, Mitchell D Probasco, Kimberly Smuga-Otto,
Nature Methods Chemically defined conditions for human ipsc derivation and culture Guokai Chen, Daniel R Gulbranson, Zhonggang Hou, Jennifer M Bolin, Victor Ruotti, Mitchell D Probasco, Kimberly Smuga-Otto,
Fundamental properties of Stem Cells
 Stem cells Learning Goals: Define what a stem cell is and describe its general properties, using hematopoietic stem cells as an example. Describe to a non-scientist the current progress of human stem cell
Stem cells Learning Goals: Define what a stem cell is and describe its general properties, using hematopoietic stem cells as an example. Describe to a non-scientist the current progress of human stem cell
Immunofluorescence of organoids embedded in Basement Membrane Matrix
 Immunofluorescence of organoids embedded in Basement Membrane Matrix Sol Degese 1, Gabe Benton 1 1 Organoid Resource Lab (ORL), Trevigen, Inc., 8405 Helgerman Court, Gaithersburg, MD 20877 Introduction
Immunofluorescence of organoids embedded in Basement Membrane Matrix Sol Degese 1, Gabe Benton 1 1 Organoid Resource Lab (ORL), Trevigen, Inc., 8405 Helgerman Court, Gaithersburg, MD 20877 Introduction
GM130 Is Required for Compartmental Organization of Dendritic Golgi Outposts
 Current Biology, Volume 24 Supplemental Information GM130 Is Required for Compartmental Organization of Dendritic Golgi Outposts Wei Zhou, Jin Chang, Xin Wang, Masha G. Savelieff, Yinyin Zhao, Shanshan
Current Biology, Volume 24 Supplemental Information GM130 Is Required for Compartmental Organization of Dendritic Golgi Outposts Wei Zhou, Jin Chang, Xin Wang, Masha G. Savelieff, Yinyin Zhao, Shanshan
Stem Cell Services. Driving Innovation for Stem Cell Researchers
 Driving Innovation for Stem Cell Researchers Stem Cell Services Partner with us and have access to the most advanced and comprehensive stem cell services available today. 675 W. Kendall St. Cambridge,
Driving Innovation for Stem Cell Researchers Stem Cell Services Partner with us and have access to the most advanced and comprehensive stem cell services available today. 675 W. Kendall St. Cambridge,
Supplementary Figure S1. Immunodetection of full-length XA21 and the XA21 C-terminal cleavage product.
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure S1. Immunodetection of full-length XA21 and the XA21 C-terminal cleavage product. Total protein extracted from Kitaake wild type and rice plants carrying
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure S1. Immunodetection of full-length XA21 and the XA21 C-terminal cleavage product. Total protein extracted from Kitaake wild type and rice plants carrying
NPTEL Biotechnology Tissue Engineering. Stem cells
 Stem cells S. Swaminathan Director Centre for Nanotechnology & Advanced Biomaterials School of Chemical & Biotechnology SASTRA University Thanjavur 613 401 Tamil Nadu Joint Initiative of IITs and IISc
Stem cells S. Swaminathan Director Centre for Nanotechnology & Advanced Biomaterials School of Chemical & Biotechnology SASTRA University Thanjavur 613 401 Tamil Nadu Joint Initiative of IITs and IISc
Ets-1 Confers Cranial Features on Neural Crest Delamination
 Ets-1 Confers Cranial Features on Neural Crest Delamination Eric Théveneau 1,2, Jean-Loup Duband 1,2, Muriel Altabef 1,2 * 1 Université Pierre et Marie Curie - Paris6, UMR 7622, Laboratoire de Biologie
Ets-1 Confers Cranial Features on Neural Crest Delamination Eric Théveneau 1,2, Jean-Loup Duband 1,2, Muriel Altabef 1,2 * 1 Université Pierre et Marie Curie - Paris6, UMR 7622, Laboratoire de Biologie
PRIME-XV Cell Therapy Products by
 PRIME-XV Cell Therapy Products by Product List 2017 TRINOVA BIOCHEM now distributes the PRIME-XV Cell Therapy line by Irvine Scientific in Germany, Austria and Switzerland. Irvine Scientific is a worldwide
PRIME-XV Cell Therapy Products by Product List 2017 TRINOVA BIOCHEM now distributes the PRIME-XV Cell Therapy line by Irvine Scientific in Germany, Austria and Switzerland. Irvine Scientific is a worldwide
PRIME-XV Cell Therapy Products by
 PRIME-XV Cell Therapy Products by Product List 2017 TRINOVA BIOCHEM now distributes the PRIME-XV Cell Therapy line by Irvine Scientific in Germany, Austria and Switzerland. Irvine Scientific is a worldwide
PRIME-XV Cell Therapy Products by Product List 2017 TRINOVA BIOCHEM now distributes the PRIME-XV Cell Therapy line by Irvine Scientific in Germany, Austria and Switzerland. Irvine Scientific is a worldwide
unc-33/crmp and ankyrin organize microtubules and localize kinesin to polarize
 Supplementary Information unc-33/crmp and ankyrin organize microtubules and localize kinesin to polarize axon-dendrite sorting Tapan A. Maniar 1, Miriam Kaplan 1, George J. Wang 2, Kang Shen 2, Li Wei
Supplementary Information unc-33/crmp and ankyrin organize microtubules and localize kinesin to polarize axon-dendrite sorting Tapan A. Maniar 1, Miriam Kaplan 1, George J. Wang 2, Kang Shen 2, Li Wei
Supplementary Figure 1. Isolation of GFPHigh cells.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Isolation of GFP High cells. (A) Schematic diagram of cell isolation based on Wnt signaling activity. Colorectal cancer (CRC) cell lines were stably transduced with lentivirus encoding
Supplementary Figure 1. Isolation of GFP High cells. (A) Schematic diagram of cell isolation based on Wnt signaling activity. Colorectal cancer (CRC) cell lines were stably transduced with lentivirus encoding
GFP CCD2 GFP IP:GFP
 D1 D2 1 75 95 148 178 492 GFP CCD1 CCD2 CCD2 GFP D1 D2 GFP D1 D2 Beclin 1 IB:GFP IP:GFP Supplementary Figure 1: Mapping domains required for binding to HEK293T cells are transfected with EGFP-tagged mutant
D1 D2 1 75 95 148 178 492 GFP CCD1 CCD2 CCD2 GFP D1 D2 GFP D1 D2 Beclin 1 IB:GFP IP:GFP Supplementary Figure 1: Mapping domains required for binding to HEK293T cells are transfected with EGFP-tagged mutant
Peter Dy, Weihuan Wang, Pallavi Bhattaram, Qiuqing Wang, Lai Wang, R. Tracy Ballock, and Véronique Lefebvre
 Developmental Cell, Volume 22 Supplemental Information Sox9 Directs Hypertrophic Maturation and Blocks Osteoblast Differentiation of Growth Plate Chondrocytes Peter Dy, Weihuan Wang, Pallavi Bhattaram,
Developmental Cell, Volume 22 Supplemental Information Sox9 Directs Hypertrophic Maturation and Blocks Osteoblast Differentiation of Growth Plate Chondrocytes Peter Dy, Weihuan Wang, Pallavi Bhattaram,
Beta3 integrin promotes long-lasting activation and polarization of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor 2 by immobilized ligand
 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURES Beta3 integrin promotes long-lasting activation and polarization of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor 2 by immobilized ligand C. Ravelli et al. FIGURE S. I Figure S. I: Gremlin
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURES Beta3 integrin promotes long-lasting activation and polarization of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor 2 by immobilized ligand C. Ravelli et al. FIGURE S. I Figure S. I: Gremlin
Culture and differentiation of embryonic stem cells. Hong-Lin Su Department of Life Sciences, National Chung-Hsing University
 Culture and differentiation of embryonic stem cells Hong-Lin Su Department of Life Sciences, National Chung-Hsing University Topics-ES cell maintenance Establishment Culture condition, including the serum,
Culture and differentiation of embryonic stem cells Hong-Lin Su Department of Life Sciences, National Chung-Hsing University Topics-ES cell maintenance Establishment Culture condition, including the serum,
supplementary information
 DOI: 1.138/ncb1839 a b Control 1 2 3 Control 1 2 3 Fbw7 Smad3 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 c d IGF-1 IGF-1Rβ IGF-1Rβ-P Control / 1 2 3 4 Real-time RT-PCR Relative quantity (IGF-1/ mrna) 2 1 IGF-1 1 2 3 4 Control /
DOI: 1.138/ncb1839 a b Control 1 2 3 Control 1 2 3 Fbw7 Smad3 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 c d IGF-1 IGF-1Rβ IGF-1Rβ-P Control / 1 2 3 4 Real-time RT-PCR Relative quantity (IGF-1/ mrna) 2 1 IGF-1 1 2 3 4 Control /
Allen Chen, Yu Ming Lim, Shaul Reuveny and Steve Oh
 EXPANSION AND DIFFERENTIATION OF HUMAN PLURIPOTENT STEM CELLS TO NEURAL PROGENITORS: A SIMPLIFIED BIOREACTOR PROCESS REPLACING NOGGIN WITH 2 SMALL MOLECULES Allen Chen, Yu Ming Lim, Shaul Reuveny and Steve
EXPANSION AND DIFFERENTIATION OF HUMAN PLURIPOTENT STEM CELLS TO NEURAL PROGENITORS: A SIMPLIFIED BIOREACTOR PROCESS REPLACING NOGGIN WITH 2 SMALL MOLECULES Allen Chen, Yu Ming Lim, Shaul Reuveny and Steve
SOX2 antibody - Embryonic Stem Cell Marker (ab15830) datasheet
 -Embryonic Stem Cell Marker (ab15830) 1/8 ページ d Products: Stem Cells >> Germline Stem Cells >> Embryonic Germ Cells SOX2 antibody - Embryonic Stem Cell Marker (ab15830) datasheet Product Name Product type
-Embryonic Stem Cell Marker (ab15830) 1/8 ページ d Products: Stem Cells >> Germline Stem Cells >> Embryonic Germ Cells SOX2 antibody - Embryonic Stem Cell Marker (ab15830) datasheet Product Name Product type
Perturbation of Hoxb5 Signaling in Vagal Neural Crests Down-Regulates Ret Leading to Intestinal Hypoganglionosis in Mice
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 2008;134:1104 1115 Perturbation of Hoxb5 Signaling in Vagal Neural Crests Down-Regulates Ret Leading to Intestinal Hypoganglionosis in Mice VINCENT C. H. LUI,* WILLIAM W. C. CHENG,* THOMAS
GASTROENTEROLOGY 2008;134:1104 1115 Perturbation of Hoxb5 Signaling in Vagal Neural Crests Down-Regulates Ret Leading to Intestinal Hypoganglionosis in Mice VINCENT C. H. LUI,* WILLIAM W. C. CHENG,* THOMAS
Supplementary Fig. 1 related to Fig. 1 Clinical relevance of lncrna candidate
 Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Fig. 1 related to Fig. 1 Clinical relevance of lncrna candidate BC041951 in gastric cancer. (A) The flow chart for selected candidate lncrnas in 660 up-regulated
Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Fig. 1 related to Fig. 1 Clinical relevance of lncrna candidate BC041951 in gastric cancer. (A) The flow chart for selected candidate lncrnas in 660 up-regulated
Enhancers mutations that make the original mutant phenotype more extreme. Suppressors mutations that make the original mutant phenotype less extreme
 Interactomics and Proteomics 1. Interactomics The field of interactomics is concerned with interactions between genes or proteins. They can be genetic interactions, in which two genes are involved in the
Interactomics and Proteomics 1. Interactomics The field of interactomics is concerned with interactions between genes or proteins. They can be genetic interactions, in which two genes are involved in the
Supplementary Fig. 1. Isolation and in vitro expansion of EpCAM + cholangiocytes. For collagenase perfusion, enzyme solution was injected from the
 Supplementary Fig. 1. Isolation and in vitro expansion of EpCAM + cholangiocytes. For collagenase perfusion, enzyme solution was injected from the portal vein for digesting adult livers, whereas it was
Supplementary Fig. 1. Isolation and in vitro expansion of EpCAM + cholangiocytes. For collagenase perfusion, enzyme solution was injected from the portal vein for digesting adult livers, whereas it was
Figure S1. Figure S2. Figure S3 HB Anti-FSP27 (COOH-terminal peptide) Ab. Anti-GST-FSP27(45-127) Ab.
 / 36B4 mrna ratio Figure S1 * 2. 1.6 1.2.8 *.4 control TNFα BRL49653 Figure S2 Su bw AT p iw Anti- (COOH-terminal peptide) Ab Blot : Anti-GST-(45-127) Ab β-actin Figure S3 HB2 HW AT BA T Figure S4 A TAG
/ 36B4 mrna ratio Figure S1 * 2. 1.6 1.2.8 *.4 control TNFα BRL49653 Figure S2 Su bw AT p iw Anti- (COOH-terminal peptide) Ab Blot : Anti-GST-(45-127) Ab β-actin Figure S3 HB2 HW AT BA T Figure S4 A TAG
Recapitulation of spinal motor neuron-specific disease phenotypes in a human cell model of spinal muscular atrophy
 npg Modeling spinal muscular atrophy in human neurons 378 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Cell Research (2013) 23:378-393. 2013 IBCB, SIBS, CAS All rights reserved 1001-0602/13 $ 32.00 www.nature.com/cr npg Recapitulation
npg Modeling spinal muscular atrophy in human neurons 378 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Cell Research (2013) 23:378-393. 2013 IBCB, SIBS, CAS All rights reserved 1001-0602/13 $ 32.00 www.nature.com/cr npg Recapitulation
Activity 47.1 What common events occur in the early development of animals? 1. What key events occur at each stage of development?
 Notes to Instructors Chapter 47 Animal Development What is the focus of this activity? Chapter 21 provided a review of how genes act to control development. Chapter 47 reviews some of the major morphological
Notes to Instructors Chapter 47 Animal Development What is the focus of this activity? Chapter 21 provided a review of how genes act to control development. Chapter 47 reviews some of the major morphological
Asymmetric endocytosis and remodeling of β1-integrin adhesions during growth cone chemorepulsion by MAG
 Asymmetric endocytosis and remodeling of β1-integrin adhesions during growth cone chemorepulsion by MAG Jacob H. Hines, Mohammad Abu-Rub and John R. Henley Supplementary Figure 1. Validation of FM 5-95
Asymmetric endocytosis and remodeling of β1-integrin adhesions during growth cone chemorepulsion by MAG Jacob H. Hines, Mohammad Abu-Rub and John R. Henley Supplementary Figure 1. Validation of FM 5-95
Cortical Neural Induction Kit. Protocol version 1.0
 Cortical Neural Induction Kit Protocol version 1.0 Protocol version 1.0 Table of Contents Product Information 2 Preparation of Reagents 3 Protocol Overview 4 Seeding ipscs 4 Cortical Neural Induction
Cortical Neural Induction Kit Protocol version 1.0 Protocol version 1.0 Table of Contents Product Information 2 Preparation of Reagents 3 Protocol Overview 4 Seeding ipscs 4 Cortical Neural Induction
Role of Bmi-1 in Epigenetic Regulation. During Early Neural Crest Development
 Role of Bmi-1 in Epigenetic Regulation During Early Neural Crest Development Thesis by Jane I. Khudyakov In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of Doctor of Philosophy California Institute
Role of Bmi-1 in Epigenetic Regulation During Early Neural Crest Development Thesis by Jane I. Khudyakov In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of Doctor of Philosophy California Institute
Supplementary information
 Supplementary information Inhibition of mitochondrial dysfunction and neuronal cell death in models of Huntington s disease and in HD patients-derived cells Xing Guo 1,#, Marie-Helene Disatnik 3,#, Marie
Supplementary information Inhibition of mitochondrial dysfunction and neuronal cell death in models of Huntington s disease and in HD patients-derived cells Xing Guo 1,#, Marie-Helene Disatnik 3,#, Marie
Supplementary Information: ITGAV and ITGA5 diversely regulate proliferation and adipogenic differentiation of human adipose derived stem cells
 Supplementary Information: ITGAV and ITGA5 diversely regulate proliferation and adipogenic differentiation of human adipose derived stem cells E. M. Morandi, R. Verstappen, M. E. Zwierzina, S. Geley, G.
Supplementary Information: ITGAV and ITGA5 diversely regulate proliferation and adipogenic differentiation of human adipose derived stem cells E. M. Morandi, R. Verstappen, M. E. Zwierzina, S. Geley, G.
NEURONAL CELL CULTURE MATRIX FOR BETTER MAINTENANCE AND SURVIVAL OF NEURONAL CELL CULTURES IN TISSUE CULTURE.
 NEURONAL CELL CULTURE MATRIX FOR BETTER MAINTENANCE AND SURVIVAL OF NEURONAL CELL CULTURES IN TISSUE CULTURE. D. R. Aguirre, N. DiMassa, Chrystal Johnson, H. Eran, R. Perez, C.V.R. Sharma, M.V.R. Sharma,
NEURONAL CELL CULTURE MATRIX FOR BETTER MAINTENANCE AND SURVIVAL OF NEURONAL CELL CULTURES IN TISSUE CULTURE. D. R. Aguirre, N. DiMassa, Chrystal Johnson, H. Eran, R. Perez, C.V.R. Sharma, M.V.R. Sharma,
Nature Methods doi: /nmeth Supplementary Figure 1. Screening for cancer stem cell marker(s)
 Supplementary Figure 1 Screening for cancer stem cell marker(s) (a) Flow cytometry analysis of CD133 at increasing times to analysis. Cells were trypsinized, stained, transferred to RPMI medium and then
Supplementary Figure 1 Screening for cancer stem cell marker(s) (a) Flow cytometry analysis of CD133 at increasing times to analysis. Cells were trypsinized, stained, transferred to RPMI medium and then
Neural Stem Cells (ipsc from Blood Cells; Male)
 Applied StemCell, Inc. (866) 497-4180 www.appliedstemcell.com Datasheet Neural Stem Cells (ipsc from Blood Cells; Male) Product Information Catalog Number ASE-9234 (Male) Description Applied StemCell's
Applied StemCell, Inc. (866) 497-4180 www.appliedstemcell.com Datasheet Neural Stem Cells (ipsc from Blood Cells; Male) Product Information Catalog Number ASE-9234 (Male) Description Applied StemCell's
Nature Methods: doi: /nmeth Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Workflow for multimodal analysis using sc-gem on a programmable microfluidic device (Fluidigm). 1) Cells are captured and lysed, 2) RNA from lysed single cell is reverse-transcribed
Supplementary Figure 1 Workflow for multimodal analysis using sc-gem on a programmable microfluidic device (Fluidigm). 1) Cells are captured and lysed, 2) RNA from lysed single cell is reverse-transcribed
Supplemental Information
 Cell Stem Cell, Volume 15 Supplemental Information Generation of Naive Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells from Rhesus Monkey Fibroblasts Riguo Fang, Kang Liu, Yang Zhao, Haibo Li, Dicong Zhu, Yuanyuan Du,
Cell Stem Cell, Volume 15 Supplemental Information Generation of Naive Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells from Rhesus Monkey Fibroblasts Riguo Fang, Kang Liu, Yang Zhao, Haibo Li, Dicong Zhu, Yuanyuan Du,
Nature Protocols: doi: /nprot Supplementary Figure 1. Efficient genome editing in human pluripotent stem cells.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Efficient genome editing in human pluripotent stem cells. Our genome editing protocol was highly efficient in an additional pluripotent human cell line (CHB10) and at several different
Supplementary Figure 1 Efficient genome editing in human pluripotent stem cells. Our genome editing protocol was highly efficient in an additional pluripotent human cell line (CHB10) and at several different
Rejuvenation of the muscle stem cell population restores strength to injured aged muscles
 Rejuvenation of the muscle stem cell population restores strength to injured aged muscles Benjamin D Cosgrove, Penney M Gilbert, Ermelinda Porpiglia, Foteini Mourkioti, Steven P Lee, Stephane Y Corbel,
Rejuvenation of the muscle stem cell population restores strength to injured aged muscles Benjamin D Cosgrove, Penney M Gilbert, Ermelinda Porpiglia, Foteini Mourkioti, Steven P Lee, Stephane Y Corbel,
Supplemental Data. LMO4 Controls the Balance between Excitatory. and Inhibitory Spinal V2 Interneurons
 Neuron, Volume 61 Supplemental Data LMO4 Controls the Balance between Excitatory and Inhibitory Spinal V2 Interneurons Kaumudi Joshi, Seunghee Lee, Bora Lee, Jae W. Lee, and Soo-Kyung Lee Supplemental
Neuron, Volume 61 Supplemental Data LMO4 Controls the Balance between Excitatory and Inhibitory Spinal V2 Interneurons Kaumudi Joshi, Seunghee Lee, Bora Lee, Jae W. Lee, and Soo-Kyung Lee Supplemental
Description: Nuclear morphology and dynamics in nontargeting sirna transfected cells. HeLa Kyoto
 Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures and Supplementary Tables Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Movie 1 Description: Nuclear morphology and dynamics
Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures and Supplementary Tables Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Movie 1 Description: Nuclear morphology and dynamics
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization and high expression of Lnc-β-Catm in liver CSCs. (a) Heatmap of differently expressed lncrnas in Liver CSCs (CD13 + CD133 + ) and non-cscs (CD13 - CD133 - ) according
Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization and high expression of Lnc-β-Catm in liver CSCs. (a) Heatmap of differently expressed lncrnas in Liver CSCs (CD13 + CD133 + ) and non-cscs (CD13 - CD133 - ) according
High-Throughput Toxicity and Phenotypic Screening of 3D Human Neural. Progenitor Cell Cultures on a Microarray Chip Platform
 Stem Cell Reports, Volume 7 Supplemental Information High-Throughput Toxicity and Phenotypic Screening of 3D Human Neural Progenitor Cell Cultures on a Microarray Chip Platform Gregory J. Nierode, Brian
Stem Cell Reports, Volume 7 Supplemental Information High-Throughput Toxicity and Phenotypic Screening of 3D Human Neural Progenitor Cell Cultures on a Microarray Chip Platform Gregory J. Nierode, Brian
Neural Induction. Chapter One
 Neural Induction Chapter One Fertilization Development of the Nervous System Cleavage (Blastula, Gastrula) Neuronal Induction- Neuroblast Formation Cell Migration Mesodermal Induction Lateral Inhibition
Neural Induction Chapter One Fertilization Development of the Nervous System Cleavage (Blastula, Gastrula) Neuronal Induction- Neuroblast Formation Cell Migration Mesodermal Induction Lateral Inhibition
Initial genotyping of all new litters was performed by Transnetyx (Memphis,
 SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION MURILLO ET AL. SUPPLEMENTAL EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES Mouse Genotyping Initial genotyping of all new litters was performed by Transnetyx (Memphis, USA). Assessment of LoxPpα recombination
SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION MURILLO ET AL. SUPPLEMENTAL EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES Mouse Genotyping Initial genotyping of all new litters was performed by Transnetyx (Memphis, USA). Assessment of LoxPpα recombination
Supplementary Figure Legend
 Supplementary Figure Legend Supplementary Figure S1. Effects of MMP-1 silencing on HEp3-hi/diss cell proliferation in 2D and 3D culture conditions. (A) Downregulation of MMP-1 expression in HEp3-hi/diss
Supplementary Figure Legend Supplementary Figure S1. Effects of MMP-1 silencing on HEp3-hi/diss cell proliferation in 2D and 3D culture conditions. (A) Downregulation of MMP-1 expression in HEp3-hi/diss
To isolate single GNS 144 cell clones, cells were plated at a density of 1cell/well
 Supplemental Information: Supplemental Methods: Cell culture To isolate single GNS 144 cell clones, cells were plated at a density of 1cell/well in 96 well Primaria plates in GNS media and incubated at
Supplemental Information: Supplemental Methods: Cell culture To isolate single GNS 144 cell clones, cells were plated at a density of 1cell/well in 96 well Primaria plates in GNS media and incubated at
Versatility and performance of Lipofectamine Stem Transfection Reagent
 PPLICTION NOTE Stem Transfection Reagent Versatility and performance of Stem Transfection Reagent Introduction The ability of stem cells to self-renew and differentiate into various specialized cell types
PPLICTION NOTE Stem Transfection Reagent Versatility and performance of Stem Transfection Reagent Introduction The ability of stem cells to self-renew and differentiate into various specialized cell types
A novel stem cell for auditory neuron regeneration.
 A novel stem cell for auditory neuron regeneration. M.A.Huisman*, R. el Seady*, C.F.H.M.Löwik # en J.H.M.Frijns* Departments of Ear, Nose & Throat* and Molecular Imaging #, Leiden University Medical Centre,
A novel stem cell for auditory neuron regeneration. M.A.Huisman*, R. el Seady*, C.F.H.M.Löwik # en J.H.M.Frijns* Departments of Ear, Nose & Throat* and Molecular Imaging #, Leiden University Medical Centre,
Correction: The Leukemia-Associated Mllt10/ Af10-Dot1l Are Tcf4/β-Catenin Coactivators Essential for Intestinal Homeostasis
 CORRECTION Correction: The Leukemia-Associated Mllt10/ Af10-Dot1l Are Tcf4/β-Catenin Coactivators Essential for Intestinal Homeostasis Tokameh Mahmoudi, Sylvia F. Boj, Pantelis Hatzis, Vivian S. W. Li,
CORRECTION Correction: The Leukemia-Associated Mllt10/ Af10-Dot1l Are Tcf4/β-Catenin Coactivators Essential for Intestinal Homeostasis Tokameh Mahmoudi, Sylvia F. Boj, Pantelis Hatzis, Vivian S. W. Li,
TISSUE-SPECIFIC STEM CELLS
 TISSUE-SPECIFIC STEM CELLS Alternative Generation of CNS Neural Stem Cells and PNS Derivatives from Neural Crest-Derived Peripheral Stem Cells MARLEN WEBER, a GALINA APOSTOLOVA, b DARIUS WIDERA, c MICHEL
TISSUE-SPECIFIC STEM CELLS Alternative Generation of CNS Neural Stem Cells and PNS Derivatives from Neural Crest-Derived Peripheral Stem Cells MARLEN WEBER, a GALINA APOSTOLOVA, b DARIUS WIDERA, c MICHEL
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 A diphtheria toxin resistance marker for in vitro and in vivo selection of stably transduced human cells Gabriele Picco, Consalvo Petti, Livio Trusolino, Andrea Bertotti and Enzo Medico SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
A diphtheria toxin resistance marker for in vitro and in vivo selection of stably transduced human cells Gabriele Picco, Consalvo Petti, Livio Trusolino, Andrea Bertotti and Enzo Medico SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
Genetics - Problem Drill 19: Dissection of Gene Function: Mutational Analysis of Model Organisms
 Genetics - Problem Drill 19: Dissection of Gene Function: Mutational Analysis of Model Organisms No. 1 of 10 1. The mouse gene knockout is based on. (A) Homologous recombination (B) Site-specific recombination
Genetics - Problem Drill 19: Dissection of Gene Function: Mutational Analysis of Model Organisms No. 1 of 10 1. The mouse gene knockout is based on. (A) Homologous recombination (B) Site-specific recombination
Protocols for Neural Progenitor Cell Expansion and Dopaminergic Neuron Differentiation
 Protocols for Neural Progenitor Cell Expansion and Dopaminergic Neuron Differentiation In vitro neurological research presents many challenges due to the difficulty in establishing high-yield neuronal
Protocols for Neural Progenitor Cell Expansion and Dopaminergic Neuron Differentiation In vitro neurological research presents many challenges due to the difficulty in establishing high-yield neuronal
Supplemental Online Data
 1 Supplemental Online Data Wt1 and epicardial fate mapping Carsten Rudat and Andreas Kispert * Institut für Molekularbiologie, OE5250, Medizinische Hochschule Hannover, Carl-Neuberg- Str.1, D-30625 Hannover,
1 Supplemental Online Data Wt1 and epicardial fate mapping Carsten Rudat and Andreas Kispert * Institut für Molekularbiologie, OE5250, Medizinische Hochschule Hannover, Carl-Neuberg- Str.1, D-30625 Hannover,
INNOVATIVE PRODUCTS FOR NEUROSCIENCE RESEARCH
 INNOVATIVE PRODUCTS FOR NEUROSCIENCE RESEARCH NEURAL CELLS & MEDIA STEM CELLS & CULTURE REAGENTS TRANSFECTION CUSTOM SERVICES NEUROSCIENCE PRODUCTS CATALOG TABLE OF CONTENTS Neuroscience research demands
INNOVATIVE PRODUCTS FOR NEUROSCIENCE RESEARCH NEURAL CELLS & MEDIA STEM CELLS & CULTURE REAGENTS TRANSFECTION CUSTOM SERVICES NEUROSCIENCE PRODUCTS CATALOG TABLE OF CONTENTS Neuroscience research demands
FIG S1: Calibration curves of standards for HPLC detection of Dopachrome (Dopac), Dopamine (DA) and Homovanillic acid (HVA), showing area of peak vs
 FIG S1: Calibration curves of standards for HPLC detection of Dopachrome (Dopac), Dopamine (DA) and Homovanillic acid (HVA), showing area of peak vs amount of standard analysed. Each point represents the
FIG S1: Calibration curves of standards for HPLC detection of Dopachrome (Dopac), Dopamine (DA) and Homovanillic acid (HVA), showing area of peak vs amount of standard analysed. Each point represents the
Induction of Neural Stem Cells from Human Pluripotent Stem Cells Using PSC Neural Induction Medium
 Induction of Neural Stem Cells from Human Pluripotent Stem Cells Using PSC Neural Induction Medium Publication Number MAN0008031 Revision A.0 Introduction Human pluripotent stem cells (PSCs), including
Induction of Neural Stem Cells from Human Pluripotent Stem Cells Using PSC Neural Induction Medium Publication Number MAN0008031 Revision A.0 Introduction Human pluripotent stem cells (PSCs), including
H3K27me3 Does Not Orchestrate the Expression of Lineage-Specific
 Stem Cell Reports, Volume 7 Supplemental Information H3K27me3 Does Not Orchestrate the Expression of Lineage-Specific Markers in hesc-derived Hepatocytes In Vitro Jolien Vanhove, Mariaelena Pistoni, Marc
Stem Cell Reports, Volume 7 Supplemental Information H3K27me3 Does Not Orchestrate the Expression of Lineage-Specific Markers in hesc-derived Hepatocytes In Vitro Jolien Vanhove, Mariaelena Pistoni, Marc
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Nowakowski et al. 10.1073/pnas.1219385110 SI Materials and Methods Primary Antibodies. Primary antibodies used in this study were raised against BrdU (rat, 1:50; Abcam), cleaved
Supporting Information Nowakowski et al. 10.1073/pnas.1219385110 SI Materials and Methods Primary Antibodies. Primary antibodies used in this study were raised against BrdU (rat, 1:50; Abcam), cleaved
Human ips cell derived alveolar epithelium repopulates lung extracellular matrix
 Technical advance Human ips cell derived alveolar epithelium repopulates lung extracellular matrix Mahboobe Ghaedi, 1 Elizabeth A. Calle, 1 Julio J. Mendez, 1 Ashley L. Gard, 1 Jenna Balestrini, 1 Adam
Technical advance Human ips cell derived alveolar epithelium repopulates lung extracellular matrix Mahboobe Ghaedi, 1 Elizabeth A. Calle, 1 Julio J. Mendez, 1 Ashley L. Gard, 1 Jenna Balestrini, 1 Adam
Staining Techniques. Staining Techniques. There are many dyes. Histochemical Stains: chemical reactions. Feulgen reaction -DNA
 Staining Techniques There are many dyes. http://medinfo.ufl.edu/~dental/denhisto/stains.html Examples: Sudan black -Lipids Myelinated axons- blue ihcworld.com/imagegallery/displayimage.php?al... Weigert
Staining Techniques There are many dyes. http://medinfo.ufl.edu/~dental/denhisto/stains.html Examples: Sudan black -Lipids Myelinated axons- blue ihcworld.com/imagegallery/displayimage.php?al... Weigert
Figure 1: TDP-43 is subject to lysine acetylation within the RNA-binding domain a) QBI-293 cells were transfected with TDP-43 in the presence or
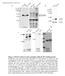 Figure 1: TDP-43 is subject to lysine acetylation within the RNA-binding domain a) QBI-293 cells were transfected with TDP-43 in the presence or absence of the acetyltransferase CBP and acetylated TDP-43
Figure 1: TDP-43 is subject to lysine acetylation within the RNA-binding domain a) QBI-293 cells were transfected with TDP-43 in the presence or absence of the acetyltransferase CBP and acetylated TDP-43
ADP, 5-Hydroxytryptamine (5-HT), EDTA and ethidium bromide were from Sigma.
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Expanded Materials and Methods Materials ADP, 5-Hydroxytryptamine (5-HT), EDTA and ethidium bromide were from Sigma. PAR-4 TRAP (AYPGKF) was custom synthesised by AnaSpec, USA. The
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Expanded Materials and Methods Materials ADP, 5-Hydroxytryptamine (5-HT), EDTA and ethidium bromide were from Sigma. PAR-4 TRAP (AYPGKF) was custom synthesised by AnaSpec, USA. The
