Supplemental Table/Figure Legends
|
|
|
- Loreen Newman
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
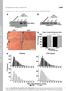
1 MiR-26a is required for skeletal muscle differentiation and regeneration in mice Bijan K. Dey, Jeffrey Gagan, Zhen Yan #, Anindya Dutta Supplemental Table/Figure Legends Suppl. Table 1: Effect of overexpression and inhibition of mir-26a on myoblast differentiation. C2C12 cells were transfected three times at 24 h intervals with mir-26a or GL2 in GM and the cells transferred to DM. Cells were stained for Myogenin at 32 hour or MHC at 60 hour. In another experiment, 2 O-methyl antisense oligonucleotide against GL2 or mir-26a were transfected as in (A) and stained for Myogenin and MHC at 32 and 60 hour respectively. Fraction of Myogenin- or MHC-positive cells was determined randomly from 10 fields and data are presented relative to the GL2 control (100%). Suppl. Table2: Sequences List of qrt-pcr primers used in this study. Sequences of qrt- PCR primers used in this study are shown. Suppl. Figure 1: (A) Cardiotoxin-induced muscle degeneration and regeneration in mouse TA muscle. H & E staining of Fresh frozen (OCT) TA muscle sections from control, Day 1, 3, 5, 7, 10 and 14 post CTX injection are shown. (B) MiR-26a is upregulated in the Pax7- positive cells during muscle regeneration. MiR-26a and Pax7 co-staining is shown on day 7 post CTX injection. Yellow or white arrows indicate mir-26a and Pax7-positive or negative cells, respectively, located outside the skeletal muscle fibers. 1
2 Suppl. Figure 2: Changes in cell cycle profile after transfection of mir-26a in C2C12 cells. Primary FACS results for Fig. 2D. Propidium iodide staining for DNA content and FACS analysis data are shown. Mean +/- standard deviation of three measurements. Suppl. Figure 3: MiR-26a promotes mouse primary myoblast differentiation. (A) Mouse primary myoblast cells transfected with GL2 or mir-26a as in Fig. 2C and qrt-pcr performed for Myogenin and MHC. The results were normalized to GAPDH in the same sample and then again to the level in GL2-transfected cells. Mean +/- standard deviation of three replicates. (B) 2 O-methyl antisense oligonucleotides against GL2 or mir-26a were transfected as in Fig. 2G and qrt-pcr performed for Myogenin and MHC and data presented as in (A). Suppl. Figure 4: Predicted mir-26a target sites on Smad1 and Smad4 3 UTR. The RNAhybrid algorithm predicted mir-26a (green) matching target sites (red) on Smad1 3 UTR (A-D) and Smad4 3 UTR (E, F). The location of the sites on the 3 UTRs and the stability of binding (mfe, minimum free energy) are shown. The point mutations created are shown as. Suppl. Figure 5: C2C12 cells stably expressing Smad1orf do not decrease Smad1 either in the DM or in GM. C2C12 cells stably expressing various constructs as indicated were held in GM or induced to differentiate by transferring to DM and held in DM for 2 days. (A) Smad1 protein detected by Western blotting and GAPDH served as a loading control. (B) Quantitation of indicated bands in (A) normalized to GAPDH and again to that in cells with empty vector in GM. The exogenous Smad1 is expressed at 3x the level of endogenous Smad1 in GM. Suppl. Figure 6: Knockdown of mir-26a by antagomir or TuD in the neonatal and adult muscles increases Ezh2 mrna level. (A) Ant26a increases Ezh2 mrna level. qrt-pcr of Ezh2 on hind leg skeletal muscle, normalized to GAPDH in the same sample and then again to 2
3 the level in controls. Mean +/-standard deviation of the sample from three mice. (B-D) Ezh2 mrna level after injection of TuD-26a but before cardiotoxin injury and during regeneration (D7 & 14). qrt-pcr was performed and data represented as in (A). Suppl. Figure 7: Ki-67-positive cells in the Ant26a injected neonatal skeletal muscles coexpress Pax7. Confocal microscopy images of Ant26a injected neonatal skeletal muscles from Fig. 5D immunostained with Pax7 and Ki-67. Arrows in yellow and white indicate presence or absence of Pax7 in the ki-67-positive cells respectively. Suppl. Figure 8: Secondary structure of AAV TuD cassette specific for mir-26a. (A) Forward and Reverse strands of template DNA that were annealed to make the 26a-TuD expression cassette. The yellow color represents the mir-26a binding sequences (MBS) and the blue represents the stem II. Below these are the sequences that are part of the entry vector and flanked the forward template. (B) The expressed RNA including the flanking sequences (stem I) fold into the secondary structure determined by the CentroidFold software. The MBS is indicated. Suppl. Figure 9: Schedule for AntagomiR, BrdU and TuD injection and tissue collection. Time course of AntagomiR & BrdU (A) or TuD & CTX (B) injection and tissue harvesting is shown. Suppl. Figure 10: AAV expressing NC-TuD or 26a-TuD infect nearly all cells including Pax7-positive cells in adult muscle, as detected by expression of GFP. GFP immunostaining was carried out in the muscle sections expressing (A) NC-TuD (upper row) and 26a-TuD (lower row). indicates an uninfected muscle fiber. (B) Co-staining of GFP and Pax7 in 26a-TuD injected muscle. Yellow arrows: co-stained satellite cells. (C) FISH for mir-26a and 3
4 immunostaining for GFP in day 7 post CTX. MiR-26a remained up-regulated in the cells that were not infected with AAV 26a-TuD expressing GFP while mir-26a was decreased in cells where GFP was expressed. Suppl. Figure 11: 26a-TuD-injected muscle samples shows smaller myofibers. Additional images from the muscles in Fig. 6I. Desmin (green) and laminin (red) staining are performed on regenerating fibers on day 7 (A-C) and day 14 (D-F) post CTX injection. NC-TuD or 26a-TuD and cardiotoxin were injected as in Fig. 6H. Suppl. Figure 12: MiR-26a target sites on human Smad1 and Smad4 3 UTR. The RNA miranda algorithm predicted mir-26a (top) matching target sites (bottom) on Smad1 3 UTR and Smad4 3 UTR. 4
5 Dey _Suppl Table1 Suppl Table 1: Effect of overexpression and inhibition of mir-26a on myoblast differentiation. Transfectant Myog-positive Cells MHC-positive Cells Total counts (10 fields) % Control Total counts (10 fields) % Control Mean SD Mean SD GL mir-26a Anti-GL Anti-26a
6 Dey _Suppl Table 2 Table 2: List of qrt-pcr primers used in this study Primer Name Length Sequence U6sn 20 CTGCGCAAGGATGACACGCA mir-26a 22 TTCAAGTAATCCAGGATAGGCT mir CTGACCTATGAATTGACAGCC mir TGGAATGTAAGGAAGTGTGTGG Myogenin Forward 24 AGCGCAGGCTCAAGAAAGTGAATG Myogenin Reverse 24 CTGTAGGCGCTCAATGTACTGGAT MHC Forward 22 TCCAAACCGTCTCTGCACTGTT MHC Reverse 22 AGCGTACAAAGTGTGGGTGTGT Pax7 Forward 24 GAACCGTCTGGATGAGGGCTCAGA Pax7 Reverse 24 GCTCCTCCAGCTGCTCGGCTGTGA Id3 Forward 24 CTCTTAGCCTCTTGGACGACATGA Id3 Reverse 24 TGTAGTCTATGACACGCTGCAGGA Smad1 Forward 24 TGACCAGCTTGTTTTCATTCACAA Smad1 Reverse 24 GGCCCCTTTCTTCTTCTTCAGTTT Smad4Forward 24 AGCCATAGTGAAGGACTGTTGCAG Smad4 Reverse 24 TACTTCCAGTCCAGGTGGTAGTGC Ezh2Forward 24 CTCTGCCTCCTGAATGTACTCCAA Ezh2 Reverse 24 GGAAGGGATGTAGGAAGCAGTCAT GAPDH Forward 24 ATGACATCAAGAAGGTGGTGAAGC GAPDH Reverse 24 GAAGAGTGGGAGTTGCTGTTGAAG
7 Dey _Suppl Fig.1 A Control Day 7 Day 1 Day 10 Day 3 Day 14 Day 5 B mir-26a Pax7 DAPI/Overlay CTX Day 7
8 Dey _Suppl Fig GL2 mir-26a 50 % cells G1 S G2/M
9 Dey _Suppl Fig.3 A B Relative Myog and MHC mrna level GL2 mir-26a Relative Myog and MHC mrna level Anti-GL2 Anti-26a 0 Myog MHC 0 Myog MHC
10 Dey _Suppl Fig.4 A Smad1 Site 1: B Smad1 Site 2: C Smad1 Site 3: D Smad1 Site 4: E Smad4 Site 1: F Smad4 Site 2:
11 Dey _Suppl Fig.5 A B Smad1 GAPDH Relative Smad1 level (normalized to GAPDH)
12 Dey _Suppl Fig.6 A B Relative Ezh2 level Relative Ezh2 level C 0 Control Ant26a D 0 NC-TuD 26a-TuD Relative Ezh2 level on Day NC-TuDCTX 26a-TuDCTX Relative Ezh2 level on Day NC-TuDCTX 26a-TuDCTX
13 DAPI Pax7 Ki67 Pax7/Ki67 Overlay/DIC Dey _Suppl Fig.7
14 A Dey _Suppl Fig.8 mir26atud Forward template: CATCAACAGCCTATCCTGGTCTCATTACTTGAACAAGTATTCTGGTCACAGAATACAACAGCCTATCCTGGTCTCATTACTTGAACAAG mir26atud Reverse template: TCATCTTGTTCAAGTAATGAGACCAGGATAGGCTGTTGTATTCTGTGACCAGAATACTTGTTCAAGTAATGAGACCAGGATAGGCTGTT For folding, forward template is flanked by GACGGCGCTAGGAT----ATGATCCTAGCGCCGTC B Stem I MiR-26a binding sites MiR-26a binding sites Stem II
15 Dey _Suppl Fig. 9 A Injection Age (Days) AntagomiR AntagomiR AntagomiR BrdU 2 hr Harvesting tissues B Injection AAV CTX 10 days Tissue harvesting days
16 Dey _Suppl Fig. 10 A DAPI DIC GFP 26a-TuD NC-TuD B DAPI DIC Pax7 GFP 26a-TuD C mir-26a GFP DAPI/Overlay
17 Dey _Suppl Fig.11 A B C NC-TuD CTX Day 7 26a-TuD CTX Day 7 26a-TuD CTX Day 7 D E F NC-TuD CTX Day 14 26a -TuD CTX Day 14 26a -TuD CTX Day 14
18 Dey _Suppl Fig.12 3' ucggauaggaccua-augaacuu 5' hsa-mir-26a : 31:5' auugagccuugcauguacuugaa 3' SMAD1 3' ucggauaggaccua--augaacuu 5' hsa-mir-26a 87:5' aaaggagccuugauaauacuugac 3' SMAD1 3' ucggauaggaccuaaugaacuu 5' hsa-mir-26a :: 1022:5' uggauauuuuug--uacuugau 3' SMAD4
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS
 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS Suppl. Fig. 1. Notch and myostatin expression is unaffected in the absence of p65 during postnatal development. A & B. Myostatin and Notch-1 expression levels were determined
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS Suppl. Fig. 1. Notch and myostatin expression is unaffected in the absence of p65 during postnatal development. A & B. Myostatin and Notch-1 expression levels were determined
Supplementary information for: Ten-Eleven Translocation-2 (Tet2) Is Involved in Myogenic Differentiation of Skeletal Myoblast Cells in
 Supplementary information for: Ten-Eleven Translocation-2 (Tet2) Is Involved in Myogenic Differentiation of Skeletal Myoblast Cells in Vitro Xia Zhong*, Qian-Qian Wang*, Jian-Wei Li, Yu-Mei Zhang, Xiao-Rong
Supplementary information for: Ten-Eleven Translocation-2 (Tet2) Is Involved in Myogenic Differentiation of Skeletal Myoblast Cells in Vitro Xia Zhong*, Qian-Qian Wang*, Jian-Wei Li, Yu-Mei Zhang, Xiao-Rong
Cell proliferation was measured with Cell Counting Kit-8 (Dojindo Laboratories, Kumamoto, Japan).
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Supplemental Materials and Methods Cell proliferation assay Cell proliferation was measured with Cell Counting Kit-8 (Dojindo Laboratories, Kumamoto, Japan). GCs were plated at 96-well
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Supplemental Materials and Methods Cell proliferation assay Cell proliferation was measured with Cell Counting Kit-8 (Dojindo Laboratories, Kumamoto, Japan). GCs were plated at 96-well
mir-26a is required for skeletal muscle differentiation and regeneration in mice
 mir-26a is required for skeletal muscle differentiation and regeneration in mice Bijan K. Dey, 1 Jeffrey Gagan, 1 Zhen Yan, 2,3 and Anindya Dutta 1,4 1 Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Genetics,
mir-26a is required for skeletal muscle differentiation and regeneration in mice Bijan K. Dey, 1 Jeffrey Gagan, 1 Zhen Yan, 2,3 and Anindya Dutta 1,4 1 Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Genetics,
Supplemental material
 Supplemental material THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Taylor et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201403021/dc1 Figure S1. Representative images of Cav 1a -YFP mutants with and without LMB treatment.
Supplemental material THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Taylor et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201403021/dc1 Figure S1. Representative images of Cav 1a -YFP mutants with and without LMB treatment.
Positive selection gates for the collection of LRCs or nonlrcs had to be drawn based on the location and
 Determining positive selection gates for LRCs and nonlrcs Positive selection gates for the collection of LRCs or nonlrcs had to be drawn based on the location and shape of the Gaussian distributions. For
Determining positive selection gates for LRCs and nonlrcs Positive selection gates for the collection of LRCs or nonlrcs had to be drawn based on the location and shape of the Gaussian distributions. For
Supplemental material
 Supplemental material THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Gillespie et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.200907037/dc1 repressor complex induced by p38- Gillespie et al. Figure S1. Reduced fiber size
Supplemental material THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Gillespie et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.200907037/dc1 repressor complex induced by p38- Gillespie et al. Figure S1. Reduced fiber size
Supplemental Material
 Supplemental Material Figure S1.(A) Immuno-staining of freshly isolated Myf5-Cre:ROSA-YFP fiber (B) Satellite cell enumeration in WT and cko mice from resting hind limb muscles. Bulk hind limb muscles
Supplemental Material Figure S1.(A) Immuno-staining of freshly isolated Myf5-Cre:ROSA-YFP fiber (B) Satellite cell enumeration in WT and cko mice from resting hind limb muscles. Bulk hind limb muscles
STAT3 signaling controls satellite cell expansion and skeletal muscle repair
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION STAT3 signaling controls satellite cell expansion and skeletal muscle repair Matthew Timothy Tierney 1 *, Tufan Aydogdu 2,3 *, David Sala 2, Barbora Malecova 2, Sole Gatto 2,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION STAT3 signaling controls satellite cell expansion and skeletal muscle repair Matthew Timothy Tierney 1 *, Tufan Aydogdu 2,3 *, David Sala 2, Barbora Malecova 2, Sole Gatto 2,
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1: Identification of new regulators of MuSC by a proteome-based shrna screen. (a) FACS plots of GFP + and GFP - cells from Pax7 ICN -Z/EG (upper panel) and
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1: Identification of new regulators of MuSC by a proteome-based shrna screen. (a) FACS plots of GFP + and GFP - cells from Pax7 ICN -Z/EG (upper panel) and
Supplementary Figure S1. Hoechst. cells/field. Myogenin. % of Myogenin+ cells. 0 h chase CONTROL. BrdU. 72 h chase. CONTROL BrdU CONTROL BrdU
 Hoechst Myogenin amyhc 24 h 48 h 72 h b cells/field 50 40 30 20 10 0 24h 48h 72h h after plating (4 days growth+ t) c e CONTROL 0 h chase % of Myogenin+ cells h after plating (4 days growth+ t) CONTROL
Hoechst Myogenin amyhc 24 h 48 h 72 h b cells/field 50 40 30 20 10 0 24h 48h 72h h after plating (4 days growth+ t) c e CONTROL 0 h chase % of Myogenin+ cells h after plating (4 days growth+ t) CONTROL
transcription and the promoter occupancy of Smad proteins. (A) HepG2 cells were co-transfected with the wwp-luc reporter, and FLAG-tagged FHL1,
 Supplementary Data Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Figure 1 FHL-mediated TGFβ-responsive reporter transcription and the promoter occupancy of Smad proteins. (A) HepG2 cells were co-transfected
Supplementary Data Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Figure 1 FHL-mediated TGFβ-responsive reporter transcription and the promoter occupancy of Smad proteins. (A) HepG2 cells were co-transfected
SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION
 UTX/KDM6A demethylase activity is required for satellite cell-mediated muscle regeneration Hervé Faralli 1,2, Chaochen Wang 3, Kiran Nakka 1,2, Soji Sebastian 1,, Aissa Benyoucef 1,2, Lenan Zhuang 3, Alphonse
UTX/KDM6A demethylase activity is required for satellite cell-mediated muscle regeneration Hervé Faralli 1,2, Chaochen Wang 3, Kiran Nakka 1,2, Soji Sebastian 1,, Aissa Benyoucef 1,2, Lenan Zhuang 3, Alphonse
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Negative regulation of initial steps in skeletal myogenesis by mtor and other kinases Raphael A. Wilson 1*, Jing Liu 1*, Lin Xu 1, James Annis 2, Sara Helmig 1, Gregory Moore
Supplementary Information Negative regulation of initial steps in skeletal myogenesis by mtor and other kinases Raphael A. Wilson 1*, Jing Liu 1*, Lin Xu 1, James Annis 2, Sara Helmig 1, Gregory Moore
1. Primers for PCR to amplify hairpin stem-loop precursor mir-145 plus different flanking sequence from human genomic DNA.
 Supplemental data: 1. Primers for PCR to amplify hairpin stem-loop precursor mir-145 plus different flanking sequence from human genomic DNA. Strategy#1: 20nt at both sides: #1_BglII-Fd primer : 5 -gga
Supplemental data: 1. Primers for PCR to amplify hairpin stem-loop precursor mir-145 plus different flanking sequence from human genomic DNA. Strategy#1: 20nt at both sides: #1_BglII-Fd primer : 5 -gga
ASPP1 Fw GGTTGGGAATCCACGTGTTG ASPP1 Rv GCCATATCTTGGAGCTCTGAGAG
 Supplemental Materials and Methods Plasmids: the following plasmids were used in the supplementary data: pwzl-myc- Lats2 (Aylon et al, 2006), pretrosuper-vector and pretrosuper-shp53 (generous gift of
Supplemental Materials and Methods Plasmids: the following plasmids were used in the supplementary data: pwzl-myc- Lats2 (Aylon et al, 2006), pretrosuper-vector and pretrosuper-shp53 (generous gift of
(a) Immunoblotting to show the migration position of Flag-tagged MAVS
 Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of six MAVS isoforms. (a) Immunoblotting to show the migration position of Flag-tagged MAVS isoforms. HEK293T Mavs -/- cells were transfected with constructs expressing
Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of six MAVS isoforms. (a) Immunoblotting to show the migration position of Flag-tagged MAVS isoforms. HEK293T Mavs -/- cells were transfected with constructs expressing
Fig. S1. eif6 expression in HEK293 transfected with shrna against eif6 or pcmv-eif6 vector.
 Fig. S1. eif6 expression in HEK293 transfected with shrna against eif6 or pcmv-eif6 vector. (a) Western blotting analysis and (b) qpcr analysis of eif6 expression in HEK293 T cells transfected with either
Fig. S1. eif6 expression in HEK293 transfected with shrna against eif6 or pcmv-eif6 vector. (a) Western blotting analysis and (b) qpcr analysis of eif6 expression in HEK293 T cells transfected with either
The non-muscle-myosin-ii heavy chain Myh9 mediates colitis-induced epithelium injury by restricting Lgr5+ stem cells
 Supplementary Information The non-muscle-myosin-ii heavy chain Myh9 mediates colitis-induced epithelium injury by restricting Lgr5+ stem cells Bing Zhao 1,3, Zhen Qi 1,3, Yehua Li 1,3, Chongkai Wang 2,
Supplementary Information The non-muscle-myosin-ii heavy chain Myh9 mediates colitis-induced epithelium injury by restricting Lgr5+ stem cells Bing Zhao 1,3, Zhen Qi 1,3, Yehua Li 1,3, Chongkai Wang 2,
supplementary information
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2015 Figure S1 Confirmation of Sca-1 CD34 stain specificity using isotypematched control antibodies. Skeletal muscle preparations were stained and gated as described in the text (Hoechst
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2015 Figure S1 Confirmation of Sca-1 CD34 stain specificity using isotypematched control antibodies. Skeletal muscle preparations were stained and gated as described in the text (Hoechst
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information SI Materials and Methods RT-qPCR The 25 µl qrt-pcr reaction mixture included 1 µl of cdna or DNA, 12.5 µl of 2X SYBER Green Master Mix (Applied Biosystems ), 5 µm of primers and
Supporting Information SI Materials and Methods RT-qPCR The 25 µl qrt-pcr reaction mixture included 1 µl of cdna or DNA, 12.5 µl of 2X SYBER Green Master Mix (Applied Biosystems ), 5 µm of primers and
b alternative classical none
 Supplementary Figure. 1: Related to Figure.1 a d e b alternative classical none NIK P-IkBa Total IkBa Tubulin P52 (Lighter) P52 (Darker) RelB (Lighter) RelB (Darker) HDAC1 Control-Sh RelB-Sh NF-kB2-Sh
Supplementary Figure. 1: Related to Figure.1 a d e b alternative classical none NIK P-IkBa Total IkBa Tubulin P52 (Lighter) P52 (Darker) RelB (Lighter) RelB (Darker) HDAC1 Control-Sh RelB-Sh NF-kB2-Sh
Supplementary Figure 1. ips_3y+mir-302b. ips_3y+mir-372. ips_3y+mir-302b + mir-372. ips_4y. ips_4y+mir-302b. ips_4y + mir-372
 Supplementary Figure 1 ips_3y+mir-32b ips_3y+ ips_3y+mir-32b + ips_4y ips_4y+mir-32b ips_4y + Nature Biotechnology: doi:1.138/nb.t.1862 TRA-1-6 DAPI Oct3/4 Supplementary Figure 1: ips cells derived from
Supplementary Figure 1 ips_3y+mir-32b ips_3y+ ips_3y+mir-32b + ips_4y ips_4y+mir-32b ips_4y + Nature Biotechnology: doi:1.138/nb.t.1862 TRA-1-6 DAPI Oct3/4 Supplementary Figure 1: ips cells derived from
Supplementary Figure 1. NORAD expression in mouse (A) and dog (B). The black boxes indicate the position of the regions alignable to the 12 repeat
 Supplementary Figure 1. NORAD expression in mouse (A) and dog (B). The black boxes indicate the position of the regions alignable to the 12 repeat units in the human genome. Annotated transposable elements
Supplementary Figure 1. NORAD expression in mouse (A) and dog (B). The black boxes indicate the position of the regions alignable to the 12 repeat units in the human genome. Annotated transposable elements
Supplementary Materials
 Supplementary Materials Table S1. Oligonucleotide sequences and PCR conditions used to amplify the indicated genes. TA = annealing temperature; gdna = genomic DNA; cdna = complementary DNA; c = concentration.
Supplementary Materials Table S1. Oligonucleotide sequences and PCR conditions used to amplify the indicated genes. TA = annealing temperature; gdna = genomic DNA; cdna = complementary DNA; c = concentration.
Supplemental Fig. 1: PEA-15 knockdown efficiency assessed by immunohistochemistry and qpcr
 Supplemental figure legends Supplemental Fig. 1: PEA-15 knockdown efficiency assessed by immunohistochemistry and qpcr A, LβT2 cells were transfected with either scrambled or PEA-15 sirna. Cells were then
Supplemental figure legends Supplemental Fig. 1: PEA-15 knockdown efficiency assessed by immunohistochemistry and qpcr A, LβT2 cells were transfected with either scrambled or PEA-15 sirna. Cells were then
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Fig. 1 shrna mediated knockdown of ZRSR2 in K562 and 293T cells. (a) ZRSR2 transcript levels in stably transduced K562 cells were determined using qrt-pcr. GAPDH was
Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Fig. 1 shrna mediated knockdown of ZRSR2 in K562 and 293T cells. (a) ZRSR2 transcript levels in stably transduced K562 cells were determined using qrt-pcr. GAPDH was
Supplementary Figure 1. Localization of MST1 in RPE cells. Proliferating or ciliated HA- MST1 expressing RPE cells (see Fig. 5b for establishment of
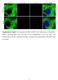 Supplementary Figure 1. Localization of MST1 in RPE cells. Proliferating or ciliated HA- MST1 expressing RPE cells (see Fig. 5b for establishment of the cell line) were immunostained for HA, acetylated
Supplementary Figure 1. Localization of MST1 in RPE cells. Proliferating or ciliated HA- MST1 expressing RPE cells (see Fig. 5b for establishment of the cell line) were immunostained for HA, acetylated
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary figure 1: List of primers/oligonucleotides used in this study. 1 Supplementary figure 2: Sequences and mirna-targets of i) mcherry expresses in transgenic fish used
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary figure 1: List of primers/oligonucleotides used in this study. 1 Supplementary figure 2: Sequences and mirna-targets of i) mcherry expresses in transgenic fish used
Supplementary Fig. 1 related to Fig. 1 Clinical relevance of lncrna candidate
 Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Fig. 1 related to Fig. 1 Clinical relevance of lncrna candidate BC041951 in gastric cancer. (A) The flow chart for selected candidate lncrnas in 660 up-regulated
Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Fig. 1 related to Fig. 1 Clinical relevance of lncrna candidate BC041951 in gastric cancer. (A) The flow chart for selected candidate lncrnas in 660 up-regulated
Table I. Primers used in quantitative real-time PCR for detecting gene expressions in mouse liver tissues
 Table I. Primers used in quantitative real-time PCR for detecting gene expressions in mouse liver tissues Gene name Forward primer 5' to 3' Gene name Reverse primer 5' to 3' CC_F TGCCCTGTTGGGGTTG CC_R
Table I. Primers used in quantitative real-time PCR for detecting gene expressions in mouse liver tissues Gene name Forward primer 5' to 3' Gene name Reverse primer 5' to 3' CC_F TGCCCTGTTGGGGTTG CC_R
At E17.5, the embryos were rinsed in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and immersed in
 Supplementary Materials and Methods Barrier function assays At E17.5, the embryos were rinsed in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and immersed in acidic X-gal mix (100 mm phosphate buffer at ph4.3, 3 mm
Supplementary Materials and Methods Barrier function assays At E17.5, the embryos were rinsed in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and immersed in acidic X-gal mix (100 mm phosphate buffer at ph4.3, 3 mm
Supplementary Figure 1. Expressions of stem cell markers decreased in TRCs on 2D plastic. TRCs were cultured on plastic for 1, 3, 5, or 7 days,
 Supplementary Figure 1. Expressions of stem cell markers decreased in TRCs on 2D plastic. TRCs were cultured on plastic for 1, 3, 5, or 7 days, respectively, and their mrnas were quantified by real time
Supplementary Figure 1. Expressions of stem cell markers decreased in TRCs on 2D plastic. TRCs were cultured on plastic for 1, 3, 5, or 7 days, respectively, and their mrnas were quantified by real time
Figure S1. Specificity of polyclonal anti stabilin-1 and anti stabilin-2 antibodies Lysates of 293T cells transfected with empty vector, mouse
 Figure S1. Specificity of polyclonal anti stabilin-1 and anti stabilin-2 antibodies Lysates of 293T cells transfected with empty vector, mouse stabilin-1, or mouse stabilin-2 were immunoblotted using anti
Figure S1. Specificity of polyclonal anti stabilin-1 and anti stabilin-2 antibodies Lysates of 293T cells transfected with empty vector, mouse stabilin-1, or mouse stabilin-2 were immunoblotted using anti
Supplementary Figure 1 Validate the expression of mir-302b after bacterial infection by northern
 Supplementary Figure 1 Validate the expression of mir-302b after bacterial infection by northern blot. Northern blot analysis of mir-302b expression following infection with PAO1, PAK and Kp in (A) lung
Supplementary Figure 1 Validate the expression of mir-302b after bacterial infection by northern blot. Northern blot analysis of mir-302b expression following infection with PAO1, PAK and Kp in (A) lung
Regulation of transcription by the MLL2 complex and MLL complex-associated AKAP95
 Supplementary Information Regulation of transcription by the complex and MLL complex-associated Hao Jiang, Xiangdong Lu, Miho Shimada, Yali Dou, Zhanyun Tang, and Robert G. Roeder Input HeLa NE IP lot:
Supplementary Information Regulation of transcription by the complex and MLL complex-associated Hao Jiang, Xiangdong Lu, Miho Shimada, Yali Dou, Zhanyun Tang, and Robert G. Roeder Input HeLa NE IP lot:
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURES AND TABLES
 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURES AND TABLES A B Flag-ALDH1A1 IP: α-ac HEK293T WT 91R 128R 252Q 367R 41/ 419R 435R 495R 412R C Flag-ALDH1A1 NAM IP: HEK293T + + - + D NAM - + + E Relative ALDH1A1 activity 1..8.6.4.2
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURES AND TABLES A B Flag-ALDH1A1 IP: α-ac HEK293T WT 91R 128R 252Q 367R 41/ 419R 435R 495R 412R C Flag-ALDH1A1 NAM IP: HEK293T + + - + D NAM - + + E Relative ALDH1A1 activity 1..8.6.4.2
Supplementary Fig. 1 Proteomic analysis of ATR-interacting proteins. ATR, ARID1A and
 Supplementary Figure Legend: Supplementary Fig. 1 Proteomic analysis of ATR-interacting proteins. ATR, ARID1A and ATRIP protein peptides identified from our mass spectrum analysis were shown. Supplementary
Supplementary Figure Legend: Supplementary Fig. 1 Proteomic analysis of ATR-interacting proteins. ATR, ARID1A and ATRIP protein peptides identified from our mass spectrum analysis were shown. Supplementary
Supplementary Figure 1, related to Figure 1. GAS5 is highly expressed in the cytoplasm of hescs, and positively correlates with pluripotency.
 Supplementary Figure 1, related to Figure 1. GAS5 is highly expressed in the cytoplasm of hescs, and positively correlates with pluripotency. (a) Transfection of different concentration of GAS5-overexpressing
Supplementary Figure 1, related to Figure 1. GAS5 is highly expressed in the cytoplasm of hescs, and positively correlates with pluripotency. (a) Transfection of different concentration of GAS5-overexpressing
Supplementary Figure 1 Muscle dystrophic phenotype is absent at P6 in PKO mice. (a) Size
 Supplementary Figure 1 Muscle dystrophic phenotype is absent at P6 in PKO mice. (a) Size comparison of the P6 control and PKO mice. (b) H&E staining of hind-limb muscles from control and PKO mice at P6.
Supplementary Figure 1 Muscle dystrophic phenotype is absent at P6 in PKO mice. (a) Size comparison of the P6 control and PKO mice. (b) H&E staining of hind-limb muscles from control and PKO mice at P6.
Supplemental Table 1 Primers used in study. Human. Mouse
 Supplemental Table 1 Primers used in study Human Forward primer region(5-3 ) Reverse primer region(5-3 ) RT-PCR GAPDH gagtcaacggatttggtcgt ttgattttggagggatctcg Raftlin atgggttgcggattgaacaagttaga ctgaggtataacaccaacgaatttcaggc
Supplemental Table 1 Primers used in study Human Forward primer region(5-3 ) Reverse primer region(5-3 ) RT-PCR GAPDH gagtcaacggatttggtcgt ttgattttggagggatctcg Raftlin atgggttgcggattgaacaagttaga ctgaggtataacaccaacgaatttcaggc
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Kawai and Amano, http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201110008/dc1 Figure S1. Regulation of mirna expression by BRCA1. (A) Confirmation
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Kawai and Amano, http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201110008/dc1 Figure S1. Regulation of mirna expression by BRCA1. (A) Confirmation
Supplementary Table 1. The Q-PCR primer sequence is summarized in the following table.
 Supplementary Table 1. The Q-PCR primer sequence is summarized in the following table. Name Sequence (5-3 ) Application Flag-u ggactacaaggacgacgatgac Shared upstream primer for all the amplifications of
Supplementary Table 1. The Q-PCR primer sequence is summarized in the following table. Name Sequence (5-3 ) Application Flag-u ggactacaaggacgacgatgac Shared upstream primer for all the amplifications of
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Endogenous gene tagging to study subcellular localization and chromatin binding. a, b, Schematic of experimental set-up to endogenously tag RNAi factors using the CRISPR Cas9 technology,
Supplementary Figure 1 Endogenous gene tagging to study subcellular localization and chromatin binding. a, b, Schematic of experimental set-up to endogenously tag RNAi factors using the CRISPR Cas9 technology,
Supplemental Table S1. RT-PCR primers used in this study
 Supplemental Table S1. RT-PCR primers used in this study -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Supplemental Table S1. RT-PCR primers used in this study -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Accelerating skin wound healing by M-CSF through generating SSEA-1 and -3 stem cells. in the injured sites
 Accelerating skin wound healing by M-CSF through generating SSEA-1 and -3 stem cells in the injured sites Yunyuan Li, Reza Baradar Jalili, Aziz Ghahary Department of Surgery, University of British Columbia,
Accelerating skin wound healing by M-CSF through generating SSEA-1 and -3 stem cells in the injured sites Yunyuan Li, Reza Baradar Jalili, Aziz Ghahary Department of Surgery, University of British Columbia,
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb3259 A Ismail et al. Supplementary Figure 1 B 60000 45000 SSC 30000 15000 Live cells 0 0 15000 30000 45000 60000 FSC- PARR 60000 45000 PARR Width 30000 FSC- 15000 Single cells 0 0 15000
DOI: 10.1038/ncb3259 A Ismail et al. Supplementary Figure 1 B 60000 45000 SSC 30000 15000 Live cells 0 0 15000 30000 45000 60000 FSC- PARR 60000 45000 PARR Width 30000 FSC- 15000 Single cells 0 0 15000
Supplementary Fig. 1. (A) Working model. The pluripotency transcription factor OCT4
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE LEGENDS Supplementary Fig. 1. (A) Working model. The pluripotency transcription factor OCT4 directly up-regulates the expression of NIPP1 and CCNF that together inhibit protein phosphatase
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE LEGENDS Supplementary Fig. 1. (A) Working model. The pluripotency transcription factor OCT4 directly up-regulates the expression of NIPP1 and CCNF that together inhibit protein phosphatase
To generate the luciferase fusion to the human 3 UTRs, we sub-cloned the 3 UTR
 Plasmids To generate the luciferase fusion to the human 3 UTRs, we sub-cloned the 3 UTR fragments downstream of firefly luciferase (luc) in pgl3 control (Promega). pgl3- CDK6 was made by amplifying a 2,886
Plasmids To generate the luciferase fusion to the human 3 UTRs, we sub-cloned the 3 UTR fragments downstream of firefly luciferase (luc) in pgl3 control (Promega). pgl3- CDK6 was made by amplifying a 2,886
Wnt16 smact merge VK/AB
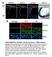 A WT Wnt6 smact merge VK/A KO ctrl IgG WT KO Wnt6 smact DAPI SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE I: Wnt6 expression in MGP-deficient aortae. Immunostaining for Wnt6 and smooth muscle actin (smact) in aortae from 7 day
A WT Wnt6 smact merge VK/A KO ctrl IgG WT KO Wnt6 smact DAPI SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE I: Wnt6 expression in MGP-deficient aortae. Immunostaining for Wnt6 and smooth muscle actin (smact) in aortae from 7 day
Site-Directed Mutagenesis. Mutations in four Smad4 sites of mouse Gat1 promoter
 Supplement Supporting Materials and Methods Site-Directed Mutagenesis. Mutations in four Smad4 sites of mouse Gat1 promoter were independently generated using a two-step PCR method. The Smad4 binding site
Supplement Supporting Materials and Methods Site-Directed Mutagenesis. Mutations in four Smad4 sites of mouse Gat1 promoter were independently generated using a two-step PCR method. The Smad4 binding site
Nature Biotechnology: doi: /nbt Supplementary Figure 1. In vitro validation of OTC sgrnas and donor template.
 Supplementary Figure 1 In vitro validation of OTC sgrnas and donor template. (a) In vitro validation of sgrnas targeted to OTC in the MC57G mouse cell line by transient transfection followed by 4-day puromycin
Supplementary Figure 1 In vitro validation of OTC sgrnas and donor template. (a) In vitro validation of sgrnas targeted to OTC in the MC57G mouse cell line by transient transfection followed by 4-day puromycin
Supplementary Figure S1. The tetracycline-inducible CRISPR system. A) Hela cells stably
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure S1. The tetracycline-inducible CRISPR system. A) Hela cells stably expressing shrna sequences against TRF2 were examined by western blotting. shcon, shrna
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure S1. The tetracycline-inducible CRISPR system. A) Hela cells stably expressing shrna sequences against TRF2 were examined by western blotting. shcon, shrna
Nature Biotechnology: doi: /nbt Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic and results of screening the combinatorial antibody library for Sox2 replacement activity. A single batch of MEFs were plated and transduced with doxycycline inducible
Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic and results of screening the combinatorial antibody library for Sox2 replacement activity. A single batch of MEFs were plated and transduced with doxycycline inducible
gacgacgaggagaccaccgctttg aggcacattgaaggtctcaaacatg
 Supplementary information Supplementary table 1: primers for cloning and sequencing cloning for E- Ras ggg aat tcc ctt gag ctg ctg ggg aat ggc ttt gcc ggt cta gag tat aaa gga agc ttt gaa tcc Tpbp Oct3/4
Supplementary information Supplementary table 1: primers for cloning and sequencing cloning for E- Ras ggg aat tcc ctt gag ctg ctg ggg aat ggc ttt gcc ggt cta gag tat aaa gga agc ttt gaa tcc Tpbp Oct3/4
supplementary information
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2116 Figure S1 CDK phosphorylation of EZH2 in cells. (a) Comparison of candidate CDK phosphorylation sites on EZH2 with known CDK substrates by multiple sequence alignments. (b) CDK1 and
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2116 Figure S1 CDK phosphorylation of EZH2 in cells. (a) Comparison of candidate CDK phosphorylation sites on EZH2 with known CDK substrates by multiple sequence alignments. (b) CDK1 and
A RRM1 H2AX DAPI. RRM1 H2AX DAPI Merge. Cont. sirna RRM1
 A H2AX DAPI H2AX DAPI Merge Cont sirna Figure S1: Accumulation of RRM1 at DNA damage sites (A) HeLa cells were subjected to in situ detergent extraction without IR irradiation, and immunostained with the
A H2AX DAPI H2AX DAPI Merge Cont sirna Figure S1: Accumulation of RRM1 at DNA damage sites (A) HeLa cells were subjected to in situ detergent extraction without IR irradiation, and immunostained with the
Supplementary Figure 1. Bone density was decreased in osteoclast-lineage cell specific Gna13 deficient mice. (a-c) PCR genotyping of mice by mouse
 Supplementary Figure 1. Bone density was decreased in osteoclast-lineage cell specific Gna13 deficient mice. (a-c) PCR genotyping of mice by mouse tail DNA. Primers were designed to detect Gna13-WT/f (~400bp/470bp)
Supplementary Figure 1. Bone density was decreased in osteoclast-lineage cell specific Gna13 deficient mice. (a-c) PCR genotyping of mice by mouse tail DNA. Primers were designed to detect Gna13-WT/f (~400bp/470bp)
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Figure S1: Activation of the ATM pathway by I-PpoI. A. HEK293T cells were either untransfected, vector transfected, transfected with an I-PpoI expression vector, or subjected to 2Gy γ-irradiation. 24 hrs
Figure S1: Activation of the ATM pathway by I-PpoI. A. HEK293T cells were either untransfected, vector transfected, transfected with an I-PpoI expression vector, or subjected to 2Gy γ-irradiation. 24 hrs
Galina Gabriely, Ph.D. BWH/HMS
 Galina Gabriely, Ph.D. BWH/HMS Email: ggabriely@rics.bwh.harvard.edu Outline: microrna overview microrna expression analysis microrna functional analysis microrna (mirna) Characteristics mirnas discovered
Galina Gabriely, Ph.D. BWH/HMS Email: ggabriely@rics.bwh.harvard.edu Outline: microrna overview microrna expression analysis microrna functional analysis microrna (mirna) Characteristics mirnas discovered
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION FIGURE LEGENDS
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION FIGURE LEGENDS Fig. S1. Radiation-induced phosphorylation of Rad50 at a specific site. A. Rad50 is an in vitro substrate for ATM. A series of Rad50-GSTs covering the entire molecule
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION FIGURE LEGENDS Fig. S1. Radiation-induced phosphorylation of Rad50 at a specific site. A. Rad50 is an in vitro substrate for ATM. A series of Rad50-GSTs covering the entire molecule
Supplemental Material Igreja and Izaurralde 1. CUP promotes deadenylation and inhibits decapping of mrna targets. Catia Igreja and Elisa Izaurralde
 Supplemental Material Igreja and Izaurralde 1 CUP promotes deadenylation and inhibits decapping of mrna targets Catia Igreja and Elisa Izaurralde Supplemental Materials and methods Functional assays and
Supplemental Material Igreja and Izaurralde 1 CUP promotes deadenylation and inhibits decapping of mrna targets Catia Igreja and Elisa Izaurralde Supplemental Materials and methods Functional assays and
Supplemental Information. DNp63 Inhibits Oxidative Stress-Induced Cell. Death, Including Ferroptosis, and Cooperates with
 Cell Reports, Volume 21 Supplemental Information DNp63 Inhibits Oxidative Stress-Induced Cell Death, Including Ferroptosis, and Cooperates with the BCL-2 Family to Promote Clonogenic Survival Gary X. Wang,
Cell Reports, Volume 21 Supplemental Information DNp63 Inhibits Oxidative Stress-Induced Cell Death, Including Ferroptosis, and Cooperates with the BCL-2 Family to Promote Clonogenic Survival Gary X. Wang,
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Kanaani et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.200912101/dc1 Figure S1. The K2 rabbit polyclonal antibody is specific for GAD67,
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Kanaani et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.200912101/dc1 Figure S1. The K2 rabbit polyclonal antibody is specific for GAD67,
Supplementary Figure 1. Reintroduction of HDAC1 in HDAC1-/- ES cells reverts the
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE LEGENDS Supplementary Figure 1. Reintroduction of HDAC1 in HDAC1-/- ES cells reverts the phenotype of HDAC1-/- teratomas. 3x10 6 HDAC1 reintroduced (HDAC1-/-re) and empty vector infected
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE LEGENDS Supplementary Figure 1. Reintroduction of HDAC1 in HDAC1-/- ES cells reverts the phenotype of HDAC1-/- teratomas. 3x10 6 HDAC1 reintroduced (HDAC1-/-re) and empty vector infected
JCB. Supplemental material THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY. Paul et al.,
 Supplemental material JCB Paul et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201502040/dc1 THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Figure S1. Mutant p53-expressing cells display limited retrograde actin flow at
Supplemental material JCB Paul et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201502040/dc1 THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Figure S1. Mutant p53-expressing cells display limited retrograde actin flow at
Grb2-Mediated Alteration in the Trafficking of AβPP: Insights from Grb2-AICD Interaction
 Journal of Alzheimer s Disease 20 (2010) 1 9 1 IOS Press Supplementary Material Grb2-Mediated Alteration in the Trafficking of AβPP: Insights from Grb2-AICD Interaction Mithu Raychaudhuri and Debashis
Journal of Alzheimer s Disease 20 (2010) 1 9 1 IOS Press Supplementary Material Grb2-Mediated Alteration in the Trafficking of AβPP: Insights from Grb2-AICD Interaction Mithu Raychaudhuri and Debashis
Supplemental Figure 1 (Figure S1), related to Figure 1 Figure S1 provides evidence to demonstrate Nfatc1Cre is a mouse line that directed gene
 Developmental Cell, Volume 25 Supplemental Information Brg1 Governs a Positive Feedback Circuit in the Hair Follicle for Tissue Regeneration and Repair Yiqin Xiong, Wei Li, Ching Shang, Richard M. Chen,
Developmental Cell, Volume 25 Supplemental Information Brg1 Governs a Positive Feedback Circuit in the Hair Follicle for Tissue Regeneration and Repair Yiqin Xiong, Wei Li, Ching Shang, Richard M. Chen,
Supplementary
 Supplementary information Supplementary Material and Methods Plasmid construction The transposable element vectors for inducible expression of RFP-FUS wt and EGFP-FUS R521C and EGFP-FUS P525L were derived
Supplementary information Supplementary Material and Methods Plasmid construction The transposable element vectors for inducible expression of RFP-FUS wt and EGFP-FUS R521C and EGFP-FUS P525L were derived
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb3240 Supplementary Figure 1 GBM cell lines display similar levels of p100 to p52 processing but respond differentially to TWEAK-induced TERT expression according to TERT promoter mutation
DOI: 10.1038/ncb3240 Supplementary Figure 1 GBM cell lines display similar levels of p100 to p52 processing but respond differentially to TWEAK-induced TERT expression according to TERT promoter mutation
Supplementary Figure Legends. Figure-S1 Molecular basis of ASS1 deficiency in myxofibrosarcoma: (A)
 Supplementary Figure Legends Figure-S1 Molecular basis of ASS1 deficiency in myxofibrosarcoma: (A) High-resolution oligonucleotide-based array comparative genomic hybridization shows normal DNA copy number
Supplementary Figure Legends Figure-S1 Molecular basis of ASS1 deficiency in myxofibrosarcoma: (A) High-resolution oligonucleotide-based array comparative genomic hybridization shows normal DNA copy number
Supplementary Figure S1. Immunodetection of full-length XA21 and the XA21 C-terminal cleavage product.
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure S1. Immunodetection of full-length XA21 and the XA21 C-terminal cleavage product. Total protein extracted from Kitaake wild type and rice plants carrying
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure S1. Immunodetection of full-length XA21 and the XA21 C-terminal cleavage product. Total protein extracted from Kitaake wild type and rice plants carrying
Supplementary Fig. 1. Multiple five micron sections of liver tissues of rats treated
 Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Fig. 1. Multiple five micron sections of liver tissues of rats treated with either vehicle (left; n=3) or CCl 4 (right; n=3) were co-immunostained for NRP-1 (green)
Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Fig. 1. Multiple five micron sections of liver tissues of rats treated with either vehicle (left; n=3) or CCl 4 (right; n=3) were co-immunostained for NRP-1 (green)
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/10/483/eaak9557/dc1 Supplementary Materials for The lncrna H19 mediates breast cancer cell plasticity during EMT and MET plasticity by differentially sponging
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/10/483/eaak9557/dc1 Supplementary Materials for The lncrna H19 mediates breast cancer cell plasticity during EMT and MET plasticity by differentially sponging
Inventory of Supplemental Information for Melkman-Zehavi et al.
 Inventory of Supplemental Information for Melkman-Zehavi et al. Supplementary methods for Melkman et al. Supplementary Figures Figure S1, related to Figure 2 Islet size and total beta cell mass of mutant
Inventory of Supplemental Information for Melkman-Zehavi et al. Supplementary methods for Melkman et al. Supplementary Figures Figure S1, related to Figure 2 Islet size and total beta cell mass of mutant
supplementary information
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2172 Figure S1 p53 regulates cellular NADPH and lipid levels via inhibition of G6PD. (a) U2OS cells stably expressing p53 shrna or a control shrna were transfected with control sirna or
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2172 Figure S1 p53 regulates cellular NADPH and lipid levels via inhibition of G6PD. (a) U2OS cells stably expressing p53 shrna or a control shrna were transfected with control sirna or
Supplementary Figure 1. Homozygous rag2 E450fs mutants are healthy and viable similar to wild-type and heterozygous siblings.
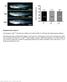 Supplementary Figure 1 Homozygous rag2 E450fs mutants are healthy and viable similar to wild-type and heterozygous siblings. (left) Representative bright-field images of wild type (wt), heterozygous (het)
Supplementary Figure 1 Homozygous rag2 E450fs mutants are healthy and viable similar to wild-type and heterozygous siblings. (left) Representative bright-field images of wild type (wt), heterozygous (het)
Table 1. Primers, annealing temperatures, and product sizes for PCR amplification.
 Table 1. Primers, annealing temperatures, and product sizes for PCR amplification. Gene Direction Primer sequence (5 3 ) Annealing Temperature Size (bp) BRCA1 Forward TTGCGGGAGGAAAATGGGTAGTTA 50 o C 292
Table 1. Primers, annealing temperatures, and product sizes for PCR amplification. Gene Direction Primer sequence (5 3 ) Annealing Temperature Size (bp) BRCA1 Forward TTGCGGGAGGAAAATGGGTAGTTA 50 o C 292
Mutagenesis and Expression of Mammalian Clotting Factor IX. Mark McCleland The Children s Hospital of Philadelphia and Lycoming College
 Mutagenesis and Expression of Mammalian Clotting Factor IX Mark McCleland The Children s Hospital of Philadelphia and Lycoming College Hemophilia B X-linked blood clotting disorder characterized by a deficiency
Mutagenesis and Expression of Mammalian Clotting Factor IX Mark McCleland The Children s Hospital of Philadelphia and Lycoming College Hemophilia B X-linked blood clotting disorder characterized by a deficiency
MicroRNA Destabilization Enables. Dynamic Regulation of the mir-16 Family. In Response to Cell-Cycle Changes SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION
 Molecular Cell, Volume 43 SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION MicroRNA Destabilization Enables Dynamic Regulation of the mir-16 Family In Response to Cell-Cycle Changes Olivia S. Risland, Sue-Jean Hong, and David
Molecular Cell, Volume 43 SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION MicroRNA Destabilization Enables Dynamic Regulation of the mir-16 Family In Response to Cell-Cycle Changes Olivia S. Risland, Sue-Jean Hong, and David
Fig. S1 TGF RI inhibitor SB effectively blocks phosphorylation of Smad2 induced by TGF. FET cells were treated with TGF in the presence of
 Fig. S1 TGF RI inhibitor SB525334 effectively blocks phosphorylation of Smad2 induced by TGF. FET cells were treated with TGF in the presence of different concentrations of SB525334. Cells were lysed and
Fig. S1 TGF RI inhibitor SB525334 effectively blocks phosphorylation of Smad2 induced by TGF. FET cells were treated with TGF in the presence of different concentrations of SB525334. Cells were lysed and
TOOLS sirna and mirna. User guide
 TOOLS sirna and mirna User guide Introduction RNA interference (RNAi) is a powerful tool for suppression gene expression by causing the destruction of specific mrna molecules. Small Interfering RNAs (sirnas)
TOOLS sirna and mirna User guide Introduction RNA interference (RNAi) is a powerful tool for suppression gene expression by causing the destruction of specific mrna molecules. Small Interfering RNAs (sirnas)
Supplementary Table 1. Sequences for BTG2 and BRCA1 sirnas.
 Supplementary Table 1. Sequences for BTG2 and BRCA1 sirnas. Target Gene Non-target / Control BTG2 BRCA1 NFE2L2 Target Sequence ON-TARGET plus Non-targeting sirna # 1 (Cat# D-001810-01-05) sirna1: GAACCGACAUGCUCCCGGA
Supplementary Table 1. Sequences for BTG2 and BRCA1 sirnas. Target Gene Non-target / Control BTG2 BRCA1 NFE2L2 Target Sequence ON-TARGET plus Non-targeting sirna # 1 (Cat# D-001810-01-05) sirna1: GAACCGACAUGCUCCCGGA
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/10/496/eaam6291/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Regulation of autophagy, NF-κB signaling, and cell viability by mir-124 in KRAS mutant mesenchymal-like NSCLC cells
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/10/496/eaam6291/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Regulation of autophagy, NF-κB signaling, and cell viability by mir-124 in KRAS mutant mesenchymal-like NSCLC cells
Kostandin V. Pajcini, Stephane Y. Corbel, Julien Sage, Jason H. Pomerantz, and Helen M. Blau
 Cell Stem Cell, Volume 7 Supplemental Information Transient Inactivation of Rb and ARF Yields Regenerative Cells from Postmitotic Mammalian Muscle Kostandin V. Pajcini, Stephane Y. Corbel, Julien Sage,
Cell Stem Cell, Volume 7 Supplemental Information Transient Inactivation of Rb and ARF Yields Regenerative Cells from Postmitotic Mammalian Muscle Kostandin V. Pajcini, Stephane Y. Corbel, Julien Sage,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:.38/nature899 Supplementary Figure Suzuki et al. a c p7 -/- / WT ratio (+)/(-) p7 -/- / WT ratio Log X 3. Fold change by treatment ( (+)/(-)) Log X.5 3-3. -. b Fold change by treatment ( (+)/(-)) 8
doi:.38/nature899 Supplementary Figure Suzuki et al. a c p7 -/- / WT ratio (+)/(-) p7 -/- / WT ratio Log X 3. Fold change by treatment ( (+)/(-)) Log X.5 3-3. -. b Fold change by treatment ( (+)/(-)) 8
Supplementary Figure 1. GST pull-down analysis of the interaction of GST-cIAP1 (A, B), GSTcIAP1
 Legends Supplementary Figure 1. GST pull-down analysis of the interaction of GST- (A, B), GST mutants (B) or GST- (C) with indicated proteins. A, B, Cell lysate from untransfected HeLa cells were loaded
Legends Supplementary Figure 1. GST pull-down analysis of the interaction of GST- (A, B), GST mutants (B) or GST- (C) with indicated proteins. A, B, Cell lysate from untransfected HeLa cells were loaded
Supplementary Figure 1. (a) The qrt-pcr for lnc-2, lnc-6 and lnc-7 RNA level in DU145, 22Rv1, wild type HCT116 and HCT116 Dicer ex5 cells transfected
 Supplementary Figure 1. (a) The qrt-pcr for lnc-2, lnc-6 and lnc-7 RNA level in DU145, 22Rv1, wild type HCT116 and HCT116 Dicer ex5 cells transfected with the sirna against lnc-2, lnc-6, lnc-7, and the
Supplementary Figure 1. (a) The qrt-pcr for lnc-2, lnc-6 and lnc-7 RNA level in DU145, 22Rv1, wild type HCT116 and HCT116 Dicer ex5 cells transfected with the sirna against lnc-2, lnc-6, lnc-7, and the
Supplementary Fig. S1. SAMHD1c has a more potent dntpase activity than. SAMHD1c. Purified recombinant SAMHD1c and SAMHD1c proteins (with
 Supplementary Fig. S1. SAMHD1c has a more potent dntpase activity than SAMHD1c. Purified recombinant SAMHD1c and SAMHD1c proteins (with concentration of 800nM) were incubated with 1mM dgtp for the indicated
Supplementary Fig. S1. SAMHD1c has a more potent dntpase activity than SAMHD1c. Purified recombinant SAMHD1c and SAMHD1c proteins (with concentration of 800nM) were incubated with 1mM dgtp for the indicated
Figure S2. Response of mouse ES cells to GSK3 inhibition. Mentioned in discussion
 Stem Cell Reports, Volume 1 Supplemental Information Robust Self-Renewal of Rat Embryonic Stem Cells Requires Fine-Tuning of Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3 Inhibition Yaoyao Chen, Kathryn Blair, and Austin
Stem Cell Reports, Volume 1 Supplemental Information Robust Self-Renewal of Rat Embryonic Stem Cells Requires Fine-Tuning of Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3 Inhibition Yaoyao Chen, Kathryn Blair, and Austin
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Figure a T m ( C) Seq. '-3' uguuugugguaacagugugaggu L 62 AttGtcAcaCtcC L2 6 ccattgtcacactcc L3 66 attgtcacactcc 7 ccattgtcacactcca L 73 ccattgtcacactcc L6 74 AttGTcaCaCtCC L7 7 attgtcacactcc
Supplementary Figure a T m ( C) Seq. '-3' uguuugugguaacagugugaggu L 62 AttGtcAcaCtcC L2 6 ccattgtcacactcc L3 66 attgtcacactcc 7 ccattgtcacactcca L 73 ccattgtcacactcc L6 74 AttGTcaCaCtCC L7 7 attgtcacactcc
Supplemental Materials and Methods
 Supplemental Materials and Methods Antibodies: Anti-SRF (cat# Sc-335) and anti-igf1r (sc-712) (Santa Cruz Biotech), and anti- ADAM-10 (14-6211) were from e-bioscience, anti-ku70 (cat# MS-329-P) (Labvision),
Supplemental Materials and Methods Antibodies: Anti-SRF (cat# Sc-335) and anti-igf1r (sc-712) (Santa Cruz Biotech), and anti- ADAM-10 (14-6211) were from e-bioscience, anti-ku70 (cat# MS-329-P) (Labvision),
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization and high expression of Lnc-β-Catm in liver CSCs. (a) Heatmap of differently expressed lncrnas in Liver CSCs (CD13 + CD133 + ) and non-cscs (CD13 - CD133 - ) according
Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization and high expression of Lnc-β-Catm in liver CSCs. (a) Heatmap of differently expressed lncrnas in Liver CSCs (CD13 + CD133 + ) and non-cscs (CD13 - CD133 - ) according
Figure S1a. The modular dcas9 fusion system works efficiently to suppress and activate endogenous gene expression in C. elegans
 Figure S1a. The modular dcas9 fusion system works efficiently to suppress and activate endogenous gene expression in C. elegans A, a normal wild-type hermaphrodite N2 is shown. B, a dpy-5-supressed F1
Figure S1a. The modular dcas9 fusion system works efficiently to suppress and activate endogenous gene expression in C. elegans A, a normal wild-type hermaphrodite N2 is shown. B, a dpy-5-supressed F1
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/323/5911/256/dc1 Supporting Online Material for HDAC4 Regulates Neuronal Survival in Normal and Diseased Retinas Bo Chen and Constance L. Cepko E-mail: bochen@genetics.med.harvard.edu,
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/323/5911/256/dc1 Supporting Online Material for HDAC4 Regulates Neuronal Survival in Normal and Diseased Retinas Bo Chen and Constance L. Cepko E-mail: bochen@genetics.med.harvard.edu,
Supplementary Figure S1 Complementarity between VR-RNA and cola mrna 5 UTR is important for cola regulation. (A) Mutation sites within VR-RNA-colA
 Supplementary Figure S1 Complementarity between VR-RNA and cola mrna 5 UTR is important for cola regulation. (A) Mutation sites within VR-RNA-colA RNA duplex. Mutation sites in cola mrna 5 UTR or VR-RNA
Supplementary Figure S1 Complementarity between VR-RNA and cola mrna 5 UTR is important for cola regulation. (A) Mutation sites within VR-RNA-colA RNA duplex. Mutation sites in cola mrna 5 UTR or VR-RNA
Partial list of differentially expressed genes from cdna microarray, comparing MUC18-
 Supplemental Figure legends Table-1 Partial list of differentially expressed genes from cdna microarray, comparing MUC18- silenced and NT-transduced A375SM cells. Supplemental Figure 1 Effect of MUC-18
Supplemental Figure legends Table-1 Partial list of differentially expressed genes from cdna microarray, comparing MUC18- silenced and NT-transduced A375SM cells. Supplemental Figure 1 Effect of MUC-18
Supplemental Information
 Supplemental Information Itemized List Materials and Methods, Related to Supplemental Figures S5A-C and S6. Supplemental Figure S1, Related to Figures 1 and 2. Supplemental Figure S2, Related to Figure
Supplemental Information Itemized List Materials and Methods, Related to Supplemental Figures S5A-C and S6. Supplemental Figure S1, Related to Figures 1 and 2. Supplemental Figure S2, Related to Figure
Sarker et al. Supplementary Material. Subcellular Fractionation
 Supplementary Material Subcellular Fractionation Transfected 293T cells were harvested with phosphate buffered saline (PBS) and centrifuged at 2000 rpm (500g) for 3 min. The pellet was washed, re-centrifuged
Supplementary Material Subcellular Fractionation Transfected 293T cells were harvested with phosphate buffered saline (PBS) and centrifuged at 2000 rpm (500g) for 3 min. The pellet was washed, re-centrifuged
Figure 1a RFLP from mouse tissue, splicing of mh2a1 isoforms.
 Figure 1a RFLP from mouse tissue, splicing of mh2a1 isoforms. Samples order in the frame: Control 1, control 2, Skeletal muscle, liver, brain, testis, kidney, spleen, small intestin, big intestin, lung.
Figure 1a RFLP from mouse tissue, splicing of mh2a1 isoforms. Samples order in the frame: Control 1, control 2, Skeletal muscle, liver, brain, testis, kidney, spleen, small intestin, big intestin, lung.
