Name Date academic Biology Final Study Guide
|
|
|
- Tyler Weaver
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Name Date academic Biology Final Study Guide Directions: This packet contains an extensive study guide that will help you prepare for the upcoming Final Exam. Pace yourself and be prepared to work on part of it on your own time. This study guide covers the majority of the material that will appear on your Final. Topics: Chapter 2 Chemistry Chapter 7 Cells (include notes on microscopes) Chapter 8 Photosynthesis Chapter 9 Cellular Respiration Chapter 10 Cell Growth and Division Chapter 11 Introduction to Genetics Chapter 12 DNA and RNA Chapter 13 Genetic Engineering Study Suggestions: Create a concept map (or other graphic organizer) to summarize all of the important information in a chapter. Explain your concept maps to classmates or family members. Work in a small study group and assign different study tasks to different people then share all of the information. Write a summary of all of the important information in each Chapter. Write a summary of all of the important information in each section of class notes. Do not just recopy the notes, summarize the information into an easy to understand paragraph. Include important vocabulary. Write a short paragraph to summarize each handout or worksheet you received in class. Answer the questions on the chapter assessments at the end of each chapter. Chapter 2 Chemistry Vocab atom nucleus electron element isotope compound chemical bond ionic bond ion covalent bond molecule van der Waals forces 1. Draw and label the atomic structure. Include proton, neutron, nucleus and electrons. 2. What is atomic number? Mass number? What are the atomic number and mass number of Carbon? 3. If an atom has an atomic number of 15, how many protons does it have? Electrons? 4. If an atom has 8 protons in its nucleus, what is its atomic number? How many electrons does it have? 5. If an atom has 8 protons and a mass number of 16, how many neutrons does it have? 1
2 6. What is an isotope? 7. Carbon-12 and Carbon-14 are isotopes. Do they have the same number of neutrons? Protons? 8. What is the definition of a chemical compound? 9. What is an element? 10. Sodium (Na) has one electron in its outer shell. What will its charge be when it becomes and ion? 11. Oxygen (O) has six electrons in its outer shell. What will its charge be when it becomes and ion? 12. What is the difference between an ionic and a covalent bond? 13. What does it mean if 2 atoms are in the same group (column)? 14. What is cohesion? Adhesion? 15. What does it mean that water is polar? 16. What is an organic compound? 17. Where does the energy come from in carbohydrates? 18. What polysaccharide do plants use to store excess sugar? What do animals use? 19. What is the subunit of proteins? 20. What are the roles of proteins? 21. Explain how enzymes work. 22. What are the roles of lipids? 23. What are the 2 parts of lipids? 24. What is the difference between saturated and unsaturated lipids? 25. What do nucleic acids do? 26. What are the 2 kinds of nucleic acids? 2
3 Chapter 7: Cells and Plasma Membrane Vocabulary cell cell theory nucleus eukaryote prokaryote 1. What is resolution? 2. Compare and contrast how compound light microscopes and electron microscopes work. 3. What kind of image does a TEM produce? An SEM? 4. Describe the main difference and 2 similarities between prokaryotes and eukaryotes. (Hint: They are both cells, or they are both alive, are not acceptable answers.) 5. What do the terms prokaryote and eukaryote mean? 6. What did each of the following scientists do to contribute to the Cell Theory? Leeuwenhoek, Schleiden, Schwann, Virchow, Hooke 7. Write the 3 parts of the cell theory. 8. What are 3 differences and 3 similarities between plant and animal cells? (Hint: They are both cells, or they are both alive, are not acceptable answers.) 9. Write a short description of the function of each of the following organelles. Cell Membrane, Cell Wall, Nucleus, Nucleolus, Cytoplasm, Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER), Ribosome, Cytoskeleton, Mitochondria, Golgi Apparatus, Lysosome, Vacuole, Plastid, Chloroplast, Cilia, Flagella. Be able to identify the organelles in cell diagram. 10. What are the 5 levels of cell organization, in order? 3
4 11. What does it mean that cells in multicellular organisms are specialized? Why aren t the cells of unicellular organisms specialized? 12. What is the Endosymbiotic Theory? 13. Define homeostasis. 14. What 2 compounds make up the plasma membrane? 15. Draw a phospholipid. Label phosphate head and fatty acid tails. Which is hydrophilic and which is hydrophobic? 16. How does the presence of cholesterol affect the plasma membrane? 17. How does the presence of unsaturated phospholipids affect the plasma membrane 18. What is the Fluid Mosaic Model? Be sure to address both words, fluid and mosaic. 19. Define diffusion. On what 2 concepts is diffusion based? 20. What is a concentration gradient? 21. What is dynamic equilibrium? 22. What is a hypotonic solution? What happens to cells placed in it? 23. What is a hypertonic solution? What happens to cells placed in it? 24. What is an isotonic solution? What happens to cells placed in it? 25. What is turgor pressure? In what kind of solution must a plant cell be placed to increase turgor pressure? 26. What organelle keeps a plant cell from bursting with too much water? 27. How does being placed in a hypertonic solution affect a plant? 4
5 28. What is plasmolysis? What does the inside of a plant cell look like that has undergone plasmolysis? 29. Which kind of transport requires a cell to expend energy, active or passive? 30. Channel and Carrier Proteins are both involved in which kind of transport, active or passive? 31. Define endocytosis and list two examples. 32. Define exocytosis. Is it an example of active or passive transport? 33. Draw 3 beakers each containing a large cell floating in a hypertonic solution, a hypotonic solution and an isotonic solution. Include which direction the water would flow. Chapter 8 Photosynthesis Vocabulary autotroph heterotroph adenosine triphosphate (ATP) 1. What are autotrophs? Give an example. 2. What are heterotrophs? Give an example. 3. What is ATP? What is its role in the cell? 4. What is photosynthesis (definition)? 5. List the 4 things required for photosynthesis to take place. 6. How are chloroplasts, thylakoids, stroma, grana and chlorophyll related? 7. Write the equation for photosynthesis. Under the equation, write the words for each symbol. 5
6 8. What is the purpose of the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis? Explain each step in the light-dependent reactions, including light absorption, electron transport, oxygen production (water splitting) and the formation of the energy-containing molecules. 9. What is ATP Synthase? What does it do in photosynthesis? 10. Why are the light-dependent reactions important to the light-independent reactions (Calvin Cycle)? What is produced from the Calvin Cycle? Chapter 9 Cellular Respiration Vocab calorie glycolysis cellular respiration NAD+ fermentation anaerobic aerobic Krebs cycle electron transport chain 1. Write the equation for cellular respiration. Under the equation, write the words for each symbol. 2. Cellular respiration has three main steps, Glycolysis, Krebs Cycle, and electron transport. Explain what goes on during these steps and how they each relate to the purpose of cellular respiration. 3. What is ATP Synthase? What does it do in cellular respiration? 4. After glycolysis, if oxygen is present, what process occurs next? If no oxygen is present, what process will occur? 5. What is fermentation? Why is it called anaerobic? 6. What is the purpose of lactic acid fermentation, in general? How does it do that? 6
7 7. What is the purpose of alcoholic fermentation, in general? How does it do that? 8. How does yeast make bread rise? 9. In the end, how many molecules of ATP are produced from all parts of cellular respiration? 10. Which organisms use photosynthesis? Which organisms use cellular respiration? 11. Compare and contrast photosynthesis and cellular respiration. Include at least 2 similarities and 3 differences. 12. Find your diagrams of photosynthesis and cellular respiration. Write a paragraph describing both cycles in detail. Chapter 10 Cell Cycle Vocab cell division mitosis cytokinesis chromatid centromere interphase cell cycle prophase centriole spindle metaphase anasphase telophase cyclin cancer 1. During most of a cell s life cycle, chromosomes exist as uncoiled. 2. Before a cell begins to divide, chromatin begins to, forming tightly packed. 3. Sister Chromatids are attached to each other by a. 4. occurs when cells stop growing because they are touching each other. 7
8 5. The is the cage-like structure that helps pull chromosomes apart during mitosis. 6. DNA is replicated during the stage of interphase. 7. During metaphase, the fibers of the spindle are anchored at the ends by the. 8. is the period of non division and growth during the cell cycle. 9. may occur as a result of a loss of control of the cell cycle. 10. What are the 3 parts of the cell cycle? What occurs during each part? 11. What is the main function of mitosis? 12. What is cytokinesis? 13. What are sister chromatids? 14. Describe the 3 parts of Interphase. 15. What is the role of the spindle during mitosis? 16. What are Cyclins and what do they do? 17. What is cancer? 18. What causes cancer? Chapter 11 Genetics Vocab genetics fertilization true-breeding trait hybrid gene alle segregation gamete probability Punnett square homozygous heterozygous phenotype genotype independent assortment 8
9 incomplete domiance codominance multiple alleles polygenetic traits homologous diploid haploid meiosis tetrad crossing-over gene map 1. For flower color, purple (P) is dominant over white (p). Cross a heterozygous purple flower with a white flower. 2. Cross a heterozygous purple flower with a heterozygous purple flower. 3. In some zebras, the allele for floppy ears (F) is dominant over the allele for rigid ears (f), and the allele for black hooves (B) is dominant over the allele for brown hooves (b). Predict the results of a cross between a parent of the genotype FfBB and a parent of the genotype ffbb. 4. Now cross two doubly heterozygous zebras (FfBb x FfBb). 5. What is a testcross? When is it used? Create an example of how it would be used. 6. List 2 differences between mitosis and meiosis. 7. How many chromosomes do human cells contain? 8. What is a zygote? 9. What does it mean if a cell is haploid? Give an example of a haploid cell. 10. What does it mean if a cell is diploid? Give an example of a diploid cell. 11. Explain crossing over. When does it occur? 9
10 12. Describe oogenesis and how it differs from spermatogenesis. Chapter 12 DNA and RNA Vocab transformation bacteriaphage nucleotide base pairing chromatin histone replication DNApolymerase gene messenger RNA ribosomal RNA transfer RNA transcription RNA polymerase promoter intron exon codon translation anticodon mutation point mutation frameshift mutation polyploidy operon operator differentiation hox gene 1. What technique did Rosalind Franklin use to get information about the structure of DNA? 2. Describe Watson and Cricks model of DNA. 3. What are the three basic parts of a nucleotide? 4. What are the two parts that make up the backbone of DNA? 5. What are Chargaff s rules with regards to base pairing? 6. Where is the DNA of eukaryotes located? 7. List the steps of replication. 10
11 8. Name and describe the functions of the three types of RNA. 9. Explain the process of going from DNA to RNA to protein. 10. What would be the complimentary strand of DNA for the following sequence? ATTCGCA 11. Complete the following sequence given the following DNA code. DNA: ATG CTC ACT TTA mrna: 12. Compare and Contrast Is it double or single stranded? What type of sugar is used? List all nitrogen bases it has. Which nitrogen base is missing? Where is it located in the cell? DNA mrna trna Chapter 13 Genetic Engineering vocab selective breeding hybridization inbreeding genetic engineering restriction enzyme gel electrophoresis recombinant DNA polymerase chain reaction (PCR) plasmid genetic marker transgenic clone 1. What is meant by selective breeding? 2. Circle the letter of each organism that has been produced by selective breeding: a. Horses b. Dogs c. Cats d. Potatoes 3. Complete the table describing the types of selective breeding: Type of Breeding Description Examples Crossing dissimilar individuals to bring together the best of both organisms The continued breeding of individuals with similar characteristics 11
12 4. True or False: Hybrids are often hardier than either of the parents. 5. True or False: To maintain the desired characteristics of a line of organisms, breeders often use hybridization. 6. What are the risks of inbreeding? 7. Circle the letter of an inheritable change in DNA: a. Variation b. Trait c. Mutation d. Genotype 8. True or False: Mutations cannot occur spontaneously. 10. Name 2 methods used by breeders to increase the rate of mutation. a. b. 11. True or False: Scientists have produced bacteria that can digest oil. 12. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about polyploidy: a.polyploid plants have many sets of chromosomes. b.polyploidy is usually fatal in animals. c.polyploidy produces new species of plants that are weaker and smaller than their diploid d.relatives. e.bananas and some citrus fruits are polyploid. 13. What is genetic engineering? 14. True or False: Making changes to the DNA code is similar to changing the code of a computer program. 15. Biologists use to cut DNA molecules at a specific sequence of nucleotides to make smaller fragments. 16. Circle the letter of the process by which DNA fragments are separated and analyzed: Gel electrophoresis b. extraction c. transformation d. restriction 17. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about gel electrophoresis: a.an electric voltage applied to the gel separates the DNA fragments. b.dna molecules are positively charged. c.gel electrophoresis is used to compare the genomes of different organisms. d.gel electrophoresis can be used to locate and identify one particular gene in an individual s genome. 18. True or False: The pattern of colored band on a gel tells the exact sequence of bases in DNA. 19. Enzymes that splice DNA together can also be used to join DNA sequences to natural DNA sequences. 20. How is recombinant DNA produced? 21. What is polymerase chain reaction (PCR)? 12
13 22. What occurs during transformation? 23. True or False: Griffith s extract of heat-killed bacteria contained DNA fragments. 24. Give 2 reasons why a plasmid is useful for DNA transfer. 25. Describe what occurs in a successful transformation of cells. 26. True or False: The DNA molecules used for transformation of animal cells do not require marker genes. 27. True or False: Gene replacement has made it possible to identify the specific functions of genes in many organisms. 28. What is a transgenic organism? 29. Describe how to make a transgenic organism. 30. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about transgenic microorganisms: a.transgenic bacteria will never produce useful substances for health and industry. b.transgenic bacteria produce human proteins cheaply and in great abundance. c.people with insulin-dependent diabetes are now treated with pure human insulin. d.in the future, transgenic organisms may produce the raw materials for plastics. 31. List 4 ways in which transgenic animals have been used. 32. Many transgenic plants contain genes that produce a natural, so the crops do not have to be sprayed with pesticides. 33. What is a clone? 34. True or False: All cloned animals are also transgenic. 13
2. Give 7 common features of all life List and give characteristics & examples of the 3 Domains & 7 Kingdoms:
 BIOLOGY 101/B EXAM REVIEW SHEETS STUDY GUIDE UNIT ONE 1. List the levels of organization in the study of biology: 2. Give 7 common features of all life 1. 5. 2. 6. 3. 7. 4. 3. List and give characteristics
BIOLOGY 101/B EXAM REVIEW SHEETS STUDY GUIDE UNIT ONE 1. List the levels of organization in the study of biology: 2. Give 7 common features of all life 1. 5. 2. 6. 3. 7. 4. 3. List and give characteristics
Cells and Energy. e. Aerobic. a. Photosynthesis c. Thylakoids
 Name: Date: Period: BIO FIRST SEMESTER STUDY GUIDE & 1 st Semester Final Exam Study Packet All the information below can be found in your notes or textbook. Remember this is only a guide. There may be
Name: Date: Period: BIO FIRST SEMESTER STUDY GUIDE & 1 st Semester Final Exam Study Packet All the information below can be found in your notes or textbook. Remember this is only a guide. There may be
amino acid nucleic acid nucleotide DNA/RNA enzymes lock and key model catalyst carbohydrate monosaccharide glucose
 Unit 1: Biomolecules I. Terms You Should Know lipid fatty acid & glycerol monomer biomolecule protein amino acid nucleic acid nucleotide DNA/RNA enzymes lock and key model catalyst carbohydrate monosaccharide
Unit 1: Biomolecules I. Terms You Should Know lipid fatty acid & glycerol monomer biomolecule protein amino acid nucleic acid nucleotide DNA/RNA enzymes lock and key model catalyst carbohydrate monosaccharide
GENERAL BIOLOGY I / REVIEW QUESTIONS
 GENERAL BIOLOGY I / REVIEW QUESTIONS NOTE: This set of questions is just to help you concentrate on important topics you should know by the end of this course. This in NO WAY means that the final exam
GENERAL BIOLOGY I / REVIEW QUESTIONS NOTE: This set of questions is just to help you concentrate on important topics you should know by the end of this course. This in NO WAY means that the final exam
General Biology 115, Summer 2014 Exam II: Form B June 23, Name Student Number
 General Biology 115, Summer 2014 Exam II: Form B June 23, 2014 Name Student Number For questions 1 2, use the following information. A particular plasmid (pbr322) has two unique gene sequences that confer
General Biology 115, Summer 2014 Exam II: Form B June 23, 2014 Name Student Number For questions 1 2, use the following information. A particular plasmid (pbr322) has two unique gene sequences that confer
General Biology 115, Summer 2014 Exam II: Form A June 23, Name Student Number
 General Biology 115, Summer 2014 Exam II: Form A June 23, 2014 Name Student Number 1. Of the following, which best describes how the free energy generated during the reactions of Photosystem I is utilized?
General Biology 115, Summer 2014 Exam II: Form A June 23, 2014 Name Student Number 1. Of the following, which best describes how the free energy generated during the reactions of Photosystem I is utilized?
Biology Spring Final Study Guide
 Biology Spring Final Study Guide The final will cover all information since the beginning of the school year, but the emphasis will be second semester (approx 20% 1 st semester, 80% 2 nd semester information,
Biology Spring Final Study Guide The final will cover all information since the beginning of the school year, but the emphasis will be second semester (approx 20% 1 st semester, 80% 2 nd semester information,
Biology Semester Exam Study Guide--January 2016
 Objective Response Reflection 3 = I totally know this! :) 2 = I remember this somewhat 1 = I don't remember this at all Explain the difference between independent and dependent variables. Explain what
Objective Response Reflection 3 = I totally know this! :) 2 = I remember this somewhat 1 = I don't remember this at all Explain the difference between independent and dependent variables. Explain what
Advanced Placement Biology Semester 1 Exam Review Name Date Per
 Advanced Placement Biology Semester 1 Exam Review Name Date Per Unit 1: Biochemistry What are the unique properties of water? What are monomers and polymer, and how are they formed? What are the types
Advanced Placement Biology Semester 1 Exam Review Name Date Per Unit 1: Biochemistry What are the unique properties of water? What are monomers and polymer, and how are they formed? What are the types
IB BIOLOGY SUMMER ASSIGNMENT 1 st Year
 IB BIOLOGY SUMMER ASSIGNMENT 1 st Year This summer, we have to immediately start becoming familiar with each of the subjects in this upcoming year. Year 1 so that we will remember them for next year s
IB BIOLOGY SUMMER ASSIGNMENT 1 st Year This summer, we have to immediately start becoming familiar with each of the subjects in this upcoming year. Year 1 so that we will remember them for next year s
6. What is the base units units of the metric system? meters (length), liters (volume), grams (mass), Kelvin/Celsius (temperature)
 THE BASICS 1. List the steps of the scientific method. 1) Identify the problem/make an observation 2) Form hypothesis 3) Create an experiment to test hypothesis 4) Gather results 5)Form conclusions 6)
THE BASICS 1. List the steps of the scientific method. 1) Identify the problem/make an observation 2) Form hypothesis 3) Create an experiment to test hypothesis 4) Gather results 5)Form conclusions 6)
Name Date REVIEW FOR FINAL EXAM
 Name Date REVIEW FOR FINAL EXAM 1. List the appropriate steps in planning/carrying out an experiment on the effect of heat on the function of a certain enzyme: Observe, define problem, form question, research
Name Date REVIEW FOR FINAL EXAM 1. List the appropriate steps in planning/carrying out an experiment on the effect of heat on the function of a certain enzyme: Observe, define problem, form question, research
Reinforcement. Cells and Life CHAPTER 1 LESSON 1
 Reinforcement Cells and Life LESSON 1 Directions: In numbers 1 through 4 below, a code letter has been substituted for each letter of the alphabet. To find out what the sentence says, use the following
Reinforcement Cells and Life LESSON 1 Directions: In numbers 1 through 4 below, a code letter has been substituted for each letter of the alphabet. To find out what the sentence says, use the following
2018 Midterm Exam Review KEY
 Name: 2018 Midterm Exam Review KEY 1. The Himalayan rabbit s habitat has cold, snowy winters and mild summers. The body is typically covered in white fur except for the nose, feet, tail and ears, which
Name: 2018 Midterm Exam Review KEY 1. The Himalayan rabbit s habitat has cold, snowy winters and mild summers. The body is typically covered in white fur except for the nose, feet, tail and ears, which
th is is re vi sio n. com
 Section (a) Cells and organelles th is is re vi sio n. com 1. Make a diagram to show the structure of a liver cell as seen using an electron microscope. On your diagram, label the following: nucleus nuclear
Section (a) Cells and organelles th is is re vi sio n. com 1. Make a diagram to show the structure of a liver cell as seen using an electron microscope. On your diagram, label the following: nucleus nuclear
Fundamentals of Genetics. 4. Name the 7 characteristics, giving both dominant and recessive forms of the pea plants, in Mendel s experiments.
 Fundamentals of Genetics 1. What scientist is responsible for our study of heredity? 2. Define heredity. 3. What plant did Mendel use for his hereditary experiments? 4. Name the 7 characteristics, giving
Fundamentals of Genetics 1. What scientist is responsible for our study of heredity? 2. Define heredity. 3. What plant did Mendel use for his hereditary experiments? 4. Name the 7 characteristics, giving
Review Quizzes Chapters 11-16
 Review Quizzes Chapters 11-16 1. In pea plants, the allele for smooth seeds (S) is dominant over the allele for wrinkled seeds (s). In an experiment, when two hybrids are crossed, what percent of the offspring
Review Quizzes Chapters 11-16 1. In pea plants, the allele for smooth seeds (S) is dominant over the allele for wrinkled seeds (s). In an experiment, when two hybrids are crossed, what percent of the offspring
DNA and DNA Replication
 Name Period PreAP Biology QCA 2 Review Your EOS exam is approximately 70 MC questions. This review, coupled with your QCA 1 review you received in October should lead you back through the important concepts
Name Period PreAP Biology QCA 2 Review Your EOS exam is approximately 70 MC questions. This review, coupled with your QCA 1 review you received in October should lead you back through the important concepts
Keystone Biology Remediation B2: Genetics
 Keystone Biology Remediation B2: Genetics Assessment Anchors: to describe and/or predict observed patterns of inheritance (i.e. dominant, recessive, codominance, incomplete dominance, sex-linked, polygenic,
Keystone Biology Remediation B2: Genetics Assessment Anchors: to describe and/or predict observed patterns of inheritance (i.e. dominant, recessive, codominance, incomplete dominance, sex-linked, polygenic,
3-Carbon. Okazaki fragments
 DNA Replication DNA strands separate and the nucleotides in the cells come in and join the nitrogenous bases Enzyme Helicase unzips the DNA ready for replication Enzyme Primase adds an RNA Primer which
DNA Replication DNA strands separate and the nucleotides in the cells come in and join the nitrogenous bases Enzyme Helicase unzips the DNA ready for replication Enzyme Primase adds an RNA Primer which
REVIEW SHEET: Units 9 & 10 Cell Cycle, DNA, & Gene Expression
 REVIEW SHEET: Units 9 & 10 Cell Cycle, DNA, & Gene Expression HONORS BIOLOGY Textbook Reading: Cell Cycle (Ch. 10.1 and 10.2), DNA (Ch. 12), and Gene Expression (Ch. 13) Handouts:! Online Tutorial: Cell
REVIEW SHEET: Units 9 & 10 Cell Cycle, DNA, & Gene Expression HONORS BIOLOGY Textbook Reading: Cell Cycle (Ch. 10.1 and 10.2), DNA (Ch. 12), and Gene Expression (Ch. 13) Handouts:! Online Tutorial: Cell
DESIGNER GENES SAMPLE TOURNAMENT
 DESIGNER GENES SAMPLE TOURNAMENT PART ONE- GENETICS PROBLEMS In dogs, the inheritance of hair color involves a gene (B) for black hair and a gene (b) for brown hair. A dominant (C) is also involved. It
DESIGNER GENES SAMPLE TOURNAMENT PART ONE- GENETICS PROBLEMS In dogs, the inheritance of hair color involves a gene (B) for black hair and a gene (b) for brown hair. A dominant (C) is also involved. It
Polymers. DNA is a polymer of nucleotides. What polymers (macromolecules) have we met so far? Proteins are polymers of amino acids
 Subatomic particles (parts of an atom) 1. Protons (+) 2. Neutrons 3. Electrons (-) H-H -Smallest unit of an element. -Parts are held together via electrostatic forces BIO101: a roadmap to the course Atoms
Subatomic particles (parts of an atom) 1. Protons (+) 2. Neutrons 3. Electrons (-) H-H -Smallest unit of an element. -Parts are held together via electrostatic forces BIO101: a roadmap to the course Atoms
DNA/RNA STUDY GUIDE. Match the following scientists with their accomplishments in discovering DNA using the statement in the box below.
 Name: Period: Date: DNA/RNA STUDY GUIDE Part A: DNA History Match the following scientists with their accomplishments in discovering DNA using the statement in the box below. Used a technique called x-ray
Name: Period: Date: DNA/RNA STUDY GUIDE Part A: DNA History Match the following scientists with their accomplishments in discovering DNA using the statement in the box below. Used a technique called x-ray
Read each question, and write your answer in the space provided. 2. How did Mendel s scientific work differ from the work of T. A. Knight?
 Name Date Class CHAPTER 8 DIRECTED READING Mendel and Heredity Section 8-1: The Origins of Genetics Mendel and Others Studied Garden-Pea Traits 1. What did T. A. Knight discover? 2. How did Mendel s scientific
Name Date Class CHAPTER 8 DIRECTED READING Mendel and Heredity Section 8-1: The Origins of Genetics Mendel and Others Studied Garden-Pea Traits 1. What did T. A. Knight discover? 2. How did Mendel s scientific
STUDY GUIDE for BIOL 110
 STUDY GUIDE for BIOL 110 1. CHEMISTRY a. Structure of the Atom i) Subatomic Particles: protons, electrons, neutrons (1) Charges (2) Mass ii) Atomic Number and Atomic Mass (1) Determine number of subatomic
STUDY GUIDE for BIOL 110 1. CHEMISTRY a. Structure of the Atom i) Subatomic Particles: protons, electrons, neutrons (1) Charges (2) Mass ii) Atomic Number and Atomic Mass (1) Determine number of subatomic
Human Anatomy & Physiology I Dr. Sullivan Unit IV Cellular Function Chapter 4, Chapter 27 (meiosis only)
 Human Anatomy & Physiology I Dr. Sullivan Unit IV Cellular Function Chapter 4, Chapter 27 (meiosis only) I. Protein Synthesis: creation of new proteins a. Much of the cellular machinery is devoted to synthesizing
Human Anatomy & Physiology I Dr. Sullivan Unit IV Cellular Function Chapter 4, Chapter 27 (meiosis only) I. Protein Synthesis: creation of new proteins a. Much of the cellular machinery is devoted to synthesizing
Curriculum Correlation
 Curriculum Correlation A: Scientific Investigation Skills and Career Exploration A1. SCIENTIFIC INVESTIGATION SKILLS SECTIONS A1. demonstrate scientific investigation skills in the four areas of skills
Curriculum Correlation A: Scientific Investigation Skills and Career Exploration A1. SCIENTIFIC INVESTIGATION SKILLS SECTIONS A1. demonstrate scientific investigation skills in the four areas of skills
DNA and GENETICS UNIT NOTES
 DNA and GENETICS UNIT NOTES NAME: DO NOT LOSE! DNA DNA - Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid Shape is called double helix DNA has the information for our cells to make proteins. DNA through transcription makes mrna
DNA and GENETICS UNIT NOTES NAME: DO NOT LOSE! DNA DNA - Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid Shape is called double helix DNA has the information for our cells to make proteins. DNA through transcription makes mrna
Chapter 9 WHAT IS DNA?
 Notes DNA Chapter 9 WHAT IS DNA? DNA= Deoxyribonucleic Acid DNA s job is to hold the entire genetic code for the organism. Human, tree, bacteria, mushroom, paramecium, etc! ALL HAVE DNA! DNA is held on
Notes DNA Chapter 9 WHAT IS DNA? DNA= Deoxyribonucleic Acid DNA s job is to hold the entire genetic code for the organism. Human, tree, bacteria, mushroom, paramecium, etc! ALL HAVE DNA! DNA is held on
Bio Study Guide. What is the structure of a DNA. A nitrogen base (ATCG/AUCG) connected to a sugar and a phosphate. nucleotide?
 What are nucleic acids? The largest organic molecules. Master organisms, they are in control of cell functions. They are found in all living organisms, and they are two types of them- DNA and RNA. They
What are nucleic acids? The largest organic molecules. Master organisms, they are in control of cell functions. They are found in all living organisms, and they are two types of them- DNA and RNA. They
Vocab Word 1: Interphase
 Vocab Word 1: Interphase Interphase is the phase of the cell cycle in which a typical cell spends most of its life. During this phase, the cell copies its DNA in preparation for mitosis. Interphase is
Vocab Word 1: Interphase Interphase is the phase of the cell cycle in which a typical cell spends most of its life. During this phase, the cell copies its DNA in preparation for mitosis. Interphase is
These molecules make up the ladder of the DNA Bound by weak hydrogen bonds. 4 Different Types (2 specific matches) look at the
 B.A.T. Review DNA & Cell Cycle Test is 11/3/16 NAME: PERIOD DNA STRUCTURE VOCABULARY Mitosis Chromosomes Interphase G1,S,G2,M Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase Cytokinesis Cleavage Furrow Spindle Fibers
B.A.T. Review DNA & Cell Cycle Test is 11/3/16 NAME: PERIOD DNA STRUCTURE VOCABULARY Mitosis Chromosomes Interphase G1,S,G2,M Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase Cytokinesis Cleavage Furrow Spindle Fibers
Bio 101 Sample questions: Chapter 10
 Bio 101 Sample questions: Chapter 10 1. Which of the following is NOT needed for DNA replication? A. nucleotides B. ribosomes C. Enzymes (like polymerases) D. DNA E. all of the above are needed 2 The information
Bio 101 Sample questions: Chapter 10 1. Which of the following is NOT needed for DNA replication? A. nucleotides B. ribosomes C. Enzymes (like polymerases) D. DNA E. all of the above are needed 2 The information
DNA DNA Profiling 18. Discuss the stages involved in DNA profiling 19. Define the process of DNA profiling 20. Give two uses of DNA profiling
 Name: 2.5 Genetics Objectives At the end of this sub section students should be able to: 2.5.1 Heredity and Variation 1. Discuss the diversity of organisms 2. Define the term species 3. Distinguish between
Name: 2.5 Genetics Objectives At the end of this sub section students should be able to: 2.5.1 Heredity and Variation 1. Discuss the diversity of organisms 2. Define the term species 3. Distinguish between
14. What is phenotype? The physical characteristic that an organism has due to genes. Ex. Red flower 15. Understand the different blood types.
 Midterm Exam Review 1. How many chromosomes are in a normal human karyotype? 46 2. How would Down s syndrome be detected on a karyotype? Extra chromosome (trisomy) #21 3. Know how to read the genetic code
Midterm Exam Review 1. How many chromosomes are in a normal human karyotype? 46 2. How would Down s syndrome be detected on a karyotype? Extra chromosome (trisomy) #21 3. Know how to read the genetic code
Griffith and Transformation (pages ) 1. What hypothesis did Griffith form from the results of his experiments?
 Section 12 1 DNA (pages 287 294) This section tells about the experiments that helped scientists discover the relationship between genes and DNA. It also describes the chemical structure of the DNA molecule.
Section 12 1 DNA (pages 287 294) This section tells about the experiments that helped scientists discover the relationship between genes and DNA. It also describes the chemical structure of the DNA molecule.
This is DUE: Tuesday, March 1, 2011 Come prepared to share your findings with your group.
 Biology 160 NAME: Reading Guide 12: Population Dynamics, Humans, Part II This is DUE: Tuesday, March 1, 2011 Come prepared to share your findings with your group. *As before, please turn in only the Critical
Biology 160 NAME: Reading Guide 12: Population Dynamics, Humans, Part II This is DUE: Tuesday, March 1, 2011 Come prepared to share your findings with your group. *As before, please turn in only the Critical
Chapter 2. An Introduction to Genes and Genomes
 PowerPoint Lectures for Introduction to Biotechnology, Second Edition William J.Thieman and Michael A.Palladino Chapter 2 An Introduction to Genes and Genomes Lectures by Lara Dowland Chapter Contents
PowerPoint Lectures for Introduction to Biotechnology, Second Edition William J.Thieman and Michael A.Palladino Chapter 2 An Introduction to Genes and Genomes Lectures by Lara Dowland Chapter Contents
DNA STRUCTURE. Nucleotides: Nitrogenous Bases (Carry the Genetic Code) Expectation Sheet: DNA & Cell Cycle. I can statements: Basic Information:
 Expectation Sheet: DNA & Cell Cycle NAME: Test is 11/8/17 I can statements: I can discuss how DNA is found in all organisms and that the structure is common to all living things. I can diagram and label
Expectation Sheet: DNA & Cell Cycle NAME: Test is 11/8/17 I can statements: I can discuss how DNA is found in all organisms and that the structure is common to all living things. I can diagram and label
Cells and Tissues. Overview CELLS
 Cells and Tissues WIll The basic unit of structure and function in the human body is the cell. Each of a cell's parts, or organelles, as well as the entire cell, is organized to perform a specific function.
Cells and Tissues WIll The basic unit of structure and function in the human body is the cell. Each of a cell's parts, or organelles, as well as the entire cell, is organized to perform a specific function.
GENETICS: BIOLOGY HSA REVIEW
 GENETICS: BIOLOGY HSA REVIEW HSA Review A. Matching: On the lines provided, write the letter of the definition of each term. a. genetics f. gamete b. trait g. probability c. hybrid h. Punnett square d.
GENETICS: BIOLOGY HSA REVIEW HSA Review A. Matching: On the lines provided, write the letter of the definition of each term. a. genetics f. gamete b. trait g. probability c. hybrid h. Punnett square d.
DNA/RNA STUDY GUIDE. Match the following scientists with their accomplishments in discovering DNA using the statement in the box below.
 Name: Period: Date: DNA/RNA STUDY GUIDE Part A: DNA History Match the following scientists with their accomplishments in discovering DNA using the statement in the box below. Used a technique called x-ray
Name: Period: Date: DNA/RNA STUDY GUIDE Part A: DNA History Match the following scientists with their accomplishments in discovering DNA using the statement in the box below. Used a technique called x-ray
Ch 12.DNA and RNA.Biology.Landis
 Identity Section 12 1 DNA (pages 287 294) This section tells about the experiments that helped scientists discover the relationship between genes and DNA. It also describes the chemical structure of the
Identity Section 12 1 DNA (pages 287 294) This section tells about the experiments that helped scientists discover the relationship between genes and DNA. It also describes the chemical structure of the
Constants Variables Qualitative data Quantitative data Control Experiment Dependent Variable Independent variable Hypothesis Mean
 Biology Study Guide Name Block I. Scientific Investigation 1 A. Parts of Experimental Design: Match the key words to the correct descriptions Constants Variables Qualitative data Quantitative data Control
Biology Study Guide Name Block I. Scientific Investigation 1 A. Parts of Experimental Design: Match the key words to the correct descriptions Constants Variables Qualitative data Quantitative data Control
2. Know the parts of a light microscope and general rules for using and focusing a microscope, such as:
 SNC 2DI Exam Review: Biology Unit 1. Understand the meaning of the following terms. Be able to recognize their definitions: Biology Mounting medium Telophase Organelle Cell Theory Cell cycle Cytokinesis
SNC 2DI Exam Review: Biology Unit 1. Understand the meaning of the following terms. Be able to recognize their definitions: Biology Mounting medium Telophase Organelle Cell Theory Cell cycle Cytokinesis
Biology 105 Syllabus Life Sciences
 B R O O K D A L E C O M M U N I T Y C O L L E G E Biology 105 Syllabus Life Sciences Biology Program Science & Health Science Division 1 CODE: BIOL 105 TITLE: Life Sciences DIVISION: Science & Health Science
B R O O K D A L E C O M M U N I T Y C O L L E G E Biology 105 Syllabus Life Sciences Biology Program Science & Health Science Division 1 CODE: BIOL 105 TITLE: Life Sciences DIVISION: Science & Health Science
2. Know the parts of a light microscope and general rules for using and focusing a microscope, such as:
 SNC 2DI Exam Review: Biology Unit 1. Understand the meaning of the following terms. Be able to recognize their definitions: Biology Mounting medium Telophase Organelle Cell Theory Cell cycle Cytokinesis
SNC 2DI Exam Review: Biology Unit 1. Understand the meaning of the following terms. Be able to recognize their definitions: Biology Mounting medium Telophase Organelle Cell Theory Cell cycle Cytokinesis
7. All living things are made of and come from cells. 8. A cell membrane is made of,, and.
 Name EOC Biology Review Period 1.List five characteristics of living organisms. 2. Some scientists say that all organisms are related to each other by common ancestor. This theory is called. 3. Many scientists
Name EOC Biology Review Period 1.List five characteristics of living organisms. 2. Some scientists say that all organisms are related to each other by common ancestor. This theory is called. 3. Many scientists
GENETICS. Chapter 1: Cell cycle. Thème 1 : La Terre dans l Univers A. Expression, stabilité et variation du patrimoine génétique.
 Introduction: GENETICS 3M = first look at genetics (study of inheritance, discovery of chromosomes, genes, dominant and recessive alleles and the DNA molecule within chromosomes) 2D = not much in fact,
Introduction: GENETICS 3M = first look at genetics (study of inheritance, discovery of chromosomes, genes, dominant and recessive alleles and the DNA molecule within chromosomes) 2D = not much in fact,
Summary 12 1 DNA RNA and Protein Synthesis Chromosomes and DNA Replication. Name Class Date
 Chapter 12 Summary DNA and RNA 12 1 DNA To understand genetics, biologists had to learn the chemical structure of the gene. Frederick Griffith first learned that some factor from dead, disease-causing
Chapter 12 Summary DNA and RNA 12 1 DNA To understand genetics, biologists had to learn the chemical structure of the gene. Frederick Griffith first learned that some factor from dead, disease-causing
EOCT Review. Class Requests by Standard
 EOCT Review Class Requests by Standard Macromolecules (SB1) Polymer Monomer Examples Function Carbohydrates Monosaccharides (simple sugars) Sugars & starches Provide rapid energy Proteins Amino acids Meats,
EOCT Review Class Requests by Standard Macromolecules (SB1) Polymer Monomer Examples Function Carbohydrates Monosaccharides (simple sugars) Sugars & starches Provide rapid energy Proteins Amino acids Meats,
Name: Class: Date: ID: A
 Class: _ Date: _ CH 12 Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. How many codons are needed to specify three amino acids? a. 6 c. 3 b. 12
Class: _ Date: _ CH 12 Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. How many codons are needed to specify three amino acids? a. 6 c. 3 b. 12
Genetics and Heredity. Mr. Gagnon
 Genetics and Heredity Mr. Gagnon Key Terms: Traits Heredity Genetics Purebred Genes Alleles Recessive Allele Dominant Allele Hybrids Key Concepts: What factors control the inheritance of traits in organisms?
Genetics and Heredity Mr. Gagnon Key Terms: Traits Heredity Genetics Purebred Genes Alleles Recessive Allele Dominant Allele Hybrids Key Concepts: What factors control the inheritance of traits in organisms?
Biology Celebration of Learning (100 points possible)
 Name Date Block Biology Celebration of Learning (100 points possible) Matching (1 point each) 1. Codon a. process of copying DNA and forming mrna 2. Genes b. section of DNA coding for a specific protein
Name Date Block Biology Celebration of Learning (100 points possible) Matching (1 point each) 1. Codon a. process of copying DNA and forming mrna 2. Genes b. section of DNA coding for a specific protein
Cell Division. Use Target Reading Skills. This section explains how cells grow and divide.
 Name Date Class Cell Processes Guided Reading and Study Cell Division This section explains how cells grow and divide. Use Target Reading Skills As you read, make a cycle diagram that shows the events
Name Date Class Cell Processes Guided Reading and Study Cell Division This section explains how cells grow and divide. Use Target Reading Skills As you read, make a cycle diagram that shows the events
REQUIRED MATERIALS: BIOLOGY; Neil A. Campbell, JB Reece, LA Urry, ML Cain, SA Wasserman, PV Minorsky, RB Jackson Eleventh Edition, 2016 Pearson.
 CODE: BIOL 101 TITLE: General Biology I Institute: STEM DEPARTMENT: Biology COURSE DESCRIPTION: This introductory level course is designed for science majors and for students in other majors that require
CODE: BIOL 101 TITLE: General Biology I Institute: STEM DEPARTMENT: Biology COURSE DESCRIPTION: This introductory level course is designed for science majors and for students in other majors that require
NON MENDELIAN GENETICS. DNA, PROTEIN SYNTHESIS, MUTATIONS DUE DECEMBER 8TH
 NON MENDELIAN GENETICS. DNA, PROTEIN SYNTHESIS, MUTATIONS DUE DECEMBER 8TH MONDAY TUESDAY WEDNESDAY THURSDAY FRIDAY 11/14 11/15 11/16 11/17 11/18 Non-Mendelian Genetics DNA Structure and Replication 11/28
NON MENDELIAN GENETICS. DNA, PROTEIN SYNTHESIS, MUTATIONS DUE DECEMBER 8TH MONDAY TUESDAY WEDNESDAY THURSDAY FRIDAY 11/14 11/15 11/16 11/17 11/18 Non-Mendelian Genetics DNA Structure and Replication 11/28
REVISION: DNA, RNA & MEIOSIS 13 MARCH 2013
 REVISION: DNA, RNA & MEIOSIS 13 MARCH 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we revise The structure and functions of DNA The structure of RNA and its role in protein synthesis The process of cell division
REVISION: DNA, RNA & MEIOSIS 13 MARCH 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we revise The structure and functions of DNA The structure of RNA and its role in protein synthesis The process of cell division
GENETICS. I. Review of DNA/RNA A. Basic Structure DNA 3 parts that make up a nucleotide chains wrap around each other to form a
 GENETICS I. Review of DNA/RNA A. Basic Structure DNA 3 parts that make up a nucleotide 1. 2. 3. chains wrap around each other to form a Chains run in opposite direction known as Type of bond between the
GENETICS I. Review of DNA/RNA A. Basic Structure DNA 3 parts that make up a nucleotide 1. 2. 3. chains wrap around each other to form a Chains run in opposite direction known as Type of bond between the
Biology Lecture 2 Genes
 Genes Definitions o Gene: DNA that codes for a single polypeptide/mrna/rrna/trna o Euchromatin: region of DNA containing genes being actively transcribed o Heterochromatin: region of DNA containing genes
Genes Definitions o Gene: DNA that codes for a single polypeptide/mrna/rrna/trna o Euchromatin: region of DNA containing genes being actively transcribed o Heterochromatin: region of DNA containing genes
UNIT 1. THE CHEMISTRY OF LIFE
 AP: END OF YEAR REVIEW UNIT 1. THE CHEMISTRY OF LIFE Section 1: Chemistry Bonds ionic covalent: polar, non-polar hydrogen Section 2: Water Properties excellent solvent high heat capacity moderating influence,
AP: END OF YEAR REVIEW UNIT 1. THE CHEMISTRY OF LIFE Section 1: Chemistry Bonds ionic covalent: polar, non-polar hydrogen Section 2: Water Properties excellent solvent high heat capacity moderating influence,
Standard B-4: The student will demonstrate an understanding of the molecular basis of heredity.
 B-4.1 Compare DNA and RNA in terms of structure, nucleotides, and base pairs. Taxonomy Level: 2.6-B Understand Conceptual Knowledge Key Concepts: Nucleic acids: deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), ribonucleic
B-4.1 Compare DNA and RNA in terms of structure, nucleotides, and base pairs. Taxonomy Level: 2.6-B Understand Conceptual Knowledge Key Concepts: Nucleic acids: deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), ribonucleic
The study of the structure, function, and interaction of cellular proteins is called. A) bioinformatics B) haplotypics C) genomics D) proteomics
 Human Biology, 12e (Mader / Windelspecht) Chapter 21 DNA Which of the following is not a component of a DNA molecule? A) a nitrogen-containing base B) deoxyribose sugar C) phosphate D) phospholipid Messenger
Human Biology, 12e (Mader / Windelspecht) Chapter 21 DNA Which of the following is not a component of a DNA molecule? A) a nitrogen-containing base B) deoxyribose sugar C) phosphate D) phospholipid Messenger
Unit 6 Molecular Genetics
 Unit 6 Molecular Genetics I. DNA and RNA structure pages 2-6 II. DNA replication pages 6-7 III. Protein Synthesis pages 7-10 South Dakota State Standard 9-12.L.1.1 Students are able to relate cellular
Unit 6 Molecular Genetics I. DNA and RNA structure pages 2-6 II. DNA replication pages 6-7 III. Protein Synthesis pages 7-10 South Dakota State Standard 9-12.L.1.1 Students are able to relate cellular
COMPETITOR NAMES: TEAM NAME: TEAM NUMBER:
 COMPETITOR NAMES: TEAM NAME: TEAM NUMBER: Section 1:Crosses In a fictional species of mice, with species name Mus SciOlyian, fur color is controlled by a single autosomal gene. The allele for brown fur
COMPETITOR NAMES: TEAM NAME: TEAM NUMBER: Section 1:Crosses In a fictional species of mice, with species name Mus SciOlyian, fur color is controlled by a single autosomal gene. The allele for brown fur
Unit 5 - Genetics. Page 1
 Living Environment Practice Exam- Parts A and B-1 1. Many years ago, a scientist grew pea plants that produced wrinkled peas. The peas from these plants produced new plants that also produced wrinkled
Living Environment Practice Exam- Parts A and B-1 1. Many years ago, a scientist grew pea plants that produced wrinkled peas. The peas from these plants produced new plants that also produced wrinkled
NAS 2 - CHAPTER 3 STUDY GUIDE
 NAS 2 - CHAPTER 3 STUDY GUIDE You are responsible for the following textbook figures/tables: Figure 3.2 Figure 3.32 Figure 3.36 Figure 3.9 Figure 3.34 Figure 24.5 Figure 3.31 1. The is the basic unit of
NAS 2 - CHAPTER 3 STUDY GUIDE You are responsible for the following textbook figures/tables: Figure 3.2 Figure 3.32 Figure 3.36 Figure 3.9 Figure 3.34 Figure 24.5 Figure 3.31 1. The is the basic unit of
A. I think it is DNA or RNA (circle your answer) because: B. I think it is DNA or RNA (circle your answer) because:
 Name: Test Date: Block: Biology I: Unit 7 Molecular Genetics and Biotechnology Review for Unit Test Directions: You should use this as a guide to help you study for your test. You should also read through
Name: Test Date: Block: Biology I: Unit 7 Molecular Genetics and Biotechnology Review for Unit Test Directions: You should use this as a guide to help you study for your test. You should also read through
Page Monday December 19, 2016
 replication and Page 5-55 Monday December 9, 06 Notebook check 0: exam review notebook pages 5-55 Proteins Enzymes Activation energy Photo Cellular respiration, replication and Learning goal: Describe
replication and Page 5-55 Monday December 9, 06 Notebook check 0: exam review notebook pages 5-55 Proteins Enzymes Activation energy Photo Cellular respiration, replication and Learning goal: Describe
Atomic number (number of protons) Element symbol. Ne Na. Kr Sr. Tm Yb Lu Th. Np Pu
 1 Figure 2.1a H Atomic number (number of protons) Element symbol Mass number (number of protons plus neutrons) 6 C 12 He 2 Li Be B C N O F Ne Na Mg Al Si P S Cl Ar K Ca Sc Ti V Cr Mn Fe Co Ni Cu Zn Ga
1 Figure 2.1a H Atomic number (number of protons) Element symbol Mass number (number of protons plus neutrons) 6 C 12 He 2 Li Be B C N O F Ne Na Mg Al Si P S Cl Ar K Ca Sc Ti V Cr Mn Fe Co Ni Cu Zn Ga
The process of new DNA to another organism. The goal is to add one or more that are not already found in that organism.
 Genetic Engineering Notes The process of new DNA to another organism. The goal is to add one or more that are not already found in that organism. Selective Breeding Carefully choosing which plants and
Genetic Engineering Notes The process of new DNA to another organism. The goal is to add one or more that are not already found in that organism. Selective Breeding Carefully choosing which plants and
Chapter 1 -- Life. Chapter 2 -- Atoms, Molecules and Bonds. Chapter 3 -- Water
 Chapter 1 -- Life In the beginning... Molecular evolution Heirarchy and organization levels of organization Form follows function Language in science Cell and Molecular Biology -- Biology 20A Chapter Outlines
Chapter 1 -- Life In the beginning... Molecular evolution Heirarchy and organization levels of organization Form follows function Language in science Cell and Molecular Biology -- Biology 20A Chapter Outlines
Sta>on 1: Enzymes and Chemical Reac>ons (Standard 2.8)
 Day 2: EOC Review Biochemistry and Protein Synthesis Study Guide Ques>ons: Standard 2 37-40 (Page 1 Back) Standard 3 18-25 (Page 2 Front) Standard 4 1-20,46-53 (Page 2 Back and 3) Sta>on 1: Enzymes and
Day 2: EOC Review Biochemistry and Protein Synthesis Study Guide Ques>ons: Standard 2 37-40 (Page 1 Back) Standard 3 18-25 (Page 2 Front) Standard 4 1-20,46-53 (Page 2 Back and 3) Sta>on 1: Enzymes and
Unit 5 Part B: Day 1 Cell Growth, Division & Reproduction
 Name Test Date Period Unit 5 Part B: Day 1 Cell Growth, Division & Reproduction CELL SIZE LIMITATIONS Cells that are will have diffusing materials through the cell. -,, and must enter cell at an efficient
Name Test Date Period Unit 5 Part B: Day 1 Cell Growth, Division & Reproduction CELL SIZE LIMITATIONS Cells that are will have diffusing materials through the cell. -,, and must enter cell at an efficient
Videos. Lesson Overview. Fermentation
 Lesson Overview Fermentation Videos Bozeman Transcription and Translation: https://youtu.be/h3b9arupxzg Drawing transcription and translation: https://youtu.be/6yqplgnjr4q Objectives 29a) I can contrast
Lesson Overview Fermentation Videos Bozeman Transcription and Translation: https://youtu.be/h3b9arupxzg Drawing transcription and translation: https://youtu.be/6yqplgnjr4q Objectives 29a) I can contrast
objective To Study basics of DNA Structure Properties Replication Transcription Translation
 Basics of DNA Dr. Amol Kharat objective To Study basics of DNA Structure Properties Replication Transcription Translation Cellular composition DNA is contained in nucleus of cell Phospho-lipids and proteins
Basics of DNA Dr. Amol Kharat objective To Study basics of DNA Structure Properties Replication Transcription Translation Cellular composition DNA is contained in nucleus of cell Phospho-lipids and proteins
1. Carry the microscope in an upright position with both hands and place the base of the microscope 5cm from the edge of the bench
 The Microscope Operating the compound light microscope 1. Carry the microscope in an upright position with both hands and place the base of the microscope 5cm from the edge of the bench 2. Check that lenses
The Microscope Operating the compound light microscope 1. Carry the microscope in an upright position with both hands and place the base of the microscope 5cm from the edge of the bench 2. Check that lenses
Chapter 12 Molecular Genetics
 Section 1: DNA: The Genetic Material Section 2: Replication of DNA Section 3: DNA, RNA, and Protein Section 4: Gene Regulation and Mutation 12.1 DNA: The Genetic Material Objectives: 1. Summarize the experiments
Section 1: DNA: The Genetic Material Section 2: Replication of DNA Section 3: DNA, RNA, and Protein Section 4: Gene Regulation and Mutation 12.1 DNA: The Genetic Material Objectives: 1. Summarize the experiments
Section DNA: The Molecule of Heredity
 Ch 11: DNA and Genes - DNA: The Molecule of Heredity Inside This Section... What is DNA? The Structure of DNA DNA Replication What is DNA? Acid DNA is the blueprint of all living organisms. It controls
Ch 11: DNA and Genes - DNA: The Molecule of Heredity Inside This Section... What is DNA? The Structure of DNA DNA Replication What is DNA? Acid DNA is the blueprint of all living organisms. It controls
Elective Type: Credit Hours: 4 Corequisites: Developmental: (yes/no) Lecture: 3 Clinical: 0 Lab: 3 Studio 0 Other: 0. TOTAL: 6 Other Requirements:
 COURSE SYLLABUS Course Title: General Biology I (lecture/lab) Department: Mathematics and Science Curriculum: Biology Date submitted: April 2016 (AAC: 16-20) Course Descriptors: Make certain that the course
COURSE SYLLABUS Course Title: General Biology I (lecture/lab) Department: Mathematics and Science Curriculum: Biology Date submitted: April 2016 (AAC: 16-20) Course Descriptors: Make certain that the course
CELLULAR PROCESSES; REPRODUCTION. Unit 5
 CELLULAR PROCESSES; REPRODUCTION Unit 5 Cell Cycle Chromosomes and their make up Crossover Cytokines Diploid (haploid diploid and karyotypes) Mitosis Meiosis What is Cancer? Somatic Cells THE CELL CYCLE
CELLULAR PROCESSES; REPRODUCTION Unit 5 Cell Cycle Chromosomes and their make up Crossover Cytokines Diploid (haploid diploid and karyotypes) Mitosis Meiosis What is Cancer? Somatic Cells THE CELL CYCLE
CHAPTER 5 Principle of Genetics Review
 CHAPTER 5 Principle of Genetics Review I. Mendel s Investigations Gregor Johann Mendel Hybridized peas 1856-1864 Formulated Principles of Heredity published in 1866 II. Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance
CHAPTER 5 Principle of Genetics Review I. Mendel s Investigations Gregor Johann Mendel Hybridized peas 1856-1864 Formulated Principles of Heredity published in 1866 II. Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance
Chapter 8 DNA STRUCTURE AND CHROMOSOMAL ORGANIZATION
 Chapter 8 DNA STRUCTURE AND CHROMOSOMAL ORGANIZATION Chapter Summary Even though DNA has been known as a biochemical compound for over 100 years, it was not implicated as the carrier of hereditary information
Chapter 8 DNA STRUCTURE AND CHROMOSOMAL ORGANIZATION Chapter Summary Even though DNA has been known as a biochemical compound for over 100 years, it was not implicated as the carrier of hereditary information
Unit 1: DNA and the Genome. Sub-Topic (1.3) Gene Expression
 Unit 1: DNA and the Genome Sub-Topic (1.3) Gene Expression Unit 1: DNA and the Genome Sub-Topic (1.3) Gene Expression On completion of this subtopic I will be able to State the meanings of the terms genotype,
Unit 1: DNA and the Genome Sub-Topic (1.3) Gene Expression Unit 1: DNA and the Genome Sub-Topic (1.3) Gene Expression On completion of this subtopic I will be able to State the meanings of the terms genotype,
DNA Structure and Analysis. Chapter 4: Background
 DNA Structure and Analysis Chapter 4: Background Molecular Biology Three main disciplines of biotechnology Biochemistry Genetics Molecular Biology # Biotechnology: A Laboratory Skills Course explorer.bio-rad.com
DNA Structure and Analysis Chapter 4: Background Molecular Biology Three main disciplines of biotechnology Biochemistry Genetics Molecular Biology # Biotechnology: A Laboratory Skills Course explorer.bio-rad.com
Unit 2: The Structure and function of Organisms. Section 4: DNA and Cell Cycle
 Unit 2: The Structure and function of Organisms Section 4: Cell Cycle Essential Question: Questions: - Vocabulary 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. DNA RNA Mitosis Meiosis Homozygous Heterozygous Gene Chromosome
Unit 2: The Structure and function of Organisms Section 4: Cell Cycle Essential Question: Questions: - Vocabulary 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. DNA RNA Mitosis Meiosis Homozygous Heterozygous Gene Chromosome
1. An alteration of genetic information is shown below. 5. Part of a molecule found in cells is represented below.
 1. An alteration of genetic information is shown below. 5. Part of a molecule found in cells is represented below. A-G-T-A-C-C-G-A-T A-G-T-G-A-T This type of alteration of the genetic information is an
1. An alteration of genetic information is shown below. 5. Part of a molecule found in cells is represented below. A-G-T-A-C-C-G-A-T A-G-T-G-A-T This type of alteration of the genetic information is an
Gregor Mendel. Austrian Monk Worked with pea plants
 Gregor Mendel Austrian Monk Worked with pea plants A. True Breeding Pea Plants Self pollinate and produce new plants genetically identical to themselves Mendel decides to cross pollinate the plants Offspring
Gregor Mendel Austrian Monk Worked with pea plants A. True Breeding Pea Plants Self pollinate and produce new plants genetically identical to themselves Mendel decides to cross pollinate the plants Offspring
Honors Biology Semester 2 Final Exam Review Guide
 Honors Biology Semester 2 Final Exam Review Guide As the final exam approaches, so should your preparation for the test. You should review all old exams given this semester: Cell Cycle, DNA, Genetics,
Honors Biology Semester 2 Final Exam Review Guide As the final exam approaches, so should your preparation for the test. You should review all old exams given this semester: Cell Cycle, DNA, Genetics,
plasma membrane Golgi apparatus cytoplasm lysosome endoplasmic reticulum nucleus nucleolus ribosome mitochondrion
 Demonstrate understanding of life processes at the cellular level 1 Achievement Standard 91156 Demonstrate understanding of life processes at the cellular level BIOLOGY 2.4 Externally assessed 4 credits
Demonstrate understanding of life processes at the cellular level 1 Achievement Standard 91156 Demonstrate understanding of life processes at the cellular level BIOLOGY 2.4 Externally assessed 4 credits
3. What was Griffith trying to figure out?
 Chapter 12 DNA and RNA Name -------------------- Section 12-1: DNA pages 287-294 What are the two key concepts? 1. 2. These are important. These are the main ideas you should know by the end of the reading!
Chapter 12 DNA and RNA Name -------------------- Section 12-1: DNA pages 287-294 What are the two key concepts? 1. 2. These are important. These are the main ideas you should know by the end of the reading!
Answers to the multiple choice questions are at the bottom of the last page of this document.
 Review for Unit Test #2: Cell Parts, Functions and Protein Synthesis, Answers Answers to the multiple choice questions are at the bottom of the last page of this document. 1. Know all of the material on
Review for Unit Test #2: Cell Parts, Functions and Protein Synthesis, Answers Answers to the multiple choice questions are at the bottom of the last page of this document. 1. Know all of the material on
2 nd Term Final. Revision Sheet. Students Name: Grade: 9 A/B. Subject: Biology. Teacher Signature. Page 1 of 12
 2 nd Term Final Revision Sheet Students Name: Grade: 9 A/B Subject: Biology Teacher Signature Page 1 of 12 Nour Al Maref International School Riyadh, Saudi Arabia Biology Worksheet (2 nd Term) Chapter-7
2 nd Term Final Revision Sheet Students Name: Grade: 9 A/B Subject: Biology Teacher Signature Page 1 of 12 Nour Al Maref International School Riyadh, Saudi Arabia Biology Worksheet (2 nd Term) Chapter-7
Study Guide A. Answer Key
 From DNA to Proteins Answer Key SECTION 1. IDENTIFYING DNA AS THE GENETIC MATERIAL 1. Mice lived 2. Mice died 3. Mice lived 4. Mice died 5. S 6. bacteria 7. DNA; DNA; DNA 8. protein 9. radioactive 10.
From DNA to Proteins Answer Key SECTION 1. IDENTIFYING DNA AS THE GENETIC MATERIAL 1. Mice lived 2. Mice died 3. Mice lived 4. Mice died 5. S 6. bacteria 7. DNA; DNA; DNA 8. protein 9. radioactive 10.
Unit IV: Foundations of Genetic Engineering
 Unit IV: Foundations of Genetic Engineering Lesson 1: The Mechanics of Cells and DNA Cells are the fundamental units of life. Biotechnology research is usually done on the cellular or subcellular level.
Unit IV: Foundations of Genetic Engineering Lesson 1: The Mechanics of Cells and DNA Cells are the fundamental units of life. Biotechnology research is usually done on the cellular or subcellular level.
KEY CONCEPT DNA was identified as the genetic material through a series of experiments. Found live S with R bacteria and injected
 Section 1: Identifying DNA as the Genetic Material KEY CONCEPT DNA was identified as the genetic material through a series of experiments. VOCABULARY bacteriophage MAIN IDEA: Griffith finds a transforming
Section 1: Identifying DNA as the Genetic Material KEY CONCEPT DNA was identified as the genetic material through a series of experiments. VOCABULARY bacteriophage MAIN IDEA: Griffith finds a transforming
John s Student Union Study Guide for Final Exam
 John s Student Union Study Guide for Final Exam 1. What organelle do Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes have in common? Ribosomes 2. Covalent vs Ionic bonds: Covalent: sharing electrons (Polar & Nonpolar) Ionic:
John s Student Union Study Guide for Final Exam 1. What organelle do Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes have in common? Ribosomes 2. Covalent vs Ionic bonds: Covalent: sharing electrons (Polar & Nonpolar) Ionic:
Biology Final Exam Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
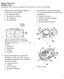 Biology Final Exam Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. What advance in technology made the discovery of cells possible? a. the ultraviolet
Biology Final Exam Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. What advance in technology made the discovery of cells possible? a. the ultraviolet
