Oxidation SMT Yau - 1
|
|
|
- Solomon Horn
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Oxidation Yau - 1
2 Objectives After studying the material in this chapter, you will be able to: 1. Describe an oxide film for semiconductor manufacturing, including its atomic structure, how it is used and its benefits. 2. State the chemical reaction for oxidation and describe how oxide grows on silicon. 3. Explain selective oxidation and give two examples. 4. State the three types of thermal processing equipment, describe the five parts of a vertical furnace, and give the attributes of a fast ramp vertical furnace. 5. Explain what is a rapid thermal processor, its usage and design. 6. Describe the critical aspects of the oxidation process, its quality measures and some common troubleshooting problems. Yau - 2
3 Diffusion Area of Wafer Fabrication Wafer fabrication (front-end) Wafer start Thin Films Polish Unpatterned wafer Completed wafer Diffusion Photo Etch Test/Sort Implant Used with permission from Advanced Micro Devices Figure 10.1 Yau - 3
4 Oxide Film Nature of Oxide Film Uses of Oxide Film Device Protection and Isolation Surface Passivation Gate Oxide Dielectric Dopant Barrier Dielectric Between Metal Layers Yau - 4
5 Atomic Structure of Silicon Dioxide Silicon Oxygen Used with permission from International SEMATECH Figure 10.2 Yau - 5
6 Field Oxide Layer Field oxide isolates active regions from each other. n-well p-well p- Epitaxial layer p+ Silicon substrate Figure 10.3 Yau - 6
7 Gate Oxide Dielectric Gate Oxide Polysilicon gate n-well p-well p- Epitaxial layer p+ Silicon substrate Figure 10.4 Yau - 7
8 Oxide Layer Dopant Barrier Phosphorus implant n-well Barrier oxide p- Epitaxial layer p+ Silicon substrate Figure 10.5 Yau - 8
9 Table 10.1 Oxide Applications: Native Oxide Purpose: This oxide is a contaminant and generally undesirable. Sometimes used in memory storage or film passivation. Silicon dioxide (oxide) p + Silicon substrate Comments: Growth rate at room temperature is 15 per hour up to about 40 Å. Table 10.1A Yau - 9
10 Table 10.1 Oxide Applications: Field Oxide Purpose: Serves as an isolation barrier between individual transistors to isolate them from each other. Field oxide Transistor site p + Silicon substrate Comments: Common field oxide thickness range from 2,500 Å to 15,000 Å. Wet oxidation is the preferred method. Table 10.1B Yau - 10
11 Table 10.1 Oxide Applications: Gate Oxide Purpose: Serves as a dielectric between the gate and sourcedrain parts of MOS transistor. Gate oxide Gate Source Drain Transistor site p + Silicon substrate Comments: Growth rate at room temperature is 15 Å per hour up to about 40 Å. Common gate oxide film thickness range from about 30 Å to 500 Å. Dry oxidation is the preferred method. Table 10.1C Yau - 11
12 Table 10.1 Oxide Applications: Barrier Oxide Purpose: Protect active devices and silicon from follow-on processing. Barrier oxide Metal Diffused resistors p + Silicon substrate Comments: Thermally grown to several hundred Angstroms thickness. Table 10.1D Yau - 12
13 Table 10.1 Oxide Applications: Dopant Barrier Purpose: Masking material when implanting dopant into wafer. Example: Spacer oxide used during the implant of dopant into the source and drain regions. Dopant barrier spacer oxide Ion implantation Gate Spacer oxide protects narrow channel from high-energy implant Comments: Dopants diffuse into unmasked areas of silicon by selective diffusion. Table 10.1E Yau - 13
14 Table 10.1 Oxide Applications: Pad Oxide Purpose: Provides stress reduction for Si 3 N 4 Nitride Pad oxide Passivation Layer Bonding pad metal M-4 ILD-5 ILD-4 M-3 Comments: Thermally grown and very thin. Table 10.1F Yau - 14
15 Table 10.1 Oxide Applications: Implant Screen Oxide Purpose: Sometimes referred to as sacrificial oxide, screen oxide, is used to reduce implant channeling and damage. Assists creation of shallow junctions. Ion implantation Screen oxide p + Silicon substrate High damage to upper Si surface + more channeling Low damage to upper Si surface + less channeling Comments: Thermally grown Table 10.1G Yau - 15
16 Table 10.1 Oxide Applications: Insulating Barrier between Metal Layers Purpose: Serves as protective layer between metal lines. Passivation layer Interlayer oxide Bonding pad metal ILD-5 M-4 ILD-4 M-3 Comments: This oxide is not thermally grown, but is deposited. Table 10.1H Yau - 16
17 Thermal Oxidation Growth Chemical Reaction for Oxidation Dry oxidation Wet oxidation Oxidation Growth Model Oxide silicon interface Use of chlorinated agents in oxidation Rate of oxide growth Factors affecting oxide growth Initial growth phase Selective oxidation LOCOS STI Yau - 17
18 Oxide Thickness Ranges for Various Requirements Semiconductor Application Typical Oxide Thickness, Å Gate oxide (0.18 µm generation) Capacitor dielectrics ,200 Dopant masking oxide (Varies depending on dopant, implant energy, time & temperature) STI Barrier Oxide 150 LOCOS Pad Oxide Field oxide 2,500 15,000 Table 10.2 Yau - 18
19 Dry Oxidation Time (Minutes) 10.0 (100) Silicon Time (minutes) Yau ,200 C 1,100 C 1000 C 900 C 800 C 700 C Figure 10.6 Oxide thickness (µm)
20 Wet Oxygen Oxidation Gas panel Furnace Exhaust Scrubber Burn box HCl N 2 O 2 H 2 Figure 10.7 Yau - 20
21 Consumption of Silicon during Oxidation t 0.55t 0.45t Before oxidation After oxidation Figure 10.8 Yau - 21
22 Liquid-State Diffusion Figure 10.9 Yau - 22
23 Charge Buildup at Si/SiO2 Interface Silicon Oxygen Positive charge SiO 2 Silicon Used with permission from International SEMATECH Figure Yau - 23
24 Diffusion of Oxygen Through Oxide Layer Oxygen supplied to reaction surface O, O 2 Oxygen-oxide interface SiO 2 Oxide-silicon interface Si Used with permission from International SEMATECH Figure Yau - 24
25 Linear & Parabolic Stages for Dry Oxidation Growth at 1100ºC Oxidation thickness 4,000 Å 3,000 Å 2,000 Å 1,000 Å Approximate linear region } Oxidation time (minutes) Used with permission from International SEMATECH Figure Yau - 25
26 LOCOS Process 1. Nitride deposition Nitride 2. Nitride mask & etch Silicon 3. Local oxidation of silicon SiO 2 growth Pad oxide (initial oxide) Silicon Silicon SiO 2 SiO 2 Silicon 4. Nitride strip Nitride Silicon Silicon Cross section of LOCOS field oxide (Actual growth of oxide is omnidirectional) Figure Yau - 26
27 Selective Oxidation and Bird s Beak Effect Silicon oxynitride Nitride oxidation mask Bird s beak region Selective oxidation Pad oxide Silicon dioxide Silicon substrate Used with permission from International SEMATECH Figure Yau - 27
28 STI Oxide Liner 1. Nitride deposition 2. Trench mask and etch 3. Sidewall oxidation and trench fill Nitride Silicon Oxide over nitride Pad oxide (initial oxide) Silicon Silicon Silicon 4. Oxide planarization (CMP) 5. Nitride strip Oxide Trench filled with deposited oxide Sidewall liner Silicon Silicon Cross section of shallow trench isolation (STI) Figure Yau - 28
29 Furnace Equipment Horizontal Furnace Vertical Furnace Rapid Thermal Processor (RTP) Yau - 29
30 Horizontal and Vertical Furnaces Performance Factor Performance Objective Horizontal Furnace Vertical Furnace Typical wafer loading size Clean room footprint Parallel processing Gas flow dynamics (GFD) Boat rotation for improved film uniformity Temperature gradient across wafer Particle control during loading/unloading Quartz change Wafer loading technique Pre-and postprocess control of furnace ambient Small, for process flexibility Small, to use less space Ideal for process flexibility Optimize for uniformity 200 wafers/batch 100 wafers/batch Larger, but has 4 process tubes Not capable Worse due to paddle and boat hardware. Bouyancy and gravity effects cause non-uniform radial gas distribution. Smaller (single process tube) Capable of loading/unloading wafers during process, which increases throughput Superior GFD and symmetric/uniform gas distribution Ideal condition Impossible to design Easy to include Ideally small Large, due to radiant shadow of paddle Small Minimum particles Relatively poor Improved particle control from top-down loading scheme Easily done in short More involved and slow Easier and quicker, leading time to reduced downtime Ideally automated Difficult to automate in a Easily automated with Control is desirable successful fashion Relatively difficult to control robotics Excellent control, with options of either vacuum or neutral ambient Table 10.3 Yau - 30
31 Horizontal Diffusion Furnace Photograph courtesy of International SEMATECH Photo 10.1 Yau - 31
32 Vertical Diffusion Furnace Photograph courtesy of International SEMATECH Photo 10.2 Yau - 32
33 Block Diagram of Vertical Furnace System Microcontroller Wafer handler controller Temperature controller Three-zone heater Heater 1 Heater 2 Quartz process chamber Gas panel Gas flow controller Boat loader Exhaust controller Heater 3 Quartz boat Process gas cylinder Wafer load/unload system Boat motor drive system Pressure Exhaust controller Figure Yau - 33
34 Vertical Furnace Process Tube Heating jacket Three-zone heating elements Quartz tube End cap Figure Yau - 34
35 Heater Element Power Distribution VAC 3φ Heater element transformer Trigger circuit SCRs SCRs SCRs Zone 1 Zone 2 Zone 3 Furnace heater elements Used with permission from International SEMATECH Figure Yau - 35
36 Locations of Thermocouples in the Furnace Chamber System controller Temperature controller Heater 1 Thermocouple measurements Profile TCs Control TCs Overtemperature TCs Heater 2 Heater 3 TC Figure Yau - 36
37 Common Gases used in Furnace Processes Gases Classifications Examples Inert gas Argon (Ar), Nitrogen (N 2 ) Bulk Reducing gas Hydrogen (H 2 ) Oxidizing gas Oxygen (O 2 ) Silicon-precursor gas Silane (SiH 4 ), dichlorosilane (DCS) or (H 2 SiCl 2 ) Dopant gas Arsine (AsH 3 ), phosphine (PH 3 ) Diborane (B 2 H 6 ) Specialty Reactant gas Atmospheric/purge gas Ammonia (NH 3 ), hydrogen chloride (HCl) Nitrogen (N 2 ), helium (He) Other specialty gases Tungsten hexafluoride (WF 6 ) Table 10.4 Yau - 37
38 Burn Box to Combust Exhaust To facility s exhaust system Wet scrubber Excess combustible gas burns in hot oxygen rich chamber Gas from furnace process chamber Combustion chamber (burn box or flow reactor) O 2 O 2 Filter Residue Recirculated water Used with permission from International SEMATECH Figure Yau - 38
39 Thermal Profile of Conventional Versus Fast Ramp Vertical Furnace Conventional Fast Ramp Temperature ( C) Temperature ( C) Time (minutes) Time (minutes) Reprinted from the June 1996 edition of Solid State Technology, copyright 1996 by PennWell Publishing Company. Figure Yau - 39
40 The Main Advantages of a Rapid Thermal Processor Reduced thermal budget Minimized dopant movement in the silicon Ease of clustering multiple tools Reduced contamination due to cold wall heating Cleaner ambient because of the smaller chamber volume Shorter time to process a wafer (referred to as cycle time) Yau - 40
41 Comparison of Conventional Vertical Furnace and RTP Vertical Furnace RTP Batch Single-wafer Hot wall Cold wall Long time to heat and cool batch Short time to heat and cool wafer Small thermal gradient across wafer Large thermal gradient across wafer Long cycle time Short cycle time Ambient temperature measurement Wafer temperature measurement Issues: Issues: Large thermal budget Temperature uniformity Particles Minimize dopant movement Ambient control Repeatability from wafer to wafer Throughput Wafer stress due to rapid heating Absolute temperature measurement Table 10.5 Yau - 41
42 Rapid Thermal Processor Setpoint voltages Heater head Temperature controller Wafer Pyrometer Axisymmetric lamp array Reflector plate Optical fibers Feedback voltages Figure Yau - 42
43 Rapid Thermal Processor Photograph courtesy of Advanced Micro Devices, Applied Materials 5300 Centura RTP Photo 10.3 Yau - 43
44 RTP Applications Anneal of implants to remove defects and activate and diffuse dopants Densification of deposited films, such as deposited oxide layers Borophosphosilicate glass (BPSG) reflow Anneal of barrier layers, such as titanium nitride (TiN) Silicide formation, such as titanium silicide (TiSi 2 ) Contact alloying Yau - 44
45 Oxidation Process Pre Oxidation Cleaning Oxidation process recipe Quality Measurements Oxidation Troubleshooting Yau - 45
46 Critical Issues for Minimizing Contamination Maintenance of the furnace and associated equipment (especially quartz components) for cleanliness Purity of processing chemicals Purity of oxidizing ambient (the source of oxygen in the furnace) Wafer cleaning and handling practices Yau - 46
47 Thermal Oxidation Process Flow Chart Wet Clean Chemicals % solution Temperature Time Oxidation Furnace O 2, H 2, N 2, Cl Flow rate Exhaust Temperature Temperature profile Time Inspection Film thickness Uniformity Particles Defects Figure Yau - 47
48 Process Recipe for Dry Oxidation Process Step Time (min) Temp (ºC) N 2 Purge Gas (slm) Process Gas N 2 O 2 HCl (slm) (slm) (sccm) Comments Idle condition Load furnace tube Ramp 20ºC/min Ramp temperature up Temperature stabilization Dry oxidation Anneal 6 30 Ramp -5ºC/min Ramp temperature down Unload furnace tube Idle Note: gas flow units are slm (standard liters per minute) and sccm (standard cubic centimeters per minute) Table 10.6 Yau - 48
49 Wafer Loading Pattern in Vertical Furnace 160 Calibration parameters: Boat size: 160 wafers Boat pitch: 0.14 inch Wafer size: 8 inches Elevator speed: 9.29 cm/min Cool down delay: 20 minutes 4 Filler (dummy) wafers 1 Test wafer 75 Production wafers 1 Test wafer 75 Production wafers 1 Test wafer 4 Filler (dummy) wafers 1 Used with permission from International SEMATECH Figure Yau - 49
Semiconductor Manufacturing Technology. Semiconductor Manufacturing Technology
 Semiconductor Manufacturing Technology Michael Quirk & Julian Serda October 2001 by Prentice Hall Chapter 10 Oxidation 2001 2000 by Prentice Hall Diffusion Area of Wafer Fabrication Wafer fabrication (front-end)
Semiconductor Manufacturing Technology Michael Quirk & Julian Serda October 2001 by Prentice Hall Chapter 10 Oxidation 2001 2000 by Prentice Hall Diffusion Area of Wafer Fabrication Wafer fabrication (front-end)
Chapter 5 Thermal Processes
 Chapter 5 Thermal Processes 1 Topics Introduction Hardware Oxidation Diffusion Annealing Post-Implantation Alloying Reflow High Temp CVD Epi Poly Silicon Nitride RTP RTA RTP Future Trends 2 Definition
Chapter 5 Thermal Processes 1 Topics Introduction Hardware Oxidation Diffusion Annealing Post-Implantation Alloying Reflow High Temp CVD Epi Poly Silicon Nitride RTP RTA RTP Future Trends 2 Definition
Semiconductor Manufacturing Technology. IC Fabrication Process Overview
 Semiconductor Manufacturing Technology Michael Quirk & Julian Serda October 00 by Prentice Hall Chapter 9 IC Fabrication Process Overview /4 Objectives After studying the material in this chapter, you
Semiconductor Manufacturing Technology Michael Quirk & Julian Serda October 00 by Prentice Hall Chapter 9 IC Fabrication Process Overview /4 Objectives After studying the material in this chapter, you
Chapter 7 Polysilicon and Dielectric Film Deposition
 Chapter 7 Polysilicon and Dielectric Film Deposition Professor Paul K. Chu Thin Films in Microelectronics Polycrystalline silicon or polysilicon Doped or undoped silicon dioxide Stoichiometric or plasma-deposited
Chapter 7 Polysilicon and Dielectric Film Deposition Professor Paul K. Chu Thin Films in Microelectronics Polycrystalline silicon or polysilicon Doped or undoped silicon dioxide Stoichiometric or plasma-deposited
Kinetics of Silicon Oxidation in a Rapid Thermal Processor
 Kinetics of Silicon Oxidation in a Rapid Thermal Processor Asad M. Haider, Ph.D. Texas Instruments Dallas, Texas USA Presentation at the National Center of Physics International Spring Week 2010 Islamabad
Kinetics of Silicon Oxidation in a Rapid Thermal Processor Asad M. Haider, Ph.D. Texas Instruments Dallas, Texas USA Presentation at the National Center of Physics International Spring Week 2010 Islamabad
CMOS Technology. Flow varies with process types & company. Start with substrate selection. N-Well CMOS Twin-Well CMOS STI
 CMOS Technology Flow varies with process types & company N-Well CMOS Twin-Well CMOS STI Start with substrate selection Type: n or p Doping level, resistivity Orientation, 100, or 101, etc Other parameters
CMOS Technology Flow varies with process types & company N-Well CMOS Twin-Well CMOS STI Start with substrate selection Type: n or p Doping level, resistivity Orientation, 100, or 101, etc Other parameters
Why silicon? Silicon oxide
 Oxidation Layering. Oxidation layering produces a thin layer of silicon dioxide, or oxide, on the substrate by exposing the wafer to a mixture of highpurity oxygen or water at ca. 1000 C (1800 F). Why
Oxidation Layering. Oxidation layering produces a thin layer of silicon dioxide, or oxide, on the substrate by exposing the wafer to a mixture of highpurity oxygen or water at ca. 1000 C (1800 F). Why
Doping and Oxidation
 Technische Universität Graz Institute of Solid State Physics Doping and Oxidation Franssila: Chapters 13,14, 15 Peter Hadley Technische Universität Graz Institute of Solid State Physics Doping Add donors
Technische Universität Graz Institute of Solid State Physics Doping and Oxidation Franssila: Chapters 13,14, 15 Peter Hadley Technische Universität Graz Institute of Solid State Physics Doping Add donors
MICROCHIP MANUFACTURING by S. Wolf
 MICROCHIP MANUFACTURING by S. Wolf Chapter 13: THERMAL- OXIDATION of SILICON 2004 by LATTICE PRESS Chapter 13: THERMAL-OXIDATION of SILICON n CHAPTER CONTENTS Applications of Thermal Silicon-Dioxide Physical
MICROCHIP MANUFACTURING by S. Wolf Chapter 13: THERMAL- OXIDATION of SILICON 2004 by LATTICE PRESS Chapter 13: THERMAL-OXIDATION of SILICON n CHAPTER CONTENTS Applications of Thermal Silicon-Dioxide Physical
Chapter 4 : ULSI Process Integration (0.18 m CMOS Process)
 Chapter : ULSI Process Integration (0.8 m CMOS Process) Reference. Semiconductor Manufacturing Technology : Michael Quirk and Julian Serda (00). - (00). Semiconductor Physics and Devices- Basic Principles(/e)
Chapter : ULSI Process Integration (0.8 m CMOS Process) Reference. Semiconductor Manufacturing Technology : Michael Quirk and Julian Serda (00). - (00). Semiconductor Physics and Devices- Basic Principles(/e)
2. Fabrication techniques. KNU Seminar Course 2015 Robert Mroczyński
 2. Fabrication techniques KNU Seminar Course 2015 Robert Mroczyński Technological layers used in the course of the IC fabrication Semiconductors Fundamental part of each IC, active material of semiconductor
2. Fabrication techniques KNU Seminar Course 2015 Robert Mroczyński Technological layers used in the course of the IC fabrication Semiconductors Fundamental part of each IC, active material of semiconductor
HOMEWORK 4 and 5. March 15, Homework is due on Monday March 30, 2009 in Class. Answer the following questions from the Course Textbook:
 HOMEWORK 4 and 5 March 15, 2009 Homework is due on Monday March 30, 2009 in Class. Chapter 7 Answer the following questions from the Course Textbook: 7.2, 7.3, 7.4, 7.5, 7.6*, 7.7, 7.9*, 7.10*, 7.16, 7.17*,
HOMEWORK 4 and 5 March 15, 2009 Homework is due on Monday March 30, 2009 in Class. Chapter 7 Answer the following questions from the Course Textbook: 7.2, 7.3, 7.4, 7.5, 7.6*, 7.7, 7.9*, 7.10*, 7.16, 7.17*,
Figure 2.3 (cont., p. 60) (e) Block diagram of Pentium 4 processor with 42 million transistors (2000). [Courtesy Intel Corporation.
 Figure 2.1 (p. 58) Basic fabrication steps in the silicon planar process: (a) oxide formation, (b) selective oxide removal, (c) deposition of dopant atoms on wafer, (d) diffusion of dopant atoms into exposed
Figure 2.1 (p. 58) Basic fabrication steps in the silicon planar process: (a) oxide formation, (b) selective oxide removal, (c) deposition of dopant atoms on wafer, (d) diffusion of dopant atoms into exposed
Czochralski Crystal Growth
 Czochralski Crystal Growth Crystal Pulling Crystal Ingots Shaping and Polishing 300 mm wafer 1 2 Advantage of larger diameter wafers Wafer area larger Chip area larger 3 4 Large-Diameter Wafer Handling
Czochralski Crystal Growth Crystal Pulling Crystal Ingots Shaping and Polishing 300 mm wafer 1 2 Advantage of larger diameter wafers Wafer area larger Chip area larger 3 4 Large-Diameter Wafer Handling
INTEGRATED-CIRCUIT TECHNOLOGY
 INTEGRATED-CIRCUIT TECHNOLOGY 0. Silicon crystal growth and wafer preparation 1. Processing Steps 1.1. Photolitography 1.2. Oxidation 1.3. Layer Deposition 1.4. Etching 1.5. Diffusion 1.6 Backend: assembly,
INTEGRATED-CIRCUIT TECHNOLOGY 0. Silicon crystal growth and wafer preparation 1. Processing Steps 1.1. Photolitography 1.2. Oxidation 1.3. Layer Deposition 1.4. Etching 1.5. Diffusion 1.6 Backend: assembly,
CSI G SYSTEMS CSI GAS DELIVERY SUPPORT. Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
 This page discusses the CVD processes often used for integrated circuits (ICs). Particular materials are deposited best under particular conditions. Facilitation recommendations are at the bottom of the
This page discusses the CVD processes often used for integrated circuits (ICs). Particular materials are deposited best under particular conditions. Facilitation recommendations are at the bottom of the
Chapter 3 Silicon Device Fabrication Technology
 Chapter 3 Silicon Device Fabrication Technology Over 10 15 transistors (or 100,000 for every person in the world) are manufactured every year. VLSI (Very Large Scale Integration) ULSI (Ultra Large Scale
Chapter 3 Silicon Device Fabrication Technology Over 10 15 transistors (or 100,000 for every person in the world) are manufactured every year. VLSI (Very Large Scale Integration) ULSI (Ultra Large Scale
Semiconductor Technology
 Semiconductor Technology from A to Z Oxidation www.halbleiter.org Contents Contents List of Figures List of Tables II III 1 Oxidation 1 1.1 Overview..................................... 1 1.1.1 Application...............................
Semiconductor Technology from A to Z Oxidation www.halbleiter.org Contents Contents List of Figures List of Tables II III 1 Oxidation 1 1.1 Overview..................................... 1 1.1.1 Application...............................
EE 330 Lecture 9. IC Fabrication Technology Part II. -Oxidation -Epitaxy -Polysilicon -Planarization -Resistance and Capacitance in Interconnects
 EE 330 Lecture 9 IC Fabrication Technology Part II -Oxidation -Epitaxy -Polysilicon -Planarization -Resistance and Capacitance in Interconnects Review from Last Time Etching Dry etch (anisotropic) SiO
EE 330 Lecture 9 IC Fabrication Technology Part II -Oxidation -Epitaxy -Polysilicon -Planarization -Resistance and Capacitance in Interconnects Review from Last Time Etching Dry etch (anisotropic) SiO
Chapter 5 Thermal Processes
 Chapter 5 Thermal Processes Hong Xiao, Ph. D. hxiao89@hotmail.com Objective List four thermal processes Describe thermal process in IC fabrication Describe thermal oxidation process Explain the advantage
Chapter 5 Thermal Processes Hong Xiao, Ph. D. hxiao89@hotmail.com Objective List four thermal processes Describe thermal process in IC fabrication Describe thermal oxidation process Explain the advantage
Semiconductor Device Fabrication
 5 May 2003 Review Homework 6 Semiconductor Device Fabrication William Shockley, 1945 The network before the internet Bell Labs established a group to develop a semiconductor replacement for the vacuum
5 May 2003 Review Homework 6 Semiconductor Device Fabrication William Shockley, 1945 The network before the internet Bell Labs established a group to develop a semiconductor replacement for the vacuum
A discussion of crystal growth, lithography, etching, doping, and device structures is presented in
 Chapter 5 PROCESSING OF DEVICES A discussion of crystal growth, lithography, etching, doping, and device structures is presented in the following overview gures. SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICE PROCESSING: AN OVERVIEW
Chapter 5 PROCESSING OF DEVICES A discussion of crystal growth, lithography, etching, doping, and device structures is presented in the following overview gures. SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICE PROCESSING: AN OVERVIEW
EE 330 Lecture 8. IC Fabrication Technology Part II. - Oxidation - Epitaxy - Polysilicon - Interconnects
 EE 330 Lecture 8 IC Fabrication Technology Part II - Oxidation - Epitaxy - Polysilicon - Interconnects Review from Last Time MOS Transistor Bulk Source Gate Drain p-channel MOSFET Lightly-doped n-type
EE 330 Lecture 8 IC Fabrication Technology Part II - Oxidation - Epitaxy - Polysilicon - Interconnects Review from Last Time MOS Transistor Bulk Source Gate Drain p-channel MOSFET Lightly-doped n-type
Chapter 4. UEEP2613 Microelectronic Fabrication. Oxidation
 Chapter 4 UEEP2613 Microelectronic Fabrication Oxidation Prepared by Dr. Lim Soo King 24 Jun 2012 Chapter 4...113 Oxidation...113 4.0 Introduction... 113 4.1 Chemistry of Silicon Dioxide Formation... 115
Chapter 4 UEEP2613 Microelectronic Fabrication Oxidation Prepared by Dr. Lim Soo King 24 Jun 2012 Chapter 4...113 Oxidation...113 4.0 Introduction... 113 4.1 Chemistry of Silicon Dioxide Formation... 115
Chapter 2 Manufacturing Process
 Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Chapter 2 Manufacturing Process 1 CMOS Process 2 CMOS Process (n-well) Both NMOS and PMOS must be built in the same silicon material. PMOS in n-well NMOS
Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Chapter 2 Manufacturing Process 1 CMOS Process 2 CMOS Process (n-well) Both NMOS and PMOS must be built in the same silicon material. PMOS in n-well NMOS
Technology. Semiconductor Manufacturing. Hong Xiao INTRODUCTION TO SECOND EDITION SPIE PRESS
 INTRODUCTION TO Semiconductor Manufacturing Technology SECOND EDITION Hong Xiao TECHNISCHE INFORMATIONSBiBUOTHEK UNIVERSITATSBIBLIOTHEK HANNOVER SPIE PRESS Bellingham,Washington USA Contents Preface to
INTRODUCTION TO Semiconductor Manufacturing Technology SECOND EDITION Hong Xiao TECHNISCHE INFORMATIONSBiBUOTHEK UNIVERSITATSBIBLIOTHEK HANNOVER SPIE PRESS Bellingham,Washington USA Contents Preface to
Isolation Technology. Dr. Lynn Fuller
 ROCHESTER INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MICROELECTRONIC ENGINEERING Isolation Technology Dr. Lynn Fuller Motorola Professor 82 Lomb Memorial Drive Rochester, NY 14623-5604 Tel (585) 475-2035 Fax (585) 475-5041
ROCHESTER INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MICROELECTRONIC ENGINEERING Isolation Technology Dr. Lynn Fuller Motorola Professor 82 Lomb Memorial Drive Rochester, NY 14623-5604 Tel (585) 475-2035 Fax (585) 475-5041
Microelettronica. Planar Technology for Silicon Integrated Circuits Fabrication. 26/02/2017 A. Neviani - Microelettronica
 Microelettronica Planar Technology for Silicon Integrated Circuits Fabrication 26/02/2017 A. Neviani - Microelettronica Introduction Simplified crosssection of an nmosfet and a pmosfet Simplified crosssection
Microelettronica Planar Technology for Silicon Integrated Circuits Fabrication 26/02/2017 A. Neviani - Microelettronica Introduction Simplified crosssection of an nmosfet and a pmosfet Simplified crosssection
Processing of Semiconducting Materials Prof. Pallab Banerjee Department of Material Science Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur
 Processing of Semiconducting Materials Prof. Pallab Banerjee Department of Material Science Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 35 Oxidation I (Refer Slide Time: 00:24) Today s topic of
Processing of Semiconducting Materials Prof. Pallab Banerjee Department of Material Science Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 35 Oxidation I (Refer Slide Time: 00:24) Today s topic of
CHAPTER 4: Oxidation. Chapter 4 1. Oxidation of silicon is an important process in VLSI. The typical roles of SiO 2 are:
 Chapter 4 1 CHAPTER 4: Oxidation Oxidation of silicon is an important process in VLSI. The typical roles of SiO 2 are: 1. mask against implant or diffusion of dopant into silicon 2. surface passivation
Chapter 4 1 CHAPTER 4: Oxidation Oxidation of silicon is an important process in VLSI. The typical roles of SiO 2 are: 1. mask against implant or diffusion of dopant into silicon 2. surface passivation
Chemical Vapour Deposition: CVD Reference: Jaeger Chapter 6 & Ruska: Chapter 8 CVD - Chemical Vapour Deposition React chemicals to create a thin film
 Chemical Vapour Deposition: CVD Reference: Jaeger Chapter 6 & Ruska: Chapter 8 CVD - Chemical Vapour Deposition React chemicals to create a thin film layer at the surface Typically gas phase reactions
Chemical Vapour Deposition: CVD Reference: Jaeger Chapter 6 & Ruska: Chapter 8 CVD - Chemical Vapour Deposition React chemicals to create a thin film layer at the surface Typically gas phase reactions
Silicon Epitaxial CVD Want to create very sharp PN boundary grow one type layer on other in single crystal form High dopant layers on low dopant
 Silicon Epitaxial CVD Want to create very sharp PN boundary grow one type layer on other in single crystal form High dopant layers on low dopant substrate Creates latch up protection for CMOS Buried Epi
Silicon Epitaxial CVD Want to create very sharp PN boundary grow one type layer on other in single crystal form High dopant layers on low dopant substrate Creates latch up protection for CMOS Buried Epi
Lecture 030 Integrated Circuit Technology - I (5/8/03) Page 030-1
 Lecture 030 Integrated Circuit Technology - I (5/8/03) Page 030-1 LECTURE 030 INTEGRATED CIRCUIT TECHNOLOGY - I (References [7,8]) Objective The objective of this presentation is: 1.) Illustrate integrated
Lecture 030 Integrated Circuit Technology - I (5/8/03) Page 030-1 LECTURE 030 INTEGRATED CIRCUIT TECHNOLOGY - I (References [7,8]) Objective The objective of this presentation is: 1.) Illustrate integrated
Lect. 2: Basics of Si Technology
 Unit processes Thin Film Deposition Etching Ion Implantation Photolithography Chemical Mechanical Polishing 1. Thin Film Deposition Layer of materials ranging from fractions of nanometer to several micro-meters
Unit processes Thin Film Deposition Etching Ion Implantation Photolithography Chemical Mechanical Polishing 1. Thin Film Deposition Layer of materials ranging from fractions of nanometer to several micro-meters
EE40 Lec 22. IC Fabrication Technology. Prof. Nathan Cheung 11/19/2009
 Suggested Reading EE40 Lec 22 IC Fabrication Technology Prof. Nathan Cheung 11/19/2009 300mm Fab Tour http://www-03.ibm.com/technology/manufacturing/technology_tour_300mm_foundry.html Overview of IC Technology
Suggested Reading EE40 Lec 22 IC Fabrication Technology Prof. Nathan Cheung 11/19/2009 300mm Fab Tour http://www-03.ibm.com/technology/manufacturing/technology_tour_300mm_foundry.html Overview of IC Technology
Lecture #18 Fabrication OUTLINE
 Transistors on a Chip Lecture #18 Fabrication OUTLINE IC Fabrication Technology Introduction the task at hand Doping Oxidation Thin-film deposition Lithography Etch Lithography trends Plasma processing
Transistors on a Chip Lecture #18 Fabrication OUTLINE IC Fabrication Technology Introduction the task at hand Doping Oxidation Thin-film deposition Lithography Etch Lithography trends Plasma processing
EE 330 Lecture 9. IC Fabrication Technology Part 2
 EE 330 Lecture 9 IC Fabrication Technology Part 2 Quiz 8 A 2m silicon crystal is cut into wafers using a wire saw. If the wire diameter is 220um and the wafer thickness is 350um, how many wafers will this
EE 330 Lecture 9 IC Fabrication Technology Part 2 Quiz 8 A 2m silicon crystal is cut into wafers using a wire saw. If the wire diameter is 220um and the wafer thickness is 350um, how many wafers will this
Silicon Epitaxial CVD Want to create very sharp PN boundary grow one type layer on other in single crystal form High dopant layers on low dopant
 Silicon Epitaxial CVD Want to create very sharp PN boundary grow one type layer on other in single crystal form High dopant layers on low dopant substrate Creates latch up protection for CMOS Buried Epi
Silicon Epitaxial CVD Want to create very sharp PN boundary grow one type layer on other in single crystal form High dopant layers on low dopant substrate Creates latch up protection for CMOS Buried Epi
Fabrication Process. Crystal Growth Doping Deposition Patterning Lithography Oxidation Ion Implementation CONCORDIA VLSI DESIGN LAB
 Fabrication Process Crystal Growth Doping Deposition Patterning Lithography Oxidation Ion Implementation 1 Fabrication- CMOS Process Starting Material Preparation 1. Produce Metallurgical Grade Silicon
Fabrication Process Crystal Growth Doping Deposition Patterning Lithography Oxidation Ion Implementation 1 Fabrication- CMOS Process Starting Material Preparation 1. Produce Metallurgical Grade Silicon
Fabrication Technology
 Fabrication Technology By B.G.Balagangadhar Department of Electronics and Communication Ghousia College of Engineering, Ramanagaram 1 OUTLINE Introduction Why Silicon The purity of Silicon Czochralski
Fabrication Technology By B.G.Balagangadhar Department of Electronics and Communication Ghousia College of Engineering, Ramanagaram 1 OUTLINE Introduction Why Silicon The purity of Silicon Czochralski
EE 330 Lecture 9. IC Fabrication Technology Part II. -Oxidation -Epitaxy -Polysilicon -Planarization -Resistance and Capacitance in Interconnects
 EE 330 Lecture 9 IC Fabrication Technology Part II -Oxidation -Epitaxy -Polysilicon -Planarization -Resistance and Capacitance in Interconnects Review from Last Time IC Fabrication Technology Crystal Preparation
EE 330 Lecture 9 IC Fabrication Technology Part II -Oxidation -Epitaxy -Polysilicon -Planarization -Resistance and Capacitance in Interconnects Review from Last Time IC Fabrication Technology Crystal Preparation
Semiconductor Manufacturing Technology. Semiconductor Manufacturing Technology
 Semiconductor Manufacturing Technology Michael Quirk & Julian Serda October 2001 by Prentice Hall Chapter 11 Deposition Film Layers for an MSI Era NMOS Transistor Topside Nitride Pre-metal oxide Sidewall
Semiconductor Manufacturing Technology Michael Quirk & Julian Serda October 2001 by Prentice Hall Chapter 11 Deposition Film Layers for an MSI Era NMOS Transistor Topside Nitride Pre-metal oxide Sidewall
Chapter 3 CMOS processing technology
 Chapter 3 CMOS processing technology (How to make a CMOS?) Si + impurity acceptors(p-type) donors (n-type) p-type + n-type => pn junction (I-V) 3.1.1 (Wafer) Wafer = A disk of silicon (0.25 mm - 1 mm thick),
Chapter 3 CMOS processing technology (How to make a CMOS?) Si + impurity acceptors(p-type) donors (n-type) p-type + n-type => pn junction (I-V) 3.1.1 (Wafer) Wafer = A disk of silicon (0.25 mm - 1 mm thick),
CMOS Manufacturing process. Design rule set
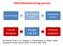 CMOS Manufacturing process Circuit design Set of optical masks Fabrication process Circuit designer Design rule set Process engineer All material: Chap. 2 of J. Rabaey, A. Chandrakasan, B. Nikolic, Digital
CMOS Manufacturing process Circuit design Set of optical masks Fabrication process Circuit designer Design rule set Process engineer All material: Chap. 2 of J. Rabaey, A. Chandrakasan, B. Nikolic, Digital
EE 434 Lecture 9. IC Fabrication Technology
 EE 434 Lecture 9 IC Fabrication Technology Quiz 7 The layout of a film resistor with electrodes A and B is shown. If the sheet resistance of the film is 40 /, determine the resistance between nodes A and
EE 434 Lecture 9 IC Fabrication Technology Quiz 7 The layout of a film resistor with electrodes A and B is shown. If the sheet resistance of the film is 40 /, determine the resistance between nodes A and
Instructor: Dr. M. Razaghi. Silicon Oxidation
 SILICON OXIDATION Silicon Oxidation Many different kinds of thin films are used to fabricate discrete devices and integrated circuits. Including: Thermal oxides Dielectric layers Polycrystalline silicon
SILICON OXIDATION Silicon Oxidation Many different kinds of thin films are used to fabricate discrete devices and integrated circuits. Including: Thermal oxides Dielectric layers Polycrystalline silicon
Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Dr. Lynn Fuller
 ROCHESTER INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MICROELECTRONIC ENGINEERING Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Dr. Lynn Fuller Webpage: http://people.rit.edu/lffeee 82 Lomb Memorial Drive Rochester, NY 14623-5604 Tel (585)
ROCHESTER INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MICROELECTRONIC ENGINEERING Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Dr. Lynn Fuller Webpage: http://people.rit.edu/lffeee 82 Lomb Memorial Drive Rochester, NY 14623-5604 Tel (585)
Thermal Oxidation and Growth of Insulators (Chapter 3 - Jaeger 3) Key advantage of Si: Oxidation of Si into SiO 2 (glass) Major factor in making
 Thermal Oxidation and Growth of Insulators (Chapter 3 - Jaeger 3) Key advantage of Si: Oxidation of Si into SiO (glass) Major factor in making Silicon the main semiconductor Grown at high temperature in
Thermal Oxidation and Growth of Insulators (Chapter 3 - Jaeger 3) Key advantage of Si: Oxidation of Si into SiO (glass) Major factor in making Silicon the main semiconductor Grown at high temperature in
Section 4: Thermal Oxidation. Jaeger Chapter 3. EE143 - Ali Javey
 Section 4: Thermal Oxidation Jaeger Chapter 3 Properties of O Thermal O is amorphous. Weight Density =.0 gm/cm 3 Molecular Density =.3E molecules/cm 3 O Crystalline O [Quartz] =.65 gm/cm 3 (1) Excellent
Section 4: Thermal Oxidation Jaeger Chapter 3 Properties of O Thermal O is amorphous. Weight Density =.0 gm/cm 3 Molecular Density =.3E molecules/cm 3 O Crystalline O [Quartz] =.65 gm/cm 3 (1) Excellent
Semiconductor Manufacturing Technology. Semiconductor Manufacturing Technology
 Semiconductor Manufacturing Technology Michael Quirk & Julian Serda October 2001 by Prentice Hall Chapter 17 Doping Processes Common Dopants Used in Semiconductor Manufacturing Acceptor Dopant Group IIIA
Semiconductor Manufacturing Technology Michael Quirk & Julian Serda October 2001 by Prentice Hall Chapter 17 Doping Processes Common Dopants Used in Semiconductor Manufacturing Acceptor Dopant Group IIIA
The Physical Structure (NMOS)
 The Physical Structure (NMOS) Al SiO2 Field Oxide Gate oxide S n+ Polysilicon Gate Al SiO2 SiO2 D n+ L channel P Substrate Field Oxide contact Metal (S) n+ (G) L W n+ (D) Poly 1 3D Perspective 2 3 Fabrication
The Physical Structure (NMOS) Al SiO2 Field Oxide Gate oxide S n+ Polysilicon Gate Al SiO2 SiO2 D n+ L channel P Substrate Field Oxide contact Metal (S) n+ (G) L W n+ (D) Poly 1 3D Perspective 2 3 Fabrication
Microelectronics. Integrated circuits. Introduction to the IC technology M.Rencz 11 September, Expected decrease in line width
 Microelectronics Introduction to the IC technology M.Rencz 11 September, 2002 9/16/02 1/37 Integrated circuits Development is controlled by the roadmaps. Self-fulfilling predictions for the tendencies
Microelectronics Introduction to the IC technology M.Rencz 11 September, 2002 9/16/02 1/37 Integrated circuits Development is controlled by the roadmaps. Self-fulfilling predictions for the tendencies
Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition
 Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition Steven Glenn July 8, 2009 Thin Films Lab 4 ABSTRACT The objective of this lab was to explore lab and the Applied Materials P5000 from a different point of view.
Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition Steven Glenn July 8, 2009 Thin Films Lab 4 ABSTRACT The objective of this lab was to explore lab and the Applied Materials P5000 from a different point of view.
EE CMOS TECHNOLOGY- Chapter 2 in the Text
 1 EE 212 FALL 1999-00 CMOS TECHOLOGY- Chapter 2 in the Text In this set of notes we will describe a modern CMOS process flow. In the simplest CMOS technologies, we need to realize simply MOS and MOS transistors
1 EE 212 FALL 1999-00 CMOS TECHOLOGY- Chapter 2 in the Text In this set of notes we will describe a modern CMOS process flow. In the simplest CMOS technologies, we need to realize simply MOS and MOS transistors
Microstructure of Electronic Materials. Amorphous materials. Single-Crystal Material. Professor N Cheung, U.C. Berkeley
 Microstructure of Electronic Materials Amorphous materials Single-Crystal Material 1 The Si Atom The Si Crystal diamond structure High-performance semiconductor devices require defect-free crystals 2 Crystallographic
Microstructure of Electronic Materials Amorphous materials Single-Crystal Material 1 The Si Atom The Si Crystal diamond structure High-performance semiconductor devices require defect-free crystals 2 Crystallographic
IC/MEMS Fabrication - Outline. Fabrication
 IC/MEMS Fabrication - Outline Fabrication overview Materials Wafer fabrication The Cycle: Deposition Lithography Etching Fabrication IC Fabrication Deposition Spin Casting PVD physical vapor deposition
IC/MEMS Fabrication - Outline Fabrication overview Materials Wafer fabrication The Cycle: Deposition Lithography Etching Fabrication IC Fabrication Deposition Spin Casting PVD physical vapor deposition
Xilinx XC4036EX FPGA
 Construction Analysis Xilinx XC4036EX FPGA Report Number: SCA 9706-544 Global Semiconductor Industry the Serving Since 1964 15022 N. 75th Street Scottsdale, AZ 85260-2476 Phone: 602-998-9780 Fax: 602-948-1925
Construction Analysis Xilinx XC4036EX FPGA Report Number: SCA 9706-544 Global Semiconductor Industry the Serving Since 1964 15022 N. 75th Street Scottsdale, AZ 85260-2476 Phone: 602-998-9780 Fax: 602-948-1925
Review of CMOS Processing Technology
 - Scaling and Integration Moore s Law Unit processes Thin Film Deposition Etching Ion Implantation Photolithography Chemical Mechanical Polishing 1. Thin Film Deposition Layer of materials ranging from
- Scaling and Integration Moore s Law Unit processes Thin Film Deposition Etching Ion Implantation Photolithography Chemical Mechanical Polishing 1. Thin Film Deposition Layer of materials ranging from
Analog Devices ADSP KS-160 SHARC Digital Signal Processor
 Construction Analysis Analog Devices ADSP-21062-KS-160 SHARC Digital Signal Processor Report Number: SCA 9712-575 Global Semiconductor Industry the Serving Since 1964 17350 N. Hartford Drive Scottsdale,
Construction Analysis Analog Devices ADSP-21062-KS-160 SHARC Digital Signal Processor Report Number: SCA 9712-575 Global Semiconductor Industry the Serving Since 1964 17350 N. Hartford Drive Scottsdale,
FABRICATION ENGINEERING MICRO- NANOSCALE ATTHE AND. Fourth Edition STEPHEN A. CAMPBELL. of Minnesota. University OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS
 AND FABRICATION ENGINEERING ATTHE MICRO- NANOSCALE Fourth Edition STEPHEN A. CAMPBELL University of Minnesota New York Oxford OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS CONTENTS Preface xiii prrt i OVERVIEW AND MATERIALS
AND FABRICATION ENGINEERING ATTHE MICRO- NANOSCALE Fourth Edition STEPHEN A. CAMPBELL University of Minnesota New York Oxford OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS CONTENTS Preface xiii prrt i OVERVIEW AND MATERIALS
Lecture 22: Integrated circuit fabrication
 Lecture 22: Integrated circuit fabrication Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 Layering 4 3 Patterning 7 4 Doping 8 4.1 Thermal diffusion......................... 10 4.2 Ion implantation.........................
Lecture 22: Integrated circuit fabrication Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 Layering 4 3 Patterning 7 4 Doping 8 4.1 Thermal diffusion......................... 10 4.2 Ion implantation.........................
9/4/2008 GMU, ECE 680 Physical VLSI Design
 ECE680: Physical VLSI Design Chapter II CMOS Manufacturing Process 1 Dual-Well Trench-Isolated CMOS Process gate-oxide TiSi 2 AlCu Tungsten SiO 2 p-well poly n-well SiO 2 n+ p-epi p+ p+ 2 Schematic Layout
ECE680: Physical VLSI Design Chapter II CMOS Manufacturing Process 1 Dual-Well Trench-Isolated CMOS Process gate-oxide TiSi 2 AlCu Tungsten SiO 2 p-well poly n-well SiO 2 n+ p-epi p+ p+ 2 Schematic Layout
Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor (CMOS)
 Technische Universität Graz Institute of Solid State Physics Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor (CMOS) Franssila: Chapters 26,28 Technische Universität Graz Institute of Solid State Physics Complementary
Technische Universität Graz Institute of Solid State Physics Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor (CMOS) Franssila: Chapters 26,28 Technische Universität Graz Institute of Solid State Physics Complementary
Altera EPM7128SQC EPLD
 Construction Analysis Altera EPM7128SQC160-15 EPLD Report Number: SCA 9712-569 Global Semiconductor Industry the Serving Since 1964 17350 N. Hartford Drive Scottsdale, AZ 85255 Phone: 602-515-9780 Fax:
Construction Analysis Altera EPM7128SQC160-15 EPLD Report Number: SCA 9712-569 Global Semiconductor Industry the Serving Since 1964 17350 N. Hartford Drive Scottsdale, AZ 85255 Phone: 602-515-9780 Fax:
Rockwell R RF to IF Down Converter
 Construction Analysis Rockwell R6732-13 RF to IF Down Converter Report Number: SCA 9709-552 Global Semiconductor Industry the Serving Since 1964 17350 N. Hartford Drive Scottsdale, AZ 85255 Phone: 602-515-9780
Construction Analysis Rockwell R6732-13 RF to IF Down Converter Report Number: SCA 9709-552 Global Semiconductor Industry the Serving Since 1964 17350 N. Hartford Drive Scottsdale, AZ 85255 Phone: 602-515-9780
Oki M A-60J 16Mbit DRAM (EDO)
 Construction Analysis Oki M5117805A-60J 16Mbit DRAM (EDO) Report Number: SCA 9707-545 Global Semiconductor Industry the Serving Since 1964 17350 N. Hartford Drive Scottsdale, AZ 85255 Phone: 602-515-9780
Construction Analysis Oki M5117805A-60J 16Mbit DRAM (EDO) Report Number: SCA 9707-545 Global Semiconductor Industry the Serving Since 1964 17350 N. Hartford Drive Scottsdale, AZ 85255 Phone: 602-515-9780
National Semiconductor LM2672 Simple Switcher Voltage Regulator
 Construction Analysis National Semiconductor LM2672 Simple Switcher Voltage Regulator Report Number: SCA 9712-570 Global Semiconductor Industry the Serving Since 1964 17350 N. Hartford Drive Scottsdale,
Construction Analysis National Semiconductor LM2672 Simple Switcher Voltage Regulator Report Number: SCA 9712-570 Global Semiconductor Industry the Serving Since 1964 17350 N. Hartford Drive Scottsdale,
Chapter 2 MOS Fabrication Technology
 Chapter 2 MOS Fabrication Technology Abstract This chapter is concerned with the fabrication of metal oxide semiconductor (MOS) technology. Various processes such as wafer fabrication, oxidation, mask
Chapter 2 MOS Fabrication Technology Abstract This chapter is concerned with the fabrication of metal oxide semiconductor (MOS) technology. Various processes such as wafer fabrication, oxidation, mask
EE THERMAL OXIDATION - Chapter 6. Basic Concepts
 EE 22 FALL 999-00 THERMAL OXIDATION - Chapter 6 Basic Concepts SiO 2 and the Si/SiO 2 interface are the principal reasons for silicon s dominance in the IC industry. SiO 2 : Easily selectively etched using
EE 22 FALL 999-00 THERMAL OXIDATION - Chapter 6 Basic Concepts SiO 2 and the Si/SiO 2 interface are the principal reasons for silicon s dominance in the IC industry. SiO 2 : Easily selectively etched using
ECSE-6300 IC Fabrication Laboratory Lecture 4: Dielectrics and Poly-Si Deposition. Lecture Outline
 ECSE-6300 IC Fabrication Laboratory Lecture 4: Dielectrics and Poly-Si Deposition Prof. Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute Troy, NY 12180 Office: CII-6229 Tel.: (518) 276-2909 e-mails: luj@rpi.edu http://www.ecse.rpi.edu/courses/s18/ecse
ECSE-6300 IC Fabrication Laboratory Lecture 4: Dielectrics and Poly-Si Deposition Prof. Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute Troy, NY 12180 Office: CII-6229 Tel.: (518) 276-2909 e-mails: luj@rpi.edu http://www.ecse.rpi.edu/courses/s18/ecse
Lattice 3256A-90LM PLD
 Construction Analysis PLD Report Number: SCA 9705-538 Global Semiconductor Industry the Serving Since 1964 17350 N. Hartford Drive Scottsdale, AZ 85255 Phone: 602-515-9780 Fax: 602-515-9781 e-mail: ice@ice-corp.com
Construction Analysis PLD Report Number: SCA 9705-538 Global Semiconductor Industry the Serving Since 1964 17350 N. Hartford Drive Scottsdale, AZ 85255 Phone: 602-515-9780 Fax: 602-515-9781 e-mail: ice@ice-corp.com
VLSI Technology Dr. Nandita Dasgupta Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras
 VLSI Technology Dr. Nandita Dasgupta Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 33 Problems in LOCOS + Trench Isolation and Selective Epitaxy So, we are discussing
VLSI Technology Dr. Nandita Dasgupta Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 33 Problems in LOCOS + Trench Isolation and Selective Epitaxy So, we are discussing
EE 143 FINAL EXAM NAME C. Nguyen May 10, Signature:
 INSTRUCTIONS Read all of the instructions and all of the questions before beginning the exam. There are 5 problems on this Final Exam, totaling 143 points. The tentative credit for each part is given to
INSTRUCTIONS Read all of the instructions and all of the questions before beginning the exam. There are 5 problems on this Final Exam, totaling 143 points. The tentative credit for each part is given to
IC Fabrication Technology Part III Devices in Semiconductor Processes
 EE 330 Lecture 10 IC Fabrication Technology Part III Metalization and Interconnects Parasitic Capacitances Back-end Processes Devices in Semiconductor Processes Resistors Diodes Review from Last Lecture
EE 330 Lecture 10 IC Fabrication Technology Part III Metalization and Interconnects Parasitic Capacitances Back-end Processes Devices in Semiconductor Processes Resistors Diodes Review from Last Lecture
NEC 79VR5000 RISC Microprocessor
 Construction Analysis NEC 79VR5000 RISC Microprocessor Report Number: SCA 9711-567 Global Semiconductor Industry the Serving Since 1964 17350 N. Hartford Drive Scottsdale, AZ 85255 Phone: 602-515-9780
Construction Analysis NEC 79VR5000 RISC Microprocessor Report Number: SCA 9711-567 Global Semiconductor Industry the Serving Since 1964 17350 N. Hartford Drive Scottsdale, AZ 85255 Phone: 602-515-9780
Process Integration. MEMS Release Techniques Sacrificial Layer Removal Substrate Undercut
 Process Integration Self-aligned Techniques LOCOS- self-aligned channel stop Self-aligned Source/Drain Lightly Doped Drain (LDD) Self-aligned silicide (SALICIDE) Self-aligned oxide gap MEMS Release Techniques
Process Integration Self-aligned Techniques LOCOS- self-aligned channel stop Self-aligned Source/Drain Lightly Doped Drain (LDD) Self-aligned silicide (SALICIDE) Self-aligned oxide gap MEMS Release Techniques
Mostafa Soliman, Ph.D. May 5 th 2014
 Mostafa Soliman, Ph.D. May 5 th 2014 Mostafa Soliman, Ph.D. 1 Basic MEMS Processes Front-End Processes Back-End Processes 2 Mostafa Soliman, Ph.D. Wafers Deposition Lithography Etch Chips 1- Si Substrate
Mostafa Soliman, Ph.D. May 5 th 2014 Mostafa Soliman, Ph.D. 1 Basic MEMS Processes Front-End Processes Back-End Processes 2 Mostafa Soliman, Ph.D. Wafers Deposition Lithography Etch Chips 1- Si Substrate
Micron Semiconductor MT4LC16M4H9 64Mbit DRAM
 Construction Analysis Micron Semiconductor MT4LC16M4H9 64Mbit DRAM Report Number: SCA 9705-539 Global Semiconductor Industry the Serving Since 1964 15022 N. 75th Street Scottsdale, AZ 85260-2476 Phone:
Construction Analysis Micron Semiconductor MT4LC16M4H9 64Mbit DRAM Report Number: SCA 9705-539 Global Semiconductor Industry the Serving Since 1964 15022 N. 75th Street Scottsdale, AZ 85260-2476 Phone:
Silicon Manufacturing
 Silicon Manufacturing Group Members Young Soon Song Nghia Nguyen Kei Wong Eyad Fanous Hanna Kim Steven Hsu th Fundamental Processing Steps 1.Silicon Manufacturing a) Czochralski method. b) Wafer Manufacturing
Silicon Manufacturing Group Members Young Soon Song Nghia Nguyen Kei Wong Eyad Fanous Hanna Kim Steven Hsu th Fundamental Processing Steps 1.Silicon Manufacturing a) Czochralski method. b) Wafer Manufacturing
Intel Pentium Processor W/MMX
 Construction Analysis Intel Pentium Processor W/MMX Report Number: SCA 9706-540 Global Semiconductor Industry the Serving Since 1964 15022 N. 75th Street Scottsdale, AZ 85260-2476 Phone: 602-998-9780 Fax:
Construction Analysis Intel Pentium Processor W/MMX Report Number: SCA 9706-540 Global Semiconductor Industry the Serving Since 1964 15022 N. 75th Street Scottsdale, AZ 85260-2476 Phone: 602-998-9780 Fax:
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) Zheng Yang
 Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) Zheng Yang ERF 3017, email: yangzhen@uic.edu Page 1 Major Fabrication Steps in MOS Process Flow UV light Mask oxygen Silicon dioxide photoresist exposed photoresist oxide
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) Zheng Yang ERF 3017, email: yangzhen@uic.edu Page 1 Major Fabrication Steps in MOS Process Flow UV light Mask oxygen Silicon dioxide photoresist exposed photoresist oxide
Oxidation Part 1. By Christopher Henderson
 Oxidation Part 1 By Christopher Henderson In this new series, we will discuss the subject of oxidation. Oxidation is a key aspect of the semiconductor process. The fact that one can easily grow an oxide
Oxidation Part 1 By Christopher Henderson In this new series, we will discuss the subject of oxidation. Oxidation is a key aspect of the semiconductor process. The fact that one can easily grow an oxide
Section 4: Thermal Oxidation. Jaeger Chapter 3
 Section 4: Thermal Oxidation Jaeger Chapter 3 Properties of O Thermal O is amorphous. Weight Density =.0 gm/cm 3 Molecular Density =.3E molecules/cm 3 O Crystalline O [Quartz] =.65 gm/cm 3 (1) Excellent
Section 4: Thermal Oxidation Jaeger Chapter 3 Properties of O Thermal O is amorphous. Weight Density =.0 gm/cm 3 Molecular Density =.3E molecules/cm 3 O Crystalline O [Quartz] =.65 gm/cm 3 (1) Excellent
EECS130 Integrated Circuit Devices
 EECS130 Integrated Circuit Devices Professor Ali Javey 9/13/2007 Fabrication Technology Lecture 1 Silicon Device Fabrication Technology Over 10 15 transistors (or 100,000 for every person in the world)
EECS130 Integrated Circuit Devices Professor Ali Javey 9/13/2007 Fabrication Technology Lecture 1 Silicon Device Fabrication Technology Over 10 15 transistors (or 100,000 for every person in the world)
EE 330 Lecture 8. IC Fabrication Technology Part II. - Masking - Photolithography - Deposition - Etching - Diffusion
 EE 330 Lecture 8 IC Fabrication Technology Part II?? - Masking - Photolithography - Deposition - Etching - Diffusion Review from Last Time Technology Files Provide Information About Process Process Flow
EE 330 Lecture 8 IC Fabrication Technology Part II?? - Masking - Photolithography - Deposition - Etching - Diffusion Review from Last Time Technology Files Provide Information About Process Process Flow
Isolation of elements
 1 In an IC, devices on the same substrate must be isolated from one another so that there is no current conduction between them. Isolation uses either the junction or dielectric technique or a combination
1 In an IC, devices on the same substrate must be isolated from one another so that there is no current conduction between them. Isolation uses either the junction or dielectric technique or a combination
SGS-Thomson M28C K EEPROM
 Construction Analysis SGS-Thomson M28C64-121 64K EEPROM Report Number: SCA 9710-559 Global Semiconductor Industry the Serving Since 1964 17350 N. Hartford Drive Scottsdale, AZ 85255 Phone: 602-515-9780
Construction Analysis SGS-Thomson M28C64-121 64K EEPROM Report Number: SCA 9710-559 Global Semiconductor Industry the Serving Since 1964 17350 N. Hartford Drive Scottsdale, AZ 85255 Phone: 602-515-9780
Integrated Circuit Engineering Corporation. DRAMs
 DRAMs As generally known, the focus of technology in this product category continues to be complex vertical polysilicon structures to reduce cell area. This not only pushes the limits of deposition and
DRAMs As generally known, the focus of technology in this product category continues to be complex vertical polysilicon structures to reduce cell area. This not only pushes the limits of deposition and
Lecture 200 BiCMOS Technology (12/12/01) Page 200-1
 Lecture 200 BiCMOS Technology (12/12/01) Page 200-1 LECTURE 200 BICMOS TECHNOLOGY (READING: Text-Sec. 2.11) INTRODUCTION Objective Illustrate BiCMOS technology Outline Introduction Physical process illustration
Lecture 200 BiCMOS Technology (12/12/01) Page 200-1 LECTURE 200 BICMOS TECHNOLOGY (READING: Text-Sec. 2.11) INTRODUCTION Objective Illustrate BiCMOS technology Outline Introduction Physical process illustration
ECE520 VLSI Design. Lecture 7: CMOS Manufacturing Process. Payman Zarkesh-Ha
 ECE520 VLSI Design Lecture 7: CMOS Manufacturing Process Payman Zarkesh-Ha Office: ECE Bldg. 230B Office hours: Wednesday 2:00-3:00PM or by appointment E-mail: pzarkesh@unm.edu Slide: 1 Review of Last
ECE520 VLSI Design Lecture 7: CMOS Manufacturing Process Payman Zarkesh-Ha Office: ECE Bldg. 230B Office hours: Wednesday 2:00-3:00PM or by appointment E-mail: pzarkesh@unm.edu Slide: 1 Review of Last
PDS Products PRODUCT DATA SHEET. BN-975 Wafers. Low Defect Boron Diffusion Systems. Features/Benefits BORON NITRIDE
 Low Defect Boron Diffusion Systems The purpose of the hydrogen injection process is to increase die yield per wafer. This is accomplished because the effects associated with the hydrogen injection process.
Low Defect Boron Diffusion Systems The purpose of the hydrogen injection process is to increase die yield per wafer. This is accomplished because the effects associated with the hydrogen injection process.
Xilinx XC4036XL-1C FPGA
 Construction Analysis Xilinx XC4036XL-1C FPGA Report Number: SCA 9709-553 Global Semiconductor Industry the Serving Since 1964 17350 N. Hartford Drive Scottsdale, AZ 85255 Phone: 602-515-9780 Fax: 602-515-9781
Construction Analysis Xilinx XC4036XL-1C FPGA Report Number: SCA 9709-553 Global Semiconductor Industry the Serving Since 1964 17350 N. Hartford Drive Scottsdale, AZ 85255 Phone: 602-515-9780 Fax: 602-515-9781
PROCESS FLOW AN INSIGHT INTO CMOS FABRICATION PROCESS
 Contents: VI Sem ECE 06EC63: Analog and Mixed Mode VLSI Design PROCESS FLOW AN INSIGHT INTO CMOS FABRICATION PROCESS 1. Introduction 2. CMOS Fabrication 3. Simplified View of Fabrication Process 3.1 Alternative
Contents: VI Sem ECE 06EC63: Analog and Mixed Mode VLSI Design PROCESS FLOW AN INSIGHT INTO CMOS FABRICATION PROCESS 1. Introduction 2. CMOS Fabrication 3. Simplified View of Fabrication Process 3.1 Alternative
SGS-Thomson M17C1001 1Mb UVEPROM
 Construction Analysis SGS-Thomson M17C1001 1Mb UVEPROM Report Number: SCA 9612-518 Global Semiconductor Industry the Serving Since 1964 15022 N. 75th Street Scottsdale, AZ 85260-2476 Phone: 602-998-9780
Construction Analysis SGS-Thomson M17C1001 1Mb UVEPROM Report Number: SCA 9612-518 Global Semiconductor Industry the Serving Since 1964 15022 N. 75th Street Scottsdale, AZ 85260-2476 Phone: 602-998-9780
Process Integration. NMOS Generic NMOS Process Flow. CMOS - The MOSIS Process Flow
 Process Integration Self-aligned Techniques LOCOS- self-aligned channel stop Self-aligned Source/Drain Lightly Doped Drain (LDD) Self-aligned silicide (SALICIDE) Self-aligned oxide gap MEMS Release Techniques
Process Integration Self-aligned Techniques LOCOS- self-aligned channel stop Self-aligned Source/Drain Lightly Doped Drain (LDD) Self-aligned silicide (SALICIDE) Self-aligned oxide gap MEMS Release Techniques
Motorola MPA1016FN FPGA
 Construction Analysis Motorola MPA1016FN FPGA Report Number: SCA 9711-561 Global Semiconductor Industry the Serving Since 1964 17350 N. Hartford Drive Scottsdale, AZ 85255 Phone: 602-515-9780 Fax: 602-515-9781
Construction Analysis Motorola MPA1016FN FPGA Report Number: SCA 9711-561 Global Semiconductor Industry the Serving Since 1964 17350 N. Hartford Drive Scottsdale, AZ 85255 Phone: 602-515-9780 Fax: 602-515-9781
MOS Front-End. Field effect transistor
 MOS Front-End Back-end Transistor Contact Front-end p-well STI n-well Front-end-of-line includes substrate, isolation, wells, transistor, silicide Field effect transistor MOSFET: Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor
MOS Front-End Back-end Transistor Contact Front-end p-well STI n-well Front-end-of-line includes substrate, isolation, wells, transistor, silicide Field effect transistor MOSFET: Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor
Silicon Wafer Processing PAKAGING AND TEST
 Silicon Wafer Processing PAKAGING AND TEST Parametrical test using test structures regularly distributed in the wafer Wafer die test marking defective dies dies separation die fixing (not marked as defective)
Silicon Wafer Processing PAKAGING AND TEST Parametrical test using test structures regularly distributed in the wafer Wafer die test marking defective dies dies separation die fixing (not marked as defective)
Semiconductor Technology
 Semiconductor Technology von A bis Z Metallization www.halbleiter.org Contents Contents List of Figures List of Tables II III 1 Metallization 1 1.1 Requirements on metallization........................
Semiconductor Technology von A bis Z Metallization www.halbleiter.org Contents Contents List of Figures List of Tables II III 1 Metallization 1 1.1 Requirements on metallization........................
